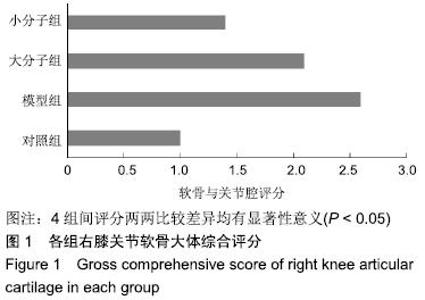
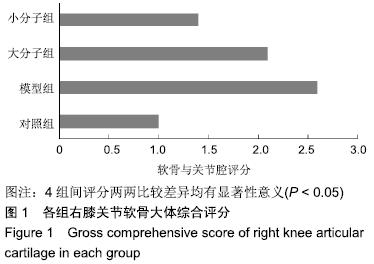
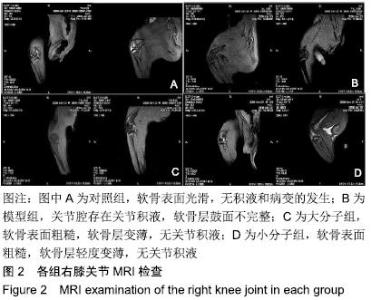
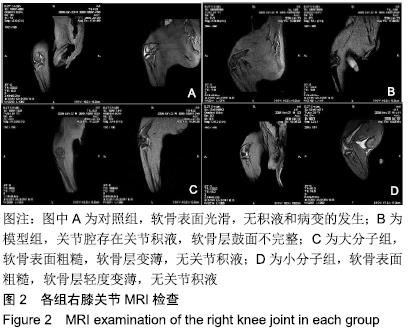
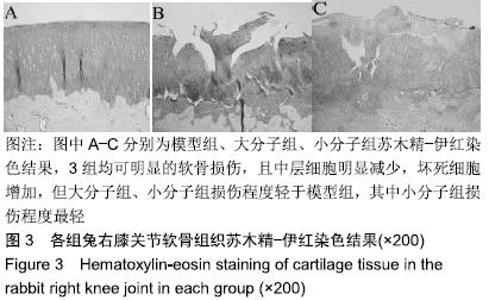
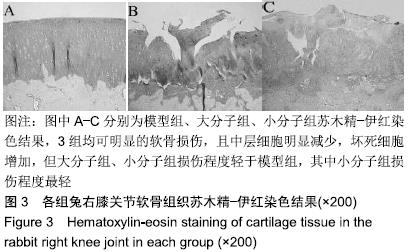
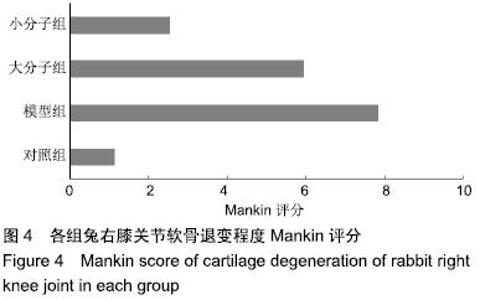
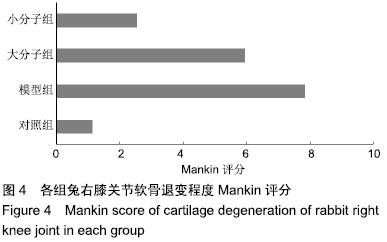
[1] 于力,冯永莉,于倩.玻璃酸钠治疗类风湿关节炎的临床观察及护理[J].现代生物医学进展,2013,7(13):1356-1357.
[2] 冯振伟,项新,黄典胜,等.玻璃酸钠联合曲安奈德关节腔内注射治疗西骨性关节炎的疗效观察[J].中国当代医药,2011,18(35):58-60.
[3] HENROTIN Y. Significant reduction of the Serum Levels of a Specific Biomarker of Cartilage Degradation (Coll2-1) following Viscosupplementation Compared to saline solution in patients with Knee Osteoarthritis:.Ekonomisk Tidskrift.2015;151(5): 108-126.
[4] LI NG, TANG YP, DUAN JA, et al.Matrix metalloproteinase inhibitors: a patent review (2011-2013). Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2014;24(9): 1039-1052.
[5] 张董喆.自拟外洗方结合玻璃酸钠注射治疗膝关节骨性关节炎效果[J].中国老年学杂志,2016,36(5):1226-1227.
[6] KRISTENSEN LE, KAPETANOVIC MC, GULFE A, et al. Predictors of response to anti-TNF therapy according to ACR and EULAR criteria in patients with established RA: results from the South Swedish Arthritis Treatment Group Register. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2008; 47(4):495-499.
[7] 李慧敏,黄俐敏,刁连娣,等.石蜡疗法配合玻璃酸钠治疗膝骨性关节炎的临床观察及护理[J].护理研究,2011,25(1):222-223.
[8] KATAOKA Y, ARIYOSHI W, OKINAGA T, et al.Mechanisms involved in suppression of ADAMTS4 expression in synoviocytes by high molecular weight hyaluronic acid.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013;432(4):580-585.
