Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2013, Vol. 17 ›› Issue (11): 2013-2019.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2013.11.017
Previous Articles Next Articles
Expression of osteopontin in the articular synovium of human knee osteoarthritis
Xiao Sheng-shi1, 2, Gao Shu-guang1, 3, Xu Mai1, 3, Zhang Kai1, 3, Zhu He-yuan1, 3, Song Yang1, 3, Yang Yang1, 3, Lei Guang-hua1, 3
- 1 Department of Orthopedics, Xiangya Hospital of Central South University, Changsha 410008, Hunan Province, China
2 Department of Traumatic Orthopedics, the First Hospital of Zhuzhou City, Zhuzhou 412000, Hunan Province, China
3 Orthopedic Research Institute, Xiangya Hospital of Central South University, Changsha 410008, Hunan Province, China
-
Received:2012-06-05Revised:2012-08-25Online:2013-03-12Published:2013-03-12 -
Contact:Lei Guang-hua, Doctor, Doctoral supervisor, Chief physician, Department of Orthopedics, Xiangya Hospital of Central South University, Changsha 410008, Hunan Province, China; Orthopedic Research Institute, Xiangya Hospital of Central South University, Changsha 410008, Hunan Province, China lgh9640@sina.com -
About author:Xiao Sheng-shi★, Master, Physician, Department of Orthopedics, Xiangya Hospital of Central South University, Changsha 410008, Hunan Province, China; Department of Traumatic Orthopedics, the First Hospital of Zhuzhou City, Zhuzhou 412000, Hunan Province, China shengshi1367@sina.com
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Xiao Sheng-shi, Gao Shu-guang, Xu Mai, Zhang Kai, Zhu He-yuan, Song Yang, Yang Yang, Lei Guang-hua. Expression of osteopontin in the articular synovium of human knee osteoarthritis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2013, 17(11): 2013-2019.
share this article
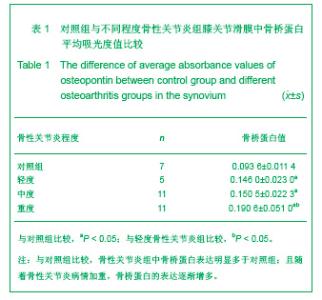
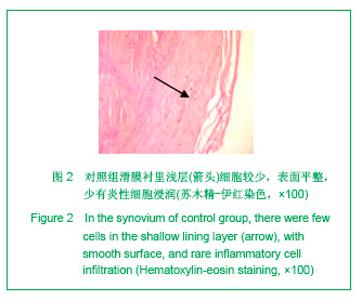
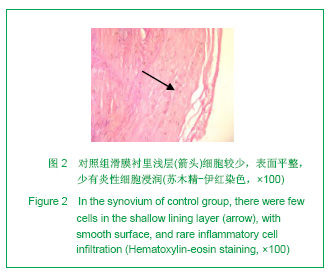
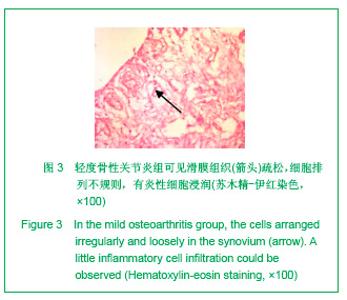
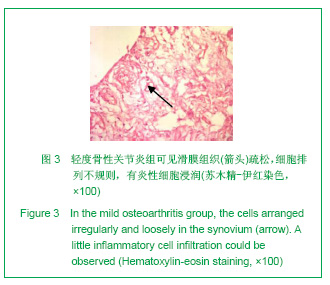
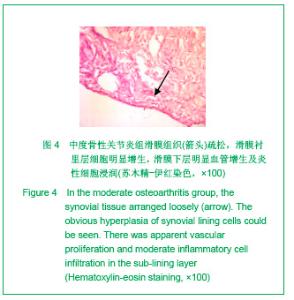
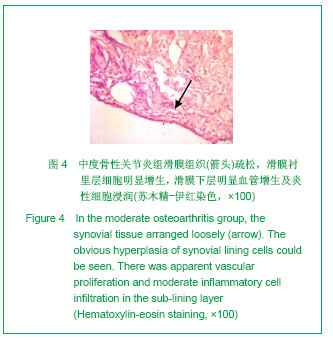
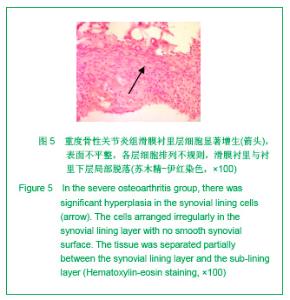
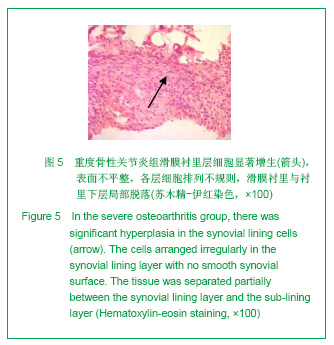
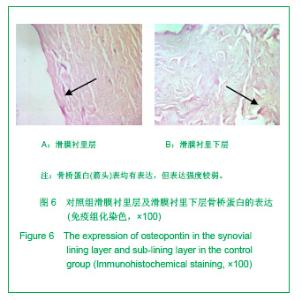
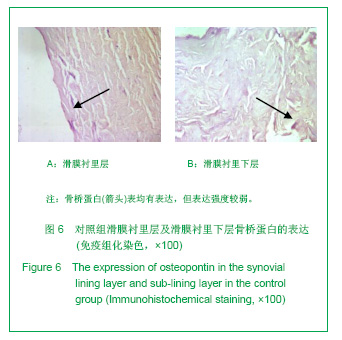
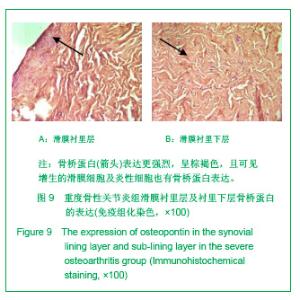
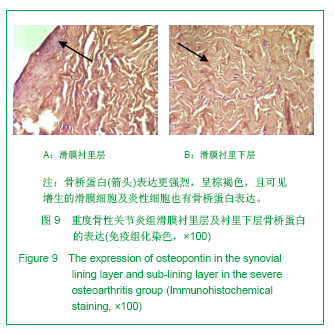
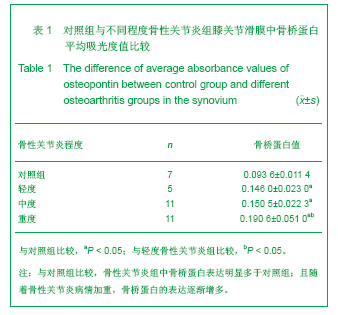
2.3 免疫组化各组骨桥蛋白水平比较 与对照组比较,骨性关节炎组中骨桥蛋白表达 (0.166 0±0.041 3)明显多于对照组(0.093 6±0.011 4),差异有非常显著性意义(P < 0.01);随着骨性关节炎病情加重,骨桥蛋白的表达逐渐增多,见表1;对照组骨桥蛋白吸光度值与轻、中、重度股性关节炎组之间差异有显著意义(P < 0.05),轻度与重度组之间差异有显著意义(P < 0.05),轻度与中度之间、中度与重度差异无显著意义(P > 0.05)。滑膜衬里层骨桥蛋白吸光度值(0.149 3±0.065 6)与衬里下层(0.153 3 ±0.054 1)比较,差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),图6-9。"
