Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (23): 5934-5942.doi: 10.12307/2026.311
Previous Articles Next Articles
Animal experimental study on the treatment of lumbar intervertebral disc degeneration with Chinese herbal compound: species selection, modeling method and drug administration
Xie Ziying1, Li Songbo1, 2, Li Jianwen2, Yin Yuchao2, Zheng Baichuan1, Hu Chengshang2
- 1The First Clinical School of Medicine, Guangdong Medical University, Zhanjiang 524023, Guangdong Province, China; 2The Tenth Affiliated Hospital of Southern Medical University (Dongguan People’s Hospital), Dongguan Key Laboratory of Basic, Clinical and Digital Research on Orthopedic Common Bone Diseases, Dongguan 523069, Guangdong Province, China
-
Received:2025-04-12Accepted:2025-06-07Online:2026-08-18Published:2025-12-30 -
Contact:Li Songbo, MS, Chief physician, Professor, The First Clinical School of Medicine, Guangdong Medical University, Zhanjiang 524023, Guangdong Province, China; The Tenth Affiliated Hospital of Southern Medical University (Dongguan People’s Hospital), Dongguan Key Laboratory of Basic, Clinical and Digital Research on Orthopedic Common Bone Diseases, Dongguan 523069, Guangdong Province, China -
About author:Xie Ziying, MS candidate, Physician, The First Clinical School of Medicine, Guangdong Medical University, Zhanjiang 524023, Guangdong Province, China -
Supported by:Fundamental and Applied Basic Research Funds of Guangdong Province, No. 2021B1515140056 (to LSB); Dongguan Social Development Science and Technology Project, No. 20221800906282 (to LJW)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Xie Ziying, Li Songbo, Li Jianwen, Yin Yuchao, Zheng Baichuan, Hu Chengshang. Animal experimental study on the treatment of lumbar intervertebral disc degeneration with Chinese herbal compound: species selection, modeling method and drug administration[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(23): 5934-5942.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks

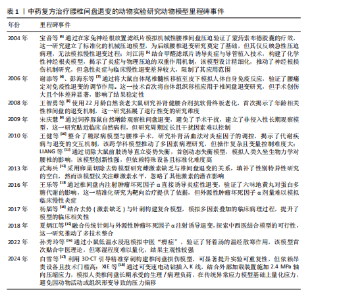
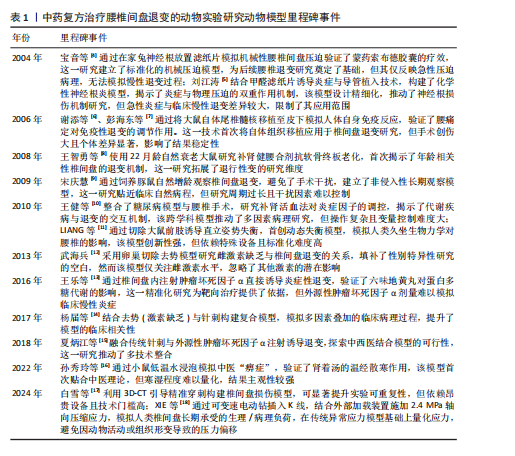
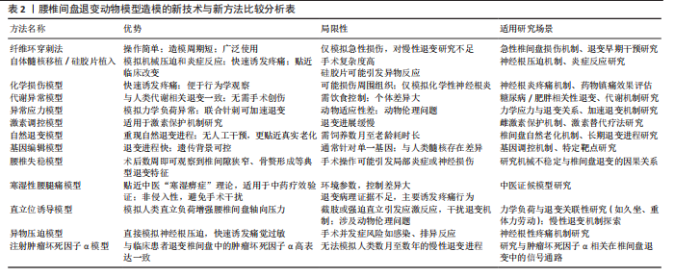
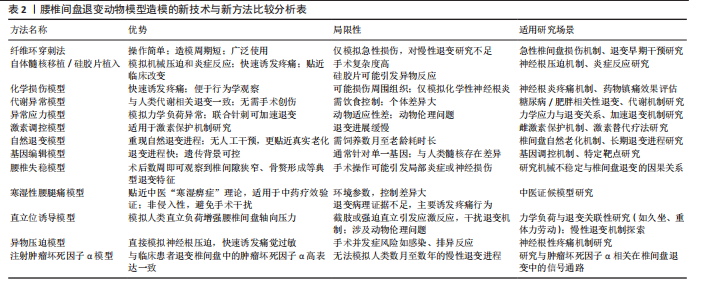
2.2.1 大鼠、沙鼠、豚鼠、小鼠模型 (1)纤维环穿刺模型:纤维环穿刺法对大鼠特定尾椎或腰椎进行急性损伤是最常用的模型,这种模型的构建方式简单,可以在直视下或X射线辅助下进行[19-64]。术后三四周即可观察到髓核细胞凋亡、蛋白多糖含量下降及胶原结构紊乱,出现明显椎间隙狭窄。为了增加造模的稳定性,白雪等[17]利用3D-CT引导精准穿刺构建椎间盘损伤模型,这种方法提升了实验可重复性,值得进一步推广。 (2)自体髓核移植/硅胶片植入:有研究者将髓核取出并移植到特定节段的椎旁肌肉或将特制硅胶片置于腰神经根[65-95],神经根压迫模型可诱发痛觉过敏,机械缩足阈值下降,造模后组织学显示神经根脱髓鞘和炎性细胞浸润,这种手术方法能更贴近临床腰椎间盘突出患者的病理过程,高度贴合临床腰椎间盘突出症的机械压迫和炎症反应。 (3)化学损伤模型:为进一步简化模型,探讨突出椎间盘对腰部神经刺激症状,姜国成[96]、罗才贵等[97]、刘洋等[98]将浸入甲醛或福尔马林溶液后滤纸置于腰神经根,构建化学损伤性神经根炎模型,这种方式聚焦神经根微循环变化且容易诱发大鼠疼痛刺激,易于行为学观察。 (4)代谢异常模型:由于手术器械选择及手术技巧各不相同,直接在腰椎间盘及其附属结构手术构建的大鼠椎间盘退变模型,造模的效果往往难以稳定。糖尿病和肥胖被认为是椎间盘退化的重要风险因素,高血糖可导致椎间盘组织细胞的早衰、凋亡及过度自噬。一些研究者给予大鼠或沙鼠实验室糖尿病饮食,成功加速椎间盘退变[99-104],椎间盘力学性能下降,脂质沉积导致氧化应激标志物升高,与人类肥胖相关性退变具有较高一致性。 (5)激素调控模型:雌激素被认为是人类椎间盘退变的保护性因素,大鼠中亦有此趋势。冯帅华等[105]通过去势操作降低雌激素水平以达到椎间盘退变目的。去势后6-12周髓核细胞分布不均匀,脊索细胞明显减少。 (6)异常应力模型:姚啸生等[106-108]截断大鼠前肢肱骨,迫使大鼠直立,以期增强腰椎间盘受到的应力诱导退变,直立姿势显著增加了腰椎间盘的垂直压力,模拟了人类因久坐、重体力劳动等不良姿势导致的慢性应力损伤。白雪等[17]通过双上肢去势联合椎间盘刺破诱导大鼠椎间盘退变,4周MRI显示退变早期征象,8周退变明显,能有效缩短造模时间。这类模型在模拟人类职业性腰椎病的病理机制方面具有较高价值,但由于截肢手术可能引发动物应激反应、降低动物生存质量,存在一定的伦理问题。 (7)自然退变模型:年龄是椎间盘退变的重要危险因素。王智勇等[8]发现22月龄大鼠与6月龄大鼠相比软骨终板血管芽相对面积显著缩小;朱立国等[109]倾向于使用椎间盘自发退变模型以更好地重现椎间盘自然退变进程,他们将健康雄性长爪沙鼠饲养至12月龄,发现其与2月龄沙鼠相比出现了与人类类似的椎间盘退行性改变。宋庆慧[9]创新性采用豚鼠作为实验动物,对不同月龄豚鼠椎间盘取材处理,发现椎间盘髓核蛋白多糖的含量随年龄增长呈降低趋势。自发退变模型耗时较长,且缺乏MRI等影像学证据,其有效性仍需进一步考究。 (8)基因编辑模型:作者注意到小鼠因遗传背景清晰、生命周期短、基因编辑技术成熟、实验成本低廉常作为基因敲除模型,敲除特定基因的转基因小鼠能够更便捷且稳定地产生衰老表征。付远飞[110]研究的14月龄sparc基因敲除小鼠、许勇等[111]繁育的缺氧诱导因子1α缺失小鼠、谢晚晴[112]繁育的软骨细胞条件性过表达β-catenin的基因修饰小鼠均能产生椎间盘退变表征,可加速退变进程,但因物种差异,与人类髓核细胞类型不同,这种结论需谨慎外推至人类。 2.2.2 新西兰兔模型 兔椎间盘周围存在小关节、肌肉、韧带,与大鼠、沙鼠、豚鼠、小鼠相比,解剖上同人类椎间盘同源性程度更高。在以兔为研究动物的实验设计中针刺模型依然应用最为广泛[113-125]。与大鼠针刺模型相似,这种急性损伤可能造成椎间盘短期退变明显,与临床中椎间盘退变的缓慢进程不符。在兔腰椎神经根处植入异物或直接诱发神经根炎也可很好地展现腰椎间盘突出病理过程[126-127]。