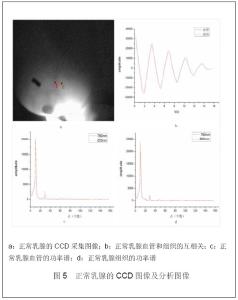
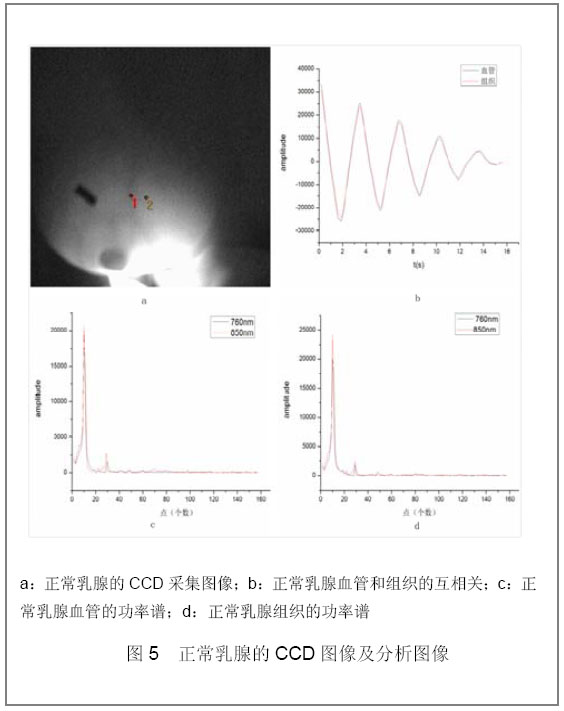
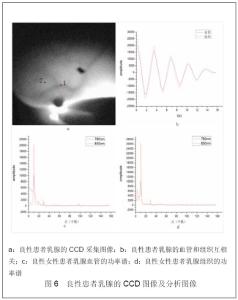
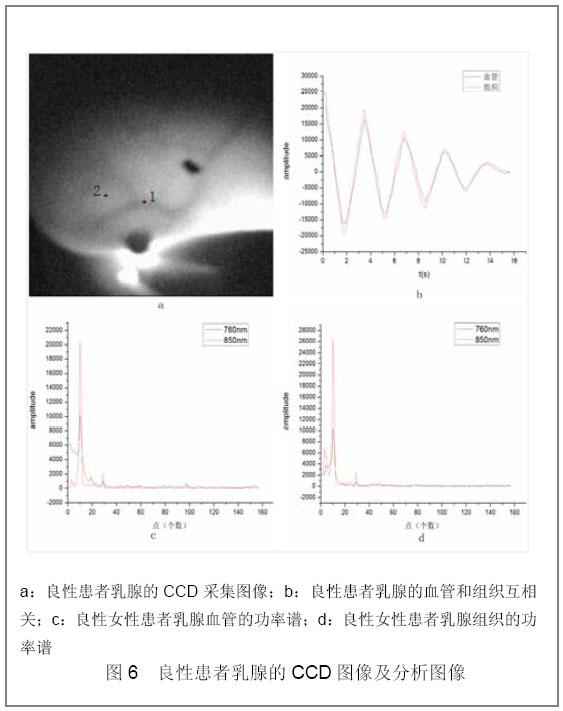
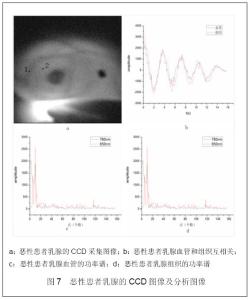
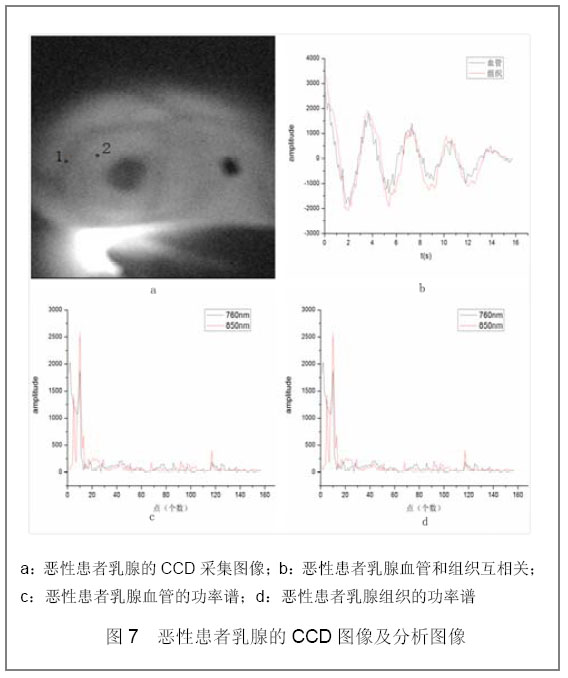
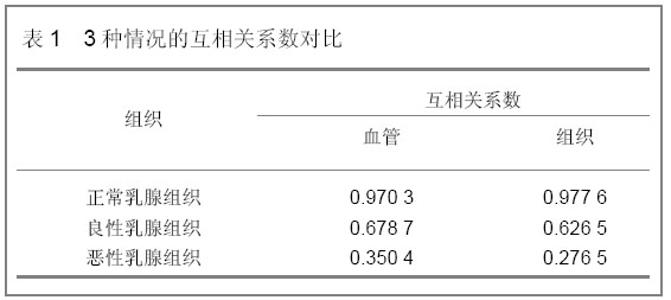
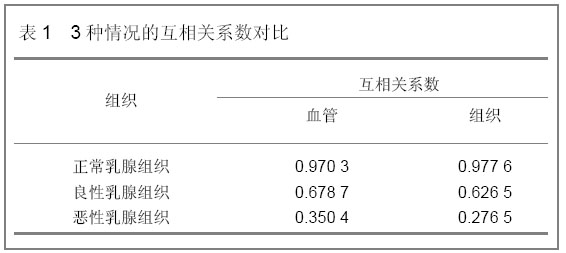
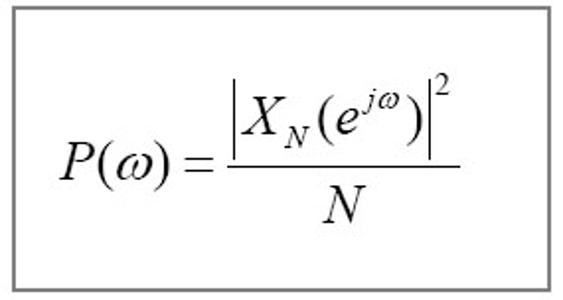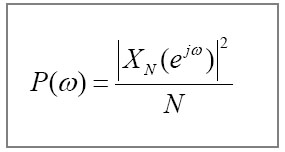| [1] |
Jiao Hui, Zhang Yining, Song Yuqing, Lin Yu, Wang Xiuli.
