Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research
Previous Articles Next Articles
Intramedullary fixation for the treatment of femoral intertrochanteric fracture: Pros and cons evaluation
Guo Xiao-liang1, Wei Xiao-chun2, Wang Xiao-hu2
- 1 Second Clinical Medical College of Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030001, Shanxi Province, China
2 Second Hospital of Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030001, Shanxi Province, China
-
Received:2012-12-20Revised:2013-03-16Online:2013-06-25Published:2013-06-25 -
Contact:Wei Xiao-chun, Professor, Doctoral supervisor, Second Hospital of Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030001, Shanxi Province, China weixiaochun06@yahoo.com.cn -
About author:Guo Xiao-liang★, Studying for master’s degree, Second Clinical Medical College of Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030001, Shanxi Province, China guoxiaoliang0@163.com
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Guo Xiao-liang1, Wei Xiao-chun2, Wang Xiao-hu2. Intramedullary fixation for the treatment of femoral intertrochanteric fracture: Pros and cons evaluation[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2013.26.021.
share this article

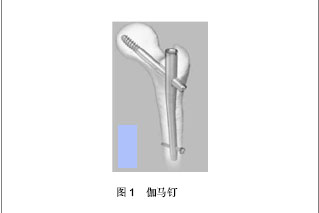
2.1 伽马钉(Gamma Nail) Gamma钉是由法国Gross于1989年最早应用于临床治疗股骨转子间骨折的髓内系统[7],目前已发展到第3代[8],见图1。Gamma钉内固定技术除感染外无绝对禁忌证,能有效的传递载荷,骨折部嵌插,增加了稳定性,允许固定后早期负重。并有效克服了股骨转子骨质粉碎局部无支撑这一力学缺陷,适用于各种类型股骨转子间骨折,疗效满意,特别是对不稳定型的股骨转子间骨折,髓内固定较钉板系统更有优势[9]。使用Gamma钉治疗不稳定性粉碎型转子间骨折,不需要过分强求解剖复位,只需达功能复位即可,以减少手术时间和手术创伤[10]。王建辉等[11]报道Gamma钉治疗104例股骨转子间骨折,随访2-91个月,骨折全部愈合,其优良率86.5%(90/104),但Gamma钉治疗初期发生股骨干骨折1例,术后发生2例,其中锁钉处骨折1例,主钉远端骨折1例,还有6例患者发生髋内翻及螺钉切割股骨头。Gamma钉的缺点是,可能出现应力骨折,股骨头颈内为单根拉力螺钉,因为它的防旋螺钉抗旋转作用不足,所以钉尖部较易导致应力集中,如果发生拉力螺钉自股骨头穿出,或者拉力螺钉位置放置不当时都比较容易导致髋内翻畸形[12],国外有学者Tarantino 等[13]报道术后骨折及患肢疼痛发生率为1%-8%。曾宪林等[14]报道50例股骨转子间骨折患者均采用Gamma钉技术手术治疗,术后随访4-29个月,其中35例负重行走有力,髋关节活动达到正常范围,其余15例出现并发症:髋内外翻5例,拉力螺钉切出及下肢短缩2例,下肢外旋畸形3例,髋关节痛2例,膝关节痛并僵直1例,股骨锁钉处骨折1例,内固定失败1例,其造成并发症的原因是多方面的,应根据骨骼的质量、骨块几何形状、复位情况、内固定设计、内固定位置以及手术设备条件和医师熟练操作程度等选择不同内固定方式,减少各种并发症的发生。李锋生等[15]研究表明与传统Gamma钉内固定治疗老年股骨转子间骨折比较,在X射线透视导航下运用Gamma钉内固定可以精确地保证尖顶距< 25 mm,且具有切口小、术中出血少及术后髋关节功能恢复好等优点,值得在临床推广。"

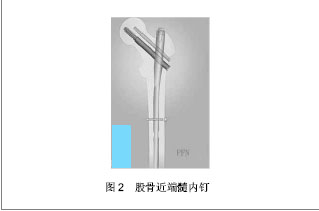
股骨近端髓内钉适用于AO分类中31-A的所有骨折和转子下高位股骨干骨折。股骨近端髓内钉远端针体直径较小,缩短了手术时间,减少手术出血以及脂肪栓塞等并发症的发生[17-18]。由于其钉尾距远端锁定螺钉,减少了应力集中,可以预防发生股骨干骨折[19]。AO 学会报道断钉率低于0.6%[20]。近端2枚螺钉的设计,有利于稳定骨折,抗旋能力也较前明显提高[21],尚益峰[22]分析并评价股骨近端髓内钉(PFN)治疗16例股骨转子下骨折的临床疗效,全部骨折患者均是闭合复位,手术用时47-195 min,平均为67 min;术中出血量为140-810 mL,平均术中出血量为590 mL,术后复查X射线片显示内固定近端髓内钉位置均较理想,患者出院后一两个月复查X射线片,未见发生骨折移位于髋内翻病例,全部患者拄拐辅助活动均较为方便,全部患者均达到解剖复位,五六个月左右骨折愈合。国外学者Simmermacher等[23]通过随访191例股骨近端髓内钉治疗的股骨转子间骨折患者,发生螺钉切割股骨头颈0.6%。但股骨近端髓内钉也有缺点:出现“Z”字效应,是由螺旋刀片切出股骨颈,防旋螺钉退出造成的[24-25]。戈涛等[26]应用股骨近端髓内钉治疗227例老年脆性股骨转子间骨折患者,16例患者在1年内出现Ⅱ期骨折旋转移位及股骨颈螺钉切头,其中行Ⅱ期手术取出内固定外展位牵引治疗8例,人工关节置换8例。通过分析得出股骨近端髓内钉手术治疗老年脆性股骨转子间骨折在手术复位、股骨颈主拉力螺钉和防旋次螺钉的放置位置要求较高,入钉转子外侧骨皮质情况、患者术后配合情况、改良Jensen-Evans 分型、Singh骨质疏松分级等多种因素均与手术预后相关。2.3 股骨近端抗旋髓内钉(proximal femoral nail antirotation,PFNA) 股骨近端抗旋髓内钉(PFN-A)是一种新型内固定物,是由国际内固定学会基于股骨近端髓内钉研制设计出的,它使手术操作更加简化,而且它的设计比较符合人体的生物力学传导方式和股骨的解剖结构[27],见图3。"


