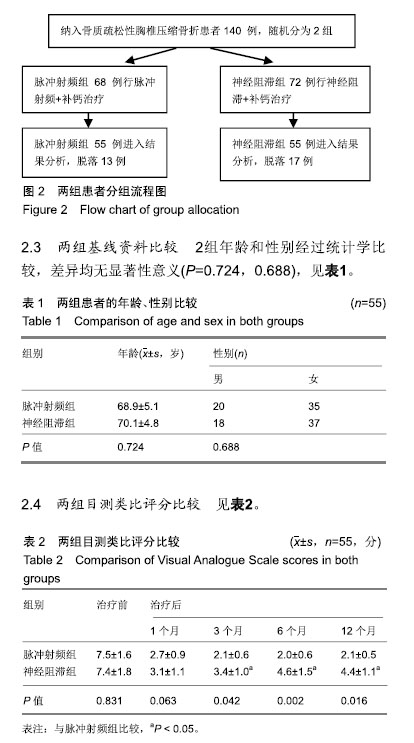
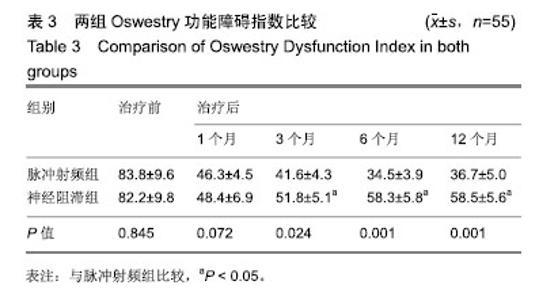
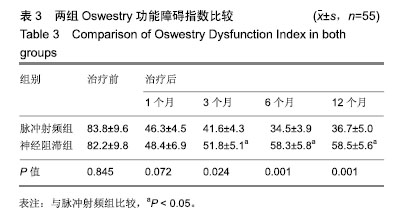
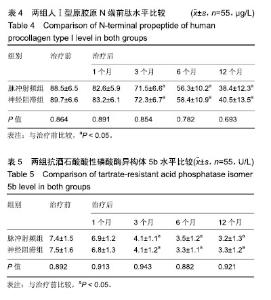
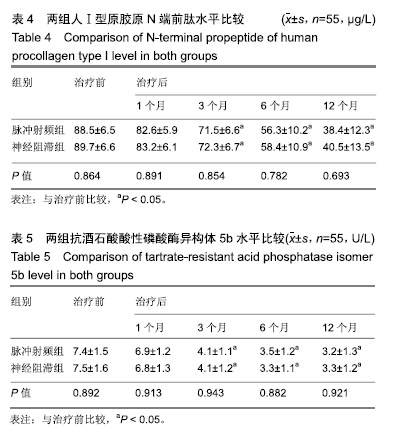
| [1]白璧辉,谢兴文,李鼎鹏,等.我国近5年来骨质疏松症流行病学研究现状[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2018,24(2):253-258.[2]印平,马远征,马迅,等.骨质疏松性椎体压缩性骨折的治疗指南[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2015,21(6):643-648.[3]Kallmes DF, Comstock BA, Heagerty PJ, et al. A randomized controlled trial of vertebroplasty for osteoporotic spine fractures. N Engl J Med. 2009;361(6):569-579.[4]时亮,段亮,董向辉.经皮椎体成形术联合碳酸钙D3和阿仑膦酸钠治疗骨质疏松椎体压缩性骨折84例[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志, 2018,26(11):64-66.[5]秦大平,张晓刚,宋敏,等.老年骨质疏松性胸腰椎压缩骨折治疗研究进展[J]. 中华中医药杂志,2017,32(2):679-682. [6]张志强,杨建东,冯新民,等.改良骨水泥推注套管治疗骨质疏松椎体压缩性骨折可减少骨水泥渗漏[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2018, 22(2):165-170.[7]张晗祥,范华华,蔡小军. 骨质疏松模型兔椎体成形术中不同剂量骨水泥对相邻椎间盘的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2018, 22(2):171-177.[8]张赢,关彦彦,李凌超,等.射频联合银质针治疗骨质疏松性胸腰椎压缩性骨折后遗痛[J]. 中国疼痛医学杂志,2016,22(3):232-234.[9]张广建,李仁淑,金文哲,等.脉冲射频治疗椎体压缩骨折性疼痛的疗效观察[J]. 中国疼痛医学杂志,2016, 22 (5):386-388.[10]印平,马远征,马迅,等.骨质疏松性椎体压缩性骨折的治疗指南[J]. 中国骨质疏松杂志,2015,21(6):643-648.[11]付晓宁,胡朝晖.骨代谢生化指标对于骨质疏松症诊断与治疗的临床意义[J]. 中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2018,33(9):1003-1005.[12]Cui L,Chen L,Xia W,et al. Vertebral fracture in postmenopausal Chinese women: a population-based stud. Osteoporos Int. 2017;28:2583-2590.[13]杨保华,李国胜,张义峰,等.经皮椎体成形和椎体后凸成形疗骨质疏松性胸腰椎骨折疗效的回顾性队列研究[J]. 中国循证医学杂志,2015,15(4):377-380.[14]郭宝英,朱魏,赵太茂. 原发性骨质疏松椎体压缩性骨折的X线?MRI影像诊断价值分析[J].中国CT和MRI杂志, 2016,14(11): 124-126.[15]薛海忠.探讨老年性骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折的临床及影像学特点[J]. 影像研究与医学应用,2018,2(8):44-46.[16]刘峰瑞 高宏.骨质疏松和转移瘤致椎体压缩骨折的MRI 早期鉴别诊断[J]. 中华临床医师杂志(电子版),2017,11(9):1518-1521.[17]杨进廉,艾双春,刘江,等.针灸对骨质疏松症椎体压缩骨折患者生存质量的影响[J]. 上海针灸杂志,2016,35(10):1229-1232.[18]徐峰,姚年伟,黄勇,等.单?双侧椎弓根穿刺行 PKP 治疗效果比较[J]. 颈腰痛杂志,2016,37(1):40-43.[19]Mattyasovszky SG, Kurth AA, Drees P, et al. Minimally invasive cement augmentation of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures with the new radiofrequency kyphoplasty. Oper Orthop Traumatol. 