Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (30): 4780-4786.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1421
Previous Articles Next Articles
Biphasic calcium phosphate scaffolds modified with collagen based on three-dimensional printing technology
- 1Zhejiang Provincial Key Lab of Medical Information and Three-Dimensional Bio-Printing, Hangzhou Dianzi University, Hangzhou 310018, Zhejiang Province, China; 2College of Automation, Hangzhou Dianzi University, Hangzhou 310018, Zhejiang Province, China
-
Received:2019-05-13Online:2019-10-28Published:2019-10-28 -
Contact:Xu Mingen, MD, Professor, Zhejiang Provincial Key Lab of Medical Information and Three-Dimensional Bio-Printing, Hangzhou Dianzi University, Hangzhou 310018, Zhejiang Province, China; College of Automation, Hangzhou Dianzi University, Hangzhou 310018, Zhejiang Province, China -
About author:Zhang Haige, Master candidate, Zhejiang Provincial Key Lab of Medical Information and Three-Dimensional Bio-Printing, Hangzhou Dianzi University, Hangzhou 310018, Zhejiang Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 61675059 (to WL); the National Key R & D Program of China, No. 2017YFC1103400 (to XME)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhang Haige, Suo Hairui, Wang Ling, Xu Mingen. Biphasic calcium phosphate scaffolds modified with collagen based on three-dimensional printing technology[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(30): 4780-4786.
share this article
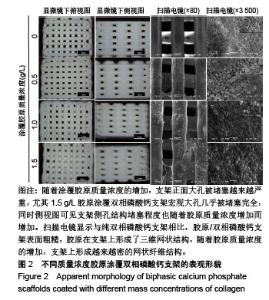
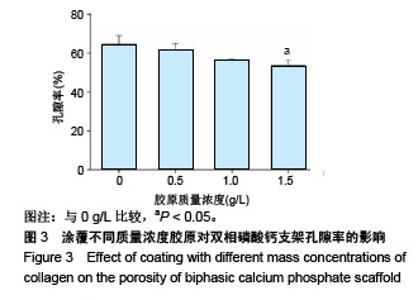
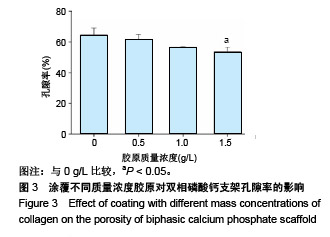
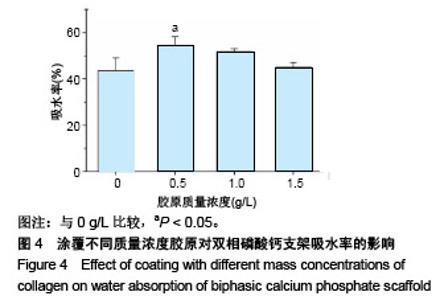
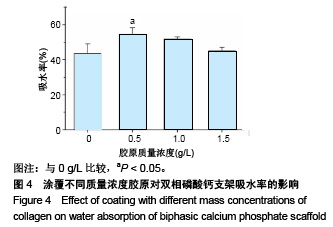
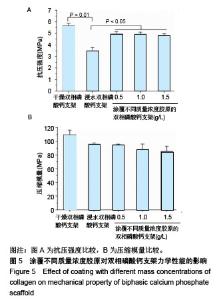
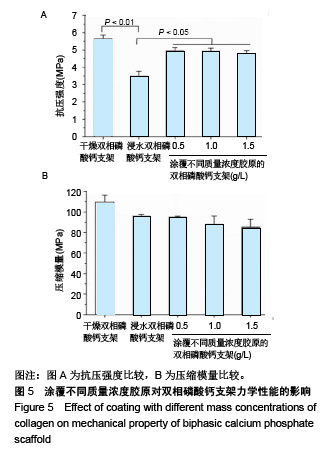
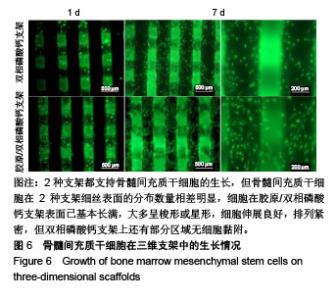
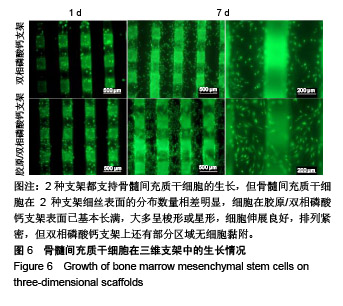
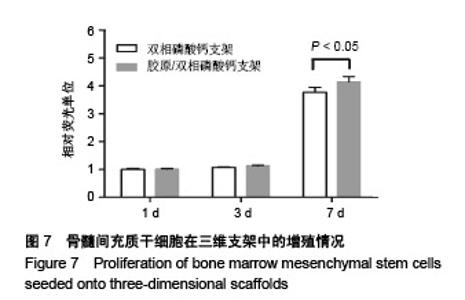
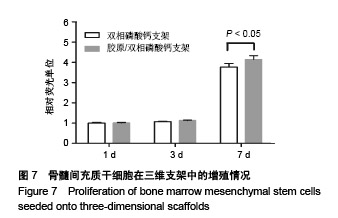
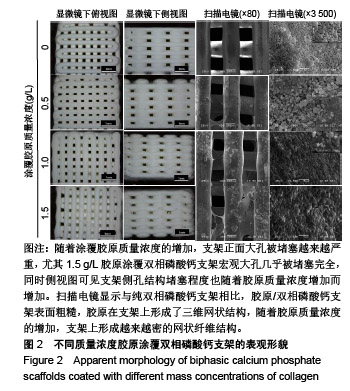
2.1 支架的表观形貌 见图2。 通过双相磷酸钙三维支架的俯视图和侧视图可见,其孔隙规则、清晰可见,且孔与孔之间保持高度的贯通性;随着涂覆胶原质量浓度的增加,支架正面大孔被堵塞越来越严重,尤其1.5 g/L胶原涂覆双相磷酸钙支架宏观大孔几乎被堵塞完全。同时侧视图可见支架侧孔结构堵塞程度也随着胶原质量浓度增加而增加。 为进一步证明支架微观孔的堵塞情况,对支架表面喷金处理后使用扫描电镜观察支架表面情况,可见双相磷酸钙支架表面较光滑,内部具有良好整齐的多孔结构且孔互连性好,大孔平均直径为(285.75±5.63) μm,能够为细胞培养液深入支架提供可能。放大3 500倍的双相磷酸钙支架扫描电镜图显示,颗粒呈现不规则形状,颗粒之间有许多约1 μm的微孔隙。与纯双相磷酸钙支架相比,胶原/双相磷酸钙支架表面粗糙,胶原在支架上形成了三维网状结构。在较高放大倍数下可明显观察到随着胶原质量浓度的增加,支架上形成越来越密的网状纤维结构,虽然胶原涂覆有利于细胞黏附,但胶原纤维越密支架孔堵塞越严重,这样将不利于细胞生长及营养物质的交换。"
