Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2013, Vol. 17 ›› Issue (13): 2439-2446.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2013.13.022
Previous Articles Next Articles
Biomechanical changes and clinical effect of internal fixator placement for the treatment of distal femoral fractures
Guan Ji-kui1, Guan Yu2, Zhao Li1, Wang Hui1, Kong Li1, Li Jing1, Liu Jian-guo3
- 1Department of Orthopedics, Daqing Oilfield General Hospita, Daqing 163001, Heilongjiang Province, China
2 Department of Stomatology, Beijing Chaoyang Hospital, Beijing 100020, China
3 Department of Orthopedics, the First Hospital of Jilin University, Changchun 130021, Jilin Province, China
-
Received:2012-10-10Revised:2013-01-20Online:2013-03-26Published:2013-03-26 -
Contact:Liu Jian-guo, Doctor, Professor, Doctoral supervisor, Chief physician, Department of Orthopedics, the First Hospital of Jilin University, Changchun 130021, Jilin Province, China Jgliu.2005@yahoo.com.cn -
About author:Guan Ji-kui★, Master, Associate chief physician, Department of Orthopedics, Daqing Oilfield General Hospita, Daqing 163001, Heilongjiang Province, China Guan1858@163.com
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Guan Ji-kui, Guan Yu, Zhao Li, Wang Hui, Kong Li, Li Jing, Liu Jian-guo. Biomechanical changes and clinical effect of internal fixator placement for the treatment of distal femoral fractures[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2013, 17(13): 2439-2446.
share this article
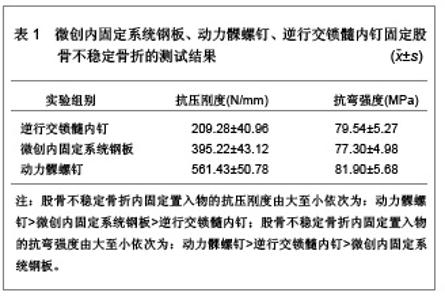
2.1 股骨远端骨折内固定物置入后的生物力学分析 实验设计:对比分析。 时间及地点:2008年5月至2009年6月在吉林大学力学试验室完成。 实验材料:由吉林大学基础医学院解剖教研室提供的成人尸体股骨标本12根,实验前拍摄X射线片,排除骨病等标本。于-20 ℃冰冻保存。 实验仪器:夹具由吉林大学力学实验中心提供;5孔微创内固定系统钢板、锁定螺钉数枚,以及相关固定工具(瑞士辛迪思医疗器械有限公司提供);逆行交锁髓内钉(江苏华森提供);电子万能试验机岛津AG-10TA型(日本岛津公司提供)。 标本制备:成人尸体股骨标本12根,随机分成3组,制成相同标准AO分型A型的斜行骨折模型,每组4根股骨分别用微创内固定系统钢板、动力髁螺钉、逆行交锁髓内钉固定。于股骨远端骨折线外、前、内、后4个不同部位“T”形黏贴高精度标距电阻应变片8枚。标本两端以牙托粉包埋。 测试方法: 轴向压缩实验:将实验标本安装在岛津AG-10T电子万能试验机上,进行轴向压缩实验。对标本进行预调处理,载荷通过载荷传感器传递,位移通过电光编码器传递。以1.5 mm/min的速度对标本施加轴向压缩载荷,施加最大载荷为600 N,依次测出100,200,300,400,500,600 N所对应的位移值。 弯曲实验:将标本置于电子万能试验机的弯曲支座上,进行弯曲实验,最大弯曲载荷为600 N,实验速度为1.5 mm/min,依次测出100,200,300,400,500,600 N所对应的位移值。 主要观察指标:标本承受轴向压缩、弯曲载荷时的位移值。 统计学分析:采用SPSS 10.0软件完成统计处理,实验数据以x(_)±s表示,P < 0.05为差异有显著性意义。 实验结果:微创内固定系统钢板、动力髁螺钉、逆行交锁髓内钉固定股骨不稳定骨折的测试结果见表1。"
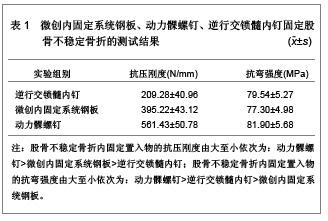
