Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (15): 3760-3771.doi: 10.12307/2026.733
Previous Articles Next Articles
Finite element analysis of combined fixation of Pauwels type III femoral neck fracture with posteromedial bone defects of varying degrees using a medial support plate
Yusufu·Reheman1, 2 , Mutalipu·Silamujiang2 , Alimujiang·Yusufu1, 2 , Zhang Ziyi 1, 2 , Ran Jian2
- 1The Sixth Clinical Medical College, Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830054, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China; 2First Department of Orthopedics and Traumatology, the Sixth Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830002, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China
-
Accepted:2025-09-06Online:2026-05-28Published:2025-11-05 -
Contact:Ran Jian, Chief physician, Master’s supervisor, First Department of Orthopedics and Traumatology, the Sixth Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830002, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Yusufu·Reheman, Master candidate, The Sixth Clinical Medical College, Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830054, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China; First Department of Orthopedics and Traumatology, the Sixth Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830002, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:Natural Science Foundation Cultivation Program of Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region, No. LFYKYZXJJ2024015 (to MS)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Yusufu·Reheman , Mutalipu·Silamujiang , Alimujiang·Yusufu , Zhang Ziyi , Ran Jian. Finite element analysis of combined fixation of Pauwels type III femoral neck fracture with posteromedial bone defects of varying degrees using a medial support plate[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(15): 3760-3771.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
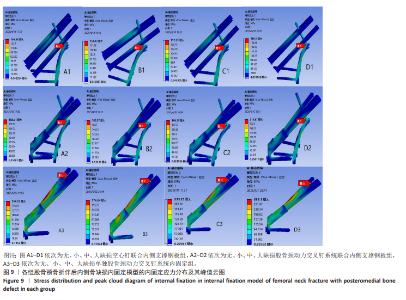
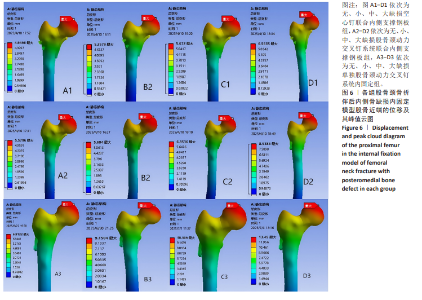
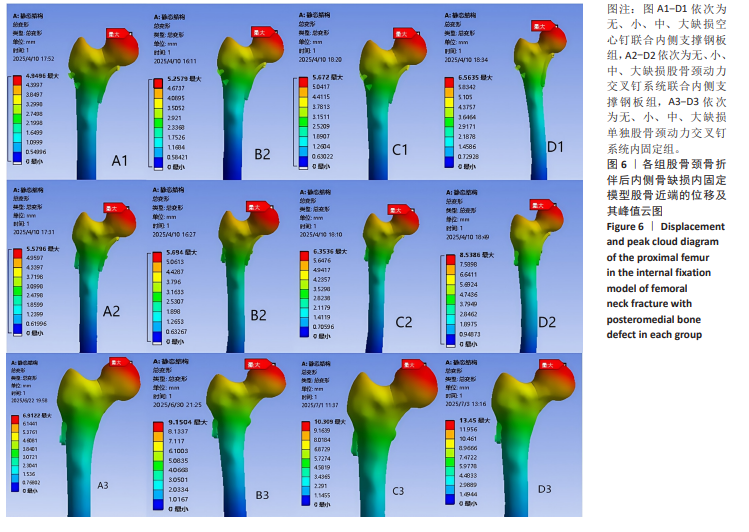