2014,26(5):497-512.[20]梁必如,肖格林. CT引导下选择性脊神经根周围注射得宝松复合液治疗颈腰根性神经痛[J]. 中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2008, 23(4): 312-313.[21]Muratore M, Ferrera A, Masse A, et al. Osteoporotic vertebral fractures: predictive factors for conservative treatment failure. A systematic review. European Spine J. 2017; 1: 1-12.[22]Tsoumakidou G, Too CW,Koch G, et al. CIRSE guidelines on percutaneous vertebral augmentation. Cardiovas Intervent Radiol. 2017;40:331-342.[23]叶生丽,康新国. 低温等离子与射频热凝脊神经后支治疗带状疱疹后遗神经痛的疗效观察[J].贵州医药, 2018,42(10): 1246-1247.[24]闵有宝,孙欢,徐文联,等.不同病程腰椎间盘突出症经CT引导下选择性神经根阻滞结合脉冲射频治疗的临床观察[J].颈腰痛杂志,2018,39(5):578-580.[25]张广建,王宗宝,李仁淑,等.脉冲射频联合神经阻滞治疗腰脊神经后支综合征临床研究[J]. 中国疼痛医学杂志,2014,20(10): 754-756.[26]中华医学会骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病分会.骨质疏松性椎体压缩性骨折诊疗与管理专家共识[J].中华骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病杂志,2018,11(5):425-437.[27]中华医学会骨科学分会骨质疏松学组.骨质疏松性骨折诊疗指南[J].中华骨科杂志, 2017,37(1):1-10.[28]Zhou J, Wang T, Zhao X, et al. Comparative efficacy of bisphosphonates to prevent fracture in men with osteoporosis: a systematic review with network meta-analyses. Rheumatol Ther. 2016;3(1):117-128.[29]Eastell R, Walsh JS, Watts NB, et al. Bisphosphonates for postmenopausal osteoporosis. Bone. 2011;49: 82-88.[30]Maraka S, Kennel KA. Bisphosphonates for the prevention and treatment of osteoporosis. BMJ. 2015;351: 461-465.[31]马远征,王以朋,刘强,等.中国老年骨质疏松症诊疗指南(2018)[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2018,24(12):1541-1567.[32]申冬冬.人参皂苷对大鼠成骨细胞增殖及成骨细胞中PINP?β- CTX分泌的影响[J]. 中华中医药学刊,2018,36(3):738-741.[33]Luo Y, Hu Z, Hao J, et al. Significant association between the A163G and G1181C polymorphisms of the osteoprotegerin gene and risk of osteoporosis, especially in postmenopausal women: a meta-analysis. Genet Test Mol Biomarkers. 2014; 18(3):211-219.[34]陈文军.老年骨质疏松性骨折患者血清BGP?BALP?TRACP- 5b表达的价值研究[J]. 国际检验医学杂志,2018,39(15): 1870-1872.[35]郑辉,罗斌,王成伟,等. 骨代谢指标BAP?BGP?CTX-I?TRACP5b等变化对老年髋部骨折后骨密度的影响及在二次骨折中的风险预测[J]. 标记免疫分析与临床, 2018,25(9): 1326-1330. |