股骨近端抗旋髓内钉(PFN-A)只有1枚螺旋刀片,避免了“Z”字效应,螺旋刀片比螺钉移除的骨量少,其末端较宽大的表面能更好的压缩骨质,具有较好的把持力,它的抗旋转、防塌陷以及抗拔除力更强;股骨近端抗旋髓内钉的主钉有6°外翻角,手术进针点不是在梨状窝而在股骨大转子的顶端,使术中插入股骨近端抗旋髓内钉时更加容易,设计出的股骨近端抗旋髓内钉尖端较长及它的凹槽,锁定螺钉距主钉末端的间距,避免了由于应力集中导致股骨干骨折的缺点[28]。Mereddy等[29]研究认为,对于不稳定性股骨转子间及转子下骨折,运用股骨近端抗旋髓内钉治疗的优点是手术时间短、出血少、创伤小,术后并发症少、负重功能锻炼早、骨折不愈合率低。但它也有缺点,术中插入螺旋刀片时易致骨折断端分离,所以术前需通过牵引治疗,使骨折良好复位,Simmernacher等[30]认为对于不稳定的股骨转子间骨折,尤其是老年骨质疏松的患者利用股骨近端抗旋髓内钉治疗是比较理想的选择。国内邓建华等[31]应用股骨近端抗旋髓内钉-Ⅱ治疗不稳定的粉碎性转子间复杂骨折具有手术疗效可靠、并发症少、操作简单等优点,推荐在治疗复杂转子间骨折时优先考虑采用股骨近端抗旋髓内钉-Ⅱ。李承杰等[32]认为股骨近端抗旋髓内钉具有操作简单、骨折固定稳定、符合生物力学固定原则等优点,对高龄不稳定的股骨转子间骨折是一种良好的内固定方法,同时股骨近端抗旋髓内钉手术围手术期隐性失血量较大,可能会导致术后贫血。 2.4 可膨胀股骨近端髓内钉(expandable proximal femoral nail,EPFN) 1999年由以色列DiscOTech公司研制出可膨胀股骨近端髓内钉,它由主钉和髋栓钉组成,其中主钉植入股骨干,髋栓钉植入股骨头内,通过主钉和髋栓钉膨胀取得牢固内固定,股骨头内还可以植入1枚锁钉,见图4。"

相对于其他髓内固定而言,可膨胀股骨近端髓内钉优点是:①髋栓钉与普通螺钉的拉力相当,但有研究表明,在生物力学的抗扭转稳定性来说,髋栓钉是普通螺钉的5倍[33],有研究表明髋栓钉膨胀后周围的骨密度是增加的,而普通交锁髓内钉周围的骨密度是减少的,骨密度增加可以加强髋栓钉的固定,可以降低螺钉切割股骨头脱出的发生率[34]。②普通的交锁髓内钉是依靠三点固定原理,它的应力过于集中,易导致远端股骨干骨折;可膨胀股骨近端髓内钉膨胀后与髓腔内壁紧密贴服,应力均匀分布于整个骨干,使整个髓腔内的负荷是一致的。③通过主钉和髋栓钉远端的膨胀,即使患者的股骨髓腔大小不一、骨质疏松的程度不同,它都能紧密贴服于股骨髓腔和股骨头骨质,确保内固定的牢靠[35]。可膨胀髓内钉FixionTM系统是髓内钉固定理念和技术的革新,汪滋民等[35]应用这一新技术治疗21例四肢骨折患者,伤口全部一期愈合,手术时间35-210 min,平均90 min,术中出血30-1 500 mL,平均出血量280 mL,术中平均透视4.9次,X射线片示股骨干、胫骨干骨折术后4周均有骨痂出现,骨折术后临床和影像学愈合时间为:胫骨干骨折12周,股骨干骨折10周,肱骨骨折12周,股骨近端骨折10周,无感染、脂肪栓塞、深静脉血栓、骨折不愈合、肢体短缩及旋转畸形发生。可膨胀髓内钉根据髓腔解剖特点呈沙漏样固定,应力分布更为均匀;节省了扩髓和锁钉的操作,减少了创伤、手术时间、医生和患者接受的X射线剂量和感染率;轴相弹性固定加快了骨折愈合时间,在掌握好适应证和正确操作的前提下,FixionTM系统治疗四肢骨干骨折和股骨近端骨折有比传统交锁髓内钉更好的效果,尤其适用于骨质疏松患者的治疗。④降低了手术并发症,因为它不需要远端锁钉,简化手术操作。国外学者Hopp等[36]认为治疗不稳定转子间骨折,可膨胀股骨髓内钉具有手术时间短、操作简单、透视少等优点。但是由于临床应用时间较短,临床上报道可膨胀股骨近端髓内钉并发症的文献较少,常见的并发症有术中主钉膨胀过度导致骨质劈裂[37],术后患肢深部感染等,但发生率都不高。 2.5 微创短重建钉(TAN) 微创短重建钉是Gamma钉的改进型,它在传统Gamma钉的基础上增加了防旋和主钉长度,其股骨颈内有2枚相同直径的拉力螺钉,它的生物力学设计增加了抗旋转稳定性,通过平行加压头颈使股骨颈错位减小,并且避免了因长度过短、髓钉远端应力集中而骨折的可能[38],见图5。有学者认为微创短重建钉有很好的临床应用前景[39],因为其应用了微创技术,缩短了手术时间,降低了手术风险。"
| [1] Liporace FA, Egol KA, Tejwani N,et al.What's new in hip fractures? Current concepts. Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ). 2005;34(2):66-74.[2] Doruk H, Mas MR, Yildiz C,et al.The effect of the timing of hip fracture surgery on the activity of daily living and mortality in elderly. Arch Gerontol Geriatr. 2004;39(2):179-185.[3] Efstathopoulos NE, Nikolaou VS, Lazarettos JT. Intramedullary fixation of intertrochanteric hip fractures: a comparison of two implant designs. Int Orthop. 2007;31(1): 71-76.[4] Menezes DF, Gamulin A, Noesberger B. Is the proximal femoral nail a suitable implant for treatment of all trochanteric fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2005;439:221-227.[5] Seral B, García JM, Cegoñino J,et al. Finite element study of intramedullary osteosynthesis in the treatment of trochanteric fractures of the hip: Gamma and PFN. Injury. 2004;35(2): 130-135.