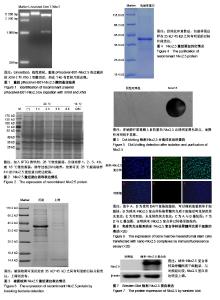
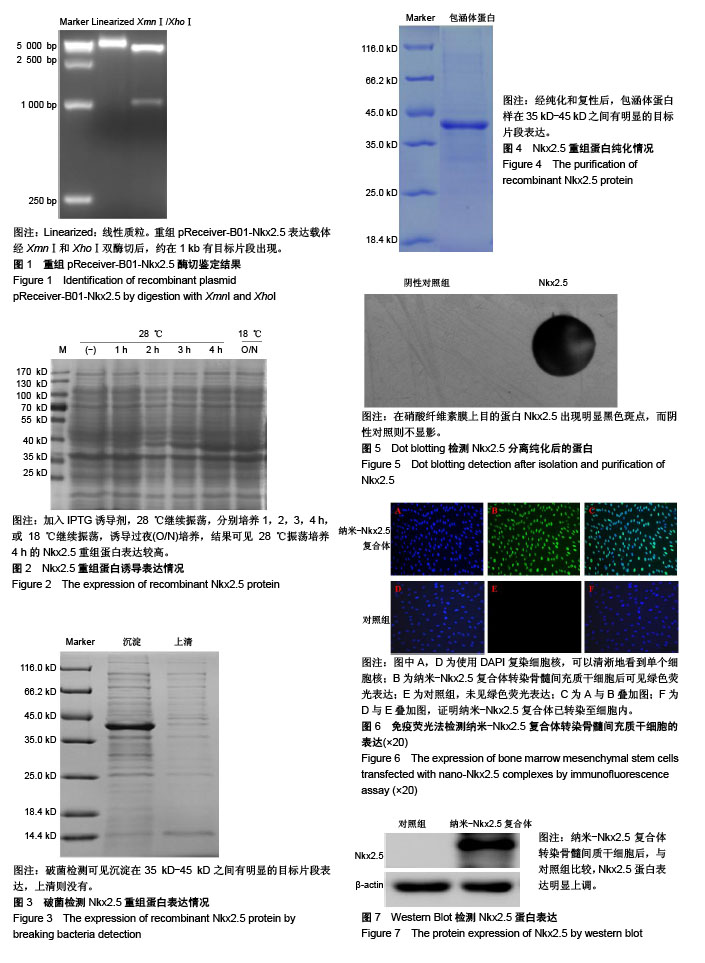
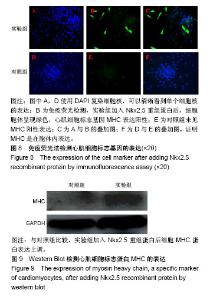
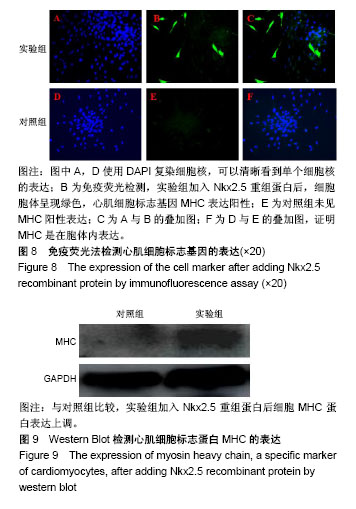
| [1] 王振华.心肌再生的研究进展[J].中国循环杂志, 2011,26(6): 480-482.[2] 蔡明清.心肌细胞再生和腔室重塑[J].中国分子心脏病学杂志, 2002,2(1):49-50.[3] Ye L, Chang YH, Xiong Q, et al. Cardiac repair in a porcine model of acute myocardial infarction with human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiovascular cells. Cell Stem Cell. 2014;15(6):750-761.[4] Cahill TJ, Choudhury RP, Riley PR. Heart regeneration and repair after myocardial infarction: translational opportunities for novel therapeutics. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2017;16(10): 699-717.[5] 杨梁,张晓刚,魏新伟.维生素C体外诱导多能干细胞向心肌细胞的分化[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2011,15(23): 4229-4232.[6] 田胜男,王博,李琦,等.诱导多能干细胞的安全性及应用研究进展[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2017,21(5):815-818.[7] 宋维文,安铁洙,王春生.microRNAs在多能干细胞向心肌细胞分化中的作用[J].中国生物化学与分子生物学报, 2015,31(3): 244-250.[8] 曾春雨.诱导多能干细胞和心脏干/祖∶细胞对心肌修复作用的研究进展[J]. 解放军医药杂志,2012,24(7):1-4.[9] Romagnuolo R, Laflamme MA. Programming cells for cardiac repair. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2017;47:43-50.[10] 尹成果,刘学刚.NKX2.5基因在先天性心脏病中的研究进展[J].蚌埠医学院学报,2015,40(11):1608-1611.[11] 许耘红,何穗镕,李丽青.心脏发育相关基因NKX2.5和GATA4突变与先天性心脏病的相关性[J].中国临床药理学杂志, 2016, 32(22):2111-2113.[12] 丁建东,方翔,李开如,等.转录因子Nkx2.5和GATA4的相互作用[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(11): 1933-1936.[13] Pradhan L, Gopal S, Li S, et al. Intermolecular Interactions of Cardiac Transcription Factors NKX2.5 and TBX5. Biochemistry. 2016;55(12):1702-1710.[14] Anderson DJ, Kaplan DI, Bell KM, et al. NKX2-5 regulates human cardiomyogenesis via a HEY2 dependent transcriptional network. Nat Commun. 2018;9(1):1373.[15] 蔡花,付四清.Nkx2.5基因与先天性心脏病[J].中国优生与遗传杂志,2014,22(4):1-3.[16] 陈炜,张雷,尹青,等.外源性Nkx2.5、GATA4促进大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞的心肌分化[J]. 中国民康医学,2015,27(14):161.[17] Li P, Zhang L. Exogenous Nkx2.5- or GATA-4-transfected rabbit bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and myocardial cell co-culture on the treatment of myocardial infarction in rabbits. Mol Med Rep. 2015;12(2):2607-2621.[18] 姜霖,吴岳恒,李晓红,等.聚乙烯亚胺-蛋白纳米复合体转染蛋白进入骨髓间充质干细胞的应用研究[J].中国病理生理杂志,2015, 31(6):1057-1063.[19] 牛玉宏,史剑慧,胡昕婴,等.骨髓基质干细胞心肌化诱导过程中转录因子NKx2.5的表达[J]. 中国临床医学,2004,11(3):300-302. [20] 林钊,周春燕.转录因子Nkx2.5和GATA4在胚胎心肌发育早期的作用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版),2002,34(6):732-734.[21] Akazawa H, Komuro I. Cardiac transcription factor Csx/Nkx2-5: Its role in cardiac development and diseases. Pharmacol Ther. 2005;107(2):252-268.[22] Maury P, Gandjbakhch E, Baruteau AE, et al. Cardiac Phenotype and Long-Term Follow-Up of Patients With Mutations in NKX2-5 Gene. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2016;68(21): 2389-2390.[23] Nimura K, Yamamoto M, Takeichi M, et al. Regulation of alternative polyadenylation by Nkx2-5 and Xrn2 during mouse heart development. Elife. 2016;5. pii: e16030.