Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2013, Vol. 17 ›› Issue (7): 1305-1312.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2013.07.027
Previous Articles Next Articles
Diabetes mellitus impacts hearing and cochlear morphology
Wei Shuang-ping1, Guo Kao-shan2, Li Rui-yu2, Li Meng3, Wu Li-ping4, Yan Jun-li5
- 1 Department of Clinical Surgery, Xingtai Medical College, Xingtai 054000, Hebei Province, China
2 Institute for Integrated Traditional and Western Medicine, the Second Affiliated Hospital of Xingtai Medical College, Xingtai 054000, Hebei Province, China
3 Department of Health, Hotan Detachment of the Xinjiang Armed Police Corps, Hotan 848011, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China
4 Department of Laboratory Medicine, Xingtai People’s Hospital, Hebei Medical University, Xingtai 054031, Hebei Province, China
5 Renxian County Hospital of Hebei Province, Xingtai 055150, Hebei Province, China
-
Received:2012-06-18Revised:2012-08-27Online:2013-02-12Published:2013-02-12 -
Contact:Li Rui-yu, Professor, Chief physician, Master’s supervisor, Institute for Integrated Traditional and Western Medicine, the Second Affiliated Hospital of Xingtai Medical College, Xingtai 054000, Hebei Province, China liruiyu651021@163.com -
About author:Wei Shuang-ping★, Master, Associate professor, Department of Clinical Surgery, Xingtai Medical College, Xingtai 054000, Hebei Province, China xtyzwsp2004@163.com
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wei Shuang-ping, Guo Kao-shan, Li Rui-yu, Li Meng, Wu Li-ping, Yan Jun-li. Diabetes mellitus impacts hearing and cochlear morphology[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2013, 17(7): 1305-1312.
share this article

2 糖尿病致听力损伤机制的研究进展 随着对糖尿病的广泛重视和深入研究,糖尿病患者的听力功能情况已引起临床医师和听力学家的重视,由其引起的听力损伤的报道逐渐增多,并且糖尿病听力损伤易与老年性耳聋不容易区分,因此,有必要对糖尿病患者听力损伤的临床特点、发病机制进行探讨,以利于了解糖尿病致听力损伤的原因[22]。 机体代谢紊乱:机体脂肪合成减少,分解加速,脂质代谢紊乱,从而引起血脂增高,甚至导致大血管和小血管动脉硬化,糖尿病患者糖代谢紊乱引起内耳疾病的概率是正常人的两倍多。 耳蜗神经细胞的损伤:高血糖、高血脂通常引起血液循环障碍,血液黏度增加,脂质代谢紊乱以及脂质沉积在耳蜗毛细胞内,损害了耳蜗神经细胞,导致患者神经细胞代谢失调,从而导致神经传导速度减慢。加重了微血管病变的发生,且听觉系统需要利用葡萄糖和高能量来进行信号的处理,所以耳蜗成为高血糖引起损害的一个靶器官。 耳蜗功能下降:糖尿病可引起包括内耳在内的微血管病变,其中耳蜗血管纹病最多见,导致神经组织的缺血缺氧引起单神经或多发性神经病变,尤其是耳蜗血管纹微血管病变可引起耳蜗毛细胞损伤及耳蜗神经变性。 