[6] Schipper IB, Steyerberg EW, Castelein RM,et al. Treatment of unstable trochanteric fractures. Randomised comparison of the gamma nail and the proximal femoral nail.J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2004;86(1):86-94.[7] Rosenblum SF, Zuckerman JD, Kummer FJ,et al. A biomechanical evaluation of the Gamma nail. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1992;74(3):352-357.[8] Sommers MB, Roth C, Hall H,et al. A laboratory model to evaluate cutout resistance of implants for pertrochanteric fracture fixation.J Orthop Trauma. 2004;18(6):361-368.[9] Bhandari M, Schemitsch E, Jönsson A, et al. Gamma nails revisited: gamma nails versus compression hip screws in the management of intertrochanteric fractures of the hip: a meta-analysis.J Orthop Trauma. 2009;23(6):460-464.[10] Bellabarba C, Herscovici D Jr, Ricci WM. Percutaneous treatment of peritrochanteric fractures using the Gamma nail. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2000;(375):30-42.[11] 王建辉,刘长贵,罗先正,等. 股骨近端髓内钉和Gamma钉治疗股骨转子间骨折的生物力学研究及临床疗效观察[J]. 中华创伤杂志,2003,19(2):83-84.[12] Haynes RC, Pöll RG, Miles AW, et al. Failure of femoral head fixation: a cadaveric analysis of lag screw cut-out with the gamma locking nail and AO dynamic hip screw. Injury. 1997; 28(5-6):337-341.[13] Tarantino U, Oliva F, Impagliazzo A,et al. A comparative prospective study of dynamic variable angle hip screw and Gamma nail in intertrochanteric hip fractures. Disabil Rehabil. 2005;27(18-19):1157-1165.[14] 曾宪林,周忠,蒋林.应用Gamma钉治疗股骨转子间骨折术后并发症发生因素的分析[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2007, 21(1): 9-11.[15] 李锋生,叶冬平,梁伟国,等.X线透视导航下运用Gamma钉治疗股骨转子间骨折18例[J].广东桥学,2012,33(4):474-476.[16] Cole PA, Bhandari M.What's new in orthopaedic trauma. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006;88(11):2545-2561.[17] Boldin C, Seibert FJ, Fankhauser F,et al.The proximal femoral nail (PFN)- a minimal invasive treatment of unstable proximal femoral fractures: a prospective study of 55 patients with a follow-up of 15 months. Acta Orthop Scand. 2003;74(1):53-58.[18] Banan H, Al-Sabti A, Jimulia T,et al.The treatment of unstable, extracapsular hip fractures with the AO/ASIF proximal femoral nail (PFN)--our first 60 cases. Injury. 2002;33(5):401-405.[19] Schipper IB, Steyerberg EW, Castelein RM,et al.Treatment of unstable trochanteric fractures. Randomised comparison of the gamma nail and the proximal femoral nail. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2004;86(1):86-94.[20] Al-yassari G, Langstaff RJ, Jones JW,et al.The AO/ASIF proximal femoral nail (PFN) for the treatment of unstable trochanteric femoral fracture. Injury. 2002;33(5):395-399.[21] 王秋根,陆晴友.骨质疏松性骨折的外科治疗进展[J].中华骨科杂志, 2004, 24(11):678-682.[22] 尚益峰.股骨近端髓内钉(PFN)治疗股骨转子下骨折16例临床分析[J].中国医药指南,2012,10(18):611-612. [23] Simmermacher RK, Bosch AM, Van der Werken C.The AO/ASIF-proximal femoral nail (PFN): a new device for the treatment of unstable proximal femoral fractures.Injury. 1999;30(5):327-332.[24] Park SY, Yang KH, Yoo JH,et al.The treatment of reverse obliquity intertrochanteric fractures with the intramedullary hip nail.J Trauma. 