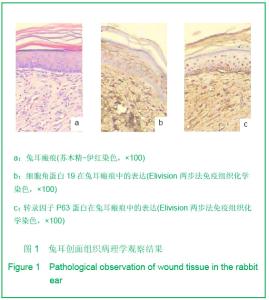
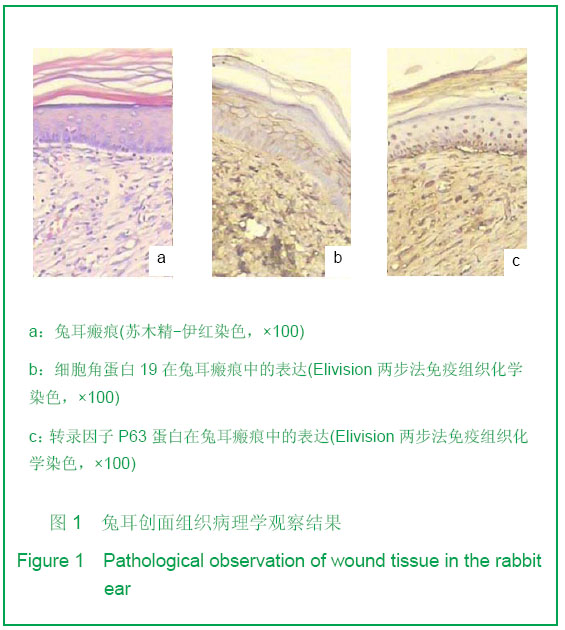
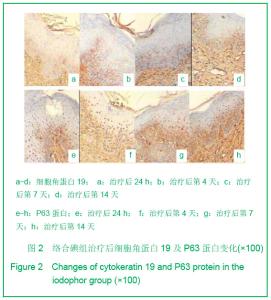
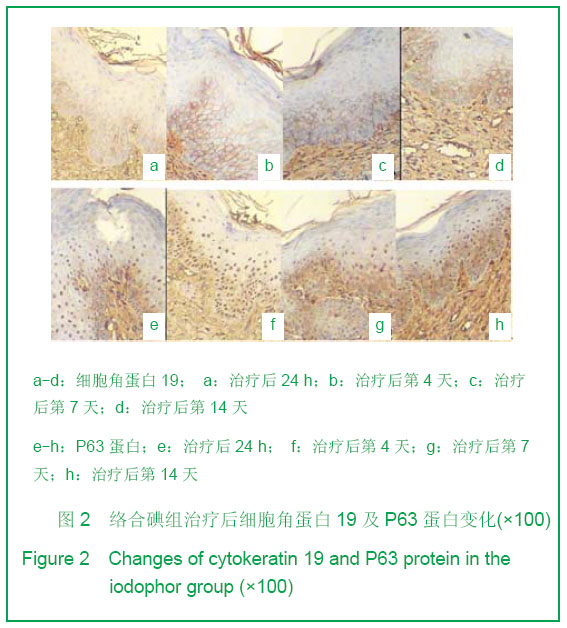
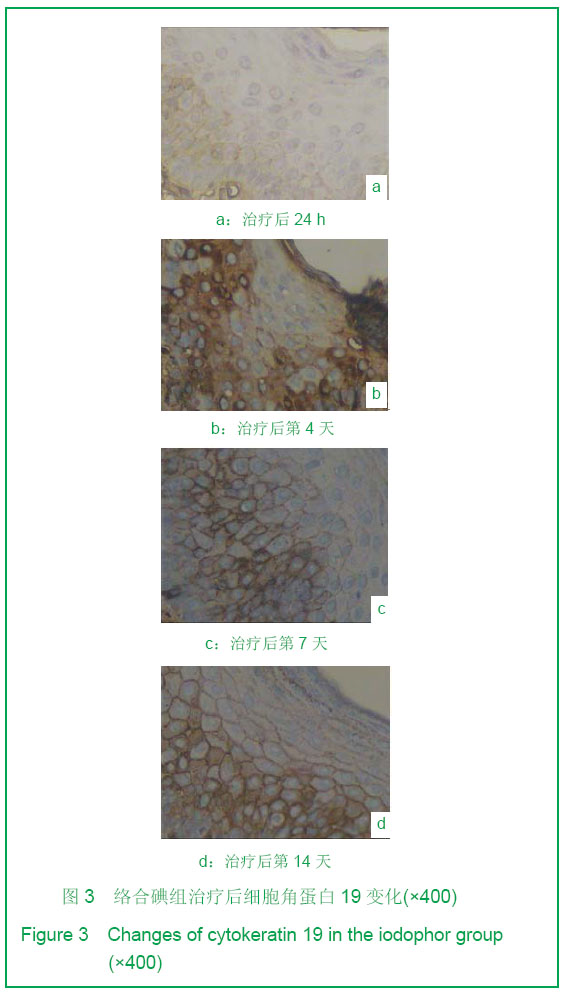
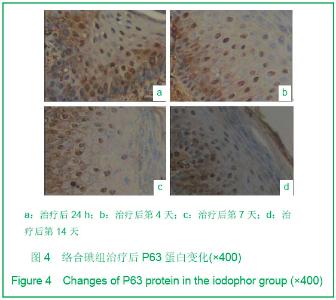
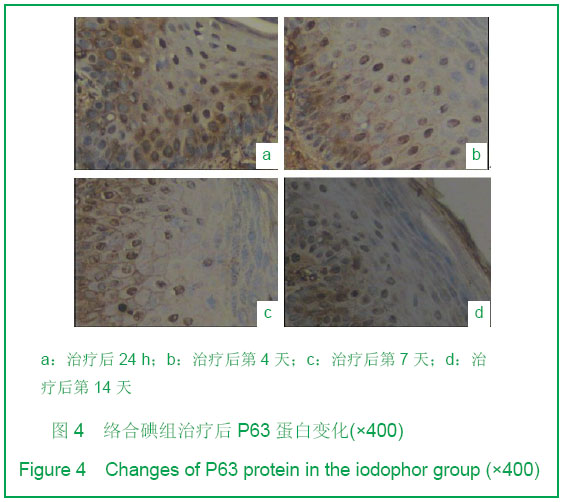
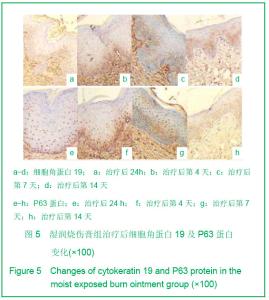
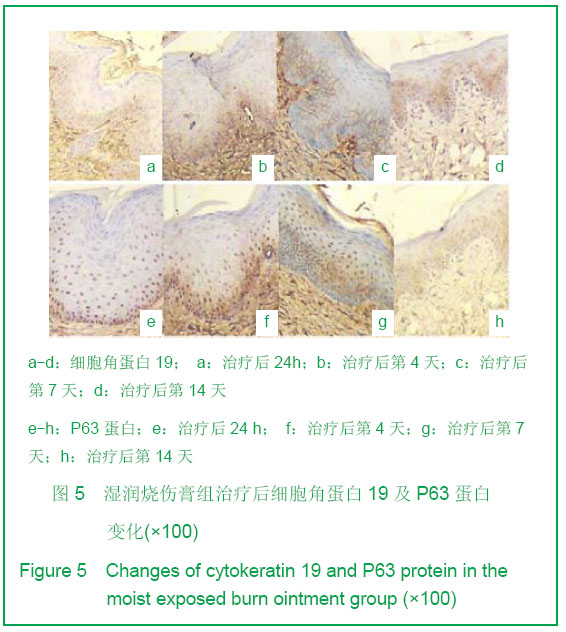
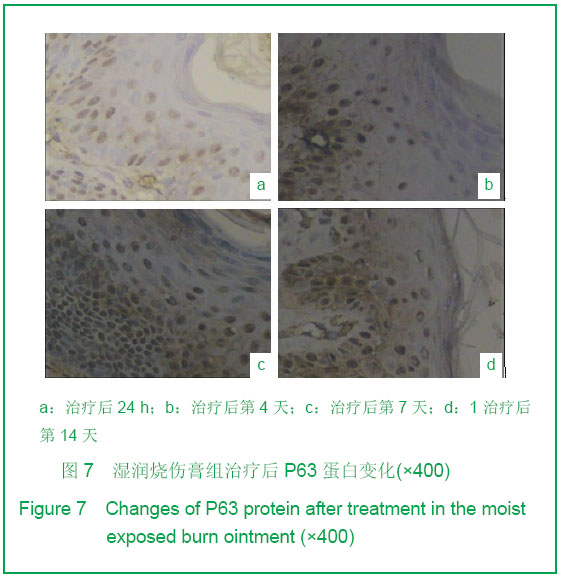
| [1] Tan J,Li GF.Zhongguo Shaoshang Chuangyang Zazhi. 2008; 20(1):30-32.谭军,李高峰.激光创面修复[J].中国烧伤疮疡杂志,2008,20(1): 30-32.[2] Tan J,Li B.Zhonghua Sunshang yu Xiufu Zazhi. 2010;5(5): 578-582.谭军,李波.点阵二氧化碳激光治疗各类瘢痕的疗效评价[J].中华损伤与修复杂志,2010,5(5):578-582.[3] Tan J,Li GF,Wu DH,et al.Zhongguo Meirong Yixue. 2008; 17(10):1508-1509.谭军,李高峰,吴东辉,等.点阵激光治疗面颈部浅表性瘢痕疗效观察[J].中国美容医学.2008,17(10):1508-1509.[4] Jiang YN.Zhongguo Shaoshang Chuangyang Zazhi. 2006;18(2):30-32.蒋友宁.MEBO在皮肤磨削术中的临床应用[J].中国烧伤疮疡杂志, 2006,18(2):30-32.[5] Chen DL,Pang XG.Zhongguo Meirong Yixue. 2005;14(5): 644-646.陈东来,庞晓纲.表皮干细胞的生物学特性与临床应用研究进展[J].中国美容医学,2005,14(5):644-646.[6] Morris DE,Wu L,Zhao LL,et al. Acute and chronic animal models for excessive dermal scarring :quantitative studies. Plast Reconstr Surg.1997; 100 :674-681.