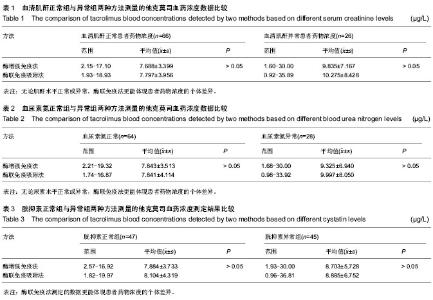
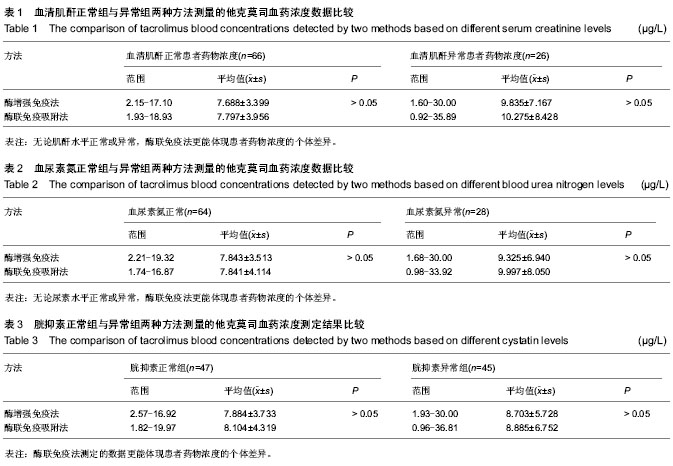
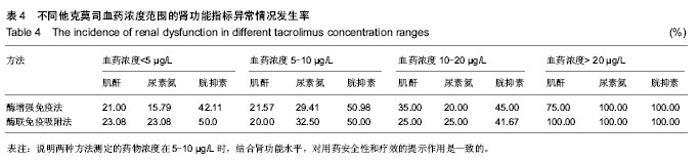
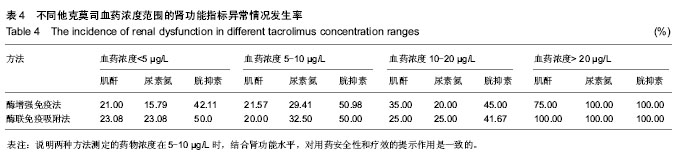
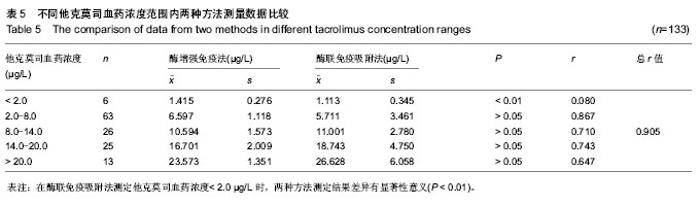
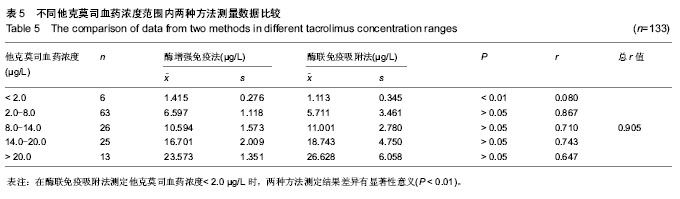
| [1] 谷峰,郭广宏,田亚平,等.肾移植患者服用药物FK506后血清细胞因子及生化指标的变化[J].解放军医学学报, 2005,21(3): 178-181.[2] Levitsky J, Gallon L, Miller J,et al.Allospecific Regulatory Effects of Sirolimus and Tacrolimus in the Human Mixed Lymphocyte Reaction. ransplantation.2010;91(2):199- 206.[3] Guethoff S, Meiser BM, Groetzner. Ten-years results of a randomized trial comparing tacrolimus versus cyclosporine a in combination with mycophenolate mofetil after heart transplantation. Tramsplantation.2013;95(4):629-634.[4] Aoun B, Decramer S, Vitkevic R, et al. Protocol blopsies in pediatric renal transplant recipients on cyclosporine versus tacrolimus-based immunosuppression. Pediatr Nepthrol. 2013;28(3):493-498.[5] 杨红英,杨达宽,陈孝红,等.肝移植病人FK506血药浓度与肾功能检测指标相关关系探讨[J].中华肝胆外科杂志, 2003,9(5): 290-292.[6] Donaldson KJ, Shaw LM. Quantitation of tacrolimus in whole blood using high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry(HPLC-MS-MS).Methods Mol Biol. 2010; 603:479-487.[7] Lee YW.Comparison between ultra-performance liqid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry and a chemiluminescence immunoassay in the determination of cyclosporine A and tacrolimus levels in whole blood.Exp Ther Med.2013;6(6):1535-1539.[8] Upadhyay V,Trivedi V,Shah G, et al.Rapid and Sensitive UPLC-MS-MS Determination of Tacrolimus in Wistar Rats and Human Blood.J Chromatogr Sci.2014;52(1):59-67.[9] Karapiril M,Kizigun M,Yesllyurt O, et al.Simultaneous determination of cyclosporine A,tacrolimus, sirolimus, and everolimus in whole-blood samples by LC-MS/MS. Scientific World J. 2012;2012:571201. [10] Dubbelboer IR, Pohanma A, Said R, et al.Quantification of tacrolimus and three demethylated metabolites in human whole blood using LC-ESI-MS/MS.Ther Drug Monit. 2012; 34(2):134-142.[11] Yamaoka M, Kawamura R, Shioda Y, et al.Analysis of the plasma concentration of tacrolimus: a useful method for distinguishing falsely elevated tacrolimus concentrations reported by the ACMIA.Rinsho Byori.2010; 58(12): 1188-1192.[12] Yargui L,Berhoune A. The EMIT Tacrolimus assay: development of application prorocol for Roche Hitachi 902 analyzer.Ann Biol Clin.2008; 66(6): 657-664.[13] Tomita T, Homma M, Hasegawa Y, et al.Use of sample hematocrit value to correct blood tacrolimus concentration derived by microparticle enzyme immunoassay.Biol Pharm Bull.2008; 31(6): 1250-1253.[14] 丁少波,陈树明,曾智杰,等.肝移植受者他克莫司治疗窗浓度的初步确定[J].中国医院药学杂志, 2003,8(23):11-13.[15] 乔小云,陈冲,蒋俊毅,等.用酶增强免疫分析法监测他克莫司血药浓度的质量评估[J].