[24] Tong YF. Mutations of NKX2.5 and GATA4 genes in the development of congenital heart disease. Gene. 2016; 588(1):86-94.[25] Ruan Z, Zhu L, Yin Y, et al. Overexpressing NKx2.5 increases the differentiation of human umbilical cord drived mesenchymal stem cells into cardiomyocyte-like cells. Biomed Pharmacother. 2016;78:110-115.[26] Deutsch MA, Doppler SA, Li X, et al. Reactivation of the Nkx2.5 cardiac enhancer after myocardial infarction does not presage myogenesis. Cardiovasc Res. 2018;114(8): 1098-1114.[27] Kinnunen SM, Tölli M, Välimäki MJ, et al. Cardiac Actions of a Small Molecule Inhibitor Targeting GATA4-NKX2-5 Interaction. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):4611. [28] Ruan ZB, Chen GC, Ren Y, et al. Expression profile of long non-coding RNAs during the differentiation of human umbilical cord derived mesenchymal stem cells into cardiomyocyte-like cells. Cytotechnology. 2018;70(4): 1247-1260.[29] Colombo S, de Sena-Tomás C, George V, et al. Nkx genes establish second heart field cardiomyocyte progenitors at the arterial pole and pattern the venous pole through Isl1 repression. Development. 2018;145(3): dev161497.[30] Dorn T, Goedel A, Lam JT, et al. Direct nkx2-5 transcriptional repression of isl1 controls cardiomyocyte subtype identity. Stem Cells. 2015;33(4):1113-1129.[31] Han SS, Wang G, Jin Y, et al. Investigating the Mechanism of Hyperglycemia-Induced Fetal Cardiac Hypertrophy. PLoS One. 2015;10(9):e0139141.[32] Ketharnathan S, Koshy T, Sethuratnam R, et al. Investigation of NKX2.5 gene mutations in congenital heart defects in an Indian population. Genet Test Mol Biomarkers. 2015;19(10): 579-583.[33] Zheng J, Li F, Liu J, et al. Investigation of Somatic NKX2-5 Mutations in Chinese Children with Congenital Heart Disease. Int J Med Sci. 2015;12(7):538-543.[34] Bouveret R, Waardenberg AJ, Schonrock N, et al. NKX2-5 mutations causative for congenital heart disease retain functionality and are directed to hundreds of targets. Elife. 2015;4: e06942.[35] Wingfield PT. Overview of the purification of recombinant proteins. Curr Protoc Protein Sci. 2015;80: 1-35.[36] Ferrer-Miralles N, Saccardo P, Corchero JL, et al. General introduction: recombinant protein production and purification of insoluble proteins. Methods Mol Biol. 2015;1258:1-24.[37] Mahalik S, Sharma AK, Mukherjee KJ. Genome engineering for improved recombinant protein expression in Escherichia coli. Microb Cell Fact. 2014;13:177.[38] Di Baldassarre A, Cimetta E, Bollini S, et al. Human-Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell Technology and Cardiomyocyte Generation: Progress and Clinical Applications. Cells. 2018; 7(6):E48.[39] Qin H, Zhao A, Fu X. Small molecules for reprogramming and transdifferentiation. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2017;74(19):3553-3575.[40] Li XH, Li Q, Jiang L, et al. Generation of Functional Human Cardiac Progenitor Cells by High-Efficiency Protein Transduction. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2015;4(12):1415-1424. |