Advances in research and application of breast cancer organoids
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1122-1128.
|
| [2] |
Cai Hongmei, Wang Wei, Wang Wenjuan, Zhou Xiaohong.
Kinesiology taping combined with manual lymph drainage reduces postoperative lymphedema related to breast cancer
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(14): 2247-2251.
|
| [3] |
Xu Guofeng, Li Xuebin, Tang Yifan, Zhao Yin, Zhou Shengyuan, Chen Xiongsheng, Jia Lianshun.
The role of autophagy in ossification of the human ligamentum
flavum
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(8): 1174-1181.
|
| [4] |
Qiu Xiaoyang, Wang Yuanyuan, Liu Chunpeng, Chen Hongcai, Wu Xuan, Zhan Xiaofen.
Application of environment-friendly bio-tissue sample
preparation kit in fluorescence in situ hybridization detection of HER2 protein 2-positive invasive breast cancer
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(16): 2572-2577.
|
| [5] |
Song Xudong, He Yunwu, Li Yonglin, Chen Jing, Hu Junlan.
Ultrasound-guided paravertebral nerve block for
zoster-associated pain: a Meta-analysis
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(11): 1797-1804.
|
| [6] |
Han Mingli, Lü Pengwei, Qian Xueke, Yang Xue, Yang Yunqing, Gu Yuanting.
MicroRNA-10b regulates aldehyde dehydrogenase 1 mRNA and protein expression in breast cancer MCF-7 cell line
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(9): 1349-1353.
|
| [7] |
Zhong Qiusheng1, Xia Weichao1, Guo Meizhen1, Zhu Haiqing1, Zhong Cuiqiong1, Shao Jieqi1, He Xiaohong2, Chen Xiumin2.
Sandwiched Moxibustion plus Bushen Quhan recipe for treating knee osteoarthritis: a randomized controlled trial
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(35): 5670-5675.
|
| [8] |
Lin Min, Wei Weili, He Yimi, Chen Zhikui.
Construction of a gene-loaded multifunctional polymer microbubble targeting breast cancer cells
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(34): 5468-5472.
|
| [9] |
Xiong Fei1, Wei Yishan2.
Reduction for developmental dysplasia of the hip in rabbits: expression levels of Caspase-3 and Bcl-2 in acetabular chondrocytes
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(31): 4974-4978.
|
| [10] |
Li Xianan, Tian Shaoqi, Wang Yuanhe, Liu Jiangjun, Ding Tao, Chu Guoqing, Sun Kang.
Hydrogen sulfide protects articular cartilage in rabbit models of knee osteoarthritis
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(31): 4992-4997.
|
| [11] |
Fan Chaoqun1, Xu Kai2, Nie Mingjian1, Xu Wenfeng1, Wang Mei1.
Evaluation of the cardiopulmonary endurance: cardiopulmonary exercise test versus 6-minute two-step test
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(23): 3686-3691.
|
| [12] |
Yang Na1, Bao Pingping2, Lei Tao2.
Adiponectin levels in plasma and periodontal tissue of mouse models of diabetic periodontitis treated by adiponectin
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(23): 3692-3697.
|
| [13] |
Ding Huan1, Chen Lihong1, Chen Yujing1, Yue Rongzhao1, Yang Min1, Xu Guihua2 .
Efficacy of different scraping protocols in the intervention of rat models of lumbar disc herniation based on urine metabolomics
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(23): 3654-3659.
|
| [14] |
Xu Qing, Fang Haolin, Liu Yang, Zhang Cunxin, Tian Baofang.
Proanthocyanidins inhibit high glucose-induced apoptosis in nucleus pulposus cells in a rabbit
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(21): 3426-3431.
|
| [15] |
Li Xiaoju, Song Guangbao, Yang Jianzhen, Wei Bo, Wu Bin.
Effect of concentrated growth factors on proliferation and differentiation of human gingival fibroblasts
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(21): 3342-3348.
|