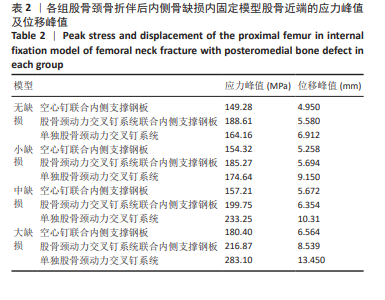
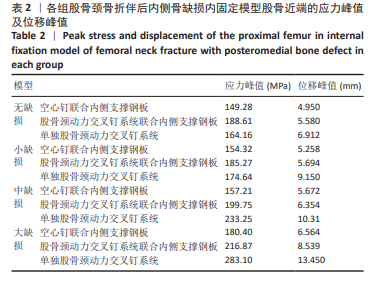
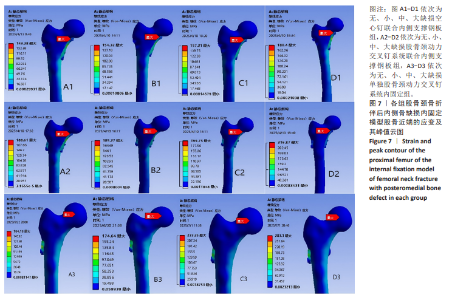
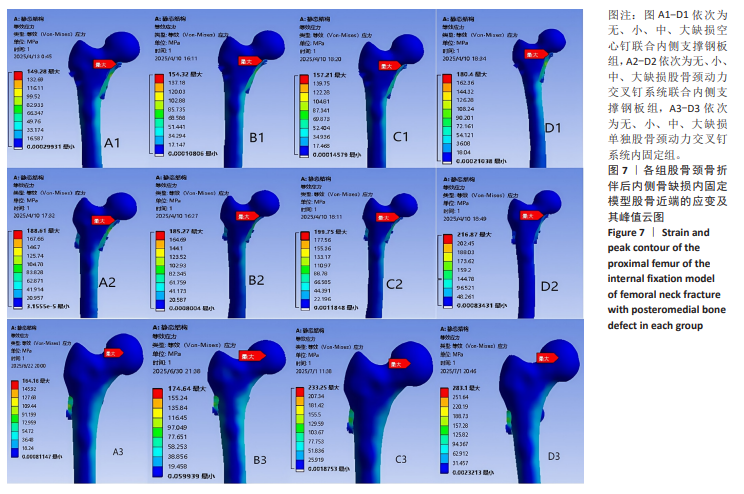
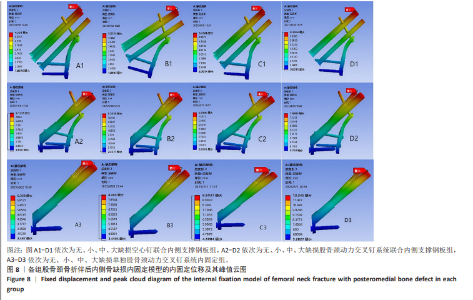
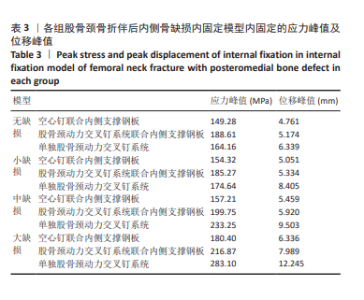
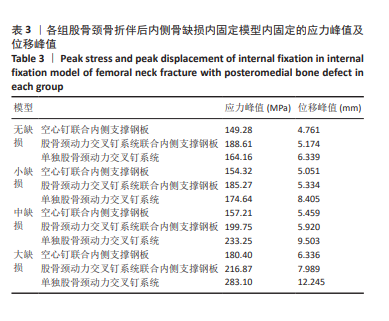
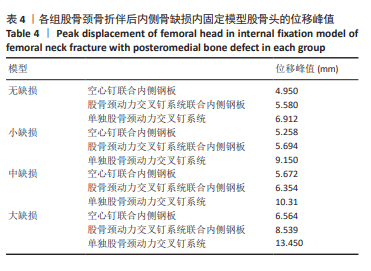
2.4 内固定应力分布及峰值 在空心钉及股骨颈动力交叉钉系统联合钢板模型中内固定应力峰值都集中于钢板近端螺钉与钢板贴股骨头的交接区域。与股骨近端应力分布一样,相同缺损程度下空心钉联合钢板组应力峰值都比其余两组内固定模型低。空心钉联合内侧支撑钢板组与股骨颈动力交叉钉系统联合内侧支撑钢板组应力主要分布于钢板与近端螺钉交接近骨折线一侧,单独股骨颈动力交叉钉系统组应力峰值在主钉顶部,而在防旋钉中部也有较大应力分布区域。可看出无论是空心钉还是股骨颈动力交叉钉系统,联合内侧支撑钢板实现了较优的应力分散效果,尤其空心钉与内侧支撑钢板组合时效果更明显、应力更分散,同时相对于空心钉联合内侧支撑钢板组,股骨颈动力交叉钉系统联合内侧支撑钢板组在内侧钢板近端螺钉上呈现出较强的应力集中。详见图9及表3。"

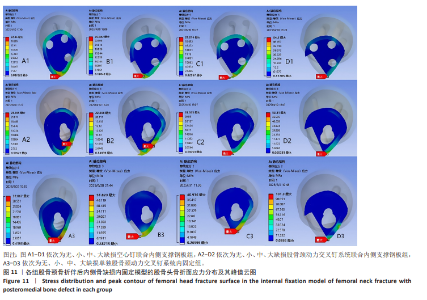
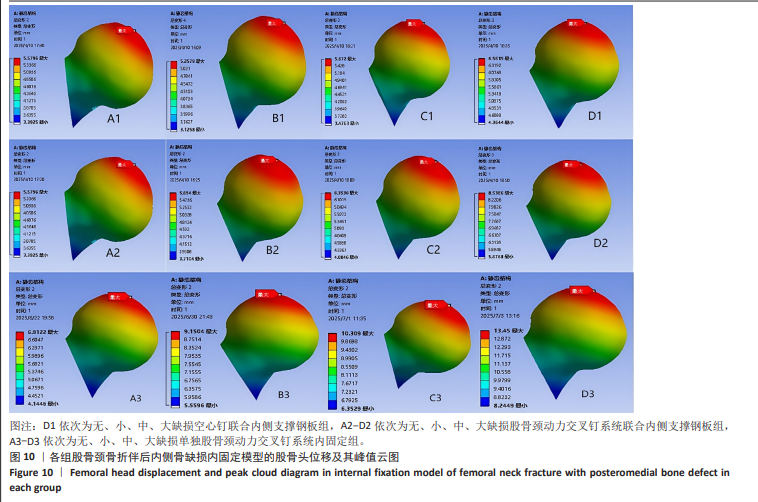
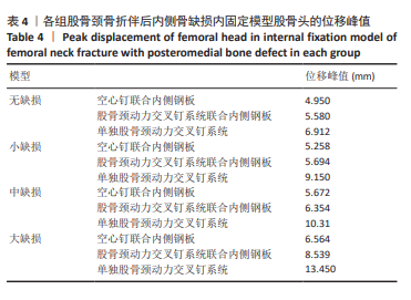
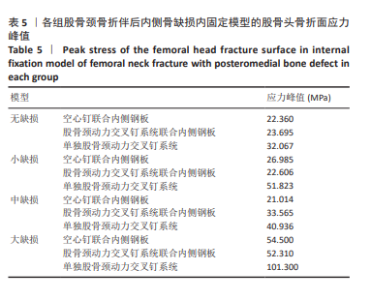
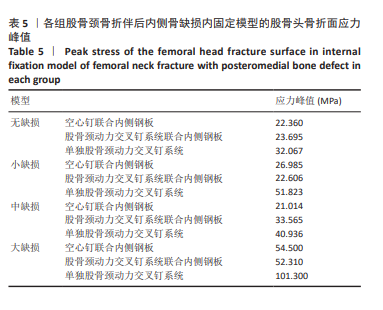
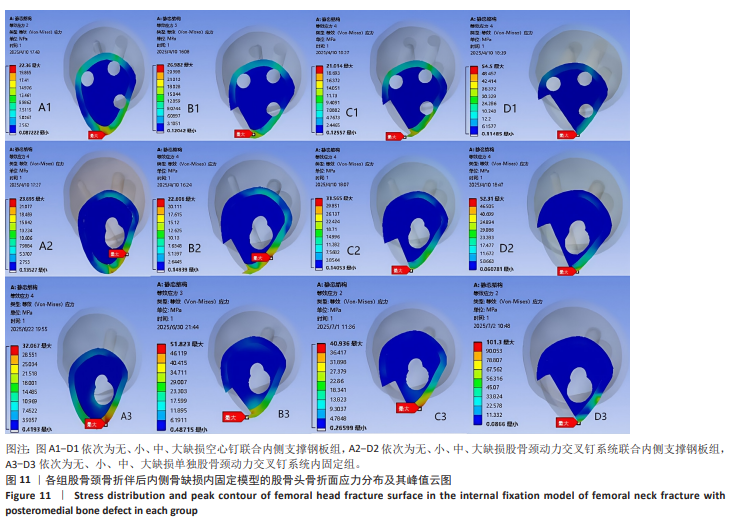
2.6 股骨头骨折面应力及峰值 在股骨头应力峰值方面各模型之间未表现出明显的递增或递减的趋势。在应力分布云图中可看出大缺损模型表现出很明显的应力集中现象。在空心钉联合内侧支撑钢板组中应力分布较分散,应力峰值都主要集中在股骨颈正下方区域,应力分布对于冠状面而言对称。而股骨颈动力交叉钉系统联合内侧支撑钢板组应力峰值虽然在小缺损、大缺损模型中比空心钉联合内侧支撑钢板组稍小,但分布不对称,呈现出较大隐患。股骨颈动力交叉钉系统联合内侧支撑钢板组与单独股骨颈动力交叉钉系统组中最大应力峰值分布在股骨颈正下方或下前方,应力主要分布于冠状面前侧的部分,而在后侧基本无应力分布,这有可能因应力分散不均匀而带来股骨颈内翻畸形的风险,尤其在单独股骨颈动力交叉钉系统固定组中、大缺损的模型中应力峰值过高,则可说明后期内翻塌陷概率也比联合钢板固定要高很多[40-41]。详见表5,图11。"
| [1] GAO Y, MA T, CHANG X, et al. Femoral neck system (FNS) versus 4 cannulated compression screws (CCSs) in the treatment of young patients with Pauwels type III femoral neck fracture: a retrospective comparative study. J Orthop Surg Res. 2025;20:65. [2] 魏更生. 青壮年股骨颈骨折的Pauwels分型及治疗策略[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2011,19(16):1398-1400. [3] 庄凯伦,武敬沂,白天模,等. 青壮年Pauwels Ⅲ型股骨颈骨折内固定术及术后并发症研究进展[J]. 中华骨与关节外科杂志,2025, 18(2):184-188. [4] CHEWAKIDAKARN C, YUENYONGVIWAT V. Comparison of bone mineral density at hip and lumbar spine in patients with femoral neck fractures and pertrochanteric fractures. Ortop Traumatol Rehabil. 2021;23(1): 45-49. [5] 初哲峰,李巍,赵军民. 人工半髋关节置换术和空心螺钉内固定治疗老年PauwelsⅠ型稳定型股骨颈骨折[J]. 