Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2013, Vol. 17 ›› Issue (9): 1665-1672.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2013.09.022
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effect of hyperbaric oxygen on blood flow velocity of vertebro-basilar artery in sympathetic nerve type of cervical spondylosis
Zhou Si-hua, Zheng Rui-lian, Yang Jun, Yu Ling-yun
- Fourth Department of General Surgery, PLA 474 Hospital, Urumqi 830013, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2012-09-01Revised:2012-09-28Online:2013-02-26Published:2013-02-26 -
About author:Zhou Si-hua, Associate chief physician, Fourth Department of General Surgery, PLA 474 Hospital, Urumqi 830013, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China 516200671@163.com
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhou Si-hua, Zheng Rui-lian, Yang Jun, Yu Ling-yun. Effect of hyperbaric oxygen on blood flow velocity of vertebro-basilar artery in sympathetic nerve type of cervical spondylosis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2013, 17(9): 1665-1672.
share this article
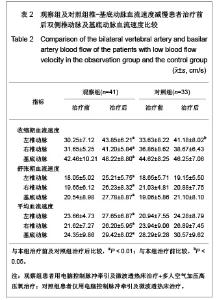
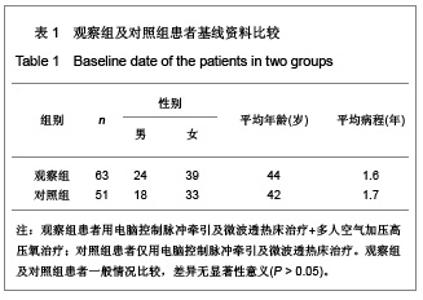
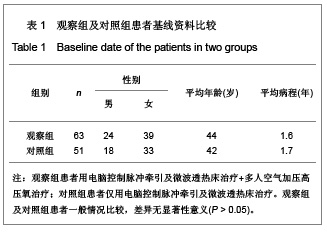
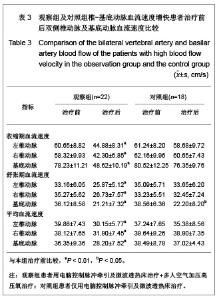
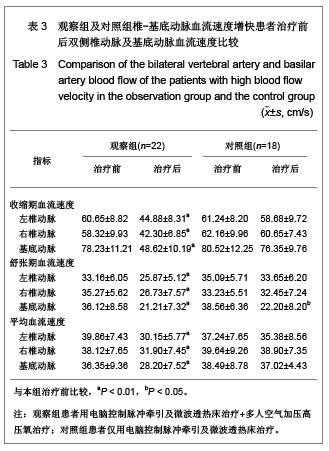
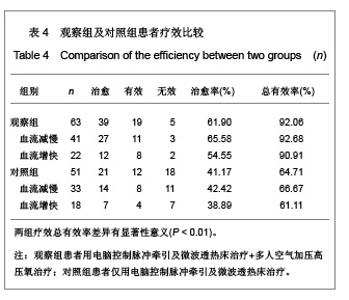
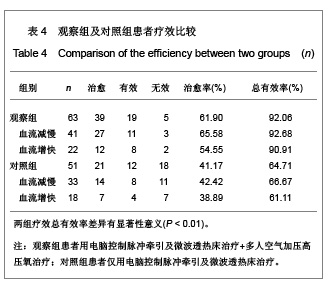
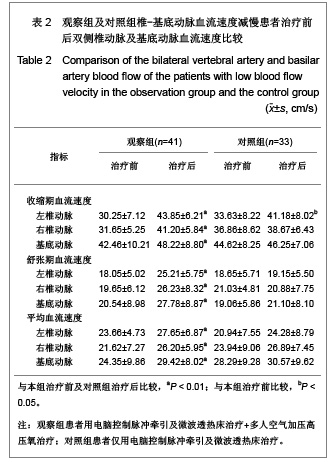
2.5 观察组及对照组患者疗效比较 观察组63例患者中,血流减慢41例,血流增快22例。对照组51例患者中,血流减慢33例,血流增快18例。观察组患者血流减慢患者治疗后左右椎动脉、基底动脉收缩期血流速度、舒张期血流速度、平均血流速度比治疗前及对照组治疗后均明显增快(P < 0.01)。观察组血流增快患者治疗后左右椎动脉、基底动脉收缩期血流速度、舒张期血流速度、平均血流速度比治疗前明显减低(P < 0.01)。对照组血流减慢患者治疗前后右椎动脉、基底动脉收缩期血流速度、舒张期血流速度、平均血流速度变化差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);左椎动脉治疗后舒张期血流速度、平均血流速度与治疗前相比差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),但收缩期血流速度较治疗前增快(P < 0.05)。对照组血流增快患者左右椎动脉治疗前后收缩期血流速度、舒张期血流速度、平均血流速度变化差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);基底动脉收缩期血流速度、平均血流速度变化差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),但治疗后舒张期血流速度较治疗前减慢(P < 0.05)。以《中医病症诊断疗效标准》为评价疗效。观察组治愈率为 61.9%,总有效率为92.06%,对照组治愈率为41.17 %,总有效率为64.70%。两组治愈率及总有效率差异均有显著性意义(P < 0.01)。具体数值详见表2-4。"