2008;65(4):852-857.[25] 沈碧城.股骨近端髓内钉治疗不稳定性转子间骨折[J].生物骨科材料与临床研究,2011,8(3):40-41.[26] 戈涛,梁英杰,林博川,等.股骨近端髓内钉治疗老年脆性股骨转子间骨折后Ⅱ期旋转移位及螺钉切头原因分析[J].中华创伤杂志, 2010,26(11):995-998.[27] Simmermacher RK, Ljungqvist J, Bail H,et al.The new proximal femoral nail antirotation (PFNA) in daily practice: results of a multicentre clinical study.Injury. 2008; 39(8): 932-939.[28] Sahin S, Ertürer E, Oztürk I,et al.Radiographic and functional results of osteosynthesis using the proximal femoral nail antirotation (PFNA) in the treatment of unstable intertrochanteric femoral fractures.Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc. 2010;44(2):127-134.[29] Mereddy P, Kamath S, Ramakrishnan M,et al.The AO/ASIF proximal femoral nail antirotation (PFNA): a new design for the treatment of unstable proximal femoral fractures.Injury. 2009;40(4):428-432.[30] Simmermacher RK, Ljungqvist J, Bail H,et al.The new proximal femoral nail antirotation (PFNA) in daily practice: results of a multicentre clinical study.Injury. 2008;39(8): 932-939.[31] 邓建华,吴俊,郭建成,等.PFNA-Ⅱ治疗复杂股骨转子间骨折疗效初步报告[J].国际骨科学杂志,2012,33(5):336-338.[32] 李承杰,王朝晖,唐艳平,等.股骨近端抗旋髓内钉治疗高龄不稳定性股骨转子间骨折的应用体会[J].创伤外科杂志,2012,14(2): 144-146.[33] Steinberg EL, Blumberg N, Dekel S.The fixion proximal femur nailing system: biomechanical properties of the nail and a cadaveric study.J Biomech. 2005;38(1):63-68.[34] Folman Y, Ron N, Shabat S,et al. Peritrochanteric fractures treated with the Fixion expandable proximal femoral nail: technical note and report of early results.Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2006;126(3):211-214. [35] 汪滋民,纪方,张秋林,等.可膨胀髓内钉Fixion系统治疗四肢骨折[J].国外医学:骨科学分册, 2005,26(4):253-255.[36] Hopp M, Werding G, Tauber M. Stabilization of proximal femoral fractures using the fixion proximal femur intramedullary nail (our first 30 cases). Societe internationale de chirurgie othopedique et detrauma tologie, XII World Congress. 2002.[37] Lepore S,Capuano N,Lepore L,et al. Clinical and radiographic results with the fixion® intramedullary nail:An inflatable self-locking system for long bone fractures.Osteo Trauma Care.2002;10:S32-S35.[38] 赖绍斌,林义明,沈立熙. 股骨重建钉治疗老年股骨粗隆间骨折[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2006,21(8):656.[39] Ruecker AH, Rupprecht M, Gruber M,et al.The treatment of intertrochanteric fractures: results using an intramedullary nail with integrated cephalocervical screws and linear compression.J Orthop Trauma. 2009;23(1):22-30.[40] Megas P, Kaisidis A, Zouboulis P,et al. Comparative study of the treatment of pertrochanteric fractures--trochanteric gamma nail vs. proximal femoral nail. Z Orthop Ihre Grenzgeb. 2005;143(2):252-257.[41] Ruecker AH, Rupprecht M, Gruber M,et al.The treatment of intertrochanteric fractures: results using an intramedullary nail with integrated cephalocervical screws and linear compression. J Orthop Trauma. 2009;23(1):22-30.[42] 吕刚,陈平波,吕发明.新一代股骨近端髓内钉INTERTAN内植物应用特征并19例回顾[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009, 13(26):5162-5166.