| [1] Gao SG, Li KH, Zeng KB, et al. Elevated osteopontin level of synovial fluid and articular cartilage is associated with disease severity in knee osteoarthritis patients. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2010;18(1):82-87. [2] Honsawek S, Tanavalee A, Sakdinakiattikoon M, et al. Correlation of plasma and synovial fluid osteopontin with disease severity in knee osteoarthritis. Clin Biochem.2009; 42(9):808-812. [3] Attur MG, Dave MN, Stuchin S, et al. Osteopontin: an intrinsic inhibitor of inflammation in cartilage. Arthritis Rheum.2001; 44(3):578-584. [4] Chen Y, Sun CJ, Fang JZ. Zhongguo Linchuang Kangfu. 2002;6(10):1426-1427. 陈游,孙才江,方建珍. 不同程度膝骨关节炎患者关节滑液中几种细胞因子水平变化[J]. 中国临床康复,2002,6(10): 1426-1427. [5] Kellgren JH, LawrEnce JS. Radiologic assement of osteoarthritis. Ann Rheum Dis.1957;16(4):494-502. [6] Take Y, Nakata K, Hashimoto J, et al. Specifically modified osteopontin in rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes supports interaction with B cells and enhances production of interleukin-6. Arthritis Rheum. 2009;60(12):3591-3601. [7] Xu G, Nie H, Li N, et al. Role of osteopontin in amplification and perpetuation of rheumatoid synovitis. J Clin Invest. 2005; 115(4):1060-1067. [8] Heilmann K, Hoffmann U, Witte E, et al. Osteopontin as two-sided mediator of intestinal inflammation. J Cell Mol Med. 2009;13(6):1162-1174. [9] Zang JW. Zhongguo Kexueyuan Yuankan. 2005;3:208-210. 臧敬五.自身免疫性疾病研究的新进展-骨桥蛋白在类风湿性关节炎中的病理机制研究[J].中国科学院院刊,2005,3:208-210. [10] Gattorno M, Gregorio A, Ferlito F, et al. Synovial expression of osteopontin correlates with angiogenesis in juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2004;43(9):1091-1096. [11] Zaka R, Stokes D, Dion AS, et al. P5L mutation in Ank results in an increase in extracellular inorganic pyrophosphate during proliferation and nonmineralizing hypertrophy in stably transduced ATDC5 cells. Arthritis Res Ther. 2006;8(6):R164. [12] Jacques C, Gosset M, Berenbaum F, et al. The role of IL-1 and IL-1Ra in joint inflammation and cartilage degradation. Vitam Horm. 2006;74:371-403. [13] Alvarez-Soria MA, Largo R, Sanchez-Pernaute O, et al. Prostaglandin E2 receptors EP1 and EP4 are up-regulated in rabbit chondrocytes by IL-1beta, but not by TNFalpha. Rheumatol Int. 2007;27(10):911-917. [14] Petrow PK, Hummel KM, Schedel J, et al. Expression of osteopontin messenger RNA and protein in rheumatoid arthritis: effects of osteopontin on the release of collagenase 1 from articular chondrocytes and synovial fibroblasts. Arthritis Rheum. 2000;43(7):1597-1605. [15] Ohshima S, Yamaguchi N, Nishioka K, et al. Enhanced local production of osteopontin in rheumatoid joints. J Rheumatol. 2002;29(10):2061-2067. [16] Xu G, Sun W, He D, et al. Overexpression of osteopontin in rheumatoid synovial mononuclear cells is associated with joint inflammation, not with genetic polymorphism. J Rheumatol. 2005;32(3):410-416. [17] Wang YY, Zhao Z, Huang F, et al. Zhonghua Fengsi Bingxue Zazhi. 2010;14(2):80-83. 王炎焱,赵征,黄烽,等.红曲对胶原诱导性关节炎大鼠血清趋化因子的影响[J].中华风湿病学杂志,2010,14(2):80-83.[18] Lv ZF, Tao Y, Chen RL, et al. ZHonghua Fengsi Bingxue Zazhi. 2011;15(1):17-21. 吕志芬,陶怡,陈瑞林,等.重组人Ⅱ型肿瘤坏死因子受体-抗体融合蛋白在胶原诱导性关节炎大鼠中的疗效观察及其对骨桥蛋白的影响[J].中华风湿病学杂志,2011,15(1):17-21.