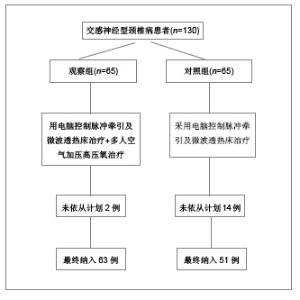
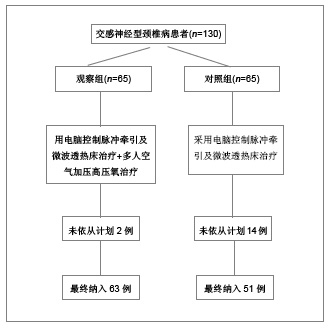
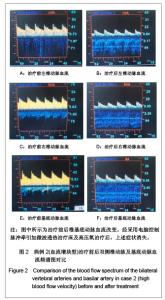
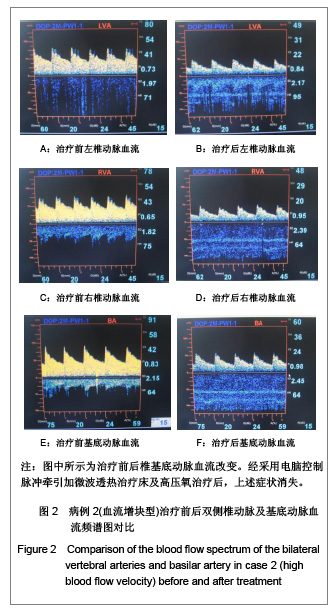
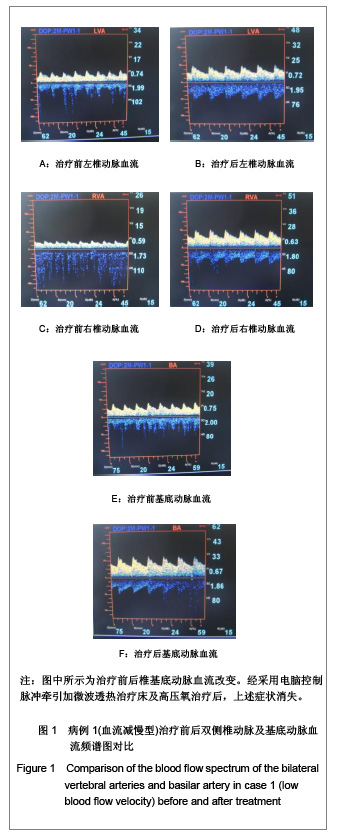
2.6 典型病例 病例1(血流减慢型):45岁女性患者,主诉:颈部疼痛伴头痛、视力模糊,眼窝胀痛,头晕,心动过缓,心慌、胸闷、四肢凉。查体:颈部活动受限,C2-7双侧棘旁明显压痛,右侧颈肌痉挛。治疗前后椎基底动脉血流改变见图1。经采用电脑控制脉冲牵引加微波透热治疗床及高压氧治疗后,上述症状消失。 病例2(血流增快型):48岁女性患者,主诉:颈部疼痛伴头晕、视力模糊,流泪,血压增高,四肢凉,一侧肢体多汗等。查体:颈部肌肉僵硬,颈部活动轻度受限,C2-7双侧棘旁明显压痛,双侧提肩胛肌处明显压痛。治疗前后椎基底动脉血流改变见图2。经采用电脑控制脉冲牵引加微波透热治疗床及高压氧治疗后,上述症状消失。"
| [1] Huang WY. Zhongguo Linchuang Kangfu. 2004;8(8):1551. 黄伟毅.颈椎病的针灸治疗近况[J].中国临床康复,2004,8(8): 1551.[2] Chen XM. Anmo yu Daoyin. 2008; 24(12): 23-24. 陈晓明.综合治疗交感神经型颈椎病60例疗效观察[J].按摩与导引, 2008,24(12):23-24.[3] Ma KY, Sun XX. Zhengzhou: Henan Science & Technology Press. 2005:322-323. 马奎云,孙孝先.颈源性疾病诊断治疗学[M].郑州:河南科学技术出版社, 2005:322-323.[4] Yu D,Wu Z, Zhang C. Zhongyi Zhenggu. 2004;16(8):502. 于栋,武震,张淳.交感型颈椎病发病机制的研究进展[J].中医正骨, 2004,16(8):502.[5] Guo JH, Lin MN, Gao H, et al. Zhongguo Wuzhenxue Zazhi. 2010;10(3):605-606. 郭健红,林木南,高晖,等.以胸闷胸痛等为首诊的交感神经型颈椎病误诊8例分析[J].中国误诊学杂志, 2010,10(3):605-606.[6] Ren LH, Fu GF, Lu WH, et al. Zhongguo Wuzhenxue Zazhi. 2012;12(6):1325. 任立红,付国芬,卢文华,等.交感神经型颈椎病误诊为心律失常1例分析[J].中国误诊学杂志, 2012,12(6):1325.[7] Yan YJ, Wang JR, Jia JW, et al. Zhongguo Chaosheng Yixue Zazhi. 2002;18(9):707-709. 杨玉杰,王金锐,贾建文,等.交感型颈椎病患者头颈部运动后椎动脉血流的观察[J].中国超声医学杂志, 2002, 18(9): 707-709.[8] Yan YJ, Jia JW, Wang JR, et al. Zhongguo Chaosheng Yixue Zazhi. 2004;20(1):45-48. 杨玉杰,贾建文,王金锐,等, 交感型颈椎病伴单侧椎动脉狭窄患者头颈部活动后椎动脉血流的观察[J].中国超声医学杂志, 2004, 20(1):45-48.[9] Zhou SH, Yang J, Zhen RL,et al. Zhongyi Zhenggu. 2008; 20(2): 10-11. 周肆华,杨军,郑瑞莲,等.高压氧及脉冲牵引对椎动脉型颈椎病患者椎动脉血流速度的影响[J].中医正骨, 2008,20(2):10-11.[10] Yan YJ, Li JF Bai ZY, et al. Zhongguo Chaosheng Yixue Zazhi. 2007;23(8):599-601. 杨玉杰,李敬府,白志勇,等.彩色多普勒超声对交感型颈椎病患者保守治疗后椎动脉血流的的观察[J].中国超声医学杂志, 2007, 23(8):599-601[11] Zhang ZH.Chinese Journal of Surgery. 1979;17(6):433. 张之虎.交感型颈椎病外科手术治疗[J].中华外科杂志, 1979, 17(6):433.[12] Yu ZS, Lui ZJ, Dan GD. Peking University. 2002; 34(5):282 284. 于泽生,刘忠军,党耕町.颈椎病外科治疗的回顾[J].北京大学学报: 医学版, 2002, 34(5):282-284[13] Sun Y, Cheng QF, Zhonghua Waike Zazhi. 1993; 31(8): 96-97. 