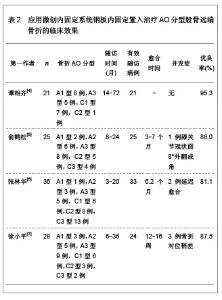
以上实验数据表明在轴向抗压刚度上逆行交锁髓内钉最小,动力髁螺钉最大;在抗弯强度上,微创内固定系统钢板最小,动力髁螺钉最大。并且3种固定测试结果之间的差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。刚度是指内固定植入物在外力作用下抵抗变形的能力。结果表明在抵抗轴向变形能力方面,动力髁螺钉>微创内固定系统钢板>逆行交锁髓内钉;在抵抗弯曲变形能力方面,动力髁螺钉>逆行交锁髓内钉>微创内固定系统钢板。 生物力学实验结果:生物力学实验中在600 N轴向压缩载荷作用下,逆行交锁髓内钉、微创内固定系统钢板和动力髁螺钉固定股骨远端不稳定性骨折的位移分别为(2.94±0.59) mm、(1.52±0.06) mm和(1.09±0.09) mm;在600 N载荷下,逆行交锁髓内钉、微创内固定系统钢板和动力髁螺钉固定股骨远端不稳定性骨折的最大桡度为(4.65±0.25) mm、(5.67± 0.21) mm和(3.05±0.11) mm,统计学显示3种固定生物力学实验结果之间差异有显著性意义 (P < 0.05)。 文章实验数据中显示动力髁螺钉工况抗压刚度分别是逆行交锁髓内钉和微创内固定系统钢板的2.68倍和1.42倍。说明动力髁螺钉固定更加坚强[27-29]。对于不稳定股骨远端骨折,动力髁螺钉应力遮挡较大,逆行交锁髓内钉刚度较低,容易造成锁钉疲劳,不宜过早负重运动,而微创内固定系统钢板既有较强的刚度,能为骨折提供良好的稳定性,又有一定变形,应力能够通过骨传导,力学性能良好。 2.2 股骨远端骨折内固定的临床应用 2.2.1 微创内固定系统钢板内固定物置入治疗股骨远端骨折的临床应用 这是一种新型的微创内固定系统,其结构设计具有3个独特的特征:固定器远端有多个交锁角度螺钉与固定器锁定、固定物放置在骨膜外肌肉下以及骨干固定可经皮单皮质自钻自攻螺钉锁定。微创内固定系统钢板独特的结构特征使其更加符合股骨远端骨折内固定治疗的生物力学原理。选取4篇微创内固定系统钢板内固定治疗股骨远端骨折的研究文献,明确微创内固定系统钢板内固定股骨远端骨折的治疗效果,具体实验研究结果见表2。"

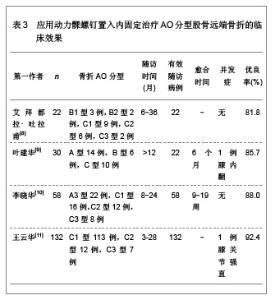
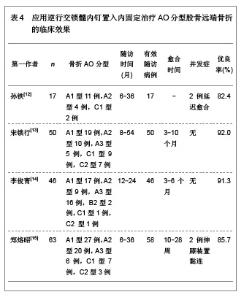
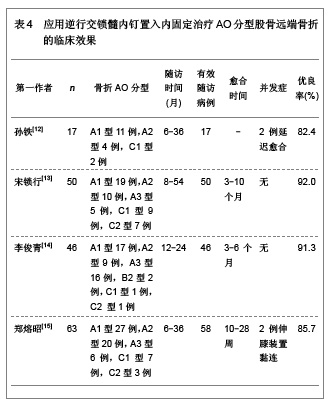
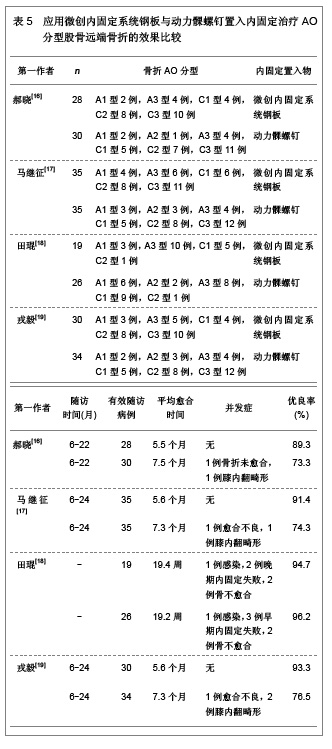
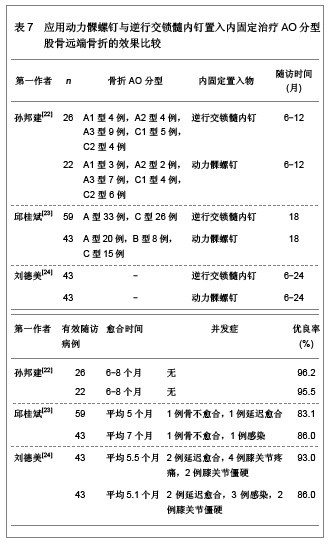
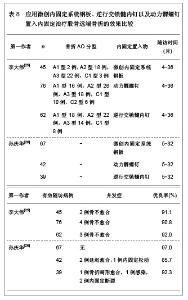
文章研究显示,股骨远端骨折分型中,以A型骨折和C型骨折较为多见,应用微创内固定系统钢板内固定治疗后骨折的愈合时间为3-7个月,并发症发生率较低,无内固定置入物松动、断裂等并发症发生,并且膝关节功能恢复评分较高,优良率达80.0%以上,甚至可高达95.0%以上。表明微创内固定系统钢板内固定治疗股骨远端骨折可以获得满意的治疗效果。 2.2.2 动力髁螺钉置入内固定治疗股骨远端骨折的临床应用 动力髁螺钉是股骨远端骨折常用的一种内固定治疗方法,然而近年来,专家学者对其研究相对较少。文章对动力髁螺钉置入内固定治疗股骨远端骨折的临床效果进行综合分析,结果见表3。 文章研究显示,动力髁螺钉内固定系统可用于股骨远端A型、B型和C型骨折的治疗,骨折愈合时间9周至6个月,可发生膝内翻以及膝关节强直等影响膝关节功能的并发症,无内固定置入物松动、断裂等并发症发生,膝关节功能恢复优良,优良率可达80.0%以上,甚至可达92.0%以上。表明动力髁螺钉是内固定股骨远端骨折较为理想的治疗方法。"
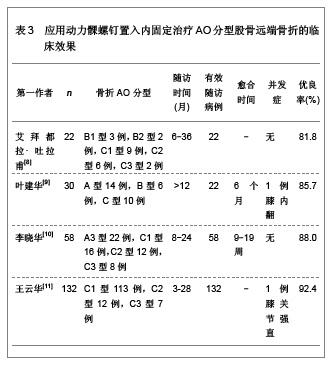
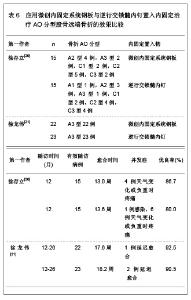
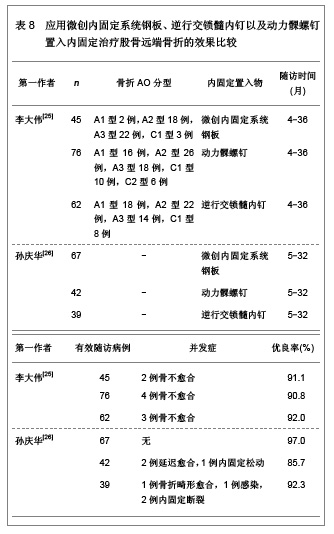
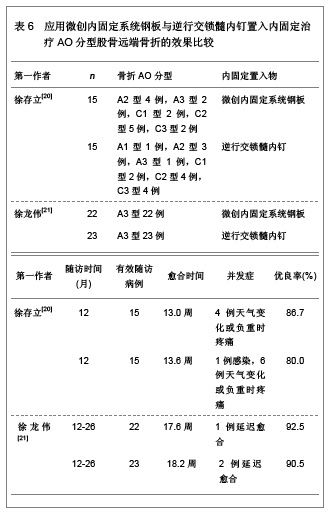
微创内固定系统钢板与动力髁螺钉均是股骨远端骨折较好的内固定治疗系统,文章对二者的临床应用效果进行了比较分析,发现微创内固定系统钢板的内固定骨折愈合时间更短,并发症的发生率更低,膝关节的功能恢复更好。表明微创内固定系统钢板内固定股骨远端骨折的治疗效果要优于动力髁螺钉内固定治疗的效果。 2.2.5 应用微创内固定系统钢板与逆行交锁髓内钉置入内固定治疗股骨远端骨折的效果比较 微创内固定系统钢板与逆行交锁髓内钉内固定系统均为微创内固定系统,因此,对二者进行比较分析的研究较少,徐存立等[20]和徐龙伟等[21]分别对微创内固定系统钢板与逆行交锁髓内钉内固定股骨远端骨折的治疗效果进行了对比分析,结果显示,微创内固定系统钢板和逆行交锁髓内钉均可应用于A型、B型和C型骨折,而微创内固定系统钢板内固定对组织创伤小,骨折愈合时间明显缩短,膝关节功能恢复明显提高,具体结果见表6。"