中国医院药学杂志, 2010,10(1):40-43.[16] 蒋进发,魏思东,陈国勇,等.五酯胶囊对肝移植受者他克莫司浓度的影响[J].中国临床药理学杂志, 2012,28(6):411-413.[17] 丁慧,董振南,贾兴旺,等.他克莫司血药方法的方法学评价[J].标记免疫分析与临床, 2010,17(4): 264-266.[18] 蔡文娥,孙煦勇,秦科,等.酶放大免疫法监测159例肾移植患者他克莫司血药浓度结果分析[J].中国药师, 2011,14(11): 1641-1642.[19] Lower DR, Cropcho L, Rosendorff A. Comparison of CEDIA FK506 assay with HPLC/MS/MS in a large cohort of pediatric patients. Am J Clin Pathol.2013; 139(6):788-792.[20] Tszyrsznic W, Borowiec A, Pawlowska E, et al. Two rapid ultra performance liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry (UPLC/MS/MS) methods with common sample pretreatment for therapeutic drug monitoring of immunosuppressants compared to immunoassay.J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2013;928: 9-15.[21] Henry H, Sobhi HR, Scheibner O, et al. Comparison between a high-resolution single-stage Orbitrap and a triple quadrupole mass spectrometer for quantitative analyses of drugs. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom.2012; 26(5):499-509.[22] 叶伟民,陆慧琦,朱烨.他克莫司在临床检测中的方法学比较[J].现代检验医学杂志,2008,23(2): 85-87.[23] 文爱东,杨志福,赵磊,等.酶联免疫法与微粒子免疫法检测全血他克莫司浓度的比较[J].中国医院药学杂志, 2002,22(6): 346-347.[24] 董新华,尚丽红.他克莫司血药浓度检测方法比较与差异研究[J]. 临床医药实践, 2010,19 (6A): 430-431.[25] 张丽萍,郝钦芳,刘元明.酶增强免疫分析法与微粒子酶联免疫吸附法检测他克莫司药物浓度的结果对比研究[J].检验医学, 2011, 26(8):501-505.[26] 吴锦,胡立芬,李嘉嘉,等.酶联免疫吸附法测定他克莫司血药浓度的质量控制[J].安徽医药, 2013, 17(7):1114-1116.[27] 刘晓雪,胡珊珊,陈中坚,等.LC-MS/MS法测定全血中他克莫司浓度及对肝移植患者药动学研究[J].药学与临床研究, 2013, 21(4): 329-333.[28] 张弋,王志玉,王兆清,等.他克莫司血药浓度检测方法的比较[J].中国药学杂志,2003, 38(5):386-388.[29] Lower DR, Cropcho L, Rosendorff A.Comparison of CEDIA FK506 Assay With HPLC/MS/MS in a Large Cohort of Pediatric Patients.Am J Clin Pathol.2013;139(6): 788-792.[30] Buchwald A, Winkler K, Epting T. Validation of an LC-MS/MS method to determine five immunosuppressants with deuterated internal standards including MPA. BMC Clin Pharmacol.2012; 12(2): 1-11.[31] Ansermot N, Fathi M, Veuthev JL, et al. Quantification of cyclosporine and tacrolimus in whole blood. Comparison of liquid chromatography-electrospray mass spectrometry with the enzyme multiplied immunoassay technique. Clin Biochem. 2008; 41(10-11): 910-913.[32] 钱文璟,李璐,田洁,等. 酶放大免疫测定法和酶联免疫吸附法测定他克莫司血药浓度的比较[J].中国药房,2013,24(26):30-33.[33] 郝堂娜,孙玲,李镇,等.他克莫司血药浓度监测中质控分析评价[J].实用药物与临床,2012,(9):575-577. [34] 冯艳青,刘振红,张杨丽,等.三种他克莫司测定试剂盒测定移植病人全血中他克莫司浓度的比较[J].中国卫生检验杂志,2012,(8). [35] 苏琴,郭亚东,吴双凤,等. 酶联免疫吸附法测定他克莫司血药浓度[J].中国民族民间医药,2010,19(23):54,57. [36] 夏东亚,史国兵,蒋苓. 6062例次他克莫司全血浓度监测结果分析[J].医药导报,2008,27(8):999-1000. [37] 赵虹,孙大军,荣墨克,等.酶联免疫法测定全血他克莫司浓度[J]. 中国实验诊断学,2006,10(7):806-807. [38] 王欣,张晋萍,黄莉莉.他克莫司血药浓度监测中质控图的应用[J]. 中国药房,2006,17(8): 600-601. [39] 呼自顺.他克莫司的血药浓度监测方法在临床中的应用[J].天津药学,2004,16(3): 44-45. |