| [1]Nerem RM,Sambanis A.Tissue engineering: from biology to biological substitutes. Tissue Eng.1995;1(1):3-13.[2]Li S,Li N.Effects of composition and temperature on porosity and pore size distribution of porous ceramics prepared from Al (OH) 3, and kaolinite gangue.Ceram Int. 2007;33(4):551-556.[3]Chen J,Wang Y,Chen X,et al.Biomimetic synthesis of porous composite scaffold composed of nano-hydroxyapatite and chitosan by freeze-drying technology.Rare Metal Mat Eng. 2009;38(12): 271-273.[4]Zhao K,Wei J,Luo D,et al.Fabrication of hydroxyapatite porous scaffolds by freeze drying.J Chin Ceram Soc.2009;37(3):432-435. [5]Sepulveda P,Binner JG,Rogero SO,et al.Production of porous hydroxyapatite by the gel-casting of foams and cytotoxic evaluation. J Biomed Mater Res.2000;50(1):27-34.[6]Chia HN,Wu BM.Recent advances in 3D printing of biomaterials. J Biol Eng.2015;9(1):4. [7]Webb PA.A review of rapid prototyping (RP) techniques in the medical and biomedical sector.J Med Eng Technol.2000;24(4):149-153.[8]Duoss EB,Twardowski M,Lewis JA.Sol-Gel inks for direct-write assembly of functional oxides.Adv Mater.2007;19(21):3485-3489.[9]尤琦,张赢心,李佳乐,等.双相磷酸钙陶瓷化学组成对其材料性能的影响[J].海南医学,2016, 27(15):2502-2504. [10]许瑾,吴晶晶,王晓冬,等.羟基磷灰石复合骨组织工程支架的研究进展[J].生物骨科材料与临床研究,2016,13(2):63-66. [11]Faruq O,Kim B,Padalhin AR,et al.A hybrid composite system of biphasic calcium phosphate granules loaded with hyaluronic acid-gelatin hydrogel for bone regeneration. J Biomater Appl. 2017;32(4):433-445.[12]Castilho M,Moseke C,Ewald A,et al.Direct 3D powder printing of biphasic calcium phosphate scaffolds for substitution of complex bone defects.Biofabrication.2014;6(1): 015006.[13]Ng A MH,Tan KK,Phang MY,et al.Differential osteogenic activity of osteoprogenitor cells on HA and TCP/HA scaffold of tissue engineered bone.J Biomed Mater Res.2008;85A(2):301-312. [14]Ebrahimi M,Botelho M.Biphasic calcium phosphates (BCP) of hydroxyapatite (HA) and tricalcium phosphate (TCP) as bone substitutes: importance of physicochemical characterizations in biomaterials studies.Data Brief.2017;10(C):93-97.[15]Kim JW,Shin KH,Koh YH,et al.Production of poly(ε-caprolactone)/ hydroxyapatite composite scaffolds with a tailored macro/micro- porous structure, high mechanical properties, and excellent bioactivity.Materials.2017;10(10):1123-1135. [16]王庆利,何丹,郑晓冬,等.有机溶剂对细胞的毒害及细胞的耐受性机制[J].微生物学通报, 2002,29(4):81-85. [17]Stratton S,Shelke NB,Hoshino K,et al.Bioactive polymeric scaffolds for tissue engineering.Bioact Mater.2016;1(2):93-108.[18]李涤尘,连芩,靳忠民,等.基于光固化和凝胶注模的镁合金/生物陶瓷骨支架及其成型方法:CN 102335460 A[P].2012.[19]Zhang D,Wu X,Chen J,et al.The development of collagen based composite scaffolds for bone regeneration.Bioact Mater. 2018; 3(1):129-138.