Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research
Previous Articles Next Articles
Anatomical measurements of proximal tibia of anterior and posterior cruciate ligament-retaining knee prosthesis
He Pei-heng, Xu Dong-liang, Zuo Jian-wei, Li Shuai-hua, Wa Qing-de
- Department of Joint Surgery, the First Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou 510080, Guangdong Province, China
-
Received:2013-03-05Revised:2013-04-23Online:2013-06-25Published:2013-06-25 -
Contact:Xu Dong-liang, Doctoral supervisor, Professor, Chief physician, Department of Joint Surgery, the First Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou 510080, Guangdong Province, China xdl1234hph@sina.com -
About author:He Pei-heng☆, Studying for doctorate, Department of Joint Surgery, the First Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou 510080, Guangdong Province, China hepeiheng1234@sina.com -
Supported by:“5010” Clinical Research Fund of Sun Yat-sen University, No.2010005
CLC Number:
Cite this article
He Pei-heng, Xu Dong-liang, Zuo Jian-wei, Li Shuai-hua, Wa Qing-de. Anatomical measurements of proximal tibia of anterior and posterior cruciate ligament-retaining knee prosthesis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2013.26.004.
share this article
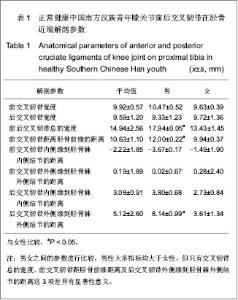
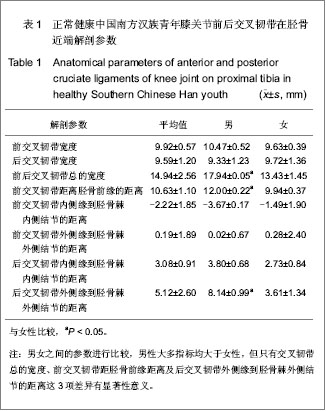
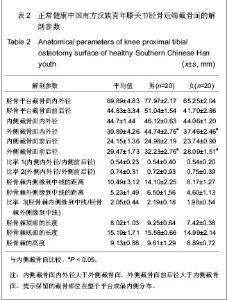
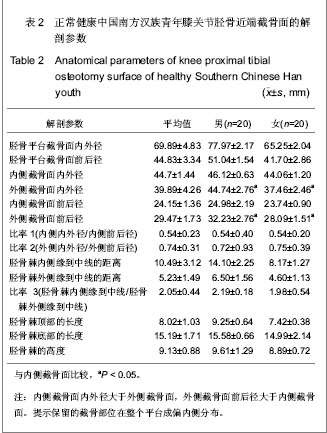
| [1] Seo JG, Moon YW, Park SH, et al. A case-control study of spontaneous patellar fractures following primary total knee replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2012;94(7):908-913. [2] Weinstein AM, Rome BN, Reichmann WM, et al. Estimating the burden of total knee replacement in the United States. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2013;95(5):385-392. [3] Weber O, Goost H, Mueller M, et al. Mid-term results after post-traumatic knee joint replacement in elderly patients. Z Orthop Unfall. 2011r;149(2):166-172.[4] Judge A, Arden NK, Cooper C, et al. Predictors of outcomes of total knee replacement surgery. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2012;51(10):1804-1813. [5] Tungtrongjit Y, Weingkum P, Saunkool P. The effect of preoperative quadriceps exercise on functional outcome after total knee arthroplasty. J Med Assoc Thai. 2012t;95 Suppl 10: S58-66. [6] Judd DL, Eckhoff DG, Stevens-Lapsley JE. Muscle strength loss in the lower limb after total knee arthroplasty. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2012;91(3):220-226. [7] Dennis DA, Komistek RD, Mahfouz MR, et al. Multicenter determination of in vivo kinematics after total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2003;(416):37-57. [8] Kitagawa A, Tsumura N, Chin T, et al. In vivo comparison of knee kinematics before and after high-flexion posterior cruciate-retaining total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2010; 25(6):964-969.[9] Hosseini A, Van de Velde S, Gill TJ, et al. Tibiofemoral cartilage contact biomechanics in patients after reconstruction of a ruptured anterior cruciate ligament. J Orthop Res. 2012; 30(11):1781-1788. [10] Chen CH, Li JS, Hosseini A,et al. Anteroposterior stability of the knee during the stance phase of gait after anterior cruciate ligament deficiency. Gait Posture. 2012;35(3):467-471. [11] Moro-oka TA, Muenchinger M, Canciani JP, et al. Comparing in vivo kinematics of anterior cruciate-retaining and posterior cruciate-retaining total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2007;15(1):93-99. [12] Mikashima Y, Tomatsu T, Horikoshi M, et al. In vivo deep-flexion kinematics in patients with posterior-cruciate retaining and anterior-cruciate substituting total knee arthroplasty. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2010;25(1):83-87.[13] Koyonos L, Stulberg SD, Moen TC, et al. Sources of error in total knee arthroplasty. Orthopedics. 