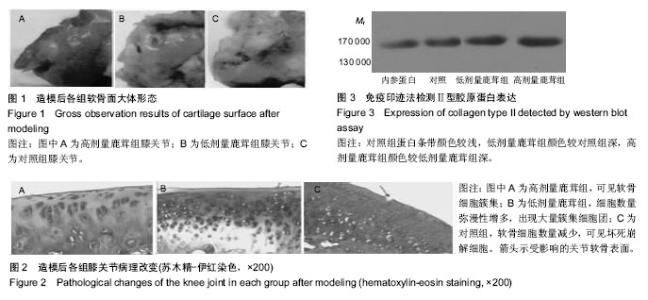
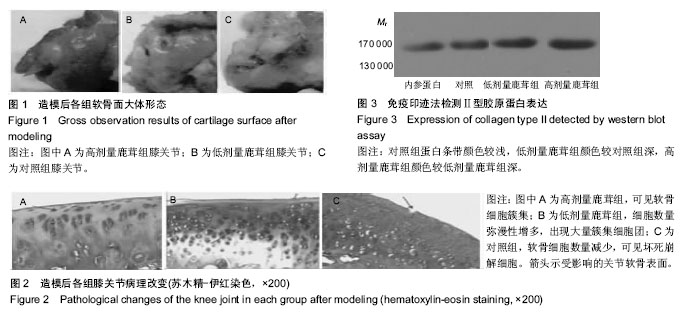
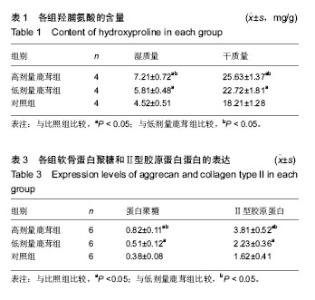
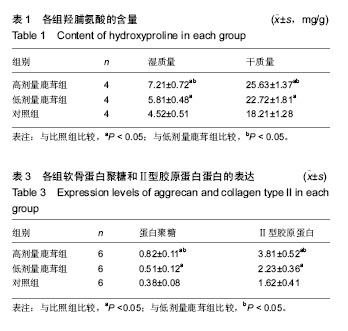
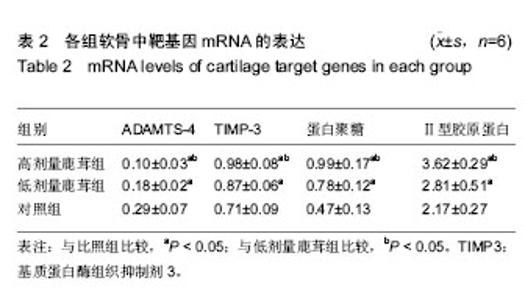
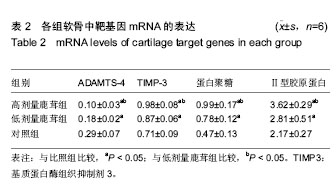
| [1] 田雪秋.骨关节炎相关危险因素研究进展[J].中国社区医师,2016, 32(15):14-17.[2] 刘康宝.中老年膝骨关节炎发病的相关因素分析[J].世界最新医学信息文摘,2015,15(31):6-8.[3] 尹丽.中老年膝骨关节炎发病的相关因素分析[J].吉林医学,2015, 36(18):4139-4141.[4] Li J, Anemaet W, Diaz MA, et al. Knockout of ADAMTS5 does not eliminate cartilage aggrecanase activity but abrogates joint fibrosis and promotes cartilage aggrecan deposition in murine osteoarthritis models. J Orthop Res. 2011;29(4): 516-522.[5] 朱剑,黄烽,张一平.类风湿关节炎患者蛋白聚糖aggrecan+G1区特异性T细胞诱导SCID小鼠产生膝关节炎的实验研究[J].解放军医学杂志,2006,31(8):787-790.[6] 周惠琼,钱宏伟,杨文芳.外周血蛋白聚糖代谢片段检测水平与类风湿关节炎影像学进展Sharp评分的相关性[J].中华风湿病学杂志,2017,21(3):172-178.[7] 杜国辉,屈爱存,陈建英.透明质酸对关节软骨蛋白聚糖aggrecan的影响[J].中国生化药物杂志,2011,32(2):125-8.[8] 高宗强,郭雄.透明质酸对体外培养大骨节病软骨细胞Ⅱ型胶原和聚集蛋白聚糖mRNA表达的影响[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009,13(46):9061-9066.[9] 周惠琼,张奉春.肿瘤坏死因子-α和白细胞介素-1β对人骨关节炎软骨细胞蛋白聚糖代谢的影响[J].中华风湿病学杂志, 2008, 12(2): 83-88.[10] Stambas J, Stanton H, Rogerson FM, et al. ADAMTS5 is the major aggrecanase in mouse cartilage in vivo and in vitro. PLoS Biol.2005;434(7033):648-652.[11] 孙志涛.不同方法提取SD大鼠膝关节软骨组织的总RNA[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(51):8201-8205.[12] 娄思权.骨关节炎的病理与发病因素[J].中华骨科杂志, 1996, 16(1):56-60.[13] 谷艳超.骨关节炎发病机制和治疗的研究进展[J].中国骨与关节杂志,2016,5(10):770-774.[14] 安丙辰,王有.不同强度张应力刺激影响关节软骨细胞Ⅱ型胶原和聚集蛋白聚糖mRNA表达的研究[J].中华关节外科杂志, 2010, 4(3):362-368.[15] 陈孟交.丹紫康膝冲剂对兔膝骨性关节炎软骨含水率及羟脯氨酸影响的研究[J].湖南中医药大学学报,2012,32(1):20-3.[16] 王坤.T140靶向阻断SDF-1%2fCXCR4信号通路对豚鼠关节软骨Ⅱ型胶原蛋白及聚集蛋白聚糖的影响[J].