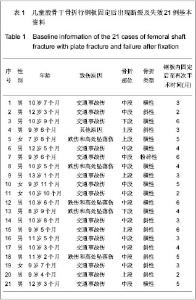
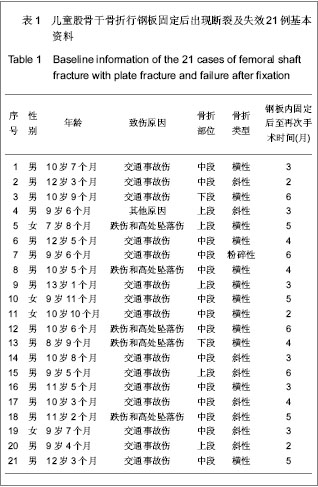
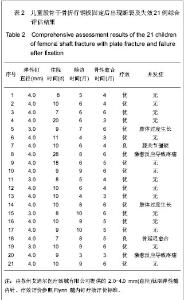
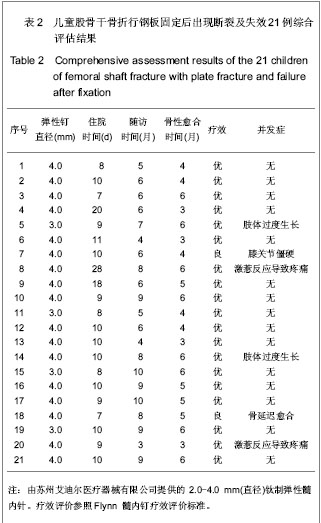
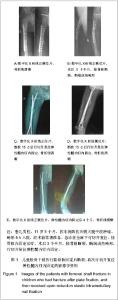
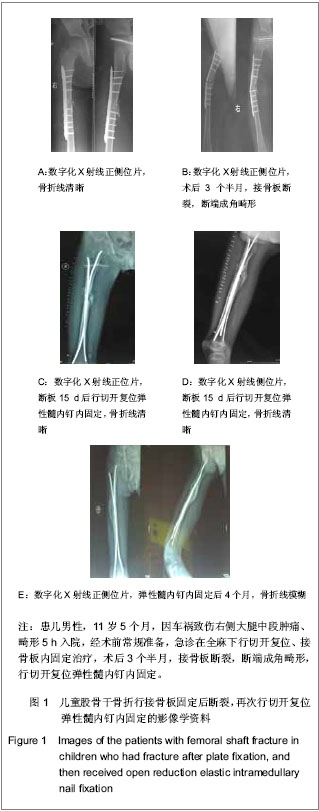
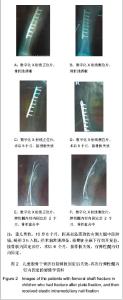
| [1] Ligier JN, Metaizeau JP, Prévot J,et al. Elastic stable intramedullary nailing of femoral shaft fractures in children.J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1988;70(1):74-77.[2] de Sanctis N, Andreacchio A. Elastic stable intramedullary nailing is the best treatment of unicameral bone cysts of the long bones in children?: Prospective long-term follow-up study. J Pediatr Orthop. 2006;26(4):520-525.[3] Flynn JM, Luedtke LM, Ganley TJ,et al.Comparison of titanium elastic nails with traction and a spica cast to treat femoral fractures in children.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2004; 86-A(4):770-777.[4] Mahar AT, Lee SS, Lalonde FD,et al. Biomechanical comparison of stainless steel and titanium nails for fixation of simulated femoral fractures.J Pediatr Orthop. 2004;24(6): 638-641.[5] Sink EL, Gralla J, Repine M.Complications of pediatric femur fractures treated with titanium elastic nails: a comparison of fracture types.J Pediatr Orthop. 2005;25(5):577-580.[6] Ballock RT, O'Keefe RJ.The biology of the growth plate. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2003;85-A(4):715-726.[7] Chen W,Ding ZQ,Kang LQ,et al. Zhonghua Xiaoer Waike Zazhi. 2007, 28(9):501-502.陈卫,丁真奇,康两奇,等.经皮钢板微创治疗儿童股骨干粉碎性骨折[J].中华小儿外科杂志, 2007, 28(9):501-502.[8] El-Adl G, Mostafa MF, Khalil MA,et al.Titanium elastic nail fixation for paediatric femoral and tibial fractures.Acta Orthop Belg. 2009;75(4):512-520.[9] Liu GR,Zhu JH,Li XN,et al. Zhonghua Xiaoer Waike Zazhi. 1998;19(5):303.刘光荣,祝敬华,李小年,等.儿童股骨干骨折畸形愈合原因分析及疗效观察[J].中华小儿外科杂志,1998,19(5):303.[10] Li Y, Hedequist DJ.Submuscular plating of pediatric femur fracture.J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2012;20(9):596-603. [11] Wenger DR, Pring ME.Beijing:People’s Medical Publishing House, 2006:106.Wenger DR, Pring ME. Rang小儿骨折[M].北京:人民卫生出版社,2006:166.[12] Khazzam M, Tassone C, Liu XC,et al.Use of flexible intramedullary nail fixation in treating femur fractures in children.Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ). 2009;38(3):E49-55.[13] Li Y, Stabile KJ, Shilt JS. Biomechanical analysis of titanium elastic nail fixation in a pediatric femur fracture model.J Pediatr Orthop. 2008;28(8):874-878.[14] Volpon JB, Perina MM, Okubo R,et al. Biomechanical performance of flexible intramedullary nails with end caps tested in distal segmental defects of pediatric femur models.J Pediatr Orthop. 2012;32(5):461-466.[15] Altay MA, Erturk C, Cece H,et al. Mini-open versus closed reduction in titanium elastic nailing of paediatric femoral shaft fractures: a comparative study.Acta Orthop Belg. 2011;77(2): 211-217.[16] Metaizeau JP. Stable elastic intramedullary nailing for fractures of the femur in children.J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2004;86(7):954-957.[17] Narayanan UG, Hyman JE, Wainwright AM,et al. Complications of elastic stable intramedullary nail fixation of pediatric femoral fractures, and how to avoid them.J Pediatr Orthop. 2004;24(4):363-369.[18] Shemshaki HR, Mousavi H, Salehi G,et al.Titanium elastic nailing versus hip spica cast in treatment of femoral-shaft fractures in children.J Orthop Traumatol. 2011;12(1):45-48. |