2009;32(5):317. [14] Perillo-Marcone A, Taylor M. Effect of varus/valgus malalignment on bone strains in the proximal tibia after TKR: an explicit finite element study. J Biomech Eng. 2007;129(1): 1-11.[15] Jenny JY, Jenny G. Preservation of anterior cruciate ligament in total knee arthroplasty. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 1998; 118(3):145-148.[16] Lozano-Calderón SA, Shen J, Doumato DF, et al. Cruciate-retaining vs posterior-substituting inserts in total knee arthroplasty: functional outcome comparison. J Arthroplasty. 2013;28(2):234-242. [17] Luo CF. Reference axes for reconstruction of the knee. Knee. 2004;11(4):251-257. [18] Nowakowski AM, Müller-Gerbl M, Valderrabano V. Assessment of knee implant alignment using coordinate measurement on three-dimensional computed tomography reconstructions. Surg Innov. 2012;19(4):375-384.[19] Nowakowski AM, Müller-Gerbl M, Valderrabano V. Surgical approach for a new knee prosthesis concept (TSTP) retaining both cruciate ligaments. Clin Anat. 2010v;23(8):985-991.[20] Nowakowski AM, Stangel M, Grupp TM, et al. Investigating the primary stability of the transversal support tibial plateau concept to retain both cruciate ligaments during total knee arthroplasty. J Appl Biomater Funct Mater. 2012 ;10(2): e127-135. [21] Siebold R, Ellert T, Metz S, et al. Tibial insertions of the anteromedial and posterolateral bundles of the anterior cruciate ligament: morphometry, arthroscopic landmarks, and orientation model for bone tunnel placement. Arthroscopy. 2008;24(2):154-161. [22] Voos JE, Mauro CS, Wente T, et al. Posterior cruciate ligament: anatomy, biomechanics, and outcomes. Am J Sports Med. 2012;40(1):222-231. [23] Han GB, Zhang S, Chen JQ, et al. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu. 2012;16(35):6489-6464.韩贵宾,张寿,陈建强,等.国人胫骨截面矢量化测量与解剖型假体形态的设计[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(35):6489- 6464.[24] Zheng YF, Qu TB, Guo XY, et al. Zhongguo Jiaoxing Waike Zazhi. 2011;19(13):1118-1121.郑寅峰,曲铁兵,郭璇瑛,等.国人胫骨平台截骨面与国人膝关节假体的涵盖率分析[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2011,19(13):1118- 1121.[25] Purnell ML, Larson AI, Clancy W. Anterior cruciate ligament insertions on the tibia and femur and their relationships to critical bony landmarks using high-resolution volume-rendering computed tomography. Am J Sports Med. 2008;36(11):2083-2090.[26] Hwang MD, Piefer JW, Lubowitz JH. Anterior cruciate ligament tibial footprint anatomy: systematic review of the 21st century literature. Arthroscopy. 2012;28(5):728-734. [27] Cheng CK, Lung CY, Lee YM, et al. A new approach of designing the tibial baseplate of total knee prostheses. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 1999;14(2):112-117. [28] Zhang YD, Liu YR, Zhao GZ, et al. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu. 2012;16(35):6466-6470.张艳东,刘奕蓉,赵国志,等.成人距骨数字化计算机三维模型解剖学测量及对个性化治疗的意义[J].中国组织工程研究,2012, 16(35):6466-6470.[29] Xu P, Li YL, Chen WD, et al. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2011;15(43):8006-8009.许鹏,李彦林,陈文栋,等. MRI影像下股骨髁间窝三维数字化解剖学数据与实体解剖测量值的差异[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(43):8006-8009.[30] Hitt K, Shurman JR 2nd, Greene K, et al. Anthropometric measurements of the human knee: correlation to the sizing of current knee arthroplasty systems. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2003;85-A Suppl 4:115-122. [31] Kwak DS, Surendran S, Pengatteeri YH, et al. Morphometry of the proximal tibia to design the tibial component of total knee arthroplasty for the Korean population. Knee. 2007; 14(4):295-300. [32] Chang TW, Huang CH, McClean CJ,et al. Morphometrical measurement of resected surface of medial and lateral proximal tibia for Chinese population. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2012p;20(9):1730-1735.[33] Yang B, Yu JK, Zheng ZZ, et al. Computed Tomography Morphometric Study of Gender Differences in Osteoarthritis Proximal Tibias. J Arthroplasty. 2012. pii: S0883- 5403(12) 00564-5. [34] Liu Z, Yuan G, Zhang W, et al. Anthropometry of the Proximal Tibia of Patients With Knee Arthritis in Shanghai. J Arthroplasty. 