听神经系统病变:糖尿病神经病变的原因是长期的高血糖对神经细胞的直接破坏作用和长期的高血糖损伤了神经细胞的供血血管。引起体内代谢紊乱、微循环障碍,造成神经缺血、缺氧而逐渐发生的全身病变。 免疫反应:糖尿病的研究表明,自身的免疫力是影响糖尿病的重要原因之一。在糖尿病的发病中,研究表 明很多是和自身免疫力有密切关系的。但引起免疫反应的主要因素及与遗传因素的关系尚待进一步阐明。 血管病变:糖尿病患者在持续高血糖的作用下,体内糖化血红蛋白合成加快并沉积在微血管壁上,以及免疫复合物对血管内皮细胞的损伤等,使微血管通透性增加,基底膜增厚,内皮细胞异常增生,导致微血管管径缩小,从而使神经发生缺血性改变而出现功能障碍。 神经病变:糖尿病微血管病变使得滋养神经的微血管狭窄、闭塞,神经营养不良,加上长期处于高血糖状态,神经细胞膜的代谢失调发生变性坏死,这就是糖尿病的周围神经病变。当糖尿病病变波及第VⅢ对脑神经时,可直接导致感音神经性耳聋。 血液改变:糖尿病是微循环障碍和血液流变性改变的始动因素,而微循环障碍和血液流变性改变又是糖尿病神经病变的加重因素。 糖尿病并发症:糖尿病的慢性并发症为微血管病变和神经病变,这些并发症会对内耳产生一定影响,是导致糖尿病患者听力下降的主要原因。 遗传因素:在母系遗传性糖尿病合并耳聋的患者中,存在着线粒体DNA的突变,线粒体突变影响线粒体功能,引起内耳结构和功能的改变,导致听力减退。"

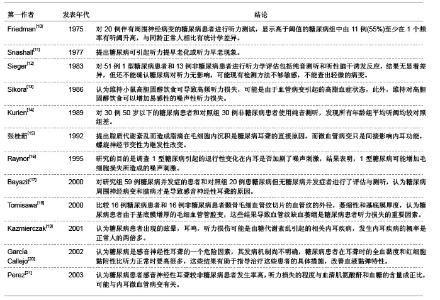
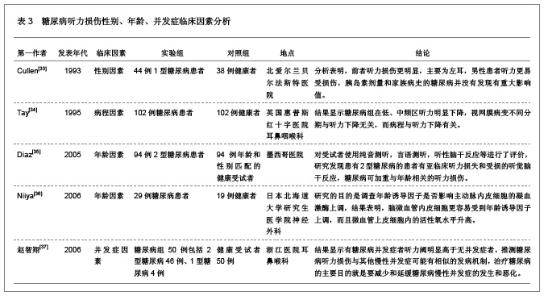
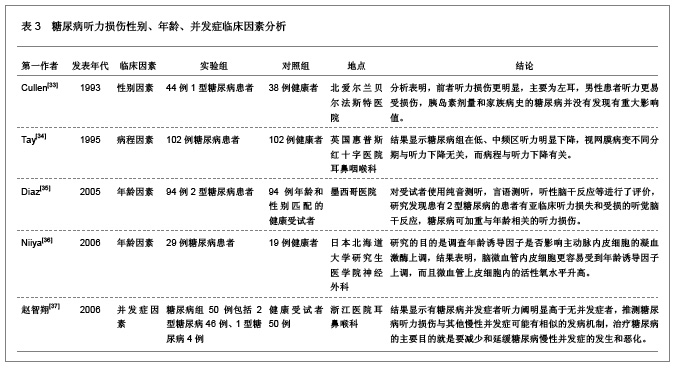
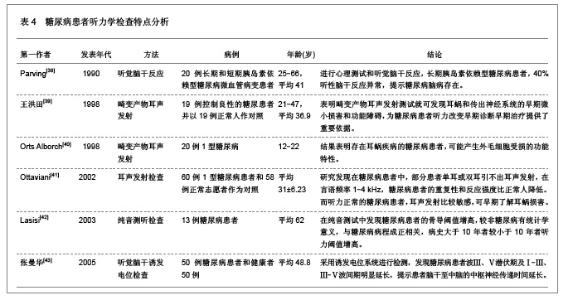
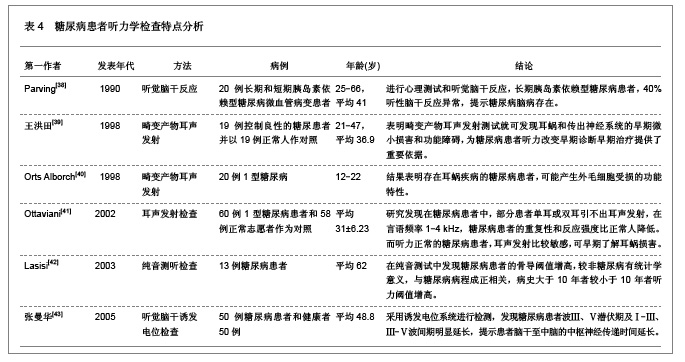
3 糖尿病对听力及耳蜗形态学结构影响的相关因素 3.1 资料来源 糖尿病对听力及耳蜗形态学结构影响的相关研究文献[23-24],检索时间范围1970至2012年,以“糖尿病(Diabetes);听力损伤(Hearing impairment);耳蜗(Cochlea);微血管病变(Microvascular lesions);神经病变(Neuropathy);”为检索词,选取文献29篇[25-53]。 3.2 纳入标准 ①糖尿病听力损害特征及相关因素分析。②糖尿病患者耳蜗病变的形态学观察。③耳蜗微循环的自身调节机制。④突发性耳聋和耳蜗微循环的关系。⑤耳蜗微循环障碍的研究。⑥实验性糖尿病大鼠内耳毛细血管超微结构变化。 3.3 排除标准 ①妊娠糖尿病。②合并严重心、脑、肾病患者。③酒精性肝病者。④重复研究的文章。 3.4 分析指标 ①糖尿病听力损害特征及相关因素分析。②糖尿病患者耳蜗病变的形态学观察。③耳蜗微循环的自身调节机制。④耳蜗微循环障碍的研究。⑤突发性耳聋和耳蜗微循环的关系。 3.5 糖尿病听力损伤特征及相关因素分析 3.5.1 糖尿病听力损伤特征临床研究相关文献分析 见表1。"
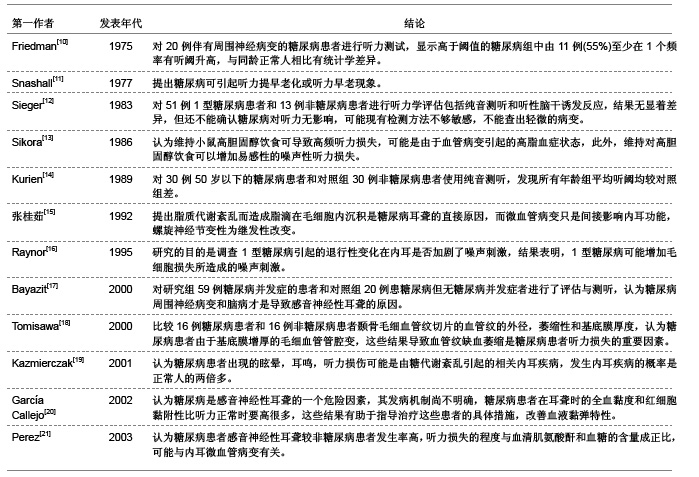

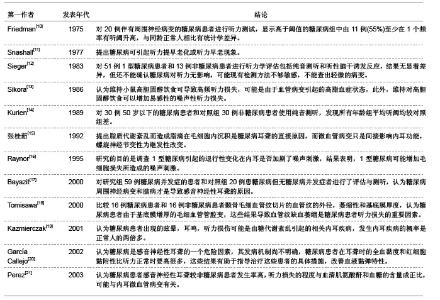
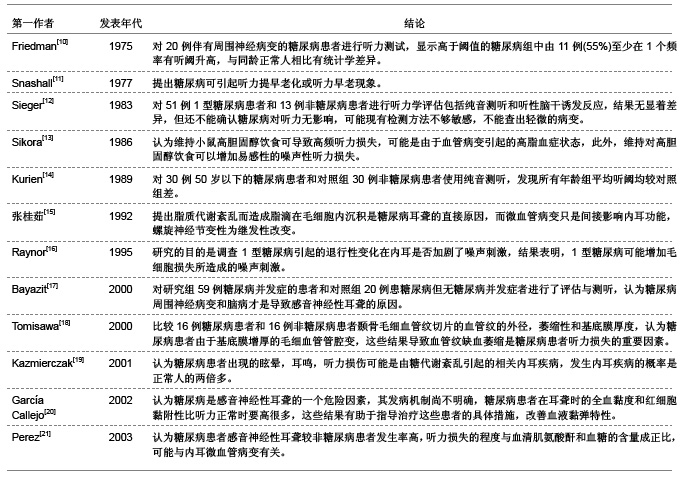
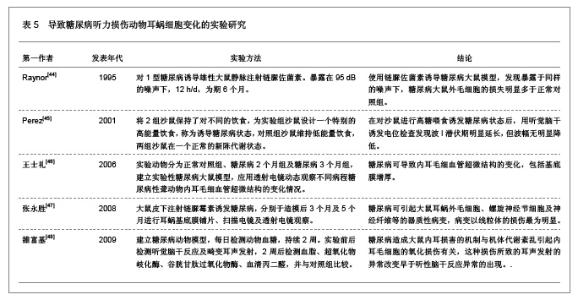
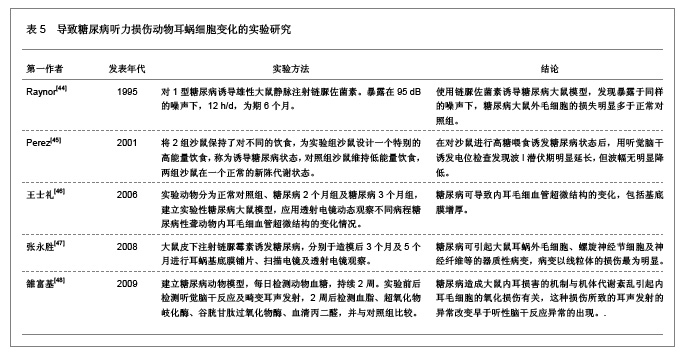
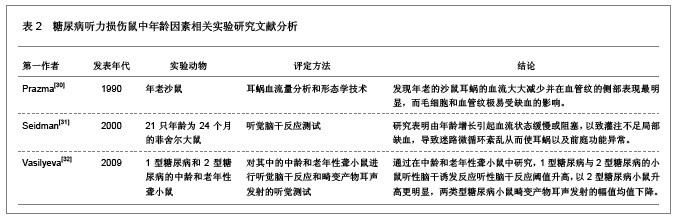
糖尿病并发血管、神经病变主要与高血糖症、脂代谢紊乱、微血管病变及血清过氧化脂质等因素有关。目前对慢性合并症的防治,尤其是在血管神经病变方面,尚没有很满意的方法。糖尿病患者普遍存在大血管和微血管病变,尤其是影响神经的小动脉和毛细血管基底膜增厚,血管内皮细胞增生,透明变性,糖蛋白沉积,管腔狭窄,同时神经的滋养血管被纤维蛋白堵塞,导致神经缺血、缺氧,使神经营养障碍和变性,引起神经病变,任何周围神经包括自主神经均可受累,且发病较早,甚至隐性糖尿病即有周围神经病变。糖尿病听力损伤特征临床研究相关文献分析。 3.5.2 糖尿病听力损伤特征实验研究相关文献分析 糖尿病是遗传性较强的疾病。即使母体在妊娠前没有表现出特有的病症,但实际上,母体在出生时就已携带了糖尿病的发病基因,而在各种诱因下,发病基因就会表现出病症。糖尿病与听力损伤之间的关系复杂,遗传、衰老等一系列的影响因素可能使这两者之间看起来很有关联,但有必要进行更仔细的研究,以确定这些因素之间真正的相互作用。糖尿病听力损伤特征实验研究相关文献分析,见表2。"