| [1] Krieg JC. Proximal tibial fractures: current treatment, results, and problems. Injury. 2003;34 Suppl 1:A2-10.[2] Schandelmaier P, Partenheimer A, Koenemann B, et al. Distal femoral fractures and LISS stabilization. Injury. 2001;32 Suppl 3:SC55-63.[3] 中国知网.中国学术期刊总库[DB/OL].2013-1-10. https://www.cnki.net[4] 谭相齐,张文祥,季祝永,等.AO微创内固定系统治疗股骨远端骨折[J].实用骨科杂志,2010,16(6):450-452.[5] 俞鹤松,周国万.LISS钢板内固定治疗股骨远端骨折的疗效分析[J].现代实用医学,2011,23(11):1236-1237.[6] 张林华,卜海富,周健,等.LISS钢板在治疗股骨远端骨折中的应用[J].安徽医药,2010,14(2):188-189.[7] 徐小平,倪卫东,高仕长,等.LISS钢板治疗老年股骨远端骨折[J].西部医学,2011,23(8):1431-1433.[8] 艾拜都拉•吐拉甫.动力髁螺钉(DCS)在股骨髁间骨折内固定的临床应用[J].新疆医学,2011,41(11):57-58.[9] 叶建华,姜建飞,金志先,等.中西医结合内固定治疗股骨远端骨折30例临床研究[J].生物医学工程学进展,2010,31(2):95-97.[10] 李晓华,廖劲松.动力髁螺钉内固定结合中药熏洗治疗股骨远端骨折58例临床观察[J].中医药导报,2010,16(6):64-65.[11] 王云华,方长昆.动力髁螺钉治疗股骨远端骨折临床分析[J].实用临床医学,2010,11(9):37-39.[12] 孙铁,卢军,李云龙,等.股骨逆向交锁钉在股骨远端骨折中的应用体会[J].中国实用医药,2011,6(4):115-116.[13] 宋锁行.股骨逆行交锁髓内钉治疗股骨远端骨折[J].临床医药实践,2012,21(4):316-318.[14] 李俊青.股骨逆行交锁髓内钉治疗股骨远端骨折疗效观察[J].临床合理用药杂志,2011,4(12):106-107.[15] 郑熔昭,罗张进,蒙显章.逆行交锁髓内钉治疗股骨远端骨折63例[J].广西医科大学学报,2010,27(4):629-630.[16] 郝晓.微创内固定系统与动力髁螺钉内固定治疗股骨远端骨折的疗效比较[J].中国医药导报,2011,8(6):162-163.[17] 马继征.微创内固定系统(LISS)与动力髁螺钉固定治疗股骨远端骨折的疗效分析[J].河南外科学杂志,2012,18(2):44-45.[18] 田琨.MIPO技术治疗股骨远端骨折:动力髁螺钉与LISS钢板的比较[J].江西中医药,2010,41(11):42-45.[19] 戎毅.微创内固定系统(LISS)与动力髁螺钉内固定治疗股骨远端骨折的疗效比较[J].中国实用医药,2011,6(16):78-79.[20] 徐存立,孙爱华.LISS及GSH内固定系统治疗股骨远端骨折的疗效分析[J].中国社区医师(医学专业),2012,14(16):148-149.[21] 徐龙伟,季卫平,李浩,等.逆行交锁髓内钉与微创内固定系统内固定治疗股骨远端A3型骨折的随机对比研究[J].浙江创伤外科, 2010,15(6):745-746.[22] 孙邦建,何磊,赵松涛.GSH和DCS治疗股骨远端骨折疗效分析[J].河北医药,2010,32(14):1917-1918.[23] 邱桂斌,温进杰,周春晖,等.不同内固定材料在成人股骨远端骨折手术治疗中的应用观察[J].山东医药,2010,50(34):74-75.[24] 刘德美.逆行交锁髓内钉与动力髁螺钉治疗股骨远端骨折的临床分析[J].中国当代医药,2012,19(7):43-44.[25] 李大伟.股骨远端A型及C型骨折不同内固定方式的疗效比较[J].河北联合大学学报(医学版),2012,14(2):226-227.[26] 孙庆华,赵东,杨龙彪,等.股骨远端骨折不同内固定方法的疗效分析[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2011,26(12):1064-1066.[27] Firoozbakhsh K, Behzadi K, DeCoster TA, et al. Mechanics of retrograde nail versus plate fixation for supracondylar femur fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 1995;9(2):152-157.[28] Mize RD. Surgical management of complex fractures of the distal femur. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1989;(240):77-86.[29] 张秋林,王家林,王秋根,等.动力髁螺钉治疗股骨远端骨折[J].第二军医大学学报,2001,22(10):938.[30] 任高宏,沈开金,林昂如.股骨远端骨折的治疗现状与进展[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2003,11(4):246-247.