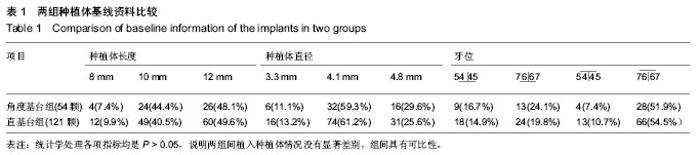
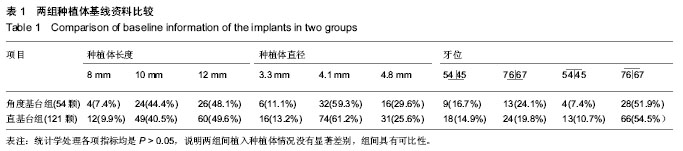
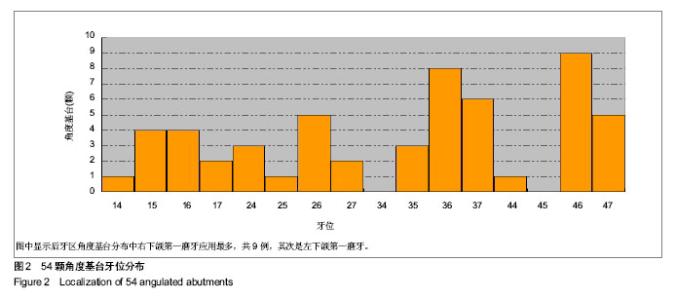
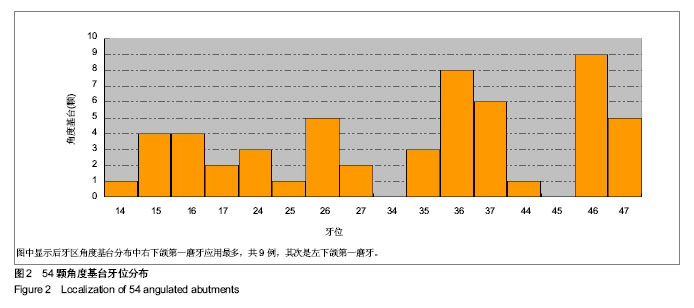
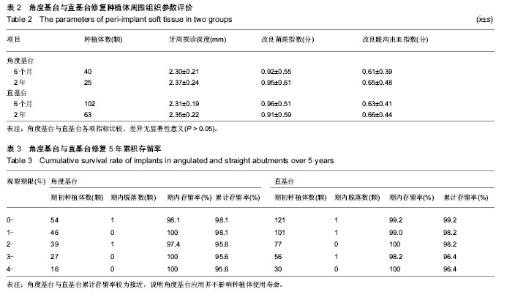
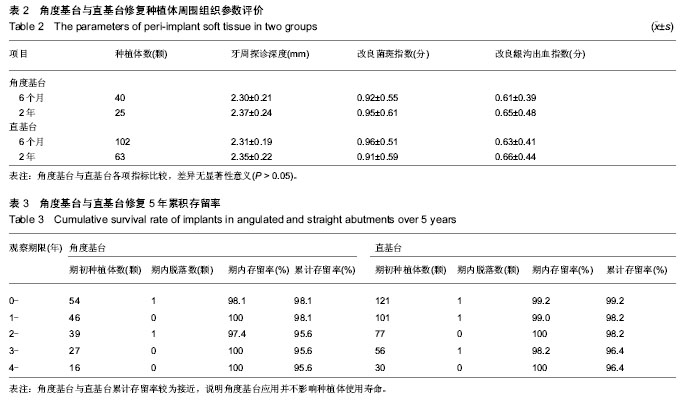
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (7): 1021-1026.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.07.007
Previous Articles Next Articles
A short-term assessment of angulated abutments for the implant denture restorations in posterior teeth
Feng Wei, Geng Jin-you, Sun Yuan-yuan, Geng Hai-xia
- Department of Stomatology, Affiliated Hospital of Jining Medical College, Jining 272000, Shandong Province, China
-
Revised:2013-12-12Online:2014-02-12Published:2014-02-12 -
Contact:Geng Hai-xia, Professor, Chief physician, Department of Stomatology, Affiliated Hospital of Jining Medical College, Jining 272000, Shandong Province, China -
About author:Feng Wei, Master, Department of Stomatology, Affiliated Hospital of Jining Medical College, Jining 272000, Shandong Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Feng Wei, Geng Jin-you, Sun Yuan-yuan, Geng Hai-xia . A short-term assessment of angulated abutments for the implant denture restorations in posterior teeth[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(7): 1021-1026.
