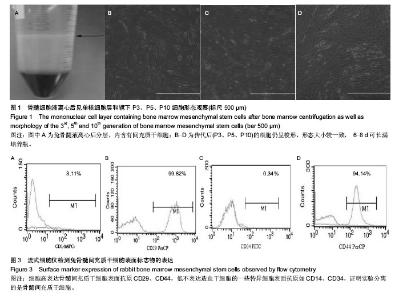
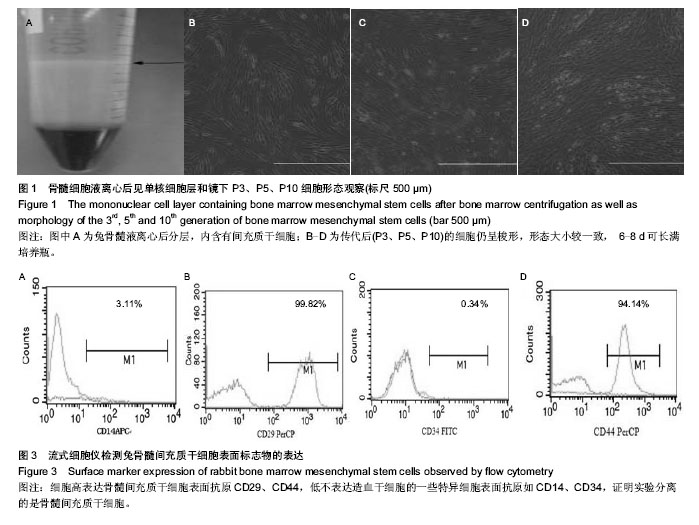
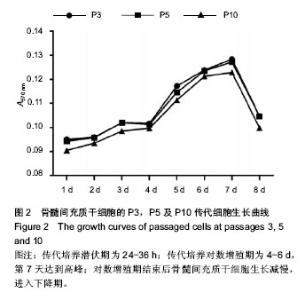
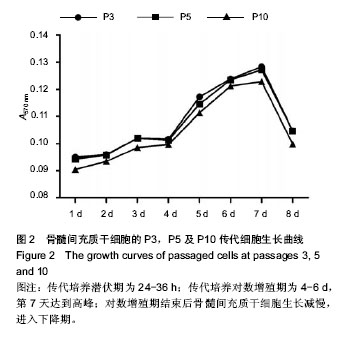
| [1] Hirota N, McCuaig S, O'Sullivan MJ, et al. Serotonin augments smooth muscle differentiation of bone marrow stromal cells. Stem Cell Res. 2014;12(3):599-609.
[2] Wu G, Cui Y, Wang YT, et al. Repair of cartilage defects in BMSCs via CDMP1 gene transfection. Genetics and molecular research: GMR. 2014;13(1):291-301.
[3] Jiang Y, Mishima H, Sakai S, et al. Gene expression analysis of major lineage-defining factors in human bone marrow cells: effect of aging, gender, and age-related disorders. J Orthop Res. 2008;26(7):910-917.
[4] Song Q, Xu R, Zhang Q, et al. Therapeutic effect of transplanting bone mesenchymal stem cells on the hind limbs' motor function of rats with acute spinal cord injury. International journal of clinical and experimental medicine. 2014;7(1):262-267.
[5] Behnia H, Khojasteh A, Soleimani M, et al. Repair of alveolar cleft defect with mesenchymal stem cells and platelet derived growth factors: a preliminary report. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2012;40(1):2-7.
[6] Zhao J, Yang C, Su C, et al. Reconstruction of orbital defects by implantation of antigen-free bovine cancellous bone scaffold combined with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in rats. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2013;251(5): 1325-1333.
[7] Alexanian AR, Fehlings MG, Zhang Z, et al. Transplanted neurally modified bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells promote tissue protection and locomotor recovery in spinal cord injured rats. Neurorehabil Neural Repair. 2011; 25(9):873-880.
[8] Wyse RD, Dunbar GL, Rossignol J. Use of genetically modified mesenchymal stem cells to treat neurodegenerative diseases. Int J Mol Sci. 2014;15(2):1719-1745.
[9] Hare JM, Fishman JE, Gerstenblith G, et al. Comparison of allogeneic vs autologous bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells delivered by transendocardial injection in patients with ischemic cardiomyopathy: the POSEIDON randomized trial. JAMA. 2012;308(22):2369-2379.
[10] Gamie Z, Tran GT, Vyzas G, et al. Stem cells combined with bone graft substitutes in skeletal tissue engineering. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2012;12(6):713-729.