| [1] Tay HL,Ray N,Ohri R,et al.Diabetes mellitus and hearing loss.Clin Otolaryngol Allied Sci.1995;20(2):130-134.[2] 蒋国秀.实用糖尿病学[M].北京:人民卫生出版社,1992:233.[3] 樊云霞,韩峰,董明,等.老年2型糖尿病患者听力损害特征及相关因素分析[J].山东大学学报:医学版,2008,46(7):707-709.[4] Orita S,Fukushima K,Orita Y,et al.Sudden hearing impairment combined with diabetes mellitus or hyperlipidemia.Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol.2007;264(4):359-362.[5] Weng SF,Chen YS,Hsu CJ,et al.Clinical features of sudden sensorineural hearing loss in diabetic patients.Laryngoscope. 2005;115(9):1676-1680.[6] Fukushima H,Cureoglu S,Schachern PA,et al.Cochlear changes in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus.Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg.2005;133(1):100-106.[7] Ren T,Brown NJ,Zhang M,et al.A reversible ischemia model in gerbil cochlea.Hear Res.1995;92(1-2):30-37.[8] Nario K,Matsunaga T,Inui H,et al.A ABR findings, electrocochleograms and caloric tests in vertebrobasilar ischemic rats.Acta Otolaryngol Suppl.1997;528(Suppl):63-66.[9] Perlman HB,Kimura R,Fernandez C.Experiments on temporary obstruction of the internal auditory artery. Laryngoscope.1959;69(6):591-613.[10] Friedman SA,Schulman RH,Weiss S.Hearing and diabetic neuropathy.Arch Intern Med.1975;135(4):573-576.[11] Snashall SE.Békésy audiometry and tone and reflex decay tests in diabetics.Arch Otolaryngol.1977;103(6):342-343.[12] Sieger A,White NH,Skinner MW,et al.Auditory function in children with diabetes mellitus.Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol.1983; 92(3Pt1):237-241.[13] Sikora MA,Morizono T,Ward WD,et al.Diet-induced hyperlipidemia and auditory dysfunction.Acta Otolaryngol.1986;102(5-6):372-381.[14] Kurien M,Thomas K,Bhanu TS.Hearing threshold in patients with diabetes mellitus.J Laryngol Otol.1989;103(2):164-168.[15] 张桂茹,倪劲松.糖尿病患者内耳病变及耳聋机理的实验研究[J].临床耳鼻咽喉科杂志,1992,6(2):82-83.[16] Raynor EM,Carrasco VN,Prazma J,et al.An assessment of cochlear hair-cell loss in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus diabetic and noise-exposed rats.Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg.1995;121(4):452-456.[17] Bayazit Y,Yilmaz M,Kepekçi Y,et al.Use of the auditory brainstem response testing in the clinical evaluation of the patients with diabetes mellitus.J Neurol Sci.2000;181(1-2): 29-32.