2013. pii: S0883-5403(13)00112-5.[35] Skovgaard C, Holm B, Troelsen A,et al. No effect of fibrin sealant on drain output or functional recovery following simultaneous bilateral total knee arthroplasty. Acta Orthop. 2013;84(2):153-158. [36] Chong DY, Hansen UN, van der Venne R, et al. The influence of tibial component fixation techniques on resorption of supporting bone stock after total knee replacement. J Biomech. 2011;44(5):948-954. [37] Roh YW, Jang J, Choi WC, et al. Preservation of the posterior cruciate ligament is not helpful in highly conforming mobile-bearing total knee arthroplasty: a randomized controlled study. |
| [1] | Chen Junming, Yue Chen, He Peilin, Zhang Juntao, Sun Moyuan, Liu Youwen. Hip arthroplasty versus proximal femoral nail antirotation for intertrochanteric fractures in older adults: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1452-1457. |
| [2] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [3] | Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei. Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| [4] | Chen Song, He Yuanli, Xie Wenjia, Zhong Linna, Wang Jian. Advantages of calcium phosphate nanoparticles for drug delivery in bone tissue engineering research and application [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3565-3570. |
| [5] | Zhang Zhenhua, Liu Zichen, Yu Baoqing. Status and problems of polycaprolactone and its composite materials in bone tissue engineering [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3571-3577. |
| [6] | Xu Hui, Kang Bingxin, Zhong Sheng, Gao Chenxin, Zhao Chi, Qiu Guowei, Sun Songtao, Xie Jun, Xiao Lianbo, Shi Qi. Pressing local acupoints plus adjustion of the knee joint in a sitting position for treating knee osteoarthritis: a randomized controlled trial [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(2): 216-221. |
| [7] | Wang Liu, Song Dongzhe, Huang Dingming. Bone morphogenetic protein 9 regulates stem cell differentiation and bone regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 3064-3070. |
| [8] | Li Yanle, Yue Xiaohua, Nie Zhen, Zhang Junwei, Li Zhaohui, Nie Weizhi, Jiang Hongjiang. Characteristics and application of bioabsorbable materials in orthopedics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(16): 2612-2617. |
| [9] | Liu Zige, Liu Xinrui, Li Yan, Song Guorui, Zhang Chen, Chen Desheng. In vitro experiment of tetrandrine on the model of osteolysis induced by wear particles around the prosthesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(15): 2358-2363. |
| [10] | Han Ningning, Zuo Jinfu, Sun Miao, Tang Shengjian, Liu Fangjun. Application and progress of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells in bone tissue engineering [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(13): 2079-2086. |
| [11] | Meng Maohua, Li Ying, Chen Xin, Cheng Lu, Dong Qiang. Effects and mechanisms of enamel matrix derivatives on osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(13): 2108-2113. |
| [12] | Wang Xiankang, Zhang Yuejing, Yang You, Liu Jun. Simulation analysis of wear performance for tibial insert of unicompartmental knee arthroplasty prosthesis under gait load [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(12): 1831-1835. |
| [13] | Li Dongdong, Liao Hongbing . MicroRNA-214 is involved in the regulation of bone metabolism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(11): 1779-1784. |
| [14] | Zhou Qi, Gao Yi, Wei Kang, Li Jun, Xu Jianda, Jiang Yang, Qu Yuxing. Total knee arthroplasty for rheumatoid arthritis: knee function and biochemical index changes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(9): 1337-1341. |
| [15] | Zhang Shengmin, Liu Chao. Research progress in osteogenic differentiation of adipose-derived stem cells induced by bioscaffold materials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(7): 1107-1116. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||