异常机械负荷是椎间盘退行性变化的一个主要诱因,陈祖彦等[128]、蔡楚豪[129]通过破坏棘上、棘间韧带及部分关节囊造成兔腰椎失稳,改变腰椎力学结构。XIE等[18]则设计了一种新的装置,即使用螺钉棒穿过椎体,并对穿透脊柱的螺钉棒施加轴向载荷压力。吕存贤等[130]则通过给予兔背部1/10体质量横向应力实现这一过程。刘奕等[131]将兔固定在聚氯乙烯(PVC)管中,PVC管直立,采用自身重力对腰椎间盘加压。该模型操作简单、对动物损伤小,可作为替代针刺模型的选择。 2.2.3 大动物模型 大动物如犬类、山羊、绵羊、猪、非灵长类动物等的椎间盘空间较大,更便于手术操作,研究者们也设计了一系列椎间盘退变模型。使用大动物模型存在重大的伦理和费用问题,同时相对较低的样本量也是采用大动物研究的一个潜在局限性。研究中药复方往往需建立不同浓度的药物剂量分组以评估最佳药效剂量及药物毒性,相对少的样本量显然难以满足这一需求,因此在中药复方的体内实验中大动物模型未见报道。 2.3 中药复方递药系统构建及给药方式选择 2.3.1 口服给药与肠吸收 中药复方涵盖了传统的经典方剂、临床应用经验的方剂和现代创新的配方,并针对不同的治疗需求设计了相应的剂型。临床实践中通常经口给药,造模后动物给药也多采用该途径。可通过人和动物间体表面积换算不同动物给药等效剂量[132],给药周期5 d至8周不等,疗程与临床用药大体一致。口服中药主要通过小肠吸收,体内的单向肠道灌流实验能够有效地重现肠道的生存环境,该技术相对成熟,可用于测定肠道的吸收功能、肠道菌群的影响、药物的生物利用度以及肠道对各种物质的反应,这些信息可进一步指导制剂处方设计。有学者注意到肠道菌群在关节稳态中起重要作用,李艺璇等[47]的实验表明,人参固本口服液能调控肠道菌群微环境延缓椎间盘退变。口服途径给药剂型设计灵活,汤剂、丸剂、胶囊等可根据复方成分设计,能更好地适应不同需求。尽管存在部分成分经肝脏代谢后活性降低、容易受食物、胃肠动力及酸碱环境影响的缺点,但其在临床实践中更易被患者接受。 2.3.2 其他给药方式 透皮给药系统因具备持久释放、低毒性和无痛等显著特点而受到广泛关注。安娟[74]对椎间盘造模后的SD大鼠行铁包金巴布膏外敷治疗,发现可减少炎症因子的释放、降低神经功能评分,并影响核因子κB信号通路代谢,减轻腰椎间盘突出带来的不适症状。刘洋等[98]对造模后大鼠外敷复方南星蠲瘀软膏,大鼠下肢神经功能得到改善。透皮给药效果受渗透速率制约。刘岩路等[118]研究发现经中药敷贴治疗的兔椎间盘肿瘤坏死因子α表达下降,这种趋势在用药4-6周后显现。因此针对透皮给药系统的相关研究应致力于加快有效成分的皮肤渗透速率和增加其透皮吸收量,直肠给药避免了胃肠道的刺激,且药物不经过肠肝循环,能减少对肝脏的损害,部分中药复方栓剂可经此途径递送[96-97]。硬膜外注射复方制剂能很好地提高局部药物浓度,实现药物精准递送,在动物实验及临床实践中显现出良好的治疗效果[127]。这种操作具有侵入性风险,需严格无菌,否则可能引发感染或神经损伤,经这种方式给药的中药单体居多,使用中药复方需高度纯化,避免杂质引发不良反应。 对于需要验证临床现有的中药复方作用与机制,实验动物给药方式尽量与临床给药途径相同,以口服给药常见。需长期干预、局部炎症控制及神经功能改善的椎间盘退变模型可考虑中药复方透皮给药,需要注意给药体系设计,提高药物利用率。若针对急性局部症状缓解,则采用硬膜外注射方式,缩短给药进程。在未来动物实验中可结合现代透皮技术(如微针、离子导入)进一步提升疗效,并与口服给药联用以实现“局部+全身”协同治疗。 2.4 中药复方治疗腰椎间盘退变模型常用的疗效评价 2.4.1 影像学评价 PFIRRMANN等[133]开发了目前使用最广泛的基于MRI-T2WI成像的椎间盘分级系统,该分级系统侧重于椎间盘结构的特征变化(椎间盘信号强度、椎间盘结构、区分核和环的能力以及椎间盘高度),用于对人类或实验动物腰椎间盘退变状况进行半定量评估。改良Pfirrmann分级是在Pfirrmann分级的基础上将Ⅰ-Ⅴ级改良为1-8级,其中Ⅲ级根据不同的高信号强度细分为3、4级,Ⅳ级根据不同椎间盘高度分为5,6,7级,Ⅰ,Ⅱ,Ⅴ级分别对应改良后的1,2,8级[134-135]。MRI 还具有很高的肌肉软组织分辨率,可对椎旁肌肉的病理生理状态进行定量分析。尽管无法在X射线片上直接看到椎间盘高度指数,但它仍是腰椎间盘退变程度的有效表征[136],在诱导动物椎间盘退变之前和之后的某些时间点测量椎间盘高度指数也可以显示继发性退行性骨性改变。随着技术