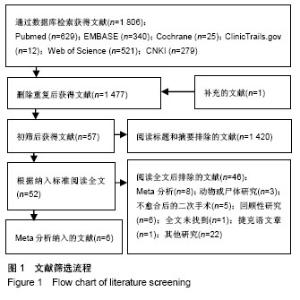
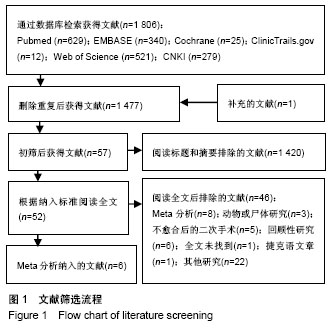
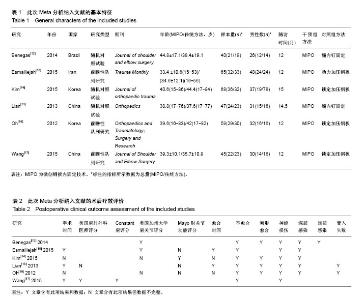
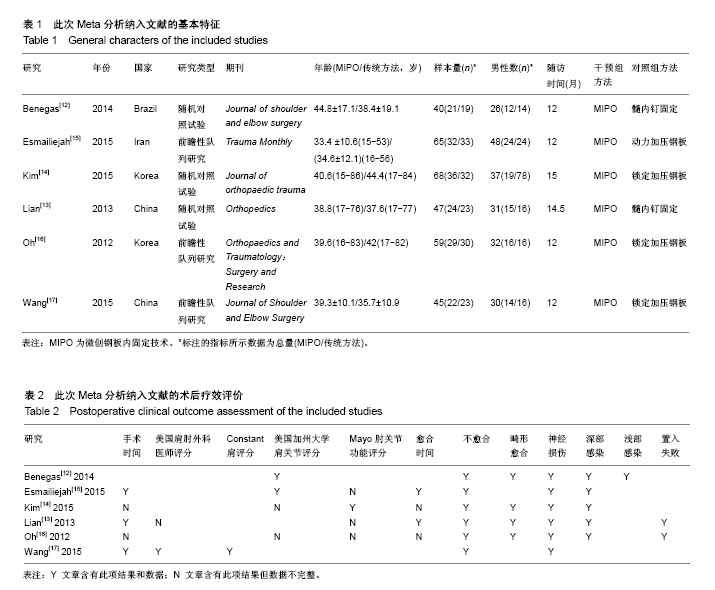
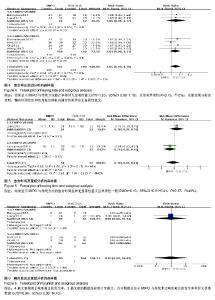
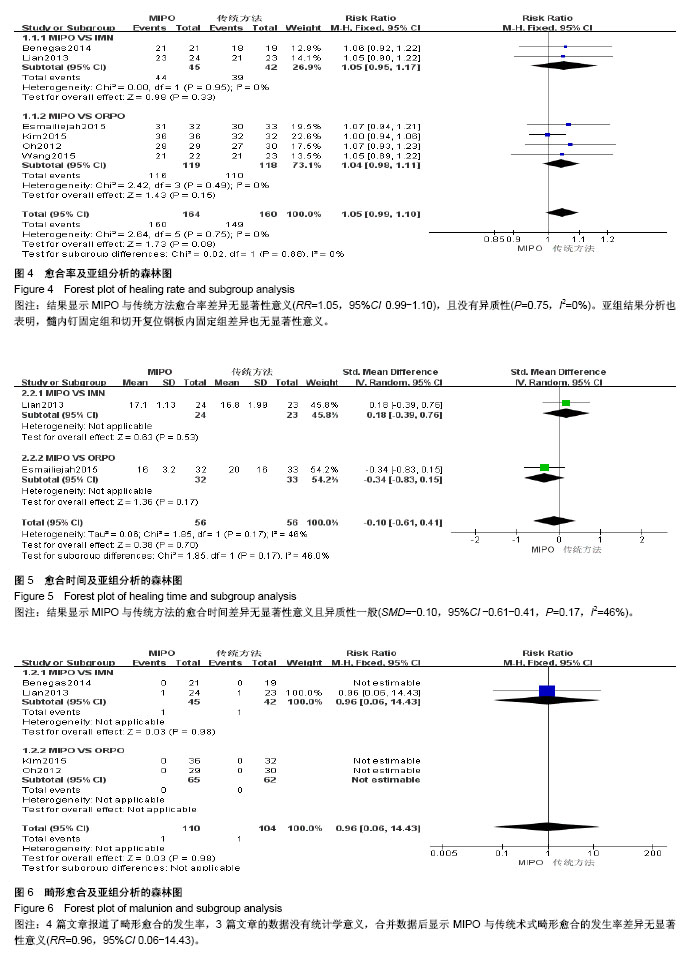
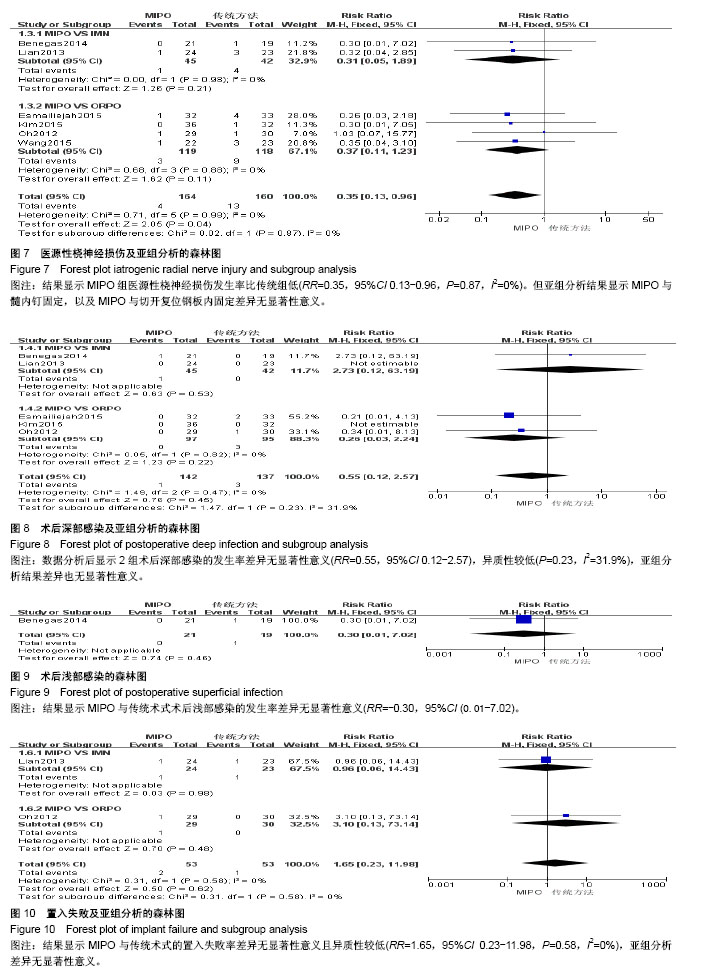
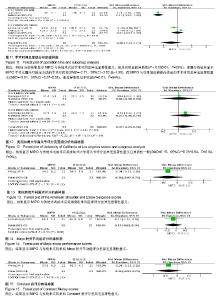
| [1] Brinker MR, O'connor DP. The incidence of fractures and dislocations referred for orthopaedic services in a capitated population. J Bone Joint Surg. 2004;86-A(2):290-297. [2] Clement ND. Management of humeral shaft fractures; non-operative versus operative. Arch Trauma Res. 2015;4(2): e28013. [3] Liu GY, Zhang CY, Wu HW. Comparison of initial nonoperative and operative management of radial nerve palsy associated with acute humeral shaft fractures. Orthopedics. 2012;35(8): 702-708. [4] Gosler MW, Testroote M, Morrenhof JW, et al. Surgical versus non-surgical interventions for treating humeral shaft fractures in adults. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012;1:CD008832. [5] Qiu H, Wei Z, Liu Y, et al. A Bayesian network Meta-analysis of three different surgical procedures for the treatment of humeral shaft fractures. Medicine (United States). 2016; 95(51):e5464. [6] 冯涛. 髓内钉和钢板置入修复成人肱骨干骨折:桡神经损伤及骨不愈合发生率比较[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2015,19(13): 2086-2090.[7] Ouyang HB, Xiong J, Xiang P, et al. Plate versus intramedullary nail fixation in the treatment of humeral shaft fractures: an updated Meta-analysis. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2013;22(3):387-395. [8] Chen H, Hu X, Yang G, et al. Clinic research on the treatment for humeral shaft fracture with minimal invasive plate osteosynthesis: a retrospective study of 128 cases. Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg. 2017;43(2):215-219. [9] Higgins JE. Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions. Naunyn. 2011;5(2):S38. [10] Higgins JPT, Altman DG, Gøtzsche PC, et al. The Cochrane Collaboration's tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. Bmj British Med J. 2011;343(7829):889-893. [11] Stang A. Critical evaluation of the Newcastle-Ottawa scale for the assessment of the quality of nonrandomized studies in Meta-analyses. Eur J Epidemiol. 2010;25(9):603-605. [12] Benegas E, Ferreira Neto AA, Gracitelli ME, et al. Shoulder function after surgical treatment of displaced fractures of the humeral shaft: a randomized trial comparing antegrade intramedullary nailing with minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2014;23(6):767-774. [13] Lian K, Wang L, Lin D, et al. Minimally invasive plating osteosynthesis for mid-distal third humeral shaft fractures. Orthopedics. 2013;36(8):e1025-1032. [14] Kim JW, Oh CW, Byun YS, et al. A prospective randomized study of operative treatment for noncomminuted humeral shaft fractures: conventional open plating versus minimal invasive plate osteosynthesis. J Orthop Trauma. 2015;29(4): 189-194. [15] Esmailiejah AA, Abbasian MR, Safdari F, et al. Treatment of humeral shaft fractures: Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis versus open reduction and internal fixation. Trauma Mon. 2015;20(3):e26271. [16] Oh CW, Byun YS, Oh JK, et al. Plating of humeral shaft fractures: Comparison of standard conventional plating versus minimally invasive plating. Orthop Traumatol. 