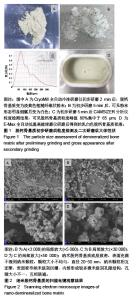
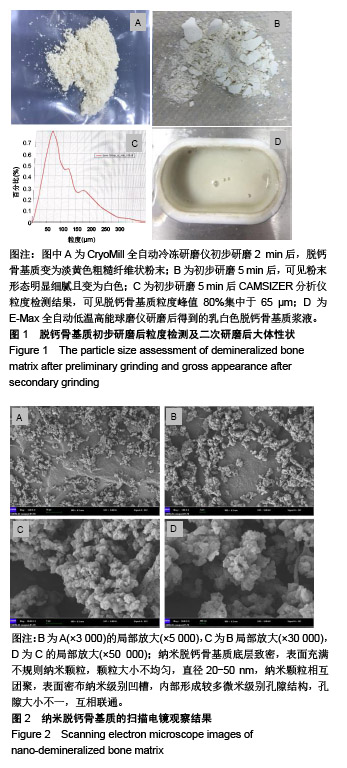
| [1]Noori A,Ashrafi SJ,Vaez-Ghaemi R,et al.A review of fibrin and fibrin composites for bone tissue engineering.Int J Nanomedicine.2017;12:4937-4961.[2]Bhattacharjee P,Kundu B,Naskar D,et al.Silk scaffolds in bone tissue engineering: An overview. Acta Biomater.2017;63:1-17.[3]Blokhuis TJ, Arts JJ.Bioactive and osteoinductive bone graft substitutes: definitions, facts and myths.Injury.2011;42 Suppl 2:S26-29.[4]Gong T, Xie J, Liao J, et al.Nanomaterials and bone regeneration. Bone Res.2015;3:15029.[5]Betz RR.Limitations of autograft and allograft: new synthetic solutions.Orthopedics.2002;25(5 Suppl):s561-570.[6]Zimmermann G, Moghaddam A.Allograft bone matrix versus synthetic bone graft substitutes.Injury. 2011;42 Suppl 2: S16-21.[7]Aryaei A,Jayatissa AH,Jayasuriya AC.Mechanical and biological properties of chitosan/carbon nanotube nanocomposite films. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2014;102(8): 2704-2712.[8]Touri R,Moztarzadeh F,Sadeghian Z,et al.The use of carbon nanotubes to reinforce 45S5 bioglass-based scaffolds for tissue engineering applications.Biomed Res Int. 2013;2013: 465086.[9]Chae T,Yang H,Leung V,et al.Novel biomimetic hydroxyapatite/alginate nanocomposite fibrous scaffolds for bone tissue regeneration.J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2013;24(8): 1885-1894.[10]Laschke MW,Strohe A,Menger MD,et al.In vitro and in vivo evaluation of a novel nanosize hydroxyapatite particles/ poly(ester-urethane) composite scaffold for bone tissue engineering. Acta Biomater.2010;6(6):2020-2027.[11]房雷,陈雄生,黄凯,等.人纳米脱钙骨基质复合物的理化性质和安全性[J].中国组织工程研究, 2013,17(38):6701-6708.[12]黄凯,陈雄生,贾连顺,等.纳米脱钙骨基质促进骨愈合[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(21):3862-3869.[13]黄凯,陈雄生,贾连顺,等.纳米脱钙骨基质的制备及其性能检测[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2009,17(13):1017-1019.[14]Grgurevic L,Pecina M, Vukicevic S,et al.Urist and the discovery of bone morphogenetic proteins.Int Orthop. 2017; 41(5):1065-1069.[15]Chen X,Wang W,Cheng S,et al.Mimicking bone nanostructure by combining block copolymer self-assembly and 1D crystal nucleation.ACS Nano.2013;7(9):8251-8257.[16]Song SH,Kim SG,Kim SE,et al.Is DBM beneficial for the enhancement of bony consolidation in distraction osteogenesis? A randomized controlled trial. Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:281738.[17]Drosos GI,Touzopoulos P,Ververidis A,et al.Use of demineralized bone matrix in the extremities. World J Orthop. 2015;6(2):269-277.[18]Stevens MM,George JH.Exploring and engineering the cell surface interface.Science.2005; 310(5751):1135-1138.[19]Hasani-Sadrabadi MM,Hajrezaei SP,Emami SH,et al. Enhanced osteogenic differentiation of stem cells via microfluidics synthesized nanoparticles. Nanomedicine. 2015; 11(7):1809-1819.[20]Dan Y,Liu O,Liu Y,et al.Development of Novel Biocomposite Scaffold of Chitosan-Gelatin/Nanohydroxyapatite for Potential Bone Tissue Engineering Applications. Nanoscale Res Lett. 2016;11(1):487.[21]钱鋆,沈尊理.冻干脱钙骨表面纳米结构对细胞行为的影响[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2005,13(12):911-914.[22]李香琴,宋克东.成骨细胞在纳米材料表面上粘附特性[J].大连理工大学学报,2005,45(5):653-657.[23]Gao X,Song J,Ji P,et al.Polydopamine-Templated Hydroxyapatite Reinforced Polycaprolactone Composite Nanofibers with Enhanced Cytocompatibility and Osteogenesis for Bone Tissue Engineering. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces.2016;8(5):3499-3515.[24]Hasani-Sadrabadi MM,Hajrezaei SP,Emami SH,et al.Enhanced osteogenic differentiation of stem cells via microfluidics synthesized nanoparticles. Nanomedicine. 2015;11(7):1809-1819.[25]Lavernia EJ, Han BQ,Schoenung JM.Cryomilled nanostructured materials: Processing and properties.Mater Sci Eng A.2008;493(1-2):207-214.[26]董亮.低温粉碎技术[J].电子质量,2008,29(3):87-88.[27]董亮,张赞蓉.粉碎技术在样品前处理中的应用—利用RETSCH研磨粉碎仪器获得有代表性的样品[J].食品安全导刊, 2011, 5(11):34-35.[28]佚名.德国Retsch(莱驰)高能纳米球磨仪E_(max)全新上市[J].中国粉体工业,2014,11(5):53-53.[29]Wahajuddin, Arora S.Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: magnetic nanoplatforms as drug carriers.Int J Nanomedicine.2012;7:3445-3471.[30]Vieira S,Vial S,Reis RL,et al.Nanoparticles for bone tissue engineering. Biotechnol Prog.2017; 33(3):590-611.[31]Fernandez-Urrusuno R,Fattal E,Rodrigues JM Jr,et al.Effect of polymeric nanoparticle administration on the clearance activity of the mononuclear phagocyte system in mice. J Biomed Mater Res.1996;31(3):401-408.[32]Verdun C,Brasseur F,Vranckx H,et al.Tissue distribution of doxorubicin associated with polyisohexylcyanoacrylate nanoparticles.Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 1990;26(1): 13-18.[33]Rouwkema J,Rivron NC,van Blitterswijk CA.Vascularization in tissue engineering.Trends Biotechnol.2008;26(8):434-441.[34]Woodard JR,Hilldore AJ,Lan SK,et al.The mechanical properties and osteoconductivity of hydroxyapatite bone scaffolds with multi-scale porosity. Biomaterials. 2007;28(1): 45-54.[35]Wang X,Zhang G,Qi F,et al.Enhanced bone regeneration using an insulin-loaded nano-hydroxyapatite/collagen/PLGA composite scaffold.Int J Nanomedicine.2017;13:117-127. |