[18] Tomisawa H.Diabetic changes in the stria vascularis in humans--a study of PAS-stained temporal bone sections. Nihon Jibiinkoka Gakkai Kaiho.2000;103(11):1227-1237.[19] Ka?mierczak H, Doroszewska G.Metabolic disorders in vertigo,tinnitus,and hearing loss.Int Tinnitus J.2001;7(1): 54-58.[20] García Callejo FJ,Orts Alborch MH,Morant Ventura A,et al.Neurosensory sudden deafness, blood hyperviscosity syndrome, and diabetes mellitu.Acta Otorrinolaringol Esp. 2002;53(3):221-224.[21] Perez R,Freeman S,Cohen D,et al.The differential vulnerability of the inner ear end-organs to several external factors.J Basic Clin Physiol Pharmacol.2003;14(2):85-93.[22] 樊云霞.老年2型糖尿病患者听力损害特征及相关因素分析[D].山东:山东大学,2007:1-40.[23] 中国知网.中国学术期刊总库[DB/OL].2012-08-10. https://www.cnki.net.[24] SCI数据库.Web of Sciencevia ISI Web of Knowledge[DB/OL]. 2012-08-10. http://ip-science.thomsonreuters.com/mjl[25] Lisowska G,Namys?owski G,Morawski K,et al.Cochlear dysfunction and diabetic microangiopathy.Scand Audiol Suppl.2001;(52):199-203.[26] 陈彦华,蒋连强,李玲,等.2型糖尿病并发血管病变的临床实验研究[J].柳州医学,2002,15(2):61-64.[27] Kakarlapudi V,Sawyer R,Staecker H.The effect of diabetes on sensorineural hearing loss.Otol Neurotol.2003;24(3):382-386.[28] Fukushima H,Cureoglu S,Schachern PA,et al.Effects of type 2 diabetes mellitus on cochlear structure in humans.Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg.2006;132(9):934-938.[29] Loader B,Stokic D,Riedl M,et al.Combined analysis of audiologic performance and the plasma biomarker stromal cell-derived factor 1a in type 2 diabetic patients.Otol Neurotol. 2008;29(6):739-744.[30] Prazma J,Carrasco VN,Butler B,et al.Cochlear microcirculation in young and old gerbils.Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg.1990;116(8):932-936.[31] Seidman MD,Khan MJ,Bai U,et al.Biologic activity of mitochondrial metabolites on aging and age-related hearing loss.Am J Otol.2000;21(2):161-167.[32] Vasilyeva ON,Frisina ST,Zhu X,et al.Interactions of hearing loss and diabetes mellitus in the middle age CBA/CaJ mouse model of presbycusis.Hear Res.2009;249(1-2):44-53.[33] Cullen JR,Cinnamond MJ.Hearing loss in diabetics.J Laryngol Otol.1993;107(3):179-182.