share this article
| [1] Reid PE, Zinner ID, Bhagat D. Fabricating a nonrotational angulated abutment for a single-tooth prosthesis.Implant Dent. 2009;18(6):486-491. [2] Bahuguna R, Anand B, Kumar D, et al. Evaluation of stress patterns in bone around dental implant for different abutment angulations under axial and oblique loading: A finite element analysis.Natl J Maxillofac Surg. 2013;4(1):46-51.[3] 铁朝荣,张文捷,陈建钢. 倾斜种植体与角度基台在种植修复中的临床应用[J]. 临床口腔医学杂志,2011,27(2):108-109.[4] Tian K, Chen J, Han L, et al. Angled abutments result in increased or decreased stress on surrounding bone of single-unit dental implants: a finite element analysis.Med Eng Phys. 2012;34(10):1526-1531.[5] Martini AP, Freitas AC Jr, Rocha EP, et al. Straight and angulated abutments in platform switching: influence of loading on bone stress by three-dimensional finite element analysis.J Craniofac Surg. 2012;23(2):415-418.[6] Tabrizi R, Pourdanesh F, Zare S, et al.Do angulated implants increase the amount of bone loss around implants in the anterior maxilla?J Oral Maxillofac Surg.2013;71(2): 272-277. [7] 封伟,江鹭鹭,张娇,等.后牙区种植义齿不同材料冠修复5年临床疗效评价[J].中国实用口腔科杂志,2012,5(12):742-747. [8] 朱啸,唐亮.影响口腔种植及修复成功的因素分析[J].国际口腔医学杂志,2007,34(6):461-463.[9] Weber HP, Kim DM, Ng MW, et al. Peri-implant soft-tissue health surrounding cement- and screw-retained implant restorations: a multi-center, 3-year prospective study.Clin Oral Implants Res. 2006 ;17(4):375-379.[10] Keller W, Brägger U, Mombelli A. Peri-implant microflora of implants with cemented and screw retained suprastructures. Clin Oral Implants Res. 1998;9(4):209-217.[11] Mombelli A, Lang NP.Antimicrobial treatment of peri-implant infections.Clin Oral Implants Res. 1992;3(4):162-168.[12] Hasan I, Heinemann F, Bourauel C.The relationship of bone resorption around dental implants to abutment design: a preliminary 1-year clinical study.Int J Prosthodont. 2011; 24(5):457-459.[13] Herzberg R, Dolev E, Schwartz-Arad D.Implant marginal bone loss in maxillary sinus grafts.Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2006;21(1):103-110. [14] 赵宝红,封伟,王丹宁,等.不同冠根比的后牙种植义齿5年临床疗效的评价[J].上海口腔医学,2013,22(2):189-194.[15] Koutouzis T, Wennström JL.Bone level changes at axial- and non-axial-positioned implants supporting fixed partial dentures. A 5-year retrospective longitudinal study.Clin Oral Implants Res. 2007;18(5):585-590. [16] Nothdurft FP, Doppler KE, Erdelt KJ, et al. Fracture behavior of straight or angulated zirconia implant abutments supporting anterior single crowns.Clin Oral Investig. 2011;15(2):157-163.[17] Reid PE, Zinner ID, Bhagat D.Fabricating a nonrotational angulated abutment for a single-tooth prosthesis.Implant Dent. 2009;18(6):486-91.[18] 高奎英,周延民.基台结构的研究和应用现状[J].现代口腔医学杂志,2007,21(1):86-88.[19] Kao HC, Gung YW, Chung TF, et al.The influence of abutment angulation on micromotion level for immediately loaded dental implants: a 3-D finite element analysis.Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2008;23(4):623-630.[20] Tada S, Stegaroiu R, Kitamura E, et al. Influence of implant design and bone quality on stress/strain distribution in bone around implants: a 3-dimensional finite element analysis.Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2003;18(3):357-368.[21] 陈祖贤,王超,王立军.上颌后牙区倾斜种植的三维有限元分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(33):5957-5962.[22] Brosh T, Pilo R, Sudai D. The influence of abutment angulation on strains and stresses along the implant/bone interface: comparison between two experimental techniques.J Prosthet Dent. 1998;79(3):328-334.[23] Cavallaro J Jr, Greenstein G.Angled implant abutments: a practical application of available knowledge.J Am Dent Assoc. 2011;142(2):150-158.[24] Kallus T, Henry P, Jemt T, et al. Clinical evaluation of angulated abutments for the Brånemark system: a pilot study. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 1990;5(1):39-45.[25] 丁熙,朱形好,陈树华,等.三维有限元分析角度基台对种植体骨界面应力分布的影响[J].医用生物力学,2005,20(3):153-156.[26] Clelland NL, Gilat A. The effect of abutment angulation on stress transfer for an implant.J Prosthodont. 1992;1(1):24-28.[27] Al-Abdullah K, Zandparsa R, Finkelman M, et al. An in vitro comparison of the accuracy of implant impressions with coded healing abutments and different implant angulations.J Prosthet Dent. 2013;110(2):90-100.[28] 李智勇,刘学军,赵丽娅,等.不同基台时种植体支持全瓷单冠的应力分析[J].口腔医学研究,2007,23(4):402-405.[29] Schwarz F, Mihatovic I, Becker J, et al. Histological evaluation of different abutments in the posterior maxilla and mandible: an experimental study in humans.J Clin Periodontol. 2013; 40(8):807-815.