中国现代手术学杂志, 2021,25(6):439-443. [6] MEDDA S, SNOAP T, CARROLL EA. Treatment of young femoral neck fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2019;33(Suppl 1):S1-S6. [7] HANCIOGLU S, GEM K, TOSYALI HK, et al. Given the encouraging results of biomechanical studies on femoral neck fractures, are locking plates more safe? Acta Orthop Belg. 2024;90(2):279-285. [8] 马季,张玉强,智晓东,等. 3种内固定方式治疗青壮年股骨颈骨折的有限元分析[J]. 临床骨科杂志,2023,26(6):890-895. [9] 季群博. 动力交叉钉系统与空心钉内固定治疗PauwelsⅢ型股骨颈骨折的有限元分析[D]. 延边:延边大学,2024. [10] 许翔宇,周方,田耘,等. 股骨颈动力交叉钉系统与动力髋螺钉固定治疗股骨颈骨折的早期疗效比较[J]. 中华创伤骨科杂志,2021, 23(9):754-760. [11] STOFFEL K, ZDERIC I, GRAS F, et al. Biomechanical evaluation of the femoral neck system in unstable Pauwels III femoral neck fractures: a comparison with the dynamic hip screw and cannulated screws. J Orthop Trauma. 2017;31(3):131-137. [12] 葛双雷,王雪飞,刘亮,等. 股骨颈动力交叉钉系统联合支撑空心螺钉对伴后内侧粉碎的中青年股骨颈骨折的疗效研究[J]. 中华医学杂志,2023,103(21):1631-1637. [13] 木塔力普·斯拉木江,玉苏甫·热合曼,任政,等. 三种内固定方法治疗Pauwels Ⅲ型股骨颈骨折伴前内侧骨缺损的有限元分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2025,29(27):5721-5727. [14] ZHU XZ, HAN CX, AI ZS, et al. A quantitative study of bone defects in displaced femoral neck fractures based on virtual reduction techniques. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2022;222:106958. [15] 钱炜,喻爱喜,漆白文,等. 股骨颈骨折CT影像分析及临床意义[J]. 中华实验外科杂志,2013,30(12):2731-2732. [16] 梅炯. 重视对股骨颈骨折的骨缺损评估以优化手术方案决策[J]. 中国骨伤,2023,36(3):199-203. [17] FELTON J, SLOBOGEAN GP, JACKSON SS, et al. Femoral neck shortening after hip fracture fixation is associated with inferior hip function: results from the FAITH trial. J Orthop Trauma. 2019;33(10):487-496. [18] KANE C, JO J, SIEGEL J, et al. Can we predict failure of percutaneous fixation of femoral neck fractures? Injury. 2020;51(2):357-360. [19] 陈宇峰. Pauwels Ⅲ型股骨颈骨折内固定选择策略的研究进展[J]. 河北医科大学学报,2022,43(1):108-113. [20] 王义冬. 空心钉附加内侧支撑钢板与FNS内固定治疗Pauwels Ⅲ型股骨颈骨折的临床观察[J]. 