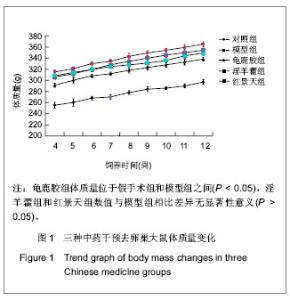
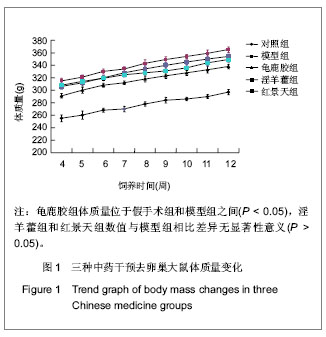
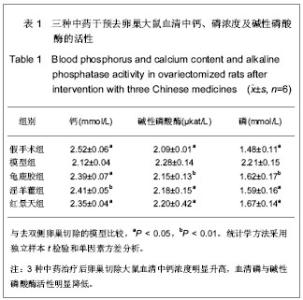
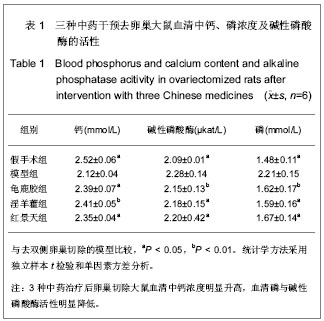
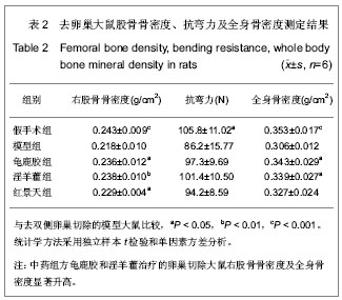
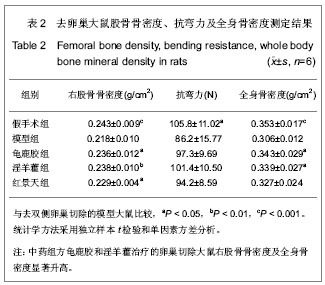
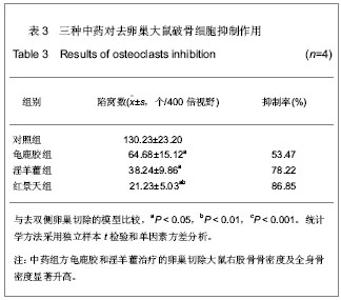
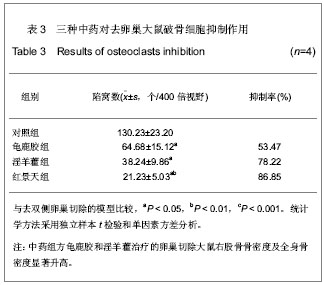
| [1] Na J, Xu Y, Ma C. Zhongguo Laonianxue Zazhi. 2011;31(20): 4070-4073.那键,许永,马超,等.老年骨质疏松的分子生物学发病机制[J].中国老年学杂志,2011,31(20):4070-4073.[2] Ma JL, Gu HY, Yang XD. Zhongguo Quanke Yixue. 2009; (18):1744-1746.马俊岭,郭海英,阳晓东.骨质疏松症的流行病学概况[J].中国全科医学,2009,(18):1744-1746.[3] Maravic M, Jouaneton B, Vainchtock A, et al. Economic burden of osteoporosis in women: data from the 2008 French hospital database (PMSI). Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2012;30(2): 222-227.[4] Kuzmanova SI, Solakov PC, Geneva-Popova MG. Adherence to bisphosphonate therapy in postmenopausal osteoporotic women. Folia Med (Plovdiv). 2011;53(3):25-31.[5] Shao AJ. Zhonghua Yixuehui Disanciguzhisusong he Gukuangyan Jiebing Huiyi Huibian. 2011.晁爱军.原发性骨质疏松症的经济和社会负担[C].中华医学会第三次骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病中青年学术会议论文汇编,2011.[6] Yang X. Zhongguoshe Quyishi. 2011;27(38):6.杨玺.骨质疏松症的药物治疗[J].中国社区医师,2011,27(38):6.[7] Yang Z, Tang DZ, Yang Z. Zhongguo Zhongyi Gushangke Zazhi. 2011;(12):70-72.杨铸,唐德志,杨洲,等.药物治疗骨质疏松症的最新研究进展[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2011,(12):70-72.[8] Liao HL. Dangdai Yixue. 2008;(16):2.廖海浪.雌激素、钙与骨质疏松症[J].当代医学(学术版), 2008, (16):2.[9] Dong L, Guo LH. Zhongguo Guzhi Shusong Zazhi. 2006;(2): 187-188.董利,郭厉华.雌激素辅以钙剂治疗绝经后骨质疏松症疗效观察[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2006,(2):187-188.[10] Lin BG, Chen ZQ, Chen LL. Zhongguo Guzhi Shusong Zazhi. 2006;(5):490-491.林伯庚,陈治卿,陈鹭玲.降钙素对骨质疏松症治疗的临床观察[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2006,(5):490-491.[11] Wang YH. Zhongguo Kexue Jishu Daxue Chubanshe. 2004.汪延华.钙、降钙素、维生素D与骨质疏松症[M].合肥:中国科学技术大学出版社,2004.