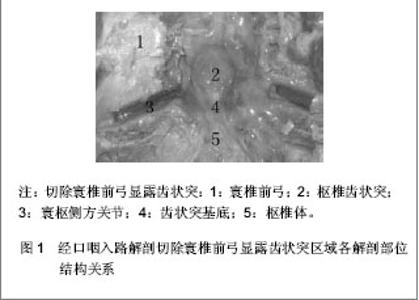
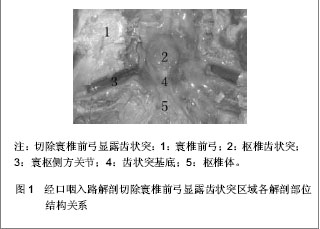
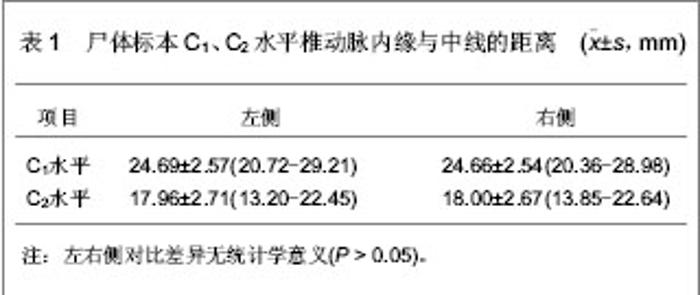
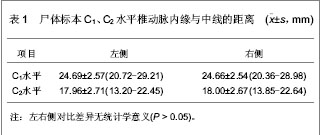
| [1] Refai D, Shin JH, Iannotti C, et al. Dorsal approaches to intradural extramedullary tumors of the craniovertebral junction. J Craniovertebr Junction Spine. 2010;1(1):49-54.[2] 林仲可,池永龙.枕颈交界区前方手术入路的应用解剖研究进展[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2011,21(9):784-787.[3] 洪健.颅颈交界区手术入路显微解剖与固定方法研究[D].天津:天津医科大学,2009:1-139.[4] Kanavel AB. Bullet locked between atlas and the base of the skull: Technique for removal through the mouth. Surg Clin. 1917;1:361-366.[5] Southwick WO, Robinson RA. Surgical approaches to the vertebral bodies in the cervical and lumbar regions. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1957;39-A(3):631-644.[6] Fang HS, Ong B. Direct anterior approach to the upper cer-ical spine. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1962;44:1588-1604. [7] Mullan S, Naunton R, Hekmat-Panah J, et al. The use of an anterior approach to ventrally placed tumors in the foramen magnum and vertebral column. J Neurosurg. 1966;24(2): 536-543.[8] Crockard HA, Sen CN. The transoral approach for the management of intradural lesions at the craniovertebral junction: review of 7 cases. Neurosurgery. 1991;28(1):88-97; discussion 97-98.[9] Salunke P, Behari S, Kirankumar MV, et al. Pediatric congenital atlantoaxial dislocation: differences between the irreducible and reducible varieties. J Neurosurg. 2006;104(2 Suppl):115-122.[10] Gempt J, Lehmberg J, Grams AE, et al. Endoscopic transnasal resection of the odontoid: case series and clinical course. Eur Spine J. 2011;20(4):661-666. [11] Kassam AB, Snyderman C, Gardner P, et al. The expanded endonasal approach: a fully endoscopic transnasal approach and resection of the odontoid process: technical case report. Neurosurgery. 2005;57(1 Suppl):E213; discussion E213. [12] Vangilder JC, Menezes AH. Craniovertebral junction abnormalities. Clin Neurosurg. 1983;30:514-530.[13] 水涛,李捷,高永中.经口入路颅颈交界区的显微外科解剖[J].中华显微外科杂志,1997,20(1):48-52. [14] 靳升荣,代生富,李华,等.经口、咽入路处理颅颈交界区病变的应用解剖[J].中国临床解剖学杂志,2001,19(1):33.[15] Kandziora F, Schulze-Stahl N, Khodadadyan-Klostermann C, et al. Screw placement in transoral atlantoaxial plate systems: an anatomical study. J Neurosurg. 2001;95(1 Suppl):80-87. [16] 中国知网.中国学术期刊总库[DB/OL].2013-04-26. https://www.cnki.net[17] 万方数据库.万方数据知识服务平台[DB/OL].2013-04-26. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/ [18] 王智运.经口咽前路颅颈交界腹侧区显露与固定的解剖和临床研究[D].广东:第一军医大学,2005:1-52.[19] 艾福志,尹庆水,王智运,等.经口咽前入路寰枢椎手术的解剖学研究[J].解放军医学杂志,2004,29(3):220-222.[20] 张朝跃,苗惊雷,易西南,等.内窥镜下经口咽入路寰枢椎手术的可行性研究[J].中华骨科杂志,2004,24(5):299-303.[21] Klekamp J, Batzdorf U, Samii M, et al. The surgical treatment of Chiari I malformation. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 1996;138(7): 788-801. [22] Ugur HC, Kahilogullari G, Attar A, et al. Neuronavigation-assisted transoral-transpharyngeal approach for basilar invagination--two case reports. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo). 2006;46(6):306-308. [23] 王智运,尹庆水,王龙江,等.经口入路颅颈交界区腹侧病变的应用解剖研究[J].中国微侵袭神经外科杂志,2004,9(11):499-501.[24] Bao JJ, Zhang ZQ, Liu XZ, et al. Management of complications of transoral odonitodectomy. ZhongHua Guke Zazhi(Chin Orthop). 1999;19:397-399.[25] Babu RP, Sekhar LN, Wright DC. Extreme lateral transcondylar approach: technical improvements and lessons learned. J Neurosurg. 1994;81(1):49-59.[26] Rocha R, Safavi-Abbasi S, Reis C, et al. Working area, safety zones, and angles of approach for posterior C-1 lateral mass screw placement: a quantitative anatomical and morphometric evaluation. J Neurosurg Spine. 2007;6(3): 247-254. [27] 尹庆水,刘景发,夏虹,等.经口咽前路手术感染的预防(附80例报告)[J].解放军医学杂志,2004,29(3):232-233.[28] 张剑宁,章翔,李安民,等.经口咽入路显微直视减压术治疗颅颈区畸形[J].中华显微外科杂志,2001,24(1):11-12. |