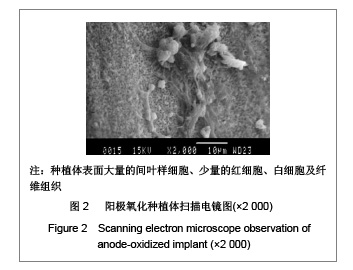
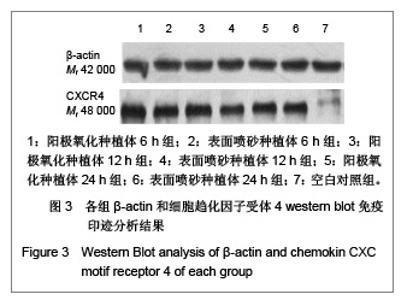
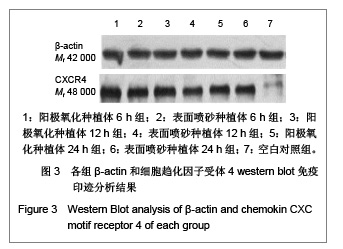
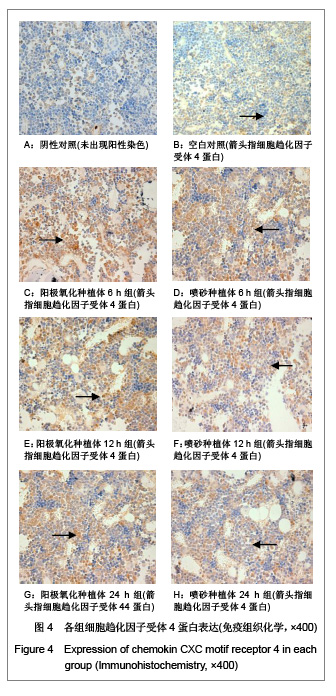
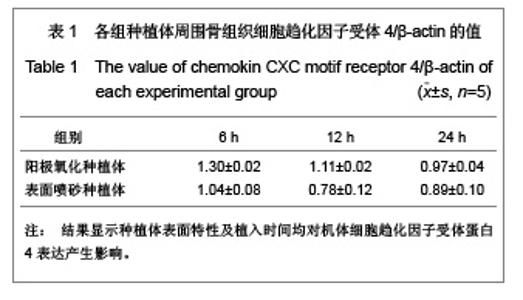
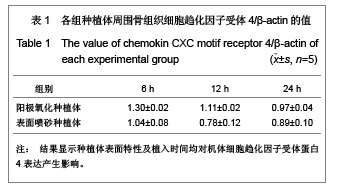
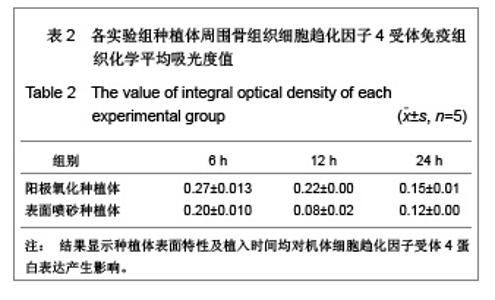
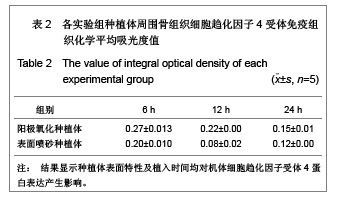
| [1] Rocci A, Martignoni M, Gottlow J. Immediate loading of Branemark System TiUnite and machined-surface implants in the posterior mandible: A randomized open-ended clinical trial.Clin Implant Dent Relat Res.2003;5(Suppl 1):57-63.[2] Zechner W, Tangl S, Furst G, et al. Osseous healing characteristics of three different implant types. Clin Oral Implants Res.2003;14(2):150-157.[3] Schupbach P, Glauser R, Rocci A, et al. The human bone-oxidized titanium implant interface: A light microscopic, scanning electron microscopic, back-scatter scanning electron microscopic, and energy-dispersive x-ray study of clinically retrieved dental implants. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2005, 7(Suppl 1):S36-43.[4] Sul YT, Johansson C, Albrektsson T. Which surface properties enhance bone response to implants? Comparison of oxidized magnesium, TiUnite, and Osseotite implant surfaces. Int J Prosthodont.2006;19(4):319-328.[5] Sun Z, Wang D. Xiandai Kouqiang Yixue Zazhi.2001; 24 (2): 152-153. 孙振,王东.种植体表面改性的现状和发展[J].现代口腔医学杂志, 2001,24 (2):152-153.[6] Cheng Z,Liu X,Ou L, et al.Mobilization of mesenchymal stem cells by granulocyte colony-stimulating factor in rats with acute myocardial infarction. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2008;22 (5):363-371.[7] Wang Y, Deng Y, Zhou GQ.SDF-1alpha/CXCR4-mediated migration of systemically transplanted bone marrow stromal cells towards ischemic brain lesion in a rat model. Brain Res. 2008;1195:104-112.[8] Ceradini DJ, Kulkarni AR, Callaghan MJ, et al. Progenitor cell trafficking is regulated by hypoxic gradients through HIF-1 induction of SDF-1. Nat Med.2004;10(8):858-864.[9] Otsuru S, Tamai K, Yamazaki T, et al.Circulating bone marrow-derived osteoblast progenitor cells are recruited to the bone-forming site by the CXCR4/stromal cellderived factor-1 pathway. Stem Cells.2008;26(1):223-234.