[11] Purandare B, Teklemariam T, Zhao L,et al. Temporal HLA profiling and immunomodulatory effects of human adult bone marrow- and adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Regen Med. 2014;9(1):67-79.
[12] Pang L, Hao W, Jiang M, et al. Bony defect repair in rabbit using hybrid rapid prototyping polylactic-co-glycolic acid/β-tricalciumphosphate collagen I/apatite scaffold and bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Indian J Orthop. 2013;47(4):388-394.
[13] 中华人民共和国科学技术部.关于善待实验动物的指导性意见. 2006-09-30.
[14] Cuiffo BG, Karnoub AE. Mesenchymal stem cells in tumor development: emerging roles and concepts. Cell Adh Migr. 2012;6(3):220-230.
[15] Jo CH, Yoon PW, Kim H,et al. Comparative evaluation of in vivo osteogenic differentiation of fetal and adult mesenchymal stem cell in rat critical-sized femoral defect model. Cell Tissue Res. 2013;353(1):41-52.
[16] Siegel G, Kluba T, Hermanutz-Klein U, et al. Phenotype, donor age and gender affect function of human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stromal cells. BMC Med. 2013; 11(1):146.
[17] Kim H, Kim HM, Jang JE, et al. Osteogenic Differentiation of Bone Marrow Stem Cell in Poly(Lactic-co-Glycolic Acid) Scaffold Loaded Various Ratio of Hydroxyapatite. International journal of stem cells. 2013;6(1):67-74.
[18] Fridenshtein A, Piatetskii S, II, Petrakova KV. Osteogenesis in transplants of bone marrow cells. Arkh Anat Gistol Embriol. 1969;56(3):3-11.
[19] Jiang J, Fan CY, Zeng BF. Osteogenic differentiation effects on rat bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stromal cells by lentivirus-mediated co-transfection of human BMP2 gene and VEGF165 gene. Biotechnol Lett. 2008;30(2):197-203.
[20] Dominici M, Le Blanc K, Mueller I, et al. Minimal criteria for defining multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells. The International Society for Cellular Therapy position statement. Cytotherapy. 2006;8(4):315-317.
[21] Kisiel AH, McDuffee LA, Masaoud E, et al. Isolation, characterization, and in vitro proliferation of canine mesenchymal stem cells derived from bone marrow, adipose tissue, muscle, and periosteum. Am J Vet Res. 2012; 73(8): 1305-1317.
[22] Kedziorek DA, Hofmann LV, Fu Y, et al. X-ray-visible microcapsules containing mesenchymal stem cells improve hind limb perfusion in a rabbit model of peripheral arterial disease. Stem Cells. 2012;30(6):1286-1296.
[23] Trivanovic D, Kocic J, Mojsilovic S, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells isolated from peripheral blood and umbilical cord Wharton's jelly. Srp Arh Celok Lek. 2013;141(3-4):178-186.
[24] Shi ZB, Wang KZ. Effects of recombinant adeno-associated viral vectors on angiopoiesis and osteogenesis in cultured rabbit bone marrow stem cells via co-expressing hVEGF and hBMP genes: a preliminary study in vitro. Tissue & cell. 2010; 42(5):314-321.
[25] Zhang W, Zhu C, Wu Y, et al. VEGF and BMP-2 promote bone regeneration by facilitating bone marrow stem cell homing and differentiation. European cells & materials. 2014; 27:1-11; discussion -2.
[26] Rohaina CM, Then KY, Ng AM, et al. Reconstruction of limbal stem cell deficient corneal surface with induced human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells on amniotic membrane. Transl Res. 2014;163(3):200-210.
[27] Houshmand B, Behnia H, Khoshzaban A, et al. Osteoblastic differentiation of human stem cells derived from bone marrow and periodontal ligament under the effect of enamel matrix derivative and transforming growth factor-beta. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2013;28(6):e440-450.
[28] 牛红星,穆军升,张健群,等. 骨髓间充质干细胞与聚3-羟基丁酸酯-co-4-羟基丁酸酯生物材料共培养细胞补片的初步研究[J]. 中国生物工程杂志,2012,32(010):74-79.
[29] Nakano N, Nakai Y, Seo TB, et al. Characterization of conditioned medium of cultured bone marrow stromal cells. Neurosci Lett. 2010;483(1):57-61.
[30] Nicaise C, Mitrecic D, Pochet R. Brain and spinal cord affected by amyotrophic lateral sclerosis induce differential growth factors expression in rat mesenchymal and neural stem cells. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 2011;37(2):179-188.
[31] Camassola M, de Macedo Braga LM, Chagastelles PC, et al. Methodology, biology and clinical applications of human mesenchymal stem cells. Methods Mol Biol. 2012;879: 491-504. |