[30] Al-Wahadni A, Al-Saleh H, Al-Quran F, et al. Fracture resistance of fixed partial dentures supported by different abutment combinations: an ex vivo study.Gen Dent. 2012; 60(5):e295-301.[31] Weber HP, Kim DM, Ng MW, et al. Peri-implant soft-tissue health surrounding cement- and screw-retained implant restorations: a multi-center, 3-year prospective study.Clin Oral Implants Res. 2006 ;17(4):375-379.[32] 宿玉成.种植外科中的软组织处理及其美学效果[J].中华口腔医学杂志,2006,41(3):148-150.[33] Tarnow DP, Magner AW, Fletcher P.The effect of the distance from the contact point to the crest of bone on the presence or absence of the interproximal dental papilla.J Periodontol. 1992; 63(12):995-996.[34] Schwarz F, Mihatovic I, Ferrari D, et al.Influence of frequent clinical probing during the healing phase on healthy peri-implant soft tissue formed at different titanium implant surfaces: a histomorphometrical study in dogs.J Clin Periodontol.2010;37(6):551-562. [35] Chai WL, Moharamzadeh K, van Noort R, et al.Contour analysis of an implant--soft tissue interface.J Periodontal Res. 2013;48(5):663-670. [36] Lee YM, Kim DY, Kim JY, et al.Peri-implant soft tissue level secondary to a connective tissue graft in conjunction with immediate implant placement: a 2-year follow-up report of 11 consecutive cases.Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 2012; 32(2):213-222.[37] 陈祖贤,王超,樊瑜波,等.上颌前牙区非埋入式种植体不同角度基台的三维有限元分析[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010, 14(30):5591-5595.[38] Eger DE, Gunsolley JC, Feldman S.Comparison of angled and standard abutments and their effect on clinical outcomes: a preliminary report.Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2000;15(6): 819-823.[39] Luo Z, Zeng R, Luo Z, et al.Single implants in the esthetic zone: analysis of recent peri-implant soft tissue alterations and patient satisfaction. A photographic study.Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2011;26(3):578-586.[40] Jung RE, Holderegger C, Sailer I, et al.The effect of all-ceramic and porcelain-fused-to-metal restorations on marginal peri-implant soft tissue color: a randomized controlled clinical trial.Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 2008;28(4):357-365.[41] Karabuda C, Tosun T, Ermis E, et al.Comparison of 2 retentive systems for implant-supported overdentures: soft tissue management and evaluation of patient satisfaction.J Periodontol. 2002;73(9):1067-1070.[42] 孙嵩,赵峰,孙勇.骨挤压对种植体初期稳定性的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(15):2698-2702.[43] VanSchoiack LR, Shubayev VI, Myers RR, et al. In vivo evaluation of quantitative percussion diagnostics for determining implant stability.Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2013;28(5):1286-1292.[44] Rungruanganunt P, Taylor T, Eckert SE, et al.The effect of static load on dental implant survival: a systematic review.Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2013;28(5):1218-1225.[45] Al-Juboori MJ, AbdulRahaman SB, Hassan A.The correlation between crestal bone resorption and implant stability during healing period using resonance frequency analysis.Implant Dent. 2013;22(4):351-355. [46] 封伟,赵宝红.微量元素在种植体骨结合中应用研究进展[J].中国实用口腔科杂志,2011,4(10):623-627.[47] Sethi A, Kaus T, Sochor P, et al. Evolution of the concept of angulated abutments in implant dentistry: 14-year clinical data.Implant Dent. 2002;11(1):41-51.[48] Balshi TJ, Ekfeldt A, Stenberg T, et al.Three-year evaluation of Brånemark implants connected to angulated abutments.Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 1997;12(1):52-58.[49] Salvi GE, Brägger U.Mechanical and technical risks in implant therapy.Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2009;24 Suppl:69-85.[50] Hasan I, Röger B, Heinemann F, et al. Influence of abutment design on the success of immediately loaded dental implants: experimental and numerical studies.Med Eng Phys. 2012; 34(7): 817-825.[51] Yu W, Jang YJ, Kyung HM. Combined influence of implant diameter and alveolar ridge width on crestal bone stress: a quantitative approach.Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2009; 24(1):88-95.[52] da Cunha HA, Francischone CE, Filho HN, et al. A comparison between cutting torque and resonance frequency in the assessment of primary stability and final torque capacity of standard and TiUnite single-tooth implants under immediate loading.Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2004;19(4): 578-585.[53] Turkyilmaz I, Tumer C, Ozbek EN, et al. Relations between the bone density values from computerized tomography, and implant stability parameters: a clinical study of 230 regular platform implants.J Clin Periodontol. 