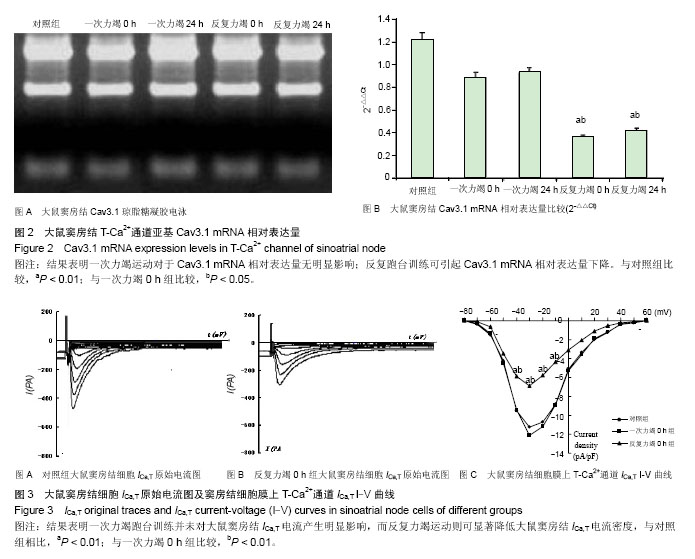
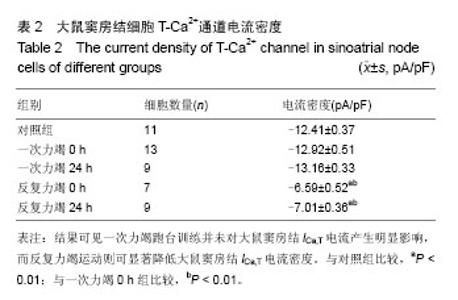
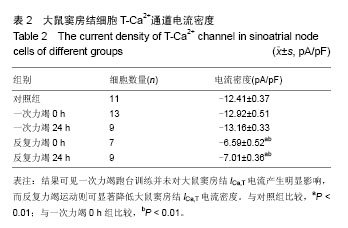
| [1] Yaniv Y, Lakatta EG. Pacemaker gene mutations, bradycardia, arrhythmias and the coupled clock theory. J Cardiovasc Electr. 2013;24(12):E28-E9.
[2] Hagiwara N, Irisawa H, Kameyama M. Contribution of two types of calcium currents to the pacemaker potentials of rabbit sino-atrial node cells. J Physiol. 1988;395(1):233-253.
[3] Mangoni ME, Nargeot J. Genesis and regulation of the heart automaticity. Physiol Rev.2008;88(3):919-982.
[4] Mangoni ME, Traboulsie A, Leoni AL, et al.Bradycardia and slowing of the atrioventricular conduction in mice lacking CaV3.1/α1G T-type calcium channels. Circ Res.2006,98(11): 1422-1430.
[5] 王凯,潘珊珊,王庆棠.心肌SarcKATP通道kir6.2亚基在运动预适应心肌保护效应中变化的研究[J]. 体育科学. 2012,32(4): 60-66.
[6] Monfredi O, Dobrzynski H, Mondal T, et al. The anatomy and physiology of the sinoatrial node-a contemporary review. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 2010;33(11):1392-1406.
[7] Sánchez-Quintana D, Pizarro G, López-Mínguez JR, et al. Standardized review of atrial anatomy for cardiac electrophysiologists. J Cardiovasc Trans Res. J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 2013;6(2):124-144
[8] 薄冰,常芸.力竭运动对大鼠窦房结超级化激活环核苷酸门控通道的影响[J].中国运动医学杂志,2012,31(9):792-800.
[9] 薄冰,常芸.力竭运动对大鼠窦房结ATP-敏感型钾离子通道的影响[J].中国运动医学杂志,2012,31(10):861-867.
[10] Rose RA, Lomax AE, Kondo CS, et al.Effects of C-type natriuretic peptide on ionic currents in mouse sinoatrial node: a role for the NPR-C receptor. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2004,286(5):H1970-7.
[11] Cho HS,Takano M,Noma A.The electrophysiological properties of spontaneously beating pacemaker cells isolated from mouse sinoatrial node.J Physiol.2003;550(Pt 1):169-80.
[12] Katona PG, McLean M, Dighton DH, et al.Sympathetic and parasympathetic cardiac control in athletes and nonathletes at rest.J Appl Physiol. 1982;52(6):1652-1657.
[13] Stein R, Medeiros CM, Rosito GA,et al.Intrinsic sinus and atrioventricular node electrophysiologic adaptations in endurance athletes. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2002;39(6):1033-1038.
[14] Boyett MR.‘And the beat goes on’The cardiac conduction system: the wiring system of the heart. Exp Physiol. 2009; 94(10):1035-1049.
[15] Lipsius SL,Huser J,Blatter LA.Intracellular Ca2+ release sparks atrial pacemaker activity. News Physiol Sci.2001; 16: 101-6.
[16] Gao Z, Chen B, Joiner M-lA, et al. If and SR Ca2+ release both contribute to pacemaker activity in canine sinoatrial node cells.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2010;49(1):33-40.
[17] Huser J, Blatter LA, Lipsius SL. Intracellular Ca2+ release contributes to automaticity in cat atrial pacemaker cells. J Physio. 2000;524 Pt 2:415-422.
[18] 朱永泽,吴庚华,王鑫,等.力竭游泳运动对大鼠心脏窦房结细胞超微结构的影响[J].中国运动医学杂志. 2007,26(1):86-89.
[19] Reil JC, Custodis F, Swedberg K, et al. Heart rate reduction in cardiovascular disease and therapy. Clin Res Cardiol. 2011; 100(1):11-19.
[20] Kato T, Iwasaki YK, Duker G, et al. Inefficacy of a highly selective T-type calcium channel blocker in preventing atrial fibrillation related remodeling.J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2014;25(5):531-536.
[21] Marger L, Mesirca P, Alig J, et al.Functional roles of Cav1.3, Cav3.1 and HCN channels in automaticity of mouse atrioventricular cells: insights into the atrioventricular pacemaker mechanism. Channels.2011;5(3):251-261.
[22] Fabritz L, Herzig S. Can T-type calcium channels make a change of heart after myocardial infarction? Fiction or fact, and for better or for worse?. Cardiovasc Res. 2011;91(3):373-375.
[23] Le Quang K, Benito B, Naud P, et al.T-Type Calcium Current Contributes to Escape Automaticity and Governs the Occurrence of Lethal Arrhythmias After Atrioventricular Block in Mice. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol. 2013;6(4):799-808.
[24] Hashem SI, Claycomb WC.Genetic isolation of stem cell-derived pacemaker-nodal cardiac myocytes. Mol Cell Biochem.2013;383(1-2):161-171.
[25] Aistrup G.Cellular Pharmacology of Cardiac Automaticity and Conduction: Implications in Antiarrhythmic Drug Assessment. Cardiac Arrhythmias: Springer; 2014:305-333. |