孙宇,陈琪福.第二届颈椎病专题座谈会纪要[J].中华外科杂志, 1993, 31(8): 96-97[14] Cheng YB. Nanjing: University Press. 1994:186. 陈佑邦.中医病症诊断疗效标准[M].南京:南京大学出版社,1994: 186[15] Chen QX, Sun BO, Zhong SZ. Nerves accpmpanying the vertebral artery and their dinical relevance. Spine. 1988;12 1360-1364.[16] Wu HR, Sheng Y, Wu ZY. et al. Zhongguo Jiaoxing Waike Zazhi. 2006;14(1):12-15. 吴华荣,申勇,吴占勇,等.颈椎病发病学中的不稳定因素[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2006,14(1):12-15.[17] Zheng SJ. Beijing: People’s Medical Publishing House. 1990: 334-342. 郑思竞.系统解剖学[M].北京:人民卫生出版社, 1990:334-342.[18] Du JM, Tian XW, Din XF, et al. Jingyaotong Zazhi. 2009; 30(2): 181-182. 杜建明,田小武,丁晓方,等.小针刀结合骶管冲击治疗交感神经型颈椎病的疗效观察[J].颈腰痛杂志, 2009,30(2):181-182.[19] Qian J,Tian Y, Qiu GX, et al. Dynamic rabiographic analysis of sympathetic cervical spondylosis instability. Chin Med Sci J. 2009;24(1):46-49.[20] Gu T, Wan XW, YW, et al. Zhonghua Shiyan Waike Zazhi. 2007; 24(6):665-668. 顾韬,王新伟,袁文,等.颈椎间盘与后纵韧带上交感神经分布的特点及临床意义[J].中华实验外科杂志, 2007,24(6):665-668.[21] Zhang BX, Wan Y. Beijing: People's Military Medical Press. 2004:362. 张伯勋,王岩.现代颈肩腰腿痛诊断与治疗学[M].北京:人民军医出版社, 2004:362.[22] Jia L. Zhongguo Jiaoxing Waike Zazhi. 2009;17(11):843-844. 贾林.交感型颈椎病的治疗进展[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志, 2009, 17(11):843-844.[23] Yang KQ. Beijing: Beijing Publishing House. 1994:513-526. 杨克勤. 脊椎疾患的临床与研究[M].北京:北京出版社, 1994: 513-526[24] Zhou HT, Tan WJ. Zhonghua Wuli Yixue yu Kangfu Yixue Zazhi. 2006;28(7): 484-485. 周宏图, 谭文捷.高压氧及颈椎牵引综合治疗椎动脉型颈椎病的疗效观察[J]. 中华物理医学与康复医学杂志, 2006, 28(7): 484-485.[25] Yan J ,Zhou SH, Wan QY. Anmo yu Kangfu Yixue. 2010;1(9): 15-16. 杨军,周肆华,王秋无.高压氧加牵引治疗交感神经型颈椎病76例疗效观察[J].按摩与康复医学, 2010, 1(9): 15-16.[26] Yi Z, Weng QB, Long Y. Guangzhou: Guangdong Science & Technology Press. 2005. 易治,翁其彪,龙颖.高压氧医学临床指引[M].广州:广东科技出版社, 2005.[27] Li WR, Ni GT. Shanghai: Shanghai Science & Technology Press. 1998: 298-300. 李温仁,倪国坛.高压氧医学[M].上海:上海科学技术出版社,1998: 298-300.[28] Li Y.Zhonghua Wuli Yixue yu Kangfu Zazhi. 2005,27(8):459. 李月.高压氧配合调制中频电治疗椎动脉型颈椎病[J].中华物理医学与康复杂志,2005,27(8):459.[29] He XL. Hubei Zhongyi Zazhi. 2009;31(11):70. 贺旭林.颈椎整复法治疗交感神经型颈椎病187例[J].湖北中医杂志, 2009, 31(11):70.[30] Wan LS, Jiang GQ. Zhongguo Chaosheng Zhenduan Zazhi. 2004;5(6):449-450. 王莉闪,蒋国卿.经颅多谱勒超声对颈椎病患者脑底动脉的评价[J].中国超声诊断杂志,2004,5(6):449-450.[31] Qian WH, Bo Y, Cheng X. Shanghai Zhenjiu Zazhi. 2002; 21(4):22-23. 钱伟华,柏杨,陈新.温针灸颈夹脊穴治疗椎动脉型颈椎病40例[J].上海针灸杂志,2002,21(4):22-23. |