实用中西医结合临床,2024,24(18): 89-92. [21] ZHAN S, JIANG D, XU J, et al. Influence of the proximal screws of buttress plates on the stability of vertical femoral neck fractures: a finite element analysis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2020;21(1):842. [22] MCGARRY L, ROTARU J, GUNARATNE R, et al. Medial Buttress Plate Use in Neck of Femur Fracture Fixations: A Systematic Review. Injury. 2025;56(2):112160. [23] 倪明,孙万驹,叶晔. 内侧支撑钢板辅助固定治疗青壮年股骨颈骨折的研究进展[J]. 中国修复重建外科杂志,2020,34(11):1454-1457. [24] 朱浩然,肖伟,向强,等.股骨颈Pauwels Ⅰ型骨折空心钉内固定治疗的有限元分析[J].创伤外科杂志,2024,26(10):739-744. [25] 章浩伟,秦燕韩,刘颖.不同内固定方式治疗股骨颈骨缺损骨折的静力学与模态分析[J].北京生物医学工程,2024,43(4):352-360. [26] 谢小平,毕淞淇,宋庆旭,等.经皮加压钢板与股骨颈系统固定Pauwels Ⅲ型股骨颈骨折的生物力学研究[J].医用生物力学,2024, 39(S1):260. [27] 齐远博,徐成,李建涛,等.基于计算机辅助设计改良的内固定装置应用于Pauwels Ⅲ型股骨颈骨折的有限元分析[J].医用生物力学,2024,39(S1):551. [28] 张成宝,余润泽,喻德富,等. 有限元分析股骨颈骨折伴下后方不同程度骨缺损空心螺钉内固定后的稳定性[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2020,24(18):2799-2804. [29] 吐松江•玉苏普,阿里木江•玉素甫,冉建. 不同位置的股骨颈动力交叉钉系统联合空心螺钉治疗不稳定型股骨颈骨折的近期疗效分析[J]. 创伤外科杂志,2024,26(7):534-541. [30] 袁高翔,张伟滨.有限元分析在骨骼肌肉系统模型材料特性研究中的应用[J].国际骨科学杂志,2011,32(6):352-355+366. [31] HAMIDI S, KHOSRAVIFARD A, HEMATIYAN MR, et al. A comparative mechanical study of two types of femur bone implant using the finite element method. Int J Numer Method Biomed Eng. 2021;37(6):e3459. [32] HUANG Q, ZHANG C, BAI H, et al. Biomechanical evaluation of two modified intramedullary fixation system for treating unstable femoral neck fractures: A finite element analysis. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023;11:1116976. [33] 王颖,马剑雄,柏豪豪,等.股骨颈骨折术后股骨在不同运动负荷条件下的生物力学研究[J].医用生物力学,2024,39(S1):46. [34] 马路遥,孙雪傲,谭青骏,等.增加一枚横向螺钉固定PauwelsⅢ型股骨颈骨折的有限元分析[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2025, 39(5):584-591. [35] 李双,李凯,袁云华,等.PauwelsⅢ型股骨颈骨折非解剖复位下不同空心钉内固定稳定性的有限元分析[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2025,40(2):174-177. [36] MAHAPATRA B, PAL B. Biomechanical analysis of various internal fracture fixation devices used for treating femoral neck fractures: A comparative finite element analysis. Injury. 2024;55(10):111717. [37] 程子文.闭合复位经钉道植骨治疗股骨颈骨折的临床研究[D].石家庄:河北医科大学,2024. [38] 刘诚,赵领财,李永奖.空心钉联合内侧支撑钢板固定治疗中青年Pauwels Ⅲ型股骨颈骨折[J].