[12] Beard MK. Bisphosphonate therapy for osteoporosis: combining optimal fracture risk reduction with patient preference. Curr Med Res Opin. 2012;28(1):141-147.[13] Rhee CW, Lee J, Oh S, et al. Use of bisphosphonate and risk of atrial fibrillation in older women with osteoporosis. Osteoporos Int. 2012;23(1):247-254.[14] Sewerynek E, Stuss M, The role of i.v.i bandronate administration in osteoporosis therapy. Endokrynol Pol. 2011; 62(1):51-60.[15] Bao LH, Lin H, Li YJ. Zhongguo Guzhi Shusong Zazhi. 2011; 17(3):232-235.包丽华,林华,李永军,等.伊班膦酸钠和阿仑膦酸钠对绝经后骨质疏松的干预研究[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2011,17(3): 232-235.[16] Pillai G, Gieschke R, Goggin T, et al. Population pharmacokinetics of ibandronate in Caucasian and Japanese healthy males and postmenopausal females. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2006;44(12):655-667.[17] Rizzoli R. Bisphosphonates treatment in patients with osteoporosis. Ther Umsch. 2012;69(3):173-181.[18] Tan X, Liu F, Ye Z. Zhongguo Guzhi Shusong Zazhi. 2011; 17(4):359-363.谭新,刘芳,叶竹,等.近五年中医药治疗骨质疏松文献分析[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2011,17(4):359-363.[19] Xin Y, Bi HY, Yin LM. Zhongguo Guzhi Shusong Zazhi. 2011; 17(12):1115-1118.邢燕,毕宏焱,尹丽梅,等.中医药治疗骨质疏松症的进展[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2011,17(12):1115-1118.[20] Zhao BL,Quan TG, Ma H. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2011;15(11):1937-1940.赵宝林,权铁刚,马洪.四种药物治疗骨质疏松模型大鼠股骨扭转力学特性对比[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(11): 1937-1940.[21] Zhang H, Zhao Y, Xu YF. Zhongyao Yaoli yu Linchuang. 2011; 27(5):76-79.张鹤,赵雨,徐云凤.等.鹿骨胶原蛋白对去卵巢所致骨质疏松大鼠的治疗作用[J].中药药理与临床,2011,27(5):76-79.[22] Yang J, Mo XM, Li JP. Zhongguo Zhongyi Jichu Yixue Zazhi. 2012;18(2)166-168.杨军,莫新民,李劲平.壮骨止痛方治疗大鼠去卵巢骨质疏松症的蛋白质组学分析[J].中国中医基础医学杂志,2012,18(2): 166-168.[23] Shen JJ. Neimogu Zhongyiyao. 2012;(3):77-78.沈建军.中药防治骨质疏松症作用机制探讨[J].内蒙古中医药, 2012,(3):77-78.[24] Zhou LZ, Ma Y. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2003;(1):74-75.周丽珍,马元.中医通补法治疗原发性骨质疏松症的作用机制研究[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2003,(1):74-75.