[31] Zlowodzki M, Williamson S, Cole PA, et al. Biomechanical evaluation of the less invasive stabilization system, angled blade plate, and retrogradeintramedullary nail for the internal fixation of distal femur fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2004; 18(8):494-502.[32] Kregor PJ, Stannard J, Zlowodzki M, et al. Distal femoral fracture fixation utilizing the Less Invasive Stabilization System (L.I.S.S.): the technique and early results. Injury. 2001;32 Suppl 3:SC32-47.[33] Cole PA, Zlowodzki M, Kregor PJ. Less Invasive Stabilization System (LISS) for fractures of the proximal tibia: indications, surgical technique andpreliminary results of the UMC Clinical Trial. Injury. 2003;34 Suppl 1:A16-29.[34] Schütz M, Müller M, Regazzoni P, et al. Use of the less invasive stabilization system (LISS) in patients with distal femoral (AO33) fractures: a prospectivemulticenter study. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2005;125(2):102-108. |
| [1] | Xu Feng, Kang Hui, Wei Tanjun, Xi Jintao. Biomechanical analysis of different fixation methods of pedicle screws for thoracolumbar fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1313-1317. |
| [2] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [3] | Chen Xinmin, Li Wenbiao, Xiong Kaikai, Xiong Xiaoyan, Zheng Liqin, Li Musheng, Zheng Yongze, Lin Ziling. Type A3.3 femoral intertrochanteric fracture with augmented proximal femoral nail anti-rotation in the elderly: finite element analysis of the optimal amount of bone cement [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1404-1409. |
| [4] | Du Xiupeng, Yang Zhaohui. Effect of degree of initial deformity of impacted femoral neck fractures under 65 years of age on femoral neck shortening [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1410-1416. |
| [5] | Zhang Shangpu, Ju Xiaodong, Song Hengyi, Dong Zhi, Wang Chen, Sun Guodong. Arthroscopic suture bridge technique with suture anchor in the treatment of acromioclavicular dislocation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1417-1422. |
| [6] | Zhou Jihui, Li Xinzhi, Zhou You, Huang Wei, Chen Wenyao. Multiple problems in the selection of implants for patellar fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1440-1445. |
| [7] | Chen Junming, Yue Chen, He Peilin, Zhang Juntao, Sun Moyuan, Liu Youwen. Hip arthroplasty versus proximal femoral nail antirotation for intertrochanteric fractures in older adults: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1452-1457. |
