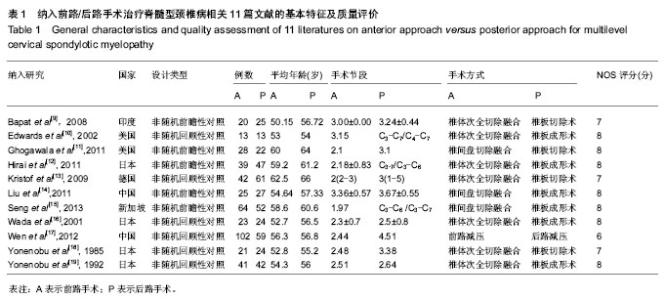
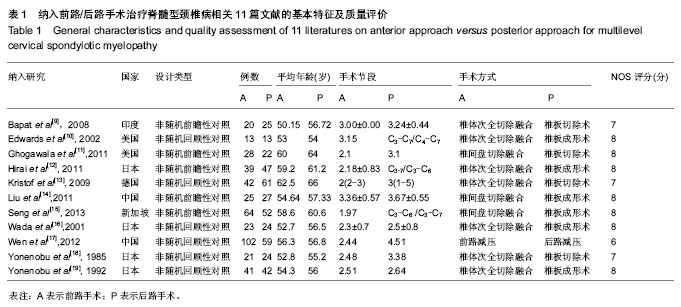
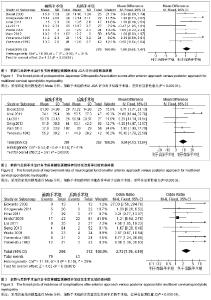
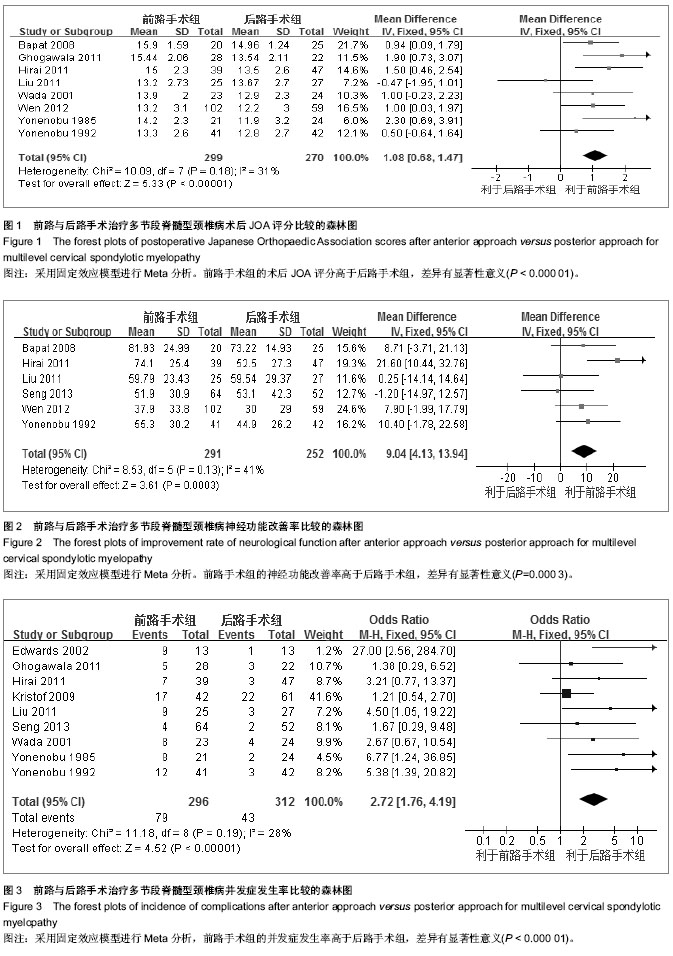
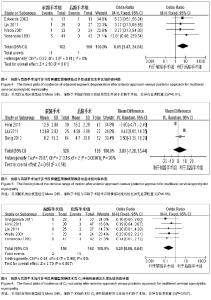
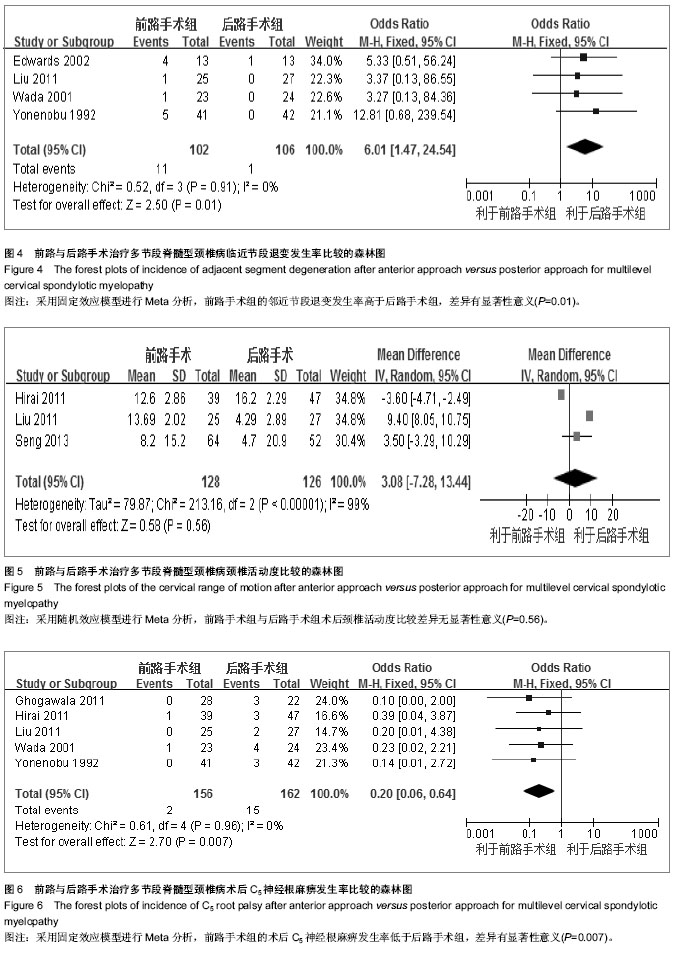
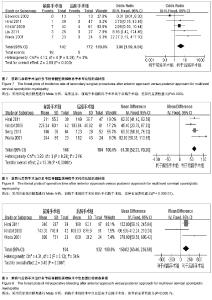
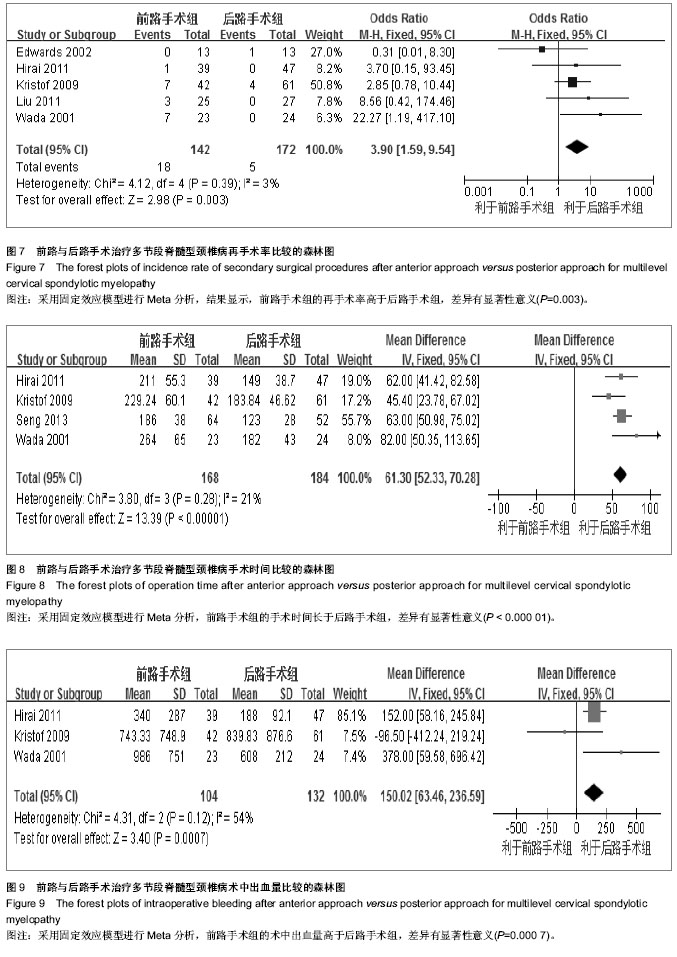
| [1] Rao RD, Gourab K, David KS. Operative treatment of cervical spondylotic myelopathy. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006;88(7): 1619-1640.[2] 何斌,范磊,成伟男,等.颈前路减压+MC+(r)颈椎融合器植骨融合与椎体次全切除融合钛板置入内固定治疗单节段脊髓型颈椎病的比较[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(9):1651-1655.[3] 曾岩,党耕町,马庆军.颈椎前路术后融合节段曲度变化与轴性症状和神经功能的相关性研究[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2004,14(9): 520-523.[4] Uchida K, Nakajima H, Sato R,et al. Cervical spondylotic myelopathy associated with kyphosis or sagittal sigmoid alignment: outcome after anterior or posterior decompression.J Neurosurg Spine. 2009;11(5):521-528.[5] 张威,廖文胜,王利民,等.颈前路2种减压并钢板植入内固定方式治疗相邻两节段脊髓型颈椎病的Meta分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(17):3134-3138.[6] 廖心远,陈德玉,陈宇,等.多节段脊髓型颈椎病的手术治疗进展[J]. 中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2013,23(1):73-76.[7] Guo Q, Bi X, Ni B,et al.Outcomes of three anterior decompression and fusion techniques in the treatment of three-level cervical spondylosis.Eur Spine J. 2011;20(9): 1539-1544. [8] Wells GA, Shea B, O'Connell D, et al. The Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) for assessing the quality of nonrandomised studies in eta-analyses.EHCSRCMethodsLibrary,2012-06-07.[9] Bapat MR, Chaudhary K, Sharma A,et al.Surgical approach to cervical spondylotic myelopathy on the basis of radiological patterns of compression: prospective analysis of 129 cases. Eur Spine J. 2008;17(12):1651-1663.