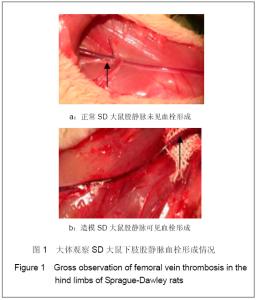
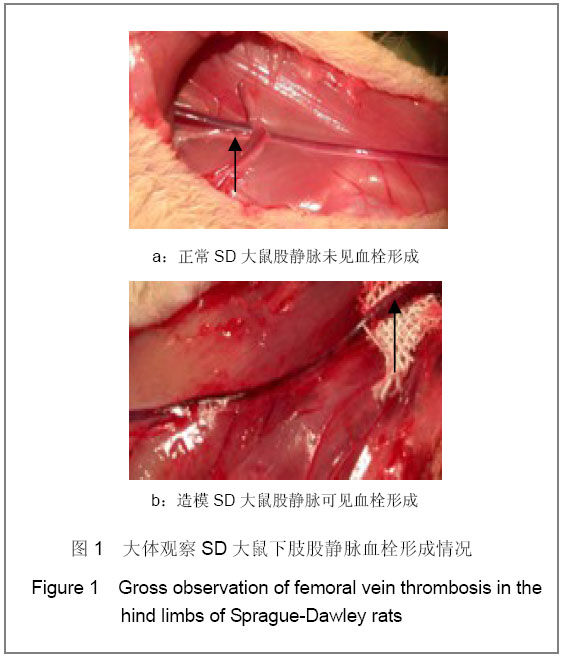
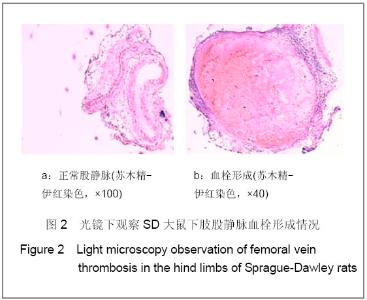
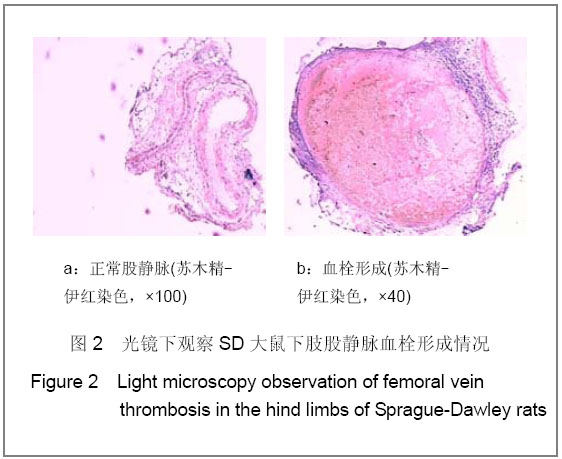
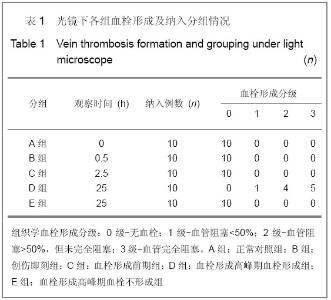
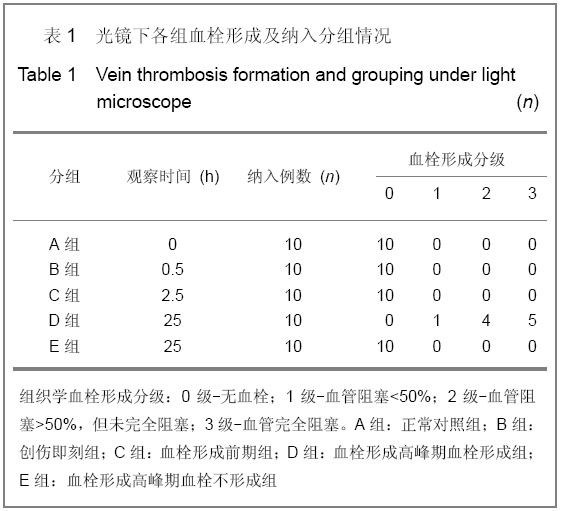
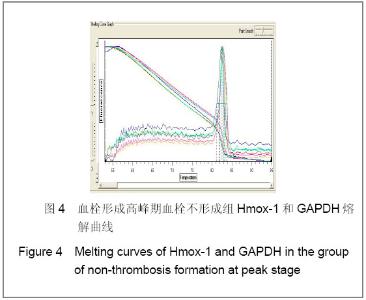
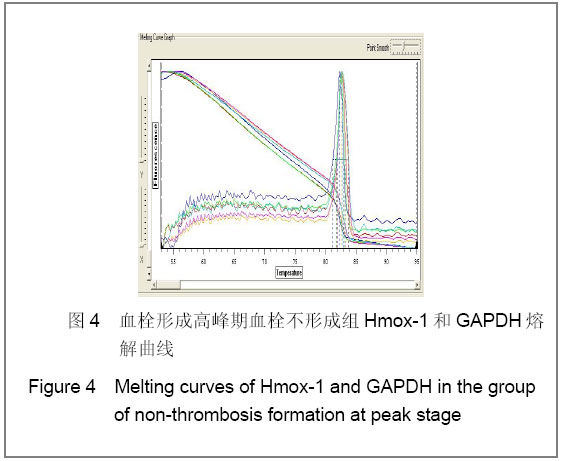
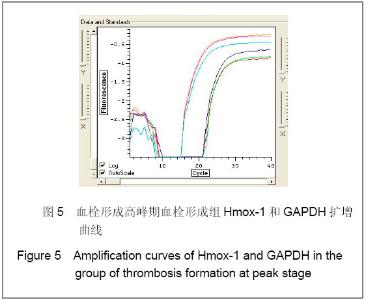
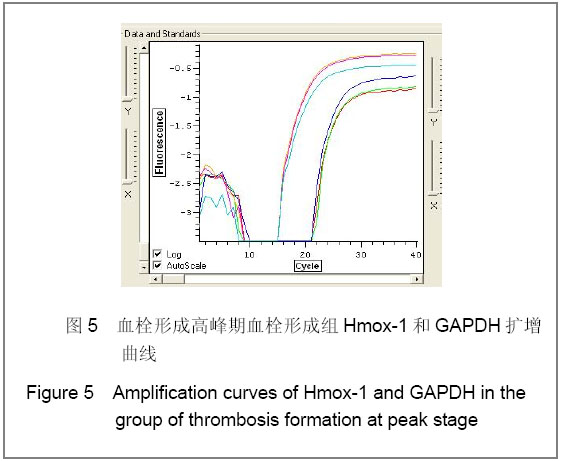
| [1] Knudson MM, Ikossi DG, Khaw L,et al. Thromboembolism after trauma: an analysis of 1602 episodes from the American College of Surgeons National Trauma Data Bank. Ann Surg. 2004;240(3):490-496. [2] Yao LQ,Ning Y,Zhao XL,et al.Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2011;15(11) :2074-2078.姚黎清,宁亚,赵学凌,等. 创伤性深静脉血栓模型大鼠组织蛋白酶B,C 基因对血管内皮细胞的作用[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2011,15(11):2074-2078.[3] Chinese Orthopaedic Association. Zhongguo Jiaoxing Waike Zazhi. 2009;17(2):118-119.中华医学会骨科学分会.预防骨科大手术深静脉血栓形成指南[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2009,17(2):118-119.