| [1] | Zeng Xianghong, Liang Bowei. A new strategy for the treatment of osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 431-437. |
| [2] | Liu Yulin, Li Guotai. Combined effects of hyperbaric oxygen, vibration training and astaxanthin on bone mineral density, glucose metabolism and oxidative stress in diabetic osteoporosis rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(20): 3117-3124. |
| [3] | Xu Hui, Kang Bingxin, Zhong Sheng, Gao Chenxin, Zhao Chi, Qiu Guowei, Sun Songtao, Xie Jun, Xiao Lianbo, Shi Qi. Pressing local acupoints plus adjustion of the knee joint in a sitting position for treating knee osteoarthritis: a randomized controlled trial [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(2): 216-221. |
| [4] | Chen Jiang, Li Jinyu, Zheng Chenying, Bai Chunxiao, Zhang Fan, Liu Chuyin, Zhao Xueqian, Yuan Qiaomei, Di Xueshi, Kang Shengqian, Jia Yusong . Changes in sagittal parameters of cervical spine after double-segment artificial cervical disc replacement and anterior cervical discectomy and fusion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(15): 2341-2346. |
| [5] | Liu Pengran, Jiao Rui, Tao Jin, Chen Hui, Dai Jihang, Yan Lianqi. Comparison of the effects of total hip arthroplasty with different interface prostheses in the treatment of elderly hip diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(15): 2347-2351. |
| [6] | Ma Long, Tan Xiaoxin, Sun Guoshao. A 5-year follow-up on sagittal alignment and radiological outcomes of consecutive three-level anterior cervical discectomy and fusion and hybrid surgery [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(12): 1879-1885. |
| [7] | Hu Yigao, Li Gaofeng. Hyperbaric oxygen alleviates scar adhesion at the base and shortens the time of revascularization of delayed skin flap in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(11): 1658-1663. |