临床骨科杂志,2024,27(6):829-833. [39] 董志军,刘福尧,潘圆,等.空心加压螺钉联合内侧支撑钢板对Pauwells Ⅲ型股骨颈骨折患者的应用及对患者下肢功能的影响[J].黔南民族医专学报,2024,37(2):135-139. [40] 刘英科,马文龙,田可为,等.三种手术方式治疗中青年PauwelsⅢ型股骨颈骨折的疗效比较[J].中国修复重建外科杂志, 2024,38(4):412-421. [41] 张伟,陈宇浩,吴沼锋,等.不同内固定方式治疗Pauwels Ⅲ型股骨颈骨折术后并发症发生率的网状Meta分析[J].现代医学, 2024,52(3):369-378. [42] 张登君,魏杰,王根伟,等.股方肌骨瓣移植联合内固定治疗青壮年股骨颈骨折有限元分析[J].实用骨科杂志,2021,27(3):235-238. [43] 苏志豪,谭宏莉,徐子环,等. Pauwels Ⅲ型股骨颈骨折骨缺损不同内固定方案的生物力学分析[J]. 中国骨伤,2023,36(3):255-261. [44] GUIMARÃES JAM, ROCHA LR, NORONHA ROCHA TH, et al. Vertical femoral neck fractures in young adults: a closed fixation strategy using a transverse cancellous lag screw. Injury. 2017;48 Suppl 4:S10-S16. [45] BOUKEBOUS B, FLOUZAT-LACHANIETTE CH, DONADIO J, et al. Femoral offset loss and internal arch restoration defect are correlated with intramedullary nail cut-out complications after pertrochanteric fractures: a case-control study. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2019; 29(7):1451-1460. [46] KORAMAN E, IYETIN Y, OZYAMAN O, et al. A biomechanical comparison of three fixation methods for unstable femoral neck fractures with medial calcar defect. J Orthop Surg Res. 2023;18(1):614. [47] HUANG ZY, SU YH, HUANG ZP, et al. Medial buttress plate and allograft bone‐assisted cannulated screw fixation for unstable femoral neck fracture with posteromedial comminution: a retrospective controlled study. Orthop Surg. 2022;14(5):911-918. [48] 赵鲁京,吴倩,赵刚,等.空心钉复合内侧支撑钢板固定Pauwels Ⅲ型股骨颈骨折[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2023,31(6):504-509. [49] XIONG WF, CHANG SM, ZHAN YQ, et al. Inferior calcar buttress reduction pattern for displaced femoral neck fractures in young adults: A preliminary report and an effective alternative. J Orthop Surg Res. 2019;14:1-8. [50] MIR H, COLLINGE C. Application of a medial buttress plate may prevent many treatment failures seen after fixation of vertical femoral neck fractures in young adults. Med Hypotheses. 2015;84(5):429-433. |