[10] Edwards CC 2nd, Heller JG, Murakami H. Corpectomy versus laminoplasty for multilevel cervical myelopathy: an independent matched-cohort analysis.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2002;27(11):1168-1175.[11] Ghogawala Z, Martin B, Benzel EC,et al.Comparative effectiveness of ventral vs dorsal surgery for cervical spondylotic myelopathy. Neurosurgery. 2011;68(3):622-630.[12] Hirai T, Okawa A, Arai Y,et al.Middle-term results of a prospective comparative study of anterior decompression with fusion and posterior decompression with laminoplasty for the treatment of cervical spondylotic myelopathy.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2011;36(23):1940-1947. [13] Kristof RA, Kiefer T, Thudium M,et al. Comparison of ventral corpectomy and plate-screw-instrumented fusion with dorsal laminectomy and rod-screw-instrumented fusion for treatment of at least two vertebral-level spondylotic cervical myelopathy. Eur Spine J. 2009;18(12):1951-1956. [14] Liu T, Yang HL, Xu YZ,et al. ACDF with the PCB cage-plate system versus laminoplasty for multilevel cervical spondylotic myelopathy.J Spinal Disord Tech. 2011 ;24(4):213-220. [15] Seng C, Tow BP, Siddiqui MA,et al.Surgically treated cervical myelopathy: a functional outcome comparison study between multilevel anterior cervical decompression fusion with instrumentation and posterior laminoplasty.Spine J. 2013; 13(7): 723-731. [16] Wada E, Suzuki S, Kanazawa A,et al. Subtotal corpectomy versus laminoplasty for multilevel cervical spondylotic myelopathy: a long-term follow-up study over 10 years.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2001;26(13):1443-1447.