| [8] | Yu Bin, Peng Yinxiao, Xue Li, Qin Hui, Liang Yijian. Comparison between anterior cervical discectomy and fusion using Zero-P and traditional anterior cervical plate plus cage for treating two-level cervical spondylosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(9): 1342-1347. |
| [9] | Ge Su, Zou Xiaobao, Ma Xiangyang, Wang Binbin, Yang Haozhi, Zhang Shuang, Ni Ling, Chen Yuyue, Xia Hong, Wu Zenghui. Design and application of fulcrum screws for atlantoaxial dislocation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(9): 1348-1352. |
| [10] | Qiao Yuqi, Fu Rongchang, Zhang Lihong. Effects of sand therapy on hemodynamics in the femoral artery bifurcation at different degrees of stenosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(8): 1218-1224. |
| [11] | Yang Xu, Zhao Xiaofeng, Qi Detai, Wang Xiaonan, Jin Yuanzhang, Zhou Runtian, Zhao Bin. Changes in cervical sagittal balance after three-dimensional printing ACT titanium cage in anterior cervical discectomy with fusion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(36): 5741-5748. |
| [12] | Peng Ruhui, Zhou Dechun. Application of tranexamic acid combined with tourniquet optimization program in total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(36): 5812-5817. |
| [13] | Li Yongtao, Song Wenhui, Liu Changwen, Liang Kaiheng, Zhang Kaixi, Liu Changfeng. Clinical efficacy of calcium sulphate/demineralized bone matrix versus bone allograft in anterior cervical discectomy and fusion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(34): 5478-5485. |
| [14] | He Li, Xu Shuai, Xu Song, Zhao Xiaoyu, Pang Shilong, Miao Jun, Liu Haiying, Liang Yan. Analysis and prediction of related factors of single-level cervical total disc replacement [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(30): 4782-4788. |
| [15] |
Shang Zhizhong, Jiang Yanbiao, Yao Lan, Wang Anan, Wang Hongxia, Tian Yuanxin, Liu Dengrui, Ma Bin .
Feasibility of stem cell therapy for renal ischemia/reperfusion injury: a systematic review based on animal experiments [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(25): 4094-4100. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||