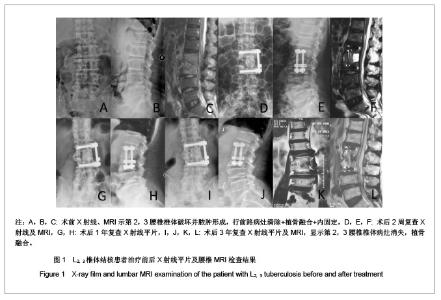
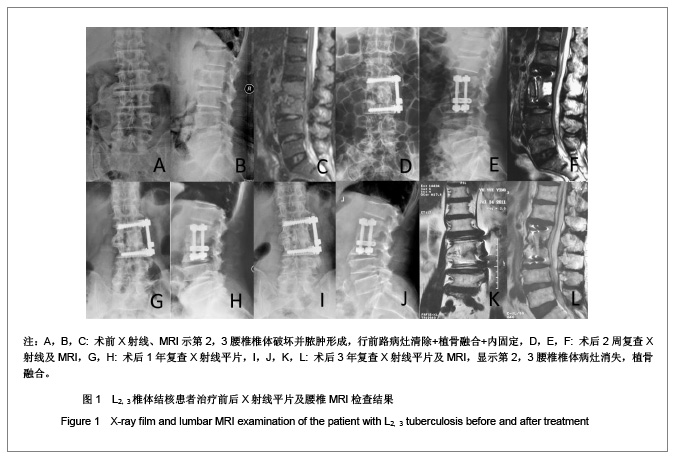
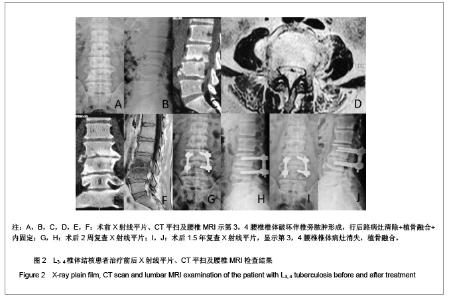
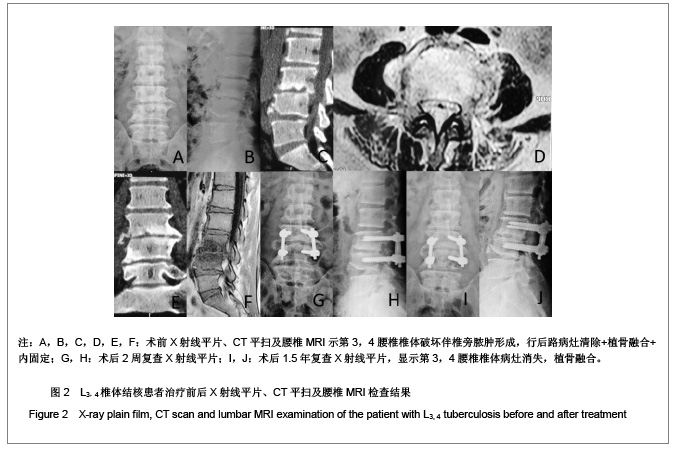
| 1] Pappou IP, Papadopoulos EC, Swanson AN, et al. Pott disease in the thoracolumbar spine with marked kyphosis and progressive paraplegia necessitating posterior vertebral column resection and anterior reconstruction with a cage. Spine. 2006;31:123-127.[2] Maeda Y, Izawa K, Nabeshima T, et al. Tuberculous spondylitis in elderly Japanese patients. J Orthop Sci.2008;13:16-20.[3] Park DW, Sohn JW, Kim EH, et al.Outcome and management of spinal tuberculosis according to the severity of disease: a retrospective study of 137 adult patients at Korean teaching hospitals. Spine. 2007;32:E130-135.[4] Bezer M, Kucukdurmaz F, Aydin N, et al. Tuberculous spondylitis of the lumbosacral region: long-term follow-up of patients treated by chemotherapy, transpedicular drainage, posterior instrumentation, and fusion. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2005;18:425-429.[5] Lee SH, Sung JK, Park YM. Single-stage transpedicular decompression and posterior instrumentation in treatment of thoracic and thoracolumbar spinal. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2006;19(8):595-602.[6] Moon MS, Kim SS, Lee BJ, et al. Surgical management of severe rigid tuberculous kyphosis of dorsolumbar spine. Int Orthop. 2011;35(1):75-81.[7] Jain AK. Simultaneous anterior decompression and posterior instrumentation of the tuberculous spine using an anterolateral extrapleural approach. J Bone Joint Surg [Br]. 2008; 90-B: 1477-1481.[8] Rajasekaran S. Buckling collapse of the spine in childhood spinal tuberculosis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2007;460:86-92.[9] Christodoulou AG, Givissis P, Karataglis D, et al. Treatment of tuberculous spondylitis with anterior stabilization and titanium cage. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2006;444:60-65.[10] Sharif HS, Morgan JL, Shahed MS, et al. Role of CT and MR imaging in the management of tuberculous spondylitis.Radiol Clin North Am. 1995;33:787-804.[11] Kim DJ, Yun YH, Moon SH, et al. Posterior instrumentation using compressive laminar hooks and anterior interbody arthrodesis for the treatment of tuberculosis of the lower lumber spine. Spine.2004;29:E275-279.[12] Ye M, Li JQ, Zou Y, et al. One stage anterior and posterior fusion and posterior fixation for the treatment of thoracic and lumbar spinal tuberculosis. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2009; 22(1): 23-25.[13] Jain AK. Tuberculosis of the spine: a fresh look at an old disease. J Bone Joint Surg Br.2010;92:905-913.[14] Arora S, Sabat D, Maini L,et al. The results of nonoperative treatment of craniovertebral junction tuberculosis: a review of twenty-six cases. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2011;93(6):540-547.