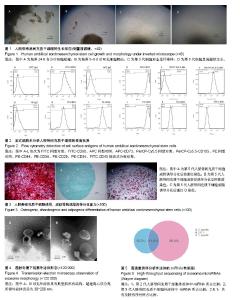
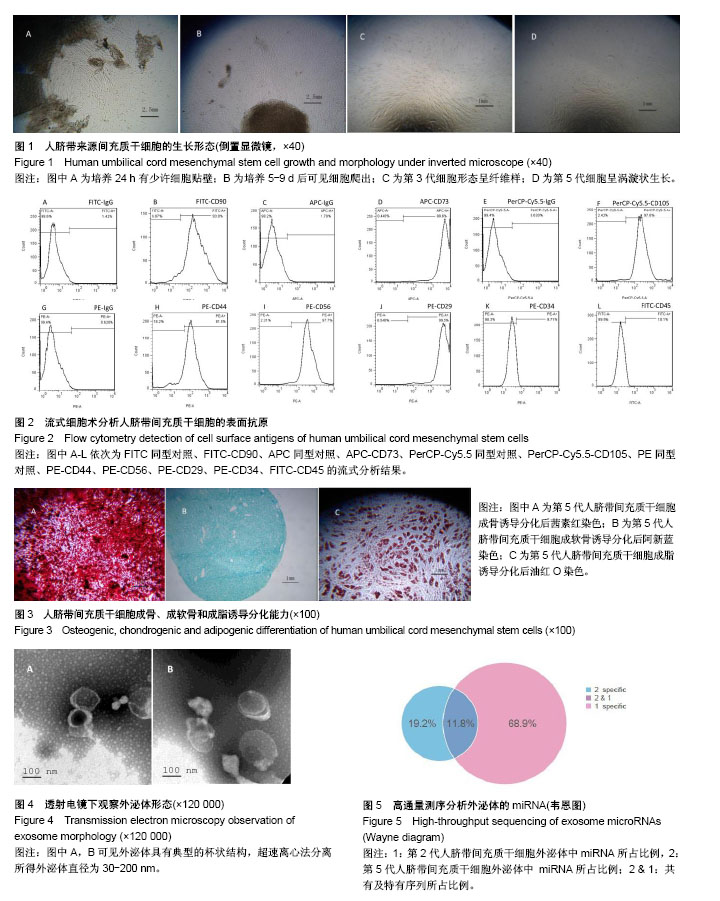
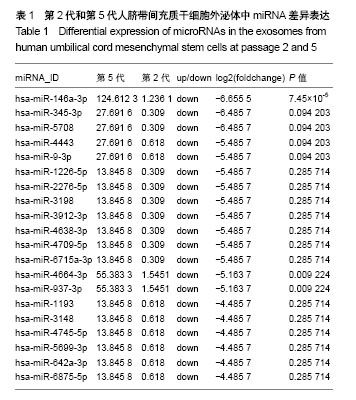
| [1] Katsha AM, Ohkouchi S, Xin H, et al. Paracrine factors of multipotent stromal cells ameliorate lung injury in an elastase-induced emphysema model. Mol Ther. 2011;19(1): 196-203.[2] Spees JL, Olson SD, Ylostalo J, et al. Differentiation, cell fusion, and nuclear fusion during ex vivo repair of epithelium by human adult stem cells from bone marrow stroma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003;100(5):2397-2402.[3] Caplan AI, Dennis JE. Mesenchymal stem cells as trophic mediators. J Cell Biochem. 2006;98(5):1076-1084.[4] Camussi G, Deregibus MC, Bruno S, et al. Exosomes/ microvesicles as a mechanism of cell-to-cell communication. Kidney Int. 2010;78(9):838-848.[5] 刘雨思,王凤昌,夏海雄,等.不同代次人脐带间充质干细胞的生物学特性及分化[J].中国组织工程研究, 2017, 21(13): 2015-2022.[6] 苏晓霞,廖立,金岩,等.体外传代对人脐带间充质干细胞生物学特性的影响[J].口腔生物医学, 2015, 6(3): 143-149.[7] Shi S, Yu L, Zhang T, et al. Smad2-dependent downregulation of miR-30 is required for TGF-β-induced apoptosis in podocytes. PLoS One. 2013;8(9):e75572.[8] Lorenzen JM, Thum T. Circulating and urinary microRNAs in kidney disease. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2012;7(9):1528-1533.[9] Kim HS, Choi DY, Yun SJ, et al. Proteomic analysis of microvesicles derived from human mesenchymal stem cells. J Proteome Res. 2012;11(2):839-849.[10] Paolini L, Zendrini A, Di Noto G, et al. Residual matrix from different separation techniques impacts exosome biological activity. Sci Rep. 2016;6:23550.[11] Lu LF, Boldin MP, Chaudhry A, et al. Function of miR-146a in controlling Treg cell-mediated regulation of Th1 responses. Cell. 2010;142(6):914-929.[12] 郭鹏辉,杜艳蕾,聂玉强. miRNA-191在胃癌组织中的表达[J]. 广东医学, 2012, 33(11): 1560-1562.[13] Elyakim E, Sitbon E, Faerman A, et al. hsa-miR-191 is a candidate oncogene target for hepatocellular carcinoma therapy. Cancer Res. 2010;70(20):8077-8087.[14] Okamoto K, Ishiguro T, Midorikawa Y, et al. miR-493 induction during carcinogenesis blocks metastatic settlement of colon cancer cells in liver. EMBO J. 2012;31(7):1752-1763.[15] Ueno K, Hirata H, Majid S, et al. Tumor suppressor microRNA-493 decreases cell motility and migration ability in human bladder cancer cells by downregulating RhoC and FZD4. Mol Cancer Ther. 2012;11(1):244-253.[16] Tijsen AJ, Creemers EE, Moerland PD, et al. MiR423-5p as a circulating biomarker for heart failure. Circ Res. 2010;106(6): 1035-1039.[17] Li J, Wang Y, Luo J, et al. miR-134 inhibits epithelial to mesenchymal transition by targeting FOXM1 in non-small cell lung cancer cells. FEBS Lett. 2012;586(20):3761-3765. |