| [8] | Hu Kai, Qiao Xiaohong, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong, Qin Sihe. Treatment of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures with cannulated screws and plates: a meta-analysis of 15 randomized controlled trials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1465-1470. |
| [9] | Huang Dengcheng, Wang Zhike, Cao Xuewei. Comparison of the short-term efficacy of extracorporeal shock wave therapy for middle-aged and elderly knee osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1471-1476. |
| [10] | Zhong Hehe, Sun Pengpeng, Sang Peng, Wu Shuhong, Liu Yi. Evaluation of knee stability after simulated reconstruction of the core ligament of the posterolateral complex [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 821-825. |
| [11] | Xu Yulin, Shen Shi, Zhuo Naiqiang, Yang Huilin, Yang Chao, Li Yang, Zhao Heng, Zhao Lu. Biomechanical comparison of three different plate fixation methods for acetabular posterior column fractures in standing and sitting positions [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 826-830. |
| [12] | Cai Qunbin, Zou Xia, Hu Jiantao, Chen Xinmin, Zheng Liqin, Huang Peizhen, Lin Ziling, Jiang Ziwei. Relationship between tip-apex distance and stability of intertrochanteric femoral fractures with proximal femoral anti-rotation nail: a finite element analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 831-836. |
| [13] | Liu Shaohua, Zhou Guanming, Chen Xicong, Xiao Keming, Cai Jian, Liu Xiaofang. Influence of anterior cruciate ligament defect on the mid-term outcome of fixed-bearing unicompartmental knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 860-865. |
| [14] | Hou Guangyuan, Zhang Jixue, Zhang Zhijun, Meng Xianghui, Duan Wen, Gao Weilu. Bone cement pedicle screw fixation and fusion in the treatment of degenerative spinal disease with osteoporosis: one-year follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 878-883. |
| [15] | He Li, Tian Wei, Xu Song, Zhao Xiaoyu, Miao Jun, Jia Jian. Factors influencing the efficacy of lumbopelvic internal fixation in the treatment of traumatic spinopelvic dissociation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 884-889. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||