[43] Bogoch ER, Ouellette G, Hastings DE. Intertrochanteric fractures of the femur in rheumatoid arthritis patients.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1993;(294):181-186.[44] 高雁卿,左立新,王晓琼,等.老年转子间骨折外科治疗方法选择[J].中华医学杂志,2012,92(29):2038-2041.[45] 陈志坚.骨水泥型人工股骨头置换术在高龄股骨转子间粉碎性骨折治疗中的临床应用[J].中国医师进修杂志,2012,35(11): 61-62.[46] 张敬东,项良碧,祖启明,等. 人工股骨头置换治疗高龄股骨转子间不稳定型骨折[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(35): 6514-6518.[47] Rodop O, Kiral A, Kaplan H, et al. Primary bipolar hemiprosthesis for unstable intertrochanteric fractures. Int Orthop. 2002;26(4):233-237.[48] Broos PL, Rommens PM, Geens VR, et al. Pertrochanteric fractures in the elderly. Is the Belgian VDP prosthesis the best treatment for unstable fractures with severe comminution.Acta Chir Belg. 1991;91(5):242-249.[49] Hsu CJ, Chou WY, Chiou CP,et al. Hemi-arthroplasty with supplemental fixation of greater trochanter to treat failed hip screws of femoral intertrochanteric fracture. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2008;128(8):841-845.[50] Haentjens P, Lamraski G. Endoprosthetic replacement of unstable, comminuted intertrochanteric fracture of the femur in the elderly, osteoporotic patient: a review. Disabil Rehabil. 2005;27(18-19):1167-1180.[51] Haentjens P, Casteleyn PP, Opdecam P. Primary bipolar arthroplasty or total hip arthroplasty for the treatment of unstable intertrochanteric and subtrochanteric fractures in elderly patients. Acta Orthop Belg. 1994;60 Suppl 1:124-128.[52] Gu GS, Wang G, Sun DH, et al. Cemented bipolar hemiarthroplasty with a novel cerclage cable technique for unstable intertrochanteric hip fractures in senile patients. Chin J Traumatol. 2008;11(1):13-17.[53] Haidukewych GJ. Intertrochanteric fractures: ten tips to improve results. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2009;91(3):712-719.[54] Geiger F, Zimmermann-Stenzel M, Heisel C,et al.Trochanteric fractures in the elderly: the influence of primary hip arthroplasty on 1-year mortality. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2007;127(10):959-966. |
| [1] | Xu Feng, Kang Hui, Wei Tanjun, Xi Jintao. Biomechanical analysis of different fixation methods of pedicle screws for thoracolumbar fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1313-1317. |
| [2] | Chen Xinmin, Li Wenbiao, Xiong Kaikai, Xiong Xiaoyan, Zheng Liqin, Li Musheng, Zheng Yongze, Lin Ziling. Type A3.3 femoral intertrochanteric fracture with augmented proximal femoral nail anti-rotation in the elderly: finite element analysis of the optimal amount of bone cement [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1404-1409. |
| [3] | Zhou Jihui, Li Xinzhi, Zhou You, Huang Wei, Chen Wenyao. Multiple problems in the selection of implants for patellar fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1440-1445. |
| [4] | Tang Hui, Yao Zhihao, Luo Daowen, Peng Shuanglin, Yang Shuanglin, Wang Lang, Xiao Jingang. High fat and high sugar diet combined with streptozotocin to establish a rat model of type 2 diabetic osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1207-1211. |