[19] Du J, Hou S, Zhong C, et al. Molecular basis of recognition of human osteopontin by 23C3, a potential therapeutic antibody for treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. J Mol Biol. 2008;382(4): 835-842.[20] Fan K, Dai J, Wang H, et al. Treatment of collagen-induced arthritis with an anti-osteopontin monoclonal antibody through promotion of apoptosis of both murine and human activated T cells. Arthritis Rheum. 2008;58(7):2041-2052. [21] Shimizu S, Okuda N, Kato N,et al.Osteopontin deficiency impairs wear debris-induced osteolysis via regulation of cytokine secretion from murine macrophages. Arthritis Rheum. 2010;62(5):1329-1337. [22] Hasegawa M, Segawa T, Maeda M,et al.Thrombin-cleaved osteopontin levels in synovial fluid correlate with disease severity of knee osteoarthritis.J Rheumatol.2011,38(1): 129-34. [23] Shio K, Kobayashi H, Asano T,et al.Thrombin-cleaved osteopontin is increased in urine of patients with rheumatoid arthritis.J Rheumatol. 2010;37(4):704-710. [24] Liu Q, Li XP, QIan L, et al. Zhonghua Linchuang Mianyi He Bintai Fanying Zazhi. 2007;1(6):43-47. 刘琼,李向培,钱龙,等.骨桥蛋白及血管内皮细胞生长因子与类风湿关节炎滑膜血管发生的关联[J].中华临床免疫和变态反应杂志, 2007,1(6):43-47. [25] Xu R, Zhong LM, Yuan B, et al. Zhonghua Fengsi Bingxue Zazhi. 2006;10(5):261-264. 许荣,钟丽民,袁斌,等.骨桥蛋白介导类风湿关节炎发病机制的初步研究[J].中华风湿病学杂志,2006,10(5):261-264. [26] Hasegawa M, Nakoshi Y, Iino T, et al. Thrombin-cleaved osteopontin in synovial fluid of subjects with rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol. 2009;36(2):240-245. [27] Huber LC, Distler O, Tarner I, et al. Synovial fibroblasts: key players in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2006;45(6):669-675.[28] Honsawek S, Tanavalee A, Yuktanandana P.Elevated circulating and synovial fluid endoglin are associated with primary knee osteoarthritis severity. Arch Med Res. 2009; 40(7):590-594.[29] Hata H, Sakaguchi N, Yoshitomi H, et al. Distinct contribution of IL-6, TNF-alpha, IL-1, and IL-10 to T cell-mediated spontaneous autoimmune arthritis in mice. J Clin Invest. 2004;114(4):582-588.[30] Andereya S,Streich N,Schmidt-Rohlfing B,et al.Comparison of modern maker proteins in serum and synovial fluid in patients with advanced osteoarthrosis and rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatol Int. 2006;26(5):432-428. |
| [1] | Huang Dengcheng, Wang Zhike, Cao Xuewei. Comparison of the short-term efficacy of extracorporeal shock wave therapy for middle-aged and elderly knee osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1471-1476. |
| [2] | Peng Zhihao, Feng Zongquan, Zou Yonggen, Niu Guoqing, Wu Feng. Relationship of lower limb force line and the progression of lateral compartment arthritis after unicompartmental knee arthroplasty with mobile bearing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1368-1374. |
| [3] | Li Jing, Xie Jianshan, Cui Huilin, Cao Ximei, Yang Yanping, Li Hairong. Expression and localization of diacylglycerol kinase zeta and protein kinase C beta II in mouse back skin with different coat colors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1196-1200. |
