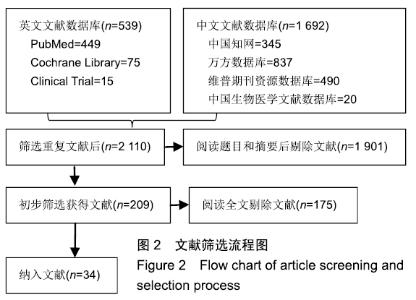
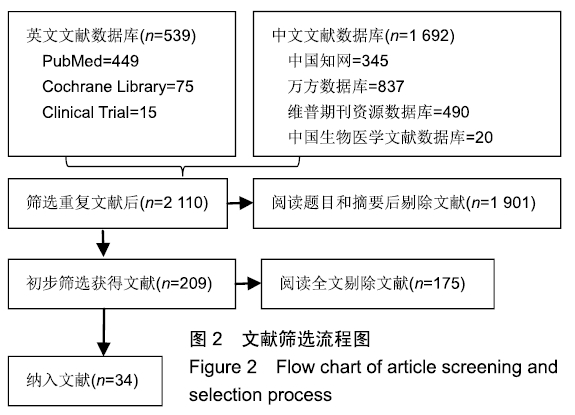
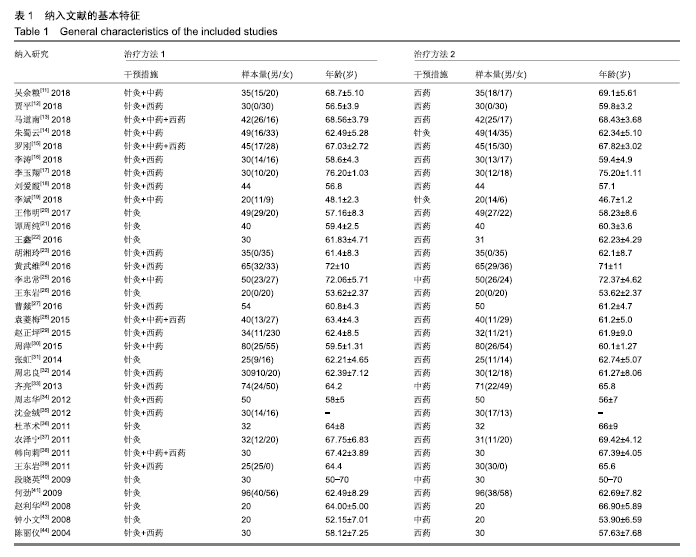
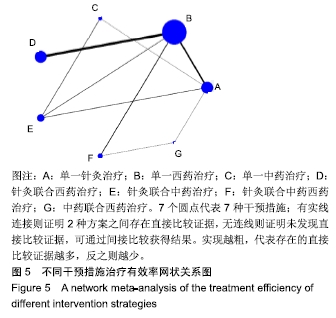
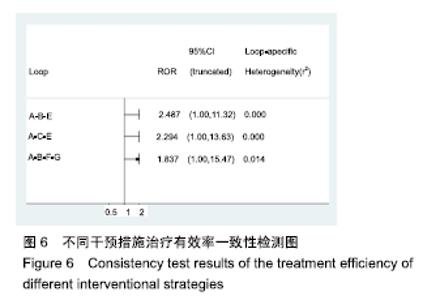
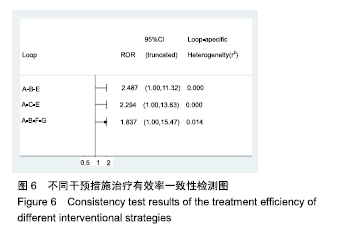
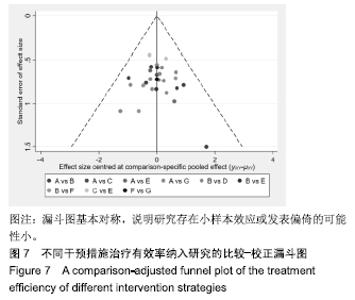
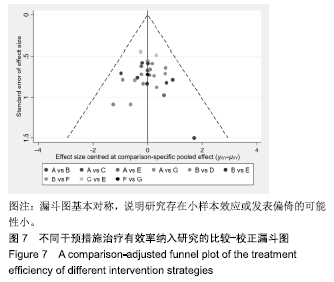
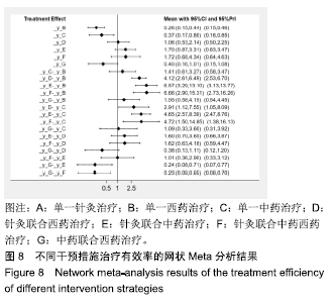
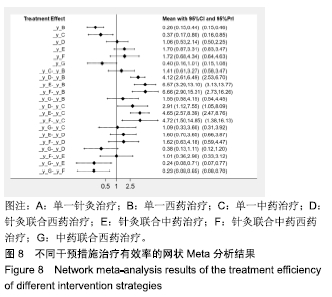
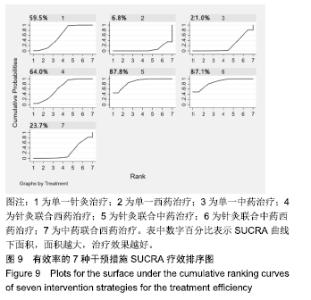
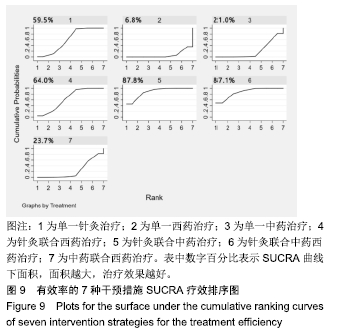
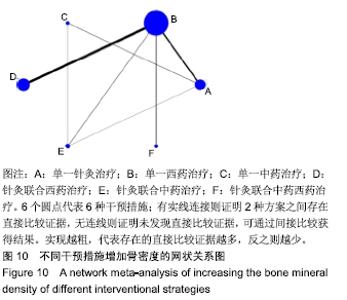
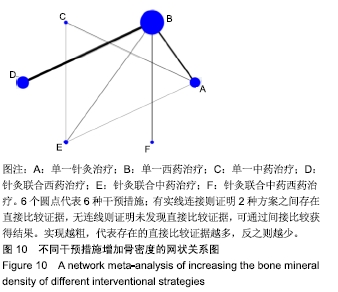
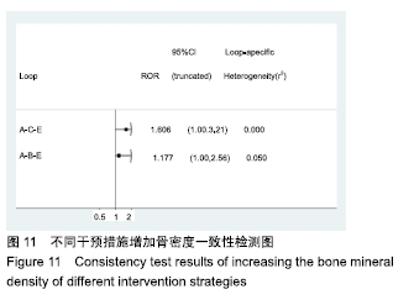
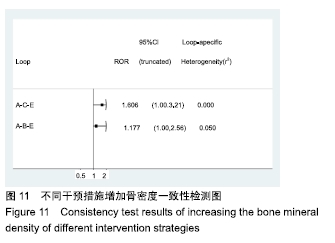
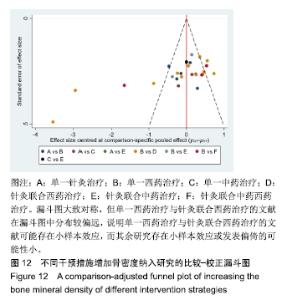
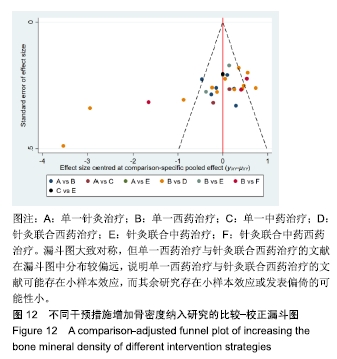
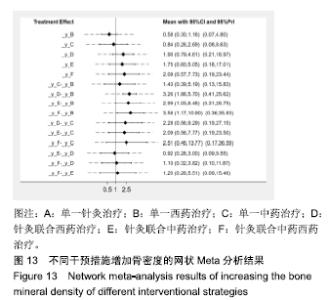
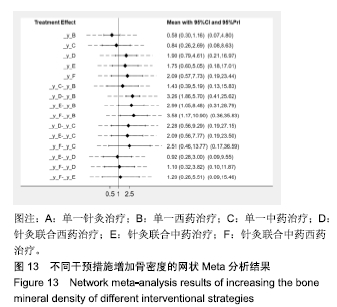
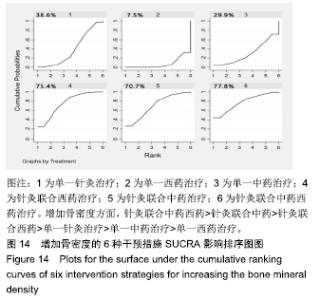
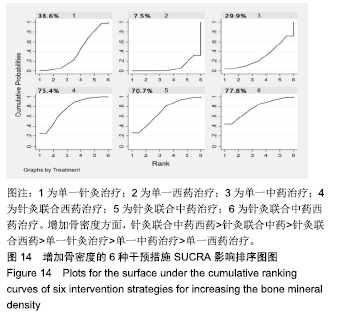
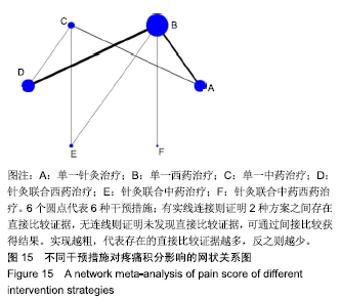
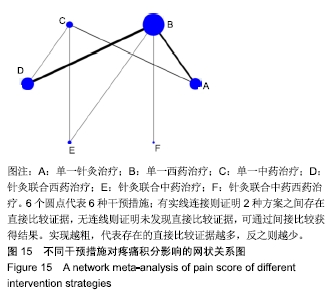
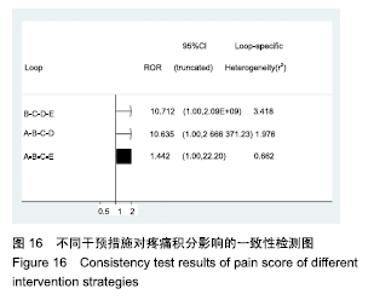
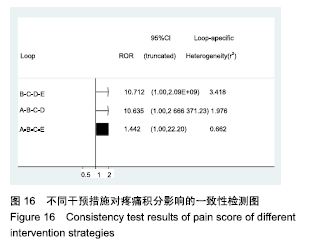
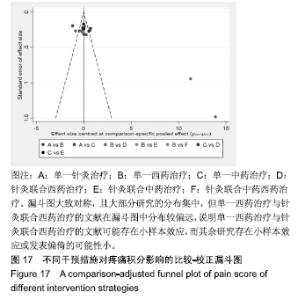
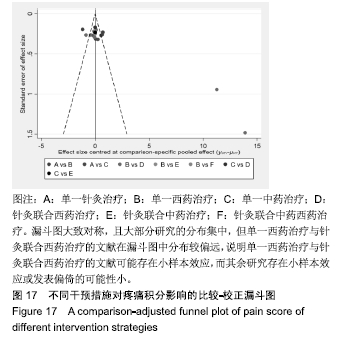
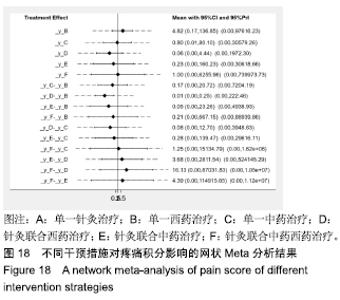
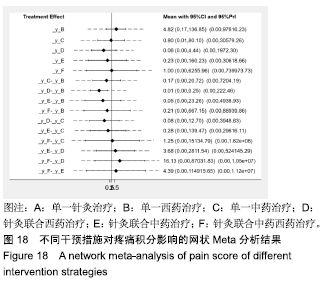
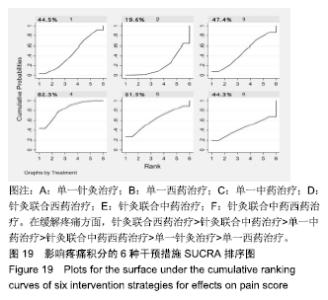
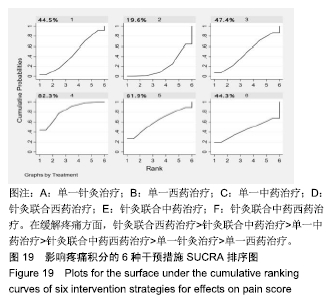
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (2): 320-328.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1919
Acupuncture combined with other therapies for osteoporosis: a network meta-analysis
Cen Zhuohao, Chen Jiena, Huang Jiahua, Shi Chushuo, Zhou Chi, Wen Junmao, Ling Min
- Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510405, Guangdong Province, China
-
Received:2019-03-28Revised:2019-04-03Accepted:2019-04-30Online:2020-01-18Published:2019-12-25 -
Contact:Ling Min, Associate professor, Master’s supervisor, Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510405, Guangdong Province, China -
About author:Cen Zhuohao, Master, Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510405, Guangdong Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81373655; the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province, No. 2015A030310203; the High-Level University Construction Project of Guangdong Province, No. A1-AFD018171Z11057
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Cen Zhuohao, Chen Jiena, Huang Jiahua, Shi Chushuo, Zhou Chi, Wen Junmao, Ling Min. Acupuncture combined with other therapies for osteoporosis: a network meta-analysis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(2): 320-328.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
| [1] 刘忠厚.骨矿与临床[M].北京:中国科学技术出版社,2006:1. [2] 中国老年学学会骨质疏松委员会.中国人群骨质疏松症防治手册2010版[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2010,16(增刊1):153. [3] EISMAN JA. Genetics of osteoporosis. Endocr Rev.1999;20(6):788. [4] ALBAYRAK I, AYDOGMUS M, OZERBIL OM, et al. The association between bone mineral density, quality of life, quality of sleep and fatigue. Acta Clin Belg.2016;71(2):92. [5] 全国卫生专业技术资格考试专家委员会.康复医学与治疗技术[M].北京:人民卫生出版社,2008:282-286. [6] 刘忠厚.中国人原发性骨质疏松症诊断标准(试行)[J].中国骨质疏松杂志, 1999,5(1):4. [7] 中国老年学学会骨质疏松委员会骨质疏松诊断标准学科组.中国人骨质疏松症建议诊断标准(第二稿)[Z].中国厦门:20007. [8] 张智海,刘忠厚,李娜,等.中国人骨质疏松症诊断标准专家共识(第三稿•2014版)[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2014,20(9):1007. [9] 原发性骨质疏松症诊治指南(2011年)[J].