| [5] | Li Zhongfeng, Chen Minghai, Fan Yinuo, Wei Qiushi, He Wei, Chen Zhenqiu. Mechanism of Yougui Yin for steroid-induced femoral head necrosis based on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1256-1263. |
| [6] | Xu Yulin, Shen Shi, Zhuo Naiqiang, Yang Huilin, Yang Chao, Li Yang, Zhao Heng, Zhao Lu. Biomechanical comparison of three different plate fixation methods for acetabular posterior column fractures in standing and sitting positions [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 826-830. |
| [7] | Cai Qunbin, Zou Xia, Hu Jiantao, Chen Xinmin, Zheng Liqin, Huang Peizhen, Lin Ziling, Jiang Ziwei. Relationship between tip-apex distance and stability of intertrochanteric femoral fractures with proximal femoral anti-rotation nail: a finite element analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 831-836. |
| [8] | Hou Guangyuan, Zhang Jixue, Zhang Zhijun, Meng Xianghui, Duan Wen, Gao Weilu. Bone cement pedicle screw fixation and fusion in the treatment of degenerative spinal disease with osteoporosis: one-year follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 878-883. |
| [9] | Song Chengjie, Chang Hengrui, Shi Mingxin, Meng Xianzhong. Research progress in biomechanical stability of lateral lumbar interbody fusion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 923-928. |
| [10] | Li Shibin, Lai Yu, Zhou Yi, Liao Jianzhao, Zhang Xiaoyun, Zhang Xuan. Pathogenesis of hormonal osteonecrosis of the femoral head and the target effect of related signaling pathways [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 935-941. |
| [11] | Xie Chongxin, Zhang Lei. Comparison of knee degeneration after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction with or without remnant preservation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 735-740. |
| [12] | Xiao Fangjun, Chen Shudong, Luan Jiyao, Hou Yu, He Kun, Lin Dingkun. An insight into the mechanism of Salvia miltiorrhiza intervention on osteoporosis based on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 772-778. |
| [13] | Liu Bo, Chen Xianghe, Yang Kang, Yu Huilin, Lu Pengcheng. Mechanism of DNA methylation in exercise intervention for osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 791-797. |
| [14] | Zhou Jihui, Li Xinzhi, Zhou You, Huang Wei, Chen Wenyao. Comparison of the advantages and disadvantages of multiple implants in treatment of traumatic dislocation of sternoclavicular joint [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 443-448. |
| [15] | Zhong Yuanming, Wan Tong, Zhong Xifeng, Wu Zhuotan, He Bingkun, Wu Sixian. Meta-analysis of the efficacy and safety of percutaneous curved vertebroplasty and unilateral pedicle approach percutaneous vertebroplasty in the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 456-462. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||