[34] Tay HL,Ray N,Ohri R,et al.Diabetes mellitus and hearing loss.Clin Otolaryngol Allied Sci.1995;20(2):130-134.[35] Díaz de León-Morales LV,Jáuregui-Renaud K,Garay-Sevilla ME,et al.Auditory impairment in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.Arch Med Res.2005;36(5):507-510.[36] Niiya Y,Abumiya T,Shichinohe H,et al.Susceptibility of brain microvascular endothelial cells to advanced glycation end products-induced tissue factor upregulation is associated with intracellular reactive oxygen species.Brain Res.2006;1108(1): 179-187.[37] 赵智翔,许敏达,陈松岳,等.糖尿病影响听力的相关因素分析[J].浙江临床医学,2006,8(8):817.[38] Parving A,Elberling C,Balle V,et al.Hearing disorders in patients with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus.Audiology. 1990;29(3):113-121.[39] 王洪田,钟乃川.畸变产物耳声发射选择注意效应测试对糖尿病人听力的评价[J].临床耳鼻咽喉科杂志,1998,12(11):483-486.[40] Orts Alborch M,Morant Ventura A,García Callejo J,et al.The study of otoacoustic emissions in diabetes mellitus.Acta Otorrinolaringol Esp.1998;49(1):25-28.[41] Ottaviani F,Dozio N,Neglia CB,et al.Absence of otoacoustic emissions in insulin-dependent diabetic patients: is there evidence for diabetic cochleopathy?J Diabetes Complications. 2002;16(5):338-343.[42] Lasisi OA,Nwaorgu OGB,Bella AF.Cochlear vestibular complications of diabetes mellitus in Ibadan,Nigeria.Int Congress Series.2003;12(40):1325-1328.[43] 张曼华,张丽.脑干听觉诱发电位对糖尿病耳聋诊断价值的探讨[J].临床内科杂志,2005,22(8):563.[44] Raynor EM,Carrasco VN,Prazma J,et al.An assessment of cochlear hair-cell loss in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus diabetic and noise-exposed rats.Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg.1995;121(4):452-456.[45] Perez R,Ziv E,Freeman S,et al.Vestibular end-organ impairment in an animal model of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Laryngoscope.2001;111(1):110-113.[46] 王士礼,陈学明,毕道周,等.实验性糖尿病大鼠内耳毛细血管超微结构变化[J].听力学及言语疾病杂志,2006,14(4):278-279.[47] 张永胜,张玉海.糖尿病大鼠耳蜗病变的形态学观察[J].中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志,2008,22(1):64-66.[48] 雒富基,陈小婉,罗维民.糖尿病早期内耳损伤听力学改变的实验研究[J].听力学及言语疾病杂志,2009,17(3):265-267.