中华骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病杂志,2011;4(01):2. [10] 章振林,金小岚,夏维波.原发性骨质疏松症诊疗指南(2017版)要点解读[J]. 中华骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病杂志,2017,10(5):411. [11] 吴余粮,谢少龙.补肾化瘀汤加减结合针灸治疗骨质疏松症腰背痛的效果评价[J]. 医临床研究,2018,10(10):34. [12] 贾平.激素替代疗法联合针灸治疗绝经期骨质疏松的效果分析[J].医学理论与实践,2018,31(19):2927. [13] 马道南,范远俊.联用中药内服和针灸疗法治疗骨质疏松症的效果研究[J].当代医药论丛,2018,16(7):58. [14] 朱蜀云,马素英. 藤黄健骨胶囊联合温针灸治疗原发性骨质疏松症的临床研究[J]. 中国中医骨伤科杂志,2018,26(1):29. [15] 罗刚. 温肾通络化瘀汤联合针灸对老年骨质疏松症伴腰背痛患者骨代谢、骨密度及临床症状的影响[J]. 四川中医, 2018,36(12):130. [16] 李涛,雷静,李秋梅,等. 针药配合治疗宁夏地区骨质疏松症的临床研究[J]. 云南中医中药杂志,2018,39(11):55. [17] 李玉翔. 针刺联合骨质疏松治疗仪治疗老年性骨质疏松症的临床疗效观察[D].福州:福建中医药大学,2018. [18] 刘爱霞,席君. 针刺夹脊穴配合督脉隔姜灸治疗绝经后骨质疏松症的临床疗效分析[J]. 智慧健康,2018,4(5):158. [19] 李斌.针灸联合独活寄生汤治疗骨质疏松症的效果研究[J].健康周刊, 2018(17):1. [20] 王伟明. 针灸调补脾胃法治疗骨质疏松腰痛症49例疗效观察[J]. 内蒙古中医药,2017,36(2):124. [21] 谭周纯. 针刺治疗绝经后骨质疏松症40例临床观察[J].中医临床研究, 2016,8(14):16. [22] 王鑫.电针治疗肝肾不足型绝经后骨质疏松症的临床观察[D]. 福州:福建中医药大学,2016. [23] 胡湘玲.针刺对绝经后骨质疏松患者骨密度及血清雌二醇的影响[J]. 湖南中医杂志,2016,32(11):86. [24] 黄武维,杨琳.补肾健脾针刺法治疗老年原发性骨质疏松的临床效果研究[J].山西医药杂志,2016,45(16):1888. [25] 李忠常.自拟骨愈汤联合电针穴位刺激治疗老年性骨质疏松症继发疼痛临床研究[J].四川中医,2016,34(11):117. [26] 林红晓,王东岩. 中西医结合治疗绝经后骨质疏松的疗效观察[J].吉林医学,2016,37(07):1614. [27] 杨丰铭,曹燚.西药结合针灸治疗原发性骨质疏松症的临床疗效[J].医药前沿,2016,6(16):166. [28] 袁菱梅,李艳明,陈丽妹,等. 电针结合加味身痛逐瘀汤治疗原发性骨质疏松症40例[J].针灸临床杂志,2015,31(8):12. [29] 赵正坪,陈小玲,石化明. 西药配合针灸疗法治疗原发性骨质疏松症的临床疗效[J].临床合理用药杂志,2015,8(24):135. [30] 周萍,胡红,郭明军,等. 补肾壮骨汤联合针灸及阿仑膦酸钠治疗骨质疏松症的临床研究[J].实用医学杂志,2015,31(22):3663. [31] 张虹.电针治疗原发性骨质疏松症的临床研究[D].武汉:湖北中医药大学, 2014. [32] 周忠良,杨永晖,郑保主,等. 温针灸特定穴联合药物治疗原发性骨质疏松的临床研究[J].中医药临床杂志,2014,26(2):156. [33] 齐亮,文利,罗文轩. 