[4] Cina G, Marra R, Cotroneo AR,et al. Treatment of deep vein thrombosis. Rays. 1996;21(3):397-416. [5] Qiu GX,Dai KR,Yang QM,et al. Zhonghua Guke Zazhi. 2005; 25(10):636-640.邱贵兴,戴尅戎,杨庆铭,等. 预防骨科大手术后深静脉血栓形成的专家建议--深静脉血栓形成预防座谈会纪要[J]. 中华骨科杂志, 2005, 25(10):636-640.[6] Qu HX,Liu YP. Zhongguo Jiaoxing Waike Zazhi. 2009;17(2): 110-112.曲洪雪,刘云鹏. 骨科深静脉血栓形成危险因素及发病机制的研究进展[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2009,17(2):110-112.[7] Woulfe DS. Akt signaling in platelets and thrombosis. Expert Rev Hematol. 2010;3(1):81-91. [8] Deshane J, Wright M, Agarwal A. Heme oxygenase-1 expression in disease states. Acta Biochim Pol. 2005;52(2): 273-284. [9] Hoshino T, Okamoto M, Takei S,et al. Redox-regulated mechanisms in asthma. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2008;10(4): 769-783.[10] Yamada N, Yamaya M, Okinaga S,et al. Microsatellite polymorphism in the heme oxygenase-1 gene promoter is associated with susceptibility to emphysema. Am J Hum Genet. 2000;66(1):187-195.[11] Dulak J, Deshane J, Jozkowicz A,et al. Heme oxygenase-1 and carbon monoxide in vascular pathobiology: focus on angiogenesis. Circulation. 2008;117(2):231-241. |