[7] Li HY,Liu JB,Xia W,et al.Zhonghua Zhengxing Waike Zazhi. 2001; 17:276-278.李荟元,刘建波,夏炜,等.增生性瘢痕动物实验模型的建立和应用[J].中华整形外科杂志,2001,17:276-278.[8] Zhang G,Tan J,Li GF.Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2007,11(9):1727-1729.张刚,谭军,李高峰.激光治疗瘢痕的特征[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2007,11(9):1727-1729.[9] Xu F,Li F,Li DT.Zhongguo Jiguang Yixue. 2008;17(6):434-437.徐芳,李大铁.激光治疗病理性瘢痕的进展[J].中国激光医学. 2008, 17(6):434-437.[10] Jiang DY,Fu XB,Chen W,et al.Zhonghua Zhengxing Waike Zazhi. 2004;20(2):128-131.姜笃银,付小兵,陈伟,等.血管生成因子及其受体过表达遭到瘢痕疙瘩侵袭性生长[J].中华整形外科杂志,2004,20(2):128-131.[11] Nouri K, Elsaie ML, Vejjabhinanta V, et al. Comparison of the effects of short-and long-pulse durations when using a 585-nm pulsed dye laser in the treatment of new surgical scars.Lasers Med Sci.2010,25:121-126.[12] Fu XB,Sun XQ.Zhonghua Chuang Zazhi. 2001;17(6): 338-340.付小兵,孙晓庆.瘢痕组织中汗腺的分布特征以及瘢痕对汗腺再生影响的实验研究[J].中华创伤杂志.2001,17(6):338-340.[13] Xie JL,Li TZ,Qi SH,et al.Zhonghua Shaoshang Zazhi. 2003; 19(6):344-346.谢举临,利天增,祁少海,等.烫伤大鼠不同深度创面组织中表皮干细胞分布的初步研究[J].中华烧伤杂志,2003,19(6):344-346.[14] Zhou PX,Luo CQ,Gu YH,et al.Zhongguo Yishi Zazhi. 2003; 5(9):1180-1182.周鹏翔,罗成群,谷永红,等.