温针灸结合中药内服治疗原发性骨质疏松症74例临床研究[J].江苏中医药,2013,45(5):56. [34] 周志华,王乃权,潘芳芳,等. 针药并用治疗绝经后骨质疏松症临床观察[J].上海针灸杂志,2012,31(6):389. [35] 沈金绒. 固本培元针刺法配合药物治疗原发性骨质疏松症腰背部疼痛的临床研究[D]. 武汉:湖北中医药大学,2012. [36] 杜革术. 针刺对绝经后骨质疏松患者骨密度及血清雌二醇的影响[J].上海针灸杂志,2011,30(2):104. [37] 农泽宁,赵利华,韦良玉,等. 补肝肾健脾温针灸法防治原发性骨质疏松症及骨量减少的临床研究[J].辽宁中医杂志, 2011,38(8):1575. [38] 韩向莉,娄志杰,林红伍. 疏肝温肾痰瘀双解汤配合针灸治疗老年性骨质疏松症[J]. 甘肃中医,2011,24(2):32. [39] 王东岩,徐小梅,欧阳钢. 针灸对男性骨质疏松症患者骨代谢的影响[J].中医杂志,2011,52(3):211. [40] 段晓英,白雪,王明礼. 培元固本针法治疗绝经后骨质疏松症临床观察[J].中国妇幼保健,2009,24(21):2974. [41] 何劲,宋道飞,向楠. 针刺悬钟、肾俞、命门穴对原发性骨质疏松症患者骨密度的影响及疗效[J].中医杂志,2009,50(2):147. [42] 赵利华,农泽宁,钟旋,等. 温针灸对绝经后骨质疏松症患者骨密度及生化指标的影响[J].中国针灸,2008,28(12):897. [43] 钟小文. 补肾健脾针法配合阿是穴治疗绝经后骨质疏松症的临床观察[D].广州:广州中医药大学,2008. [44] 陈丽仪,郭元琦,凌楠. 温针对绝经后骨质疏松症骨密度的影响及疗效研究[J].中国针灸,2004,24(11):6. [45] COSMAN F, DE BEUR SJ, LEBOFF MS, et al. Clinician's Guide to Prevention and Treatment of Osteoporosis. Osteoporos Int.2014; 25(10):2359. [46] 原发性骨质疏松症诊疗指南(2017)[J]. 中华骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病杂志,2017,10(5):413. [47] 杨海明,汪洋,张华军.针药联合治疗原发性骨质疏松症40例临床研究[J].江苏中医药,2017,49(9):59. [48] 刘兰英,林志苇,刘宪俊,等. 脾肾俞穴位埋线对原发性骨质疏松妇女内分泌激素的调控作用[J].针灸临床杂志,2011,27(4):32. [49] 陈锦明,卢阳佳,黄泳,等.基于结缔组织探讨针刺镇痛的机制[J].现代中西医结合杂志,2010,19(3):388. [50] 孙亚奇,卞艳芳,周春娜,等.中药治疗骨质疏松症研究进展[J].中国临床医学,2018,25(2):307. |
| [1] | Zhu Chan, Han Xuke, Yao Chengjiao, Zhou Qian, Zhang Qiang, Chen Qiu. Human salivary components and osteoporosis/osteopenia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1439-1444. |
| [2] | Jing Jinpeng, Zhang Yue, Liu Xiaomin, Liu Yi. Traditional Chinese medicine injection for promoting blood circulation in prevention of deep vein thrombosis after orthopedic surgery: network meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1467-1476. |