[49] Masutani H,Takahashi H,Sando I.Stria vascularis in Ménière's disease: a quantitative histopathological study.Auris Nasus Larynx.1992;19(3):145-152.[50] Gutmann R,Wollenberg B,Krampert B,et al.Incidence of Doppler ultrasound detectable stenoses of cervical arteries in patients with cochlear-vestibular symptoms. Laryngorhinootologie.1993;72(10):502-505.[51] 董民声,董明敏,娄卫华.内耳疾病研究进展[M].郑州:河南医科大学出版社,1999:109-110.[52] 罗志强,孔维佳.耳蜗微循环的自身调节机制[J].国外医学:耳鼻咽喉科学分册,2001,25(4):216-219.[53] Aird WC.Endothelium as an organ system.Crit Care Med.2004;32(5Suppl):271-279. |
| [1] | Zhou Jihui, Li Xinzhi, Zhou You, Huang Wei, Chen Wenyao. Multiple problems in the selection of implants for patellar fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1440-1445. |
| [2] | Tang Hui, Yao Zhihao, Luo Daowen, Peng Shuanglin, Yang Shuanglin, Wang Lang, Xiao Jingang. High fat and high sugar diet combined with streptozotocin to establish a rat model of type 2 diabetic osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1207-1211. |
| [3] | Wang Shiqi, Zhang Jinsheng. Effects of Chinese medicine on proliferation, differentiation and aging of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells regulating ischemia-hypoxia microenvironment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1129-1134. |
| [4] | Fan Quanbao, Luo Huina, Wang Bingyun, Chen Shengfeng, Cui Lianxu, Jiang Wenkang, Zhao Mingming, Wang Jingjing, Luo Dongzhang, Chen Zhisheng, Bai Yinshan, Liu Canying, Zhang Hui. Biological characteristics of canine adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells cultured in hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1002-1007. |
| [5] | Wang Hanyue, Li Furong, Yang Xiaofei, Hu Chaofeng. Direct reprogramming hepatocytes into islet-like cells by efficiently targeting and activating the endogenous genes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1056-1063. |
| [6] | Xiang Feifan, Ye Junwu, Zhang Xihai, Ge Jianhua, Tang Lian, Yang Yunkang. Comparison of three different internal fixation methods in treatment of ipsilateral femoral neck and shaft fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 403-408. |