| [4] | Liu Xiangxiang, Huang Yunmei, Chen Wenlie, Lin Ruhui, Lu Xiaodong, Li Zuanfang, Xu Yaye, Huang Meiya, Li Xihai. Ultrastructural changes of the white zone cells of the meniscus in a rat model of early osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1237-1242. |
| [5] | Liu Xin, Yan Feihua, Hong Kunhao. Delaying cartilage degeneration by regulating the expression of aquaporins in rats with knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 668-673. |
| [6] | Ma Zetao, Zeng Hui, Wang Deli, Weng Jian, Feng Song. MicroRNA-138-5p regulates chondrocyte proliferation and autophagy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 674-678. |
| [7] | Liu Qing, Wan Bijiang. Effect of acupotomy therapy on the expression of Bcl-2/Bax in synovial tissue of collagen-induced arthritis rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 729-734. |
| [8] | Cao Xuhan, Bai Zixing, Sun Chengyi, Yang Yanjun, Sun Weidong. Mechanism of “Ruxiang-Moyao” herbal pair in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis based on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 746-753. |
| [9] | Li Yonghua, Feng Qiang, Tan Renting, Huang Shifu, Qiu Jinlong, Yin Heng. Molecular mechanism of Eucommia ulmoides active ingredients treating synovitis of knee osteoarthritis: an analysis based on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 765-771. |
| [10] | Song Shan, Hu Fangyuan, Qiao Jun, Wang Jia, Zhang Shengxiao, Li Xiaofeng. An insight into biomarkers of osteoarthritis synovium based on bioinformatics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 785-790. |
| [11] | Deng Zhenhan, Huang Yong, Xiao Lulu, Chen Yulin, Zhu Weimin, Lu Wei, Wang Daping. Role and application of bone morphogenetic proteins in articular cartilage regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 798-806. |
| [12] | Zheng Li, Li Dadi, Hu Weifan, Tang Jinlong, Zhao Fengchao. Risk assessment of contralateral knee arthroplasty after unilateral total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 374-379. |
| [13] | Lü Jiaxing, Bai Leipeng, Yang Zhaoxin, Miao Yuesong, Jin Yu, Li Zhehong, Sun Guangpu, Xu Ying, Zhang Qingzhu. Evaluation of internal fixation with proximal femoral nail antirotation in elderly knee osteoarthritis patients with femoral intertrochanteric fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 391-396. |
| [14] | Luo Anyu, Liu Hanlin, Xie Xiaofei, Huang Chen. Effect of antioxidant mixture on structural degeneration of an osteoarthritis rat model [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(23): 3625-3629. |
| [15] | Gao Kun, Chen Dayu, Zhang Yong, Liu Weidong, Sun Shufen, Lai Wenqiang, Ma Dujun, Wu Yihong, Lin Zhanpeng, Jiang Yinglu, Yu Weiji. Achyranthes bidentata alcohol extract inhibits extracellular matrix degradation of the cartilage by regulating synovial fibroblast exosomes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(23): 3636-3640. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||