[17] Wen SF, Wong IO, Long MJ,et al.Effectiveness of 3 surgical decompression strategies for treatment of multilevel cervical myelopathy in 3 spinal centers in China: a retrospective study.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2012;37(17):1463-1469.[18] Yonenobu K, Fuji T, Ono K,et al. Choice of surgical treatment for multisegmental cervical spondylotic myelopathy.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1985;10(8):710-716.[19] Yonenobu K, Hosono N, Iwasaki M,et al.Laminoplasty versus subtotal corpectomy. A comparative study of results in multisegmental cervical spondylotic myelopathy.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1992;17(11):1281-1284.[20] 陈耀龙,李幼平,杜亮,等.医学研究中证据分级和推荐强度的演进[J].中国循证医学杂志,2008,8(2):127-133.[21] 盛伟斌,刘忠军,华强,等.同种异体骨在脊髓型颈椎病椎体次全切除减压融合术中的应用[J].中华外科杂志,2004,42(19): 1174-1177.[22] 刘勇,陈亮,顾勇,等.两种前路减压植骨融合并钛钢板置入内固定治疗相邻两个节段脊髓型颈椎病的比较[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(4):597-601.[23] 舒冬平,何敏,刘仕良.颈椎前路钢板置入内固定并减压植骨治疗脊髓型颈椎病118例[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010, 14(48):9117-9120.[24] 胡朝晖,李兵,李龙,等.不同减压植骨及内固定方式治疗多节段脊髓型颈椎病:MRI测量硬脊膜囊矢状径及膨胀恢复率的疗效评价[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2007,11(25):5020-5023.[25] Okawa A, Sakai K, Hirai T,et al.Risk factors for early reconstruction failure of multilevel cervical corpectomy with dynamic plate fixation.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2011 ;36(9): E582-587.[26] 樊仕才,刘成恩,王宏波,等.颈椎前路手术后邻近节段运动变化的生物力学研究[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2005,7(10):924-927.[27] 陈科,陈仲,靳安民,等.比较4种方案治疗脊髓型颈椎病效果的系统性评价[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(48): 9059-9063.[28] 何高,张建湘,申才良,等.颈椎病术后第5颈椎神经根麻痹的临床研究[J].中华外科杂志,2005,43(12):781-783.[29] 陈德玉,贾连顺,赵定麟,等. 颈椎病前路减压术后再手术[J].中华骨科杂志,2002,22(3):134-137. |