| [3] | Jiang Huanchang, Zhang Zhaofei, Liang De, Jiang Xiaobing, Yang Xiaodong, Liu Zhixiang. Comparison of advantages between unilateral multidirectional curved and straight vertebroplasty in the treatment of thoracolumbar osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1407-1411. |
| [4] | Li Wei, Zhu Hanmin, Wang Xin, Gao Xue, Cui Jing, Liu Yuxin, Huang Shuming. Effect of Zuogui Wan on bone morphogenetic protein 2 signaling pathway in ovariectomized osteoporosis mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1173-1179. |
| [5] | Xiao Yang, Gong Liqiong, Fei Jing, Li Leiji. Effect of electroacupuncture on nerve growth factor and its receptor expression in facial nerve nucleus after facial nerve injury in rabbits [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1253-1259. |
| [6] | Xiao Hao, Liu Jing, Zhou Jun. Research progress of pulsed electromagnetic field in the treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1266-1271. |
| [7] | Zhu Chan, Han Xuke, Yao Chengjiao, Zhang Qiang, Liu Jing, Shao Ming. Acupuncture for Parkinson’s disease: an insight into the action mechanism in animal experiments [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1272-1277. |
| [8] | Gao Yujin, Peng Shuanglin, Ma Zhichao, Lu Shi, Cao Huayue, Wang Lang, Xiao Jingang. Osteogenic ability of adipose stem cells in diabetic osteoporosis mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 999-1004. |