[9] BANNURU RR, NATOV NS, OBADAN IE, et al.Therapeutic trajectory of hyaluronic acid versus corticosteroids in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis: a systematic review and meta analysis.Arthritis Rheum.2009;61(12):1704-1711.
[10] MATHIEU P, CONROZIER T, VIGNON E, et al.Rheologic behavior of osteoarthritic synovial fluid after addition of hyaluronic acid:a pilot study.Clin Orthop Relat Res.2009;467(11):3002.
[11] 龚俊华,王怀举,宋德明,等.药物联合治疗膝关节骨性关节炎对患者膝关节液IL-1β、TNF-α及MMP-3水平的影响[J].临床合理用药杂志, 2015,8(12A):72-73.
[12] 何启荣,林伟文.关节液中TNF-α、IL-1、MMPS水平对膝骨性关节炎患者的预后的评估价值[J].中国医学创新,2016,13(21):1-4.
[13] 刘爱峰,裴开源,王平,等.玻璃酸钠注射液与生理盐水对照对于膝骨性关节炎临床疗效的Meta分析[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2016,24(17): 1581-1586.
[14] 路明珠,陆文铨,伊佳.不同分子量构成的玻璃酸钠对骨关节炎治疗作用的实验研究[J].药学实践杂志,2010,1,28(1):19-22.
[15] 周悦.益肾壮骨汤经验方内服、推拿联合玻璃酸钠膝关节注射治疗退行性膝骨关节炎患者的临床效果[J].医疗装备,2016,29(19):13-15.
[16] 李彦林,王国梁,曹斌,等.玻璃酸钠与膝骨关节炎患者关节液中基质细胞衍生因子1和基质金属蛋白酶3,9,13水平的相关性[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(7):1323-1326.
[17] 麻圣达,卢雄,罗利飞.玻璃酸钠对膝骨性关节炎患者关节液中基质金属蛋白酶-3、9水平的影响及疗效观察[J].中国现代医生, 2014,52(1): 42-44.
[18] HULMES DJ, MARSDEN ME, STRACHAN RK, et al. Intra-articular hyaluronate in experimental rabbit osteoarthritis can prevent changes in cartilage proteoglycan content.Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2004;12(3):232-238.
[19] MARTIN LS, MASSAFRA U, BIZZI E, et al.A double blind randomized active-controlled clinical trial on the intra-articular use of Md-Knee versus sodium hyaluronate in patients with knee osteoarthritis ("Joint").BMC Musculoskelet Disord.2016;17:94.
[20] 姚传龙,刘伟恒,黄其满,等.阳和汤联合医用三氧对膝骨性关节炎患者关节滑液MMP-3/TIMP-1的影响[J].中国实用医药,2016,11(27): 227-229.
[21] BANNURU RR, BRODIE CR, SULLIVAN MC, et al.Safety of Repeated Injections of Sodium Hyaluronate (SUPARTZ) for Knee Osteoarthritis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cartilage. 2016;7(4):322.
[22] 康建华,查振刚,陈仲新,等.不同分子量的透明质酸钠治疗膝骨性关节炎的疗效分析[J].实用医学杂志, 2007,23(16):2593-2595.
[23] ZHANG H, ZHANG K, ZHANG X, et al.Comparison of two hyaluronic acid formulations for safety and efficacy (CHASE) study in knee osteoarthritis: a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, 26-week non-inferiority trial comparing Durolane to Artz.Arthritis Res Ther. 2015;17:51.
[24] 孟涛,苏晨.玻璃酸钠联合臭氧治疗膝关节骨性关节炎的近期临床疗效观察[J].重庆医学,2018, 47(24):66-69.
[25] ZHANG W, WANG S, ZHANG R, et al.Evidence of Chinese herbal medicine Duhuo Jisheng decoction for knee osteoarthritis: a systematic review of randomised clinical trials.BMJ Open. 2016; 6(1):e008973.
[26] ABATE M, PELOTTI P, DE AMICIS D,et al.Viscosupplementation with Hyaluronic Acid in Hip Osteoarthritis(a review).Ups J Med Sci. 2008;113(3):261-278.
[27] MOLDEZ MA, CAMONES VR, RAMOS GE, et al.Effectiveness of Intra-Articular Injections of Sodium Hyaluronate or Corticosteroids for Intracapsular Temporomandibular Disorders: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.J Oral Facial Pain Headache.2018;32(1):53-66.
[28] CHEN R, CHEN M, SU T, et al.Heat-sensitive moxibustion in patients with osteoarthritis of the knee: a three-armed multicentre randomised active control trial.Acupunct Med.2015;33(4):262-269.
[29] 赵森.玻璃酸钠注射法与臭氧联合使用治疗膝关节骨性关节炎的疗效观察[J].世界最新医学信息文摘(电子版),2018,18(55):152-152.
[30] 陆斌,李建武,杨艳,等.臭氧联合玻璃酸钠对膝关节骨性关节炎患者膝关节功能及疼痛症状的改善效果观察[J].临床和实验医学杂志, 2018, 17(11):70-73.
|