| [1] | Chen Huiting, Zeng Weiquan, Zhou Jianhong, Wang Jie, Zhuang Congying, Chen Peiyou, Liang Zeqian, Deng Weiming. Tail anchoring technique of vertebroplasty in treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures with intravertebral cleft: a finite element analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(9): 2145-2152. |
| [2] | Cheng Qisheng, Julaiti·Maitirouzi, Xiao Yang, Zhang Chenwei, Paerhati·Rexiti. Finite element analysis of novel variable-diameter screws in modified cortical bone trajectory of lumbar vertebrae [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(9): 2162-2171. |
| [3] | Liu Jiafu, Ren Ruxia, Liao Zhouwei, Zhou Xiali, Wu Yihong, Zhang Shaoqun. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of cervical spine biomechanical characteristics in a rat model of cervical vertigo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(9): 2182-2190. |
| [4] | Zhang Zizheng, Luo Wang, Liu Changlu. Application value of finite element analysis on unicompartmental knee arthroplasty for medial knee compartmental osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(9): 2313-2322. |
| [5] | Zhao Feifan, Cao Yujing. Risk factors and coping strategies of internal fixation failure in treatment of intertrochanteric fracture with proximal femoral nail antirotation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(9): 2323-2333. |
| [6] | Liu Wenlong, Dong Lei, Xiao Zhengzheng, Nie Yu. Finite element analysis of tibial prosthesis loosening after fixed-bearing unicompartmental knee arthroplasty for osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(9): 2191-2198. |
| [7] | Zheng Wangyang, Fei Ji, Yang Di, Zhao Lang, Wang Lingli, Liu Peng, Li Haiyang. Finite element analysis of the force changes of the supraspinatus tendon and glenohumeral joint during the abduction and flexion of the humerus [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(9): 2199-2207. |
| [8] | Cai Qirui, Dai Xiaowei, Zheng Xiaobin, Jian Sili, Lu Shaoping, Liu Texi, Liu Guoke, Lin Yuanfang. Mechanical effects of Long’s traction orthopedic method on cervical functional units: quantitative analysis of biomechanical model of head and neck [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(9): 2208-2216. |