2012; 98(1):54-60. [17] Wang C, Li J, Li Y, et al. Is minimally invasive plating osteosynthesis for humeral shaft fracture advantageous compared with the conventional open technique? J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2015;24(11):1741-1748. [18] Walker M, Palumbo B, Badman B, et al. Humeral shaft fractures: a review. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2011;20(5):833. [19] Young S, Lie SA, Hallan G, et al. Risk Factors for Infection after 46, 113 Intramedullary Nail Operations in Low- and Middle-income Countries. World J Surg. 2013;37(2):349-355. [20] 李连华,王浩,张妍,等. 钢板和髓内针固定治疗成人肱骨干骨折的系统评价[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2013,17(39):6970-6977.[21] 姜朝来,安智全. 髓内钉和微创钢板在肱骨干骨折内固定治疗中的应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2011,15(22):4119-4122.[22] Yu BF, Liu LL, Yang GJ, et al. Comparison of minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis and conventional plate osteosynthesis for humeral shaft fracture A Meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016;95(39):e4955. [23] Vilaca PR Jr, Uezumi MK. Anterior minimally invasive bridge-plate technique for treatment of humeral shaft nonunion. J Orthop Traumatol. 2012;13(4):211-216. [24] Hu XQ, Xu SQ, Lu HG, et al. Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis vs conventional fixation techniques for surgically treated humeral shaft fractures: a Meta-analysis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2016;11(1):59. [25] Zhao JG, Wang J, Meng XH, et al. Surgical interventions to treat humerus shaft fractures: A network Meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. PLoS ONE. 2017;12(3): e0173634. |