| [9] | Peng Kun. Improvement of the treatment effect of osteoporotic fractures: research status and strategy analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 980-984. |
| [10] | Wang Nan, Qian Yuzhang, Xie Lin. Network Meta-analysis of different acupuncture methods for the treatment of lumbar disc herniation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 813-820. |
| [11] | Fan Jianchao, Xu Paidi, Han Yongli, Wen Caiyuzhu, Zhang Hongxing, Pan Xiaoli. Effects of electroacupuncture at Zusanli acupoint on visceral hypersensitivity in rats with functional dyspepsia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 663-668. |
| [12] | Dong Miaomiao, Lai Han, Li Manling, Xu Xiuhong, Luo Meng, Wang Wenhao, Zhou Guoping. Effect of electroacupuncture on expression of nucleotide binding oligomerization domain-like receptor protein 3/cysteinyl aspartate specific proteinase 1 in rats with cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 749-755. |
| [13] | Shen Song, Xu Bin. Diffuse distribution of bone cement in percutaneous vertebroplasty reduces the incidence of refracture of adjacent vertebral bodies [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 499-503. |
| [14] | Ou Liang, Kong Dezhong, Xu Daoqing, Ni Jing, Fu Xingqian, Huang Weichen. Comparative clinical efficacy of polymethyl methacrylate and self-solidifying calcium phosphate cement in vertebroplasty: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 649-656. |
| [15] | Cai Feng, Yu Bo, Zeng Duo, Chen Qincan, Liao Qi. Cortical bone trajectory in elderly patients with osteoporosis of lumbar disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(3): 403-407. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||