[20]Lim MM,Sun T,Sultana N.In vitro biological evaluation of electrospun polycaprolactone/gelatine nanofibrous scaffold for tissue engineering. J Nanomater.2015;(2):1-10.[21]Bostman OM,Pihlajamaki HK.Adverse tissue reactions to bioabsorbable: Saos-2 are influenced by collagen fibers in xenogenic bone biomaterial: fixation devices.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2000;(371):216-227.[22]臧晓龙,孙健,李亚莉,等.3D生物打印构建聚乳酸羟基乙酸/纳米羟基磷灰石支架骨形态发生蛋白2缓释复合体的实验研究[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(16):2405-2411.[23]马艺娟.三维可控微结构多孔生物活性陶瓷的制备及其性能研究[D].华南理工大学, 2015. [24]Lee MH,You C,Kim KH.Combined effect of a microporous layer and type I collagen coating on a biphasic calcium phosphate scaffold for bone tissue engineering.Materials.2015; 8(3):1150-1161. [25]Takeuchi Y,Nakayama K,Matsumoto T.Differentiation and cell surface expression of transforming growth factor-beta receptors are regulated by interaction with matrix collagen in murine osteoblastic cells.J Biol Chem.1996;271(7):3938-3944.[26]Mizuno M,Fujisawa R,Kuboki Y.Type I collagen‐induced osteoblastic differentiation of bone‐marrow cells mediated by collagen‐α2β1 integrin interaction.J Cell Physiol. 2000;184(2): 207-213. [27]Roehlecke C, Witt M, Kasper M,et al.Synergistic effect of titanium alloy and collagen type I on cell adhesion, proliferation and differentiation of osteoblast-like cells. Cells Tissues Organs. 2001; 168(3):178-187.[28]Dorozhkin SV. Calcium orthophosphate-based biocomposites and hybrid biomaterials. J Mater Sci.2009;44(9):2343-2387.[29]Wei QR,Lu J,Zhao HC,et al.Preparation and characterization of the microspheres comprised of atelocollagen and BCP.Key Eng Mater. 2007;330-332:423-426.[30]Ebrahimi M,Pripatnanont P,Monmaturapoj N,et al.Fabrication and characterization of novel nano hydroxyapatite/β-tricalcium phosphate scaffolds in three different composition ratios.J Biomed Mater Res.2012;100(9):2260-2268.[31]胡涛.下颌骨三维重建及计算机辅助低温沉积制造研究[D].杭州:杭州电子科技大学,2015.[32]Suo H,Xu K,Zheng X.Using glucosamine to improve the properties of photocrosslinked gelatin scaffolds.J Biomater Appl. 2015;29(7): 977-987. [33]Zheng H, Bai Y, Shih MS,et al.Effect of a β-TCP collagen composite bone substitute on healing of drilled bone voids in the distal femoral condyle of rabbits.J Biomed Mater Res.2014;102(2):376-383.[34]Curran JM,Gallagher JA,Hunt JA.The inflammatory potential of biphasic calcium phosphate granules in osteoblast/macrophage co-culture.Biomaterials.2005;26(26): 5313-5320. [35]Lin F,Liao C,Chen K,et al.Preparation of β-TCP/HAP biphasic ceramics with natural bone structure by heating bovine cancellous bone with the addition of (NH4)2HPO4.J Biomed Mater Res. 2000; 51(2):157-163.