角蛋白19在Ⅲ度烧伤创面修复过程中的表达及意义[J].中国医师杂志,2003,5(9):1180-1182.[15] Cotsarelis G, Kaur P, Dhouailly D,et al. Epithelial stem cells in the skin : definition, markers, localization and functions .Exp Dermatol.1999;8(1):80-88.[16] Sun XY,Fu XB.Ganran Yanzheng Xiufu. 2008;9(1):52-54.孙晓艳,付小兵.表皮干细胞的研究进展[J].感染、炎症、修复. 2008,9(1):52-54.[17] Alonsoh L,Fuchs E.Stem cells of the skin epithelium.Proc.Natl Acad Sci USA.2003;100(Suppl);19830-19835.[18] Oshima H,Rochat A,Kednia C.et al.Morphogenesis and renewal of hair follicles from adult multipotent stem cells. Cell.2001;104:233-245.[19] Michel M, Torok N,Godbout MJ,et al.Keratin 19 as a biochemical marker of skin stem cells in vivo and in vitro:Keratin 19 expressing cells are differential 2ly localized in function of anatomic sites,and their number varies with donor age and culture stage.J Cell Science.1996; 109(5): 1017.[20] Si SY,Zhang JZ.Shijie Huaren Xiaohua Zazhi. 2003;11(5): 606-609.司少艳,张建中.P63基因研究进展[J].世界华人消化杂志,2003,11(5):606-609.[21] Slack J.Stem cell in epithelial tissues. Science.2000;287 (5457): 1431-1433[22] Yang J,Hui J.Zhongguo Shaoshang Chuangyang Zazhi. 2008; 20(4):314-316.杨军,惠捷.MEBO与红霉素眼膏治疗CO2激光创面的疗效分析[J].