[15] Erturer E, Tezer M, Aydogan M, et al. The results of simultaneous posterior-anterior-posterior surgery in multilevel tuberculosis spondylitis associated with severe kyphosis. Eur Spine J. 2010;19(12):2209-2215.[16] Huang QS, Zheng C, Hu Y, et al. One-stage surgical management for children with spinal tuberculosis by anterior decompression and posterior instrumentation. Int Orthop. 2009;33(5):1385-1390.[17] Rajasekaran S, Vijay K, Shetty AP. Single-stage closingopening wedge osteotomy of spine to correct severe posttubercular kyphotic deformities of the spine: a 3-year follow-up of 17 patients. Eur Spine J. 2010;19(4):583-592.[18] Ito Z, Matsuyama Y, Sakai Y, et al. Bone Union Rate With Autologous Iliac Bone Versus Local Bone Graft in Posterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion.Spine. 2010;35(21):1101-1105.[19] Karaeminogullari O, Aydinli U, Ozerdemoglu R, et al. Tuberculosis of the lumbar spine: outcomes after combined treatment of two-drug therapy and surgery. Orthopedics. 2007; 30:55-59.[20] Mihir B, Vinod L, Umesh M, et al. Anterior Instrumentation of the Cervicothoracic Vertebrae. Approach Based on Clinical and Radiologic Criteria. Spine. 2006;31:E244-249.[21] Ma YZ, Cui X, Li HW, et al. Outcomes of anterior and posterior instrumentation under different surgical procedures for treating thoracic and lumbar spinal tuberculosis in adults. Int Orthop. 2012;36(2):299-305.[22] Issack PS, Boachie-Adjei O. Surgical correction of kyphotic deformity in spinal tuberculosis. Int Orthop. 2012;36(2):353- 357.[23] Cormican L, Hammal R, Messenger J, et al. Current difficulties in the diagnosis and management of spinal tuberculosis. Postgrad Med J. 2006;82(963):46-51.[24] Godlwana L, Gounden P, Ngubo P, et al. Incidence and profile of spinal tuberculosis in patients at the only public hospital admitting such patients in KwaZulu-Natal. Spinal Cord. 2008; 46(5):372-374.[25] Talu U, Gogus A, Ozturk C, et al. The role of posterior instrumentation and fusion after anterior radical debridement and fusion in the surgical treatment of spinal tuberculosis: experience of 127 cases. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2006;19(8): 554-559.[26] Jain AK, Jain S. Instrumented stabilization in spinal tuberculosis. Int Orthop. 2012;36(2):285-292.[27] He Q, Xu J. Comparison between the antero-posterior and anterior approaches for treating L5-S1 vertebral tuberculosis. Int Orthop. 2012;36(2):345-351.[28] Sheng WB, Hua Q, Cao L, et al. Zhonghua Waike Zazhi. 2005; 43(2):205-209. 盛伟斌,华强,曹力,等.一期后路病灶清除、楔形截骨矫形治疗胸腰椎结核并后凸或侧后凸畸形[J].中华外科杂志,2005,43(2): 205-209.[29] Pawar UM, Kundnani V, Agashe V, et al. Multidrug-resistant tuberculosis of the spine-is it the beginning of the end? A study of twenty-five culture proven multidrug-resistant tuberculosis spine patients. Spine. 2009;34:E806-810.[30] Liu P, Zhu Q, Jiang J. Distribution of three antituberculous drugs and their metabolites in different parts of pathological vertebrae with spinal tuberculosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2011;36:E1290-1295. |