[36]孙开瑜,徐铭恩,周永勇.基于3D 打印的 I 型胶原涂覆 β-TCP 骨组织工程支架研究[J]. 中国生物医学工程学报,2018,37(3):335-343.[37]Morra M Cassinelli C,Cascardo G,et al.Surface engineering of titanium by collagen immobilization. Surface characterization and in vitro and in vivo studies. Biomaterials.2003;24(25):4639-4654.[38]Henkel J,Woodruff MA,Epari DR,et al.Bone regeneration based on tissue engineering conceptions-a 21st century perspective.Bone Res.2013;1(3):216-248.[39]Olszta MJ,Cheng X,Sang SJ,et al.Bone structure and formation: a new perspective. Mater Sci Eng R.2007;58(3):77-116.[40]Wang Y,Wang K,Li X,et al.3D fabrication and characterization of phosphoric acid scaffold with a HA/β-TCP weight ratio of 60:40 for bone tissue engineering applications.PLoS One.2017;12(4):e0174870.[41]尤琦.三维打印技术构建双相磷酸钙陶瓷支架及其性能研究[D].长春:吉林大学,2016.[42]袁景,甄平,赵红斌.高性能多孔β-磷酸三钙骨组织工程支架的3D打印[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(43):6914-6921. [43]Andrew G,Dafydd V,Jing Y,et al.Review of additive manufactured tissue engineering scaffolds: relationship between geometry and performance.Burns Trauma.2018;6(1):19.[44]Pilliar RM,Filiaggi MJ,Wells JD,et al.Porous calcium polyphosphate scaffolds for bone substitute applications-in vitro characterization. Biomaterials.2001;22(9): 963-972.[45]Ma Z,Mao Z,Gao C.Surface modification and property analysis of biomedical polymers used for tissue engineering.Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces.2007;60(2):137-157. [46]Daculsi G,Legeros R.Biphasic Calcium Phosphate (BCP) bioceramics: chemical, physical, and biological properties.Encycl Biomater Biomed Eng.2008:359-366. [47]LeGeros RZ,Lin S,Rohanizadeh R,et al.Biphasic calcium phosphate bioceramics: preparation, properties and applications.J Mater Sci Mater Med.2003;14(3):201-209. |
| [1] | Lu Dezhi, Mei Zhao, Li Xianglei, Wang Caiping, Sun Xin, Wang Xiaowen, Wang Jinwu. Digital design and effect evaluation of three-dimensional printing scoliosis orthosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1329-1334. |
| [2] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [3] | Liu Zhichao, Zhang Fan, Sun Qi, Kang Xiaole, Yuan Qiaomei, Liu Genzhe, Chen Jiang. Morphology and activity of human nucleus pulposus cells under different hydrostatic pressures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1172-1176. |
| [4] | Shen Jinbo, Zhang Lin. Micro-injury of the Achilles tendon caused by acute exhaustive exercise in rats: ultrastructural changes and mechanism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1190-1195. |