中国烧伤创疡杂志,2008,20(4):314-316. [23] Zou BS,Tan J,Wu DH,et al.Zhongguo Shaoshang Chuangyang Zazhi. 2009;21(2):150-152.邹勃生,谭军,吴东辉,等.湿润烧伤膏在面部微小凹陷瘢痕激光修复中的作用[J].中国烧伤疮疡杂志,2009,21(2):150-152.[24] Sasaki GH, Travis HM, Tucker B. Fractional CO2 laser resurfacing of photoaged facial and non-facial skin: Histologic and clinical results and side effects. Journal of Cosmetic and Laser Therapy. 2009; 11: 190–201.[25] Cho SB, Lee SJ, Kang JM, et al.The Efficacy and Safety of 10,600-nm Carbon Dioxide Fractional Laser for Acne Scars in Asian Patients. Dermatol Surg.2009;35:1955-1961.[26] Jordan P,Farkas,MD,James A,et al.TUNEL Assay to characterize acute histopathological injury following treatment with the Active and Deep FX Fractional short-pulse CO2 devices. Aesthetic Surgery.2011;31(4):603-613.[27] Zhao ZL,Fu XB,Sun TZ.Ganran Yanzheng Xiufu. 2002;3(4): 229-231.赵志力,付小兵,孙同柱.成人正常皮肤和瘢痕组织表皮干细胞定位与表达特征的比较研究[J].感染、炎症、修复,2002;3(4): 229-231.[28] Yang JH, Shim SW, Lee BY, et al. Skin-Derived Stem Cells in Human Scar Tissues: A Novel Isolation and Proliferation Technique and Their Differentiation Potential to Neurogenic Progenitor Cells. Tissue Engineering Part C: Methods. August. 2010;16(4): 619-629. |