| [9] | Rao Jingcheng, Li Yuwan, Zheng Hongbing, Xu Zhi, Zhu Aixiang, Shi Ce, Wang Bing, Yang Chun, Kong Xiangru, Zhu Dawei. Biomechanical differences between the new proximal femoral stable intramedullary nail and traditional intramedullary nail#br# [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(9): 2217-2225. |
| [10] | Chen Long, Wang Xiaozhen, Xi Jintao, Lu Qilin. Biomechanical performance of short-segment screw fixation combined with expandable polyetheretherketone vertebral body replacement in osteoporotic vertebrae [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(9): 2226-2235. |
| [11] | Wu Yanting, Li Yu, Liao Jinfeng. Magnesium oxide nanoparticles regulate osteogenesis- and angiogenesis-related gene expressions to promote bone defect healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 1885-1895. |
| [12] | Zheng Xuying, Hu Hongcheng, Xu Libing, Han Jianmin, Di Ping. Stress magnitude and distribution in two-piece cement-retained zirconia implants under different loading conditions and with varying internal connection shapes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 1979-1987. |
| [13] | Liu Dawei, Cui Yingying, Wang Fanghui, Wang Zixuan, Chen Yuhan, Li Yourui, Zhang Ronghe. Epigallocatechin gallate-mediated bidirectional regulation of reactive oxygen species and its application in nanomaterials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 2101-2112. |
| [14] | Ding Yifan, Yin Wenjie, Zhang Li, Yuan Shuya, Sun Guoju, Zhang Naili, Zhao Dongmei, Ma Lina. Repair of segmental bone defect of rabbit radius by decalcified bone matrix loaded with adipose-derived stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(7): 1679-1686. |
| [15] | Zhong Caihong, Xiao Xiaoge, Li Ming, Lin Jianhong, Hong Jing. Biomechanical mechanism of sports-related patellar tendinitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1417-1423. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||