[10] Kitaori T, Ito H, Schwarz EM, et al. Stromal cell-derived factor 1/CXCR4 signaling is critical for the recruitment of mesenchymal stem cells to the fracture site during skeletal repair in a mouse model. Arthritis Rheum. 2009; 60(3): 813-823.[11] Furze RC, Rankin SM. Neutrophil mobilization and clearance in the bone marrow. Immunology. 2008;125(3):281-288.[12] Coelho PG, Granjeiro JM, Romanos GE, et al. Basic research methods and current trends of dental implant surfaces. Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2009; 88 (2):579-96.[13] Nagase H, Miyamasu M, Yamaguchi M, et al. Cytokine-mediated regulation of CXCR4 expression in human neutrophils. Leukoc Biol.2002;71(4):711-717.[14] Ma J, Ge J, Zhang S, et al. Time course of myocardial stromal cell-derived factor 1 expression and beneficial effects of intravenously administered bone marrow stem cells in rats with experimental myocardial infarction. Basic Res Cardiol. 2005;100(3):217-223.[15] Son BR, Marquez-Curtis LA, Kucia M, et al. Migration of bone marrow and cord blood mesenchymal stem cells in vitro is regulated by stromal-derived factor-1-CXCR4 and hepatocyte growth factor-c-met axes and involves matrix metalloproteinases. Stem Cells. 2006;24(5):1254-1264.[16] Gazitt Y. Homing and mobilization of hematopoietic stemcells and hematopoietic cancer cells are mirror image processes, utilizing similar signaling pathways and occurring concurrently: circulating cancer cells constitute an ideal target for concurrent treatment with chemotherapy andantilineage- specific antibodies. Leukemia.2004;18(1):1-10.[17] Hernández-López C, Varas A, Sacedón R, et al. The CXCL12/CXCR4 pair in aged human thymus. Neuroimmunomodulation.2010;17(3): 217-220.[18] Salvucci O, Bouchard A, Baccarelli A, et al. The role of CXCR4 receptor expression in breast cancer: a large tissue microarray study.Breast Cancer Res Treat.2006;97(3): 275-283.[19] Wang MH, Huang TZ, Hui Z, et al. Zhongliu Fangzhi Yanjiu. 2008; 35(2):107-109. 王明华,黄铁柱,惠震,等.趋化因子受体CXCR4在甲状腺癌中的表达[J].肿瘤防治研究,2008,35(2):107-109.[20] Otsuru S, Tamai K,Yamazaki T,et al.Circulating bone marrow-derived osteoblast progenitor cells are recruited to the bone-forming site by the CXCR4/stromal cell-derived factor-1 pathway. Stem Cells.2008;26(1):223-234.[21] Liao XG,Yin M,Li SY,et al.Shengming Kexue. 2010;22 (10): 1069-1073. 廖新根,殷明,李士勇,等. SDF-1/CXCR4轴在骨再生修复中的研究进展[J].生命科学,2010,22 (10):1069-1073. |