[25] Chen XF, Chen SH, Lu GY. Zhongchengyao. 2011;(7): 1130-1134.陈晓飞,陈素红,吕圭源,等.补肾活血方治疗骨质疏松症机制研究及探讨[J].中成药,2011,(7):1130-1134.[26] Li SP. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2011;15(20):3767-3770.李素萍.骨质疏松动物模型的研究现状[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(20):3767-3770.[27] The Ministry of Science and Technology of the People’s Republic of China. Guidance Suggestions for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. 2006-09-30.[28] Liu SP, Liao EY, Wu HW. Hunan Yike Daxue Xuebao. 2001; (2):111-115.刘石平,廖二元,伍汉文,等.绝经后骨质疏松大鼠模型的综合评价[J].湖南医科大学学报,2001,(2):111-115.[29] Long T, Zhu ZA. Shengwu Guoke Cailiao yu Linchuang Yanjiu. 2009;(4):20-23.龙腾,朱振安.绝经后妇女体脂、瘦体质量与骨密度的相关性[J].生物骨科材料与临床研究,2009,(4):20-23.[30] Liu ZH. Beijing: Huaxue Gongye Chubaishe. 1992.刘忠厚.骨质疏松症[M].北京:化学工业出版社,1992.[31] Zhu XL. Tianjin: Tianjin Keji Chubanshe. 1982.朱宪彝.代谢性骨病学[M].天津:天津科技出版社,1982.[32] Yang XZ, Chen XL, Wang DC. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2007;(49):9980-9983.杨希重,陈晓亮,王德春.番茄红素与成骨细胞、破骨细胞及骨质疏松症[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2007,(49): 9980-9983.[33] Ma HP, Yang YJ, Jia ZP. Lanzou Yixueyuan Xuebao. 2001; 27(4):69-70.马慧萍,杨永建,贾正平.淫羊藿防治骨质疏松症的研究进展[J].兰州医学院学报,2001,27(4):69-70.[34] Xiu CY, Cai H, Guo JH. Anhui Zhongyi Xueyuan Xuebao. 2004;23(6):57-59.修春英,蔡辉,郭郡浩.淫羊藿防治骨质疏松症的研究进展[J].安徽中医学院学报,2004,23(6):57-59.[35] Dong YF. Zhongyaocai. 2004;27(8):620-622.董远芳.淫羊藿等中药治疗骨质疏松症的临床观察[J].中药材, 2004, 27(8):620-622.[36] Yang WA. Fujian Zhongyiyao. 2005;(5):19.杨伟岸.龟鹿二仙汤加味治疗老年脊椎骨质疏松性腰背部疼痛63例[J].福建中医药,2005,(5):19.[37] Zhou XD. Shanghai zhongyiyao zazhi. 2001;35(11):24-24.周修道.“龟鹿二仙汤”为主治疗骨质疏松症临床观察[J].上海中医药杂志,2001,35(11):24-24.[38] Liu JM, Ge BF, Bai MH, et al. Zhongguo Linchuang Kangfu. 2004;8(27):5910-5912.刘剑梅,葛宝丰,白孟海,等.红景天壮骨丸治疗骨质疏松症的实验研究[J].中国临床康复,2004,8(27):5910-5912.[39] Bai MH, Ge BF, Zhao XP, et al. Xibei Guofang Yixue Zazhi. 2006;27(6):414-417.白孟海,葛宝丰,赵新平,等.高原对去势大鼠骨密度、生物力学和骨组织学的影响及复方红景天对其保护作用[J].西北国防医学杂志,2006,27(6):414-417. |