2007;34(8):716-722.[54] 陈少武,肖微,李智勇,等.种植体上部不同结构对下颌游离端义齿应力分布的影响[J].实用口腔医学杂志,2012,28(3):294-297.[55] 高军,王朝俭,张雷,等.短种植体在骨量不足时种植的临床效果[J]. 口腔医学,2012,32(9):567-569.[56] Celletti R, Pameijer CH, Bracchetti G, et al. Histologic evaluation of osseointegrated implants restored in nonaxial functional occlusion with preangled abutments.Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 1995;15(6):562-573.[57] Stegaroiu R, Kusakari H, Nishiyama S, et al. Influence of prosthesis material on stress distribution in bone and implant: a 3-dimensional finite element analysis.Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 1998;13(6):781-790. |
| [1] | Huo Hua, Cheng Yuting, Zhou Qian, Qi Yuhan, Wu Chao, Shi Qianhui, Yang Tongjing, Liao Jian, Hong Wei. Effects of drug coating on implant surface on the osseointegration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3558-3564. |
| [2] |
Zhang Xuan, Li Yunpeng, Zhang Xuejian, Yin Chuanrong, Deng Yue.
Guided bone regeneration using preformed titanium mesh combined with bioabsorbable membranes in aesthetic area [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(26): 4112-4117. |
| [3] | Liu Dan, Min Changqin, Lu Shuai, Chen Yue, Sun Yong. Osseointegration induced by beta-tricalcium phosphate loaded with advanced platelet-rich fibrin [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(6): 888-893. |
| [4] | Li Fang, Cheng Yuting, Huang Xiaolin, Zhou Qian, Wu Chao, Shi Qianhui, Wang Yong, Liao Jian. Maxillary sinus floor augmentation: with or without bone grafting [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(6): 971-977. |
| [5] | Zou Yingnan, Wang Yibo, Ding Chao, Pan Xinyu, Shi Jiuhui . Three-dimensional finite element analysis of dental implant combined with residual tooth after hemisection under dynamic loads [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(2): 178-183. |
| [6] | Wang Liping, Chen Weihong, Zha Jun, Chen Xili, Su Yucheng, Fang Ying, Dong Yu, Guo Xueqi, Ge Linhu. Short-term efficacy evaluation of Mis Seven implant system repairing dentition loss [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(14): 2208-2214. |
| [7] | Li Ying, You Yapeng, Li Baoe, Song Yunjia, Ma Aobo, Chen Bo, Han Wen, Li Changyi. Type I collagen combined titanium dioxide nanotube composite coating modified titanium surface improves osteoblast adhesion and osseointegration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(14): 2169-2176. |
| [8] | Wei Wei, Shu Jing-ai, Wang Jing, Zheng Li-xia, Li Lu, Wang Qing-shan. Application of hydroxyapatite functional graded biomaterials in human hard tissue replacement [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(6): 971-978. |
| [9] | Li Yi-dan, Xu Nuo, Li Yue-ling, Yu Ming, Chen Jie, Li Xiao-jie. Implanting two kinds of bone substitutes into the sockets after wisdom tooth extraction to recover alveolar bone height [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(6): 846-851. |
| [10] | Liu Ou, Gao Zhu, Li Tao, Zhou Bo. Minocycline hydrochloride ointment is available for the treatment of peri-implantitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(6): 852-857. |
| [11] | Chang Lijun, Tang Tian, Zhang Xiaoge. Periodontal tissue changes in a Beagle dog model of peri-implantitis under orthodontic force [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(34): 5464-5468. |
| [12] | Wang Zhong-da, Wang Yi-bo, Ding Chao, Shi Jiu-hui. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of implant denture for anterior tooth missing with different arch shapes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(30): 4818-4823. |
| [13] | Ma Yan, Zhang Hua, Shang Jian-ping, Jiang Qi. Acid etching and anodic oxidation of titanium surface of nanotubes promotes the proliferation and osteogenesis of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(29): 4614-4619. |
| [14] | Lin Yi, Tao Xian-fa, Wang Yi-bo, Ding Chao, Xing Jian-yu, Xu Ran, Shi Jiu-hui. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of splinted crown restoration of molars with different implant platform positions [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(26): 4123-4127. |
| [15] |
Liu Li-ping, Lv Xiao-fei, Deng Shu, Peng Cheng .
Biomechanical finite element analysis on the bone interface of posterior mandibular area under different setting forces after inclined implantation with angled abutment
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(2): 196-203.
|
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||