中国运动医学杂志, 2016,36(1):23-27.[17] 董琪.黄芪桂枝五物汤对肩周炎兔模型羟脯氨酸与总蛋白含量测定的实验研究[J].陕西中医,2015,36(8):1081-1083.[18] 陈喜德,宋丽君.骨关节炎SD大鼠关节软骨中蛋白多糖与YKL-40的相关性[J].重庆医学,2016,43(10):1214-1218.[19] van den Boom R, Brama PA, Kiers GH, et al. Assessment of the effects of age and joint disease on hydroxyproline and glycosaminoglycan concentrations in synovial fluid from the metacarpophalangeal joint of horses. Am J Vet Res. 2004; 65(3):296-302.[20] Smith SM, Shu C, Melrose J. Comparative immunolocalisation of perlecan with collagen II and aggrecan in human foetal, newborn and adult ovine joint tissues demonstrates perlecan as an early developmental chondrogenic marker. Histochem Cell Biol. 2010;134(3): 251-263.[21] 刘晓斌,候瑞.软硬食性对生长早期小鼠颞下颌关节髁突软骨中Aggrecan与ADAMTS-5表达的影响[J].医学研究杂志, 2016, 45(6):161-164.[22] 李彦林.体外阻断基质细胞衍生因子1/CXC趋化因子受体4信号通路后人关节软骨组织Ⅱ型胶原和聚集蛋白聚糖的表达[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(46):8607-8611.[23] Feng J, Gu Z, Lin X, et al. Postnatal development of type II collagen and aggrecan mRNA expression in a rabbit craniomandibular joint. Anat Rec (Hoboken). 2010;293(9): 1574-1580.[24] Azadi M, Nia HT, Gauci SJ, et al. Wide bandwidth nanomechanical assessment of murine cartilage reveals protection of aggrecan knock-in mice from joint-overuse. J Biomech.2016;49(9):1634-1640.[25] 杜清峰,张海宁.慢病毒介导的aggrecanase-2+shRNA转染对类风湿关节炎患者软骨细胞aggrecan的影响[J].中华骨科杂志, 2014,34(9):936-945.[26] 袁红,陈榕.平衡针灸对肩周炎模型兔转化生长因子β1、前列腺素+E2、羟脯氨酸影响的实验研究[J].环球中医药, 2015,8(1): 42-46.[27] 牛维.单味药鹿茸调控大鼠骨关节炎软骨组织Smad2_3表达的研究[J].中国中西医结合杂志,2014,34(2):209-214.[28] 牛维.单味中药鹿茸调控骨关节炎软骨组织TGF-β1表达的研究[J].时珍国医国药,2014,25(3):528-532.[29] 牛维.鹿茸归经与早期骨关节炎软骨靶器官TGF_受体的相关性研究[J].中华中医药杂志,2014,29(11):3626-3630. |