| [7] | Chen Ziyang, Pu Rui, Deng Shuang, Yuan Lingyan. Regulatory effect of exosomes on exercise-mediated insulin resistance diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 4089-4094. |
| [8] | Xie Jingshu, Zhang Xianglin, Liu Jinlei, Wen Jing. Application of High Resolution reconstruction algorithm in precision CT scans of the middle and inner ears [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(23): 3614-3618. |
| [9] | Fan Junchao, Chen Yong, Song Junjie. Sevoflurance combined with xenon pretreatment protects against spinal cord ischemia-reperfusion injury in a rat model [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(23): 3660-3665. |
| [10] | Fu Panfeng, Shang Wei, Kang Zhe, Deng Yu, Zhu Shaobo. Efficacy of anterolateral minimally invasive approach versus traditional posterolateral approach in total hip arthroplasty: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(21): 3409-3415. |
| [11] | Ren Xingyu, Zhang Yi, Xu Haoran, Fan Bin, Dai Shifeng, Liang Chunyu. Meta-analysis of the postoperative effects of robot-assisted unicompartmental knee arthroplasty versus conventional surgery [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(21): 3416-3422. |
| [12] | Dong Liping, Luo Huaiqing, Yuan Heng, Long Juan, Xu Shaohui. Effect of aging on collateral vessel growth in rats with ischemic hind limbs [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(20): 3156-3161. |
| [13] | Tian Lin, Shi Xiaoqing, Duan Zhenglan, Wang Kuan, Zhang Li, Wang Peimin. Efficacy and safety of transverse tibial bone transport technique in the treatment of diabetic foot:a meta-analysis#br# [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(20): 3275-3280. |
| [14] | Xia Wenshen, He Renjiao, Ai Jinwei, Wang Jun, Li Desheng, Pei Bin. Stem cell transplantation for diabetic patients with lower-extremity arterial disease: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 3110-3116. |
| [15] | Dai Min, Wang Shuai, Zhang Nini, Huang Guilin, Yu Limei, Hu Xiaohua, Yi Jie, Yao Li, Zhang Ligang. Biological characteristics of hypoxic preconditioned human amniotic mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 3004-3008. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||