| [5] | Liu Cong, Liu Su. Molecular mechanism of miR-17-5p regulation of hypoxia inducible factor-1α mediated adipocyte differentiation and angiogenesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1069-1074. |
| [6] | Liang Xueqi, Guo Lijiao, Chen Hejie, Wu Jie, Sun Yaqi, Xing Zhikun, Zou Hailiang, Chen Xueling, Wu Xiangwei. Alveolar echinococcosis protoscolices inhibits the differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into fibroblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 996-1001. |
| [7] | Duan Liyun, Cao Xiaocang. Human placenta mesenchymal stem cells-derived extracellular vesicles regulate collagen deposition in intestinal mucosa of mice with colitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1026-1031. |
| [8] | Li Cai, Zhao Ting, Tan Ge, Zheng Yulin, Zhang Ruonan, Wu Yan, Tang Junming. Platelet-derived growth factor-BB promotes proliferation, differentiation and migration of skeletal muscle myoblast [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1050-1055. |
| [9] | Liu Zhengpeng, Wang Yahui, Zhang Yilong, Ming Ying, Sun Zhijie, Sun He. Application of 3D printed interbody fusion cage for cervical spondylosis of spinal cord type: half-year follow-up of recovery of cervical curvature and intervertebral height [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 849-853. |
| [10] | Xu Junma, Yu Yuechao, Liu Zhi, Liu Yu, Wang Feitong. Application of 3D-printed coplanar template combined with fixed needle technique in percutaneous accurate biopsy of small pulmonary nodules [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 761-764. |
| [11] | Ma Zetao, Zeng Hui, Wang Deli, Weng Jian, Feng Song. MicroRNA-138-5p regulates chondrocyte proliferation and autophagy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 674-678. |
| [12] | Wang Yujiao, Liu Dan, Sun Song, Sun Yong. Biphasic calcium phosphate loaded with advanced platelet rich fibrin can promote the activity of rabbit bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 504-509. |
| [13] | Zhou Jihui, Yao Meng, Wang Yansong, Li Xinzhi, Zhou You, Huang Wei, Chen Wenyao. Influence of novel nanoscaffolds on biological behaviors of neural stem cells and the related gene expression [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 532-536. |
| [14] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [15] | Shi Xiaoxiu, Mao Shilong, Liu Yang, Ma Xingshuang, Luo Yanfeng. Comparison of tantalum and titanium (alloy) as orthopedic materials: physical and chemical indexes, antibacterial and osteogenic ability [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 593-599. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||