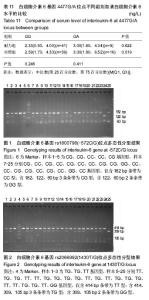
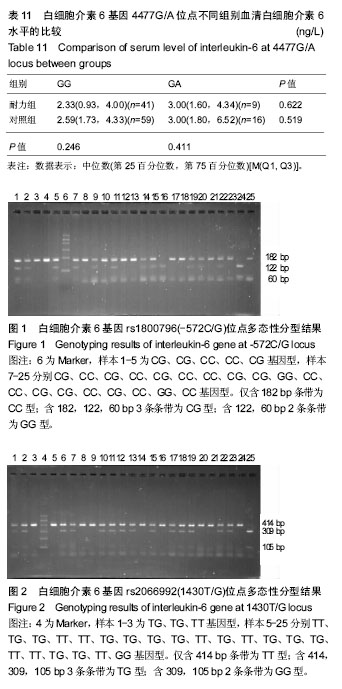
| [1] 胡扬.基因多态性和竞技体育金牌战略[J].体育科学, 2013,33(12):14-15.[2] 杨若愚,王予彬,沈勋章,等.基因多态性与杰出运动能力[J].中国组织工程研究, 2014,18(7):1121-1128.[3] He ZH, Hu Y,Li Y C, et al. PGC-related gene variants and elite endurance athletic status in a Chinese cohort: A functional study. Scand J MedSci Sports.2015;25(2):184-195.[4] Pedersen BK, Akerstrom TC, Nielsen AR,et al.Role of myokines in exercise and metabolism.J Appl Physiol. 2007;103(3):1093-1098.[5] Ahima RS,Park HK.Connecting Myokines and Metabolism. Endocrinol Metab.2015;30(3):235-245.[6] Li F,Li Y,Duan Y,et al. Myokines and adipokines: Involvement in the crosstalk between skeletal muscle and adipose tissue. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2017;33:73-82.[7] Nielsen AR,Pedersen BK.The biological roles of exercise-induced cytokines: IL-6, IL-8, and IL-15. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2007;32(5): 833-839.[8] Pedersen BK, Steensberg A, Fischer C, et al. The metabolic role of IL-6 produced during exercise: is IL-6 an exercise factor? ProcNutr Soc.2004;63(2):263-267.[9] 中国肥胖问题工作组,季成叶.中国学龄儿童青少年超重、肥胖筛查体重指数值分类标准[J].中华流行病学杂志, 2004,25(2):10-15.[10] 韦叶生,蓝艳,刘运广,等.广西壮族与汉族IL-6基因启动子-634C/G多态性的研究[J].中国优生与遗传杂志, 2005,13(3):11-12.[11] Hirano T,Matsuda T,Nakajima K.Signal transduction through gp130 that is shared among the receptors for the interleukin 6 related cytokine subfamily.Stem Cells.1994;12(3):262-277.[12] Mohamed-Ali V,Goodrick S,Rawesh A,et al.Subcutaneous adipose tissue releases interleukin-6, but not tumor necrosis factor-alpha, in vivo.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1997;82(12):4196-4200.[13] Boeta-Lopez K, Duran J, Elizondo D, et al. Association of Interleukin-6 Polymorphisms with Obesity or Metabolic Traits in Young Mexican-Americans.: IL6 SNPs in Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome. Obes Sci Pract.2017:1-12[14] Lajunen TK, Jaakkola JJK, Jaakkola MS. Interleukin 6 SNP rs1800797 associates with the risk of adult-onset asthma. Genes Immun. 2016; 17(3):193-198.[15] 王跃帮,魏红霞,徐志晔,等.IL-6-174G>C基因多态性与南京地区汉族人群冠心病的相关性[J].临床检验杂志, 2017,35(11):853-856.[16] Mitrokhin V, Nikitin A, Brovkina O, et al. Association between interleukin-6/6R gene polymorphisms and coronary artery disease in Russian population: influence of interleukin-6/6R gene polymorphisms on inflammatory markers.JInflamm Res. 2017;10:151-160.[17] Fishman D,Faulds G,Jeffery R,et al.The effect of novel polymorphisms in the interleukin-6 (IL-6) gene on IL-6 transcription and plasma IL-6 levels, and an association with systemic-onset juvenile chronic arthritis. J Clin Invest. 1998;102(7):1369-1376.[18] Jones KG, Brull DJ, Brown LC, et al. Interleukin-6 (IL-6) and the prognosis of abdominal aortic aneurysms. Circulation. 2001;103(18): 2260-2265.[19] Zhai R, Liu G, Yang C, et al, Christiani DC. The G to C polymorphism at -174 of the interleukin-6 gene is rare in a Southern Chinese population.Pharmacogenetics. 2001;11(8):699-701.[20] Lim CS, Zheng S, Kim YS, et al.The -174 G to C polymorphism of interleukin-6 gene is very rare in koreans. Cytokine. 2002;19(1):52-54.[21] Toutouzas K,Klettas D,Anousakis-Vlachochristou N,et al.The -174 G>C Interleukin-6 Gene Polymorphism is Associated with Angiographic Progression of Coronary Artery Disease in a 4-Year period. Hellenic J Cardiol.2017;58(1):80-86.[22] 陈俊飞. IL-6基因-572C/G位点与-634C/G位点系同一位点的分析[J]. 科教导刊,2012,(6):224-225.[23] Tang RG, Wei YS, Chen HM, et al. Serum level and genotype of interleukin-6 in patients with esophageal cancer.Zhonghua yi xue za zhi.2007;87(16):1126-1128.[24] Saijo Y,Yoshioka E,Fukui T,et al.Effects of the Interaction between Interleukin-6 -634C/G Polymorphism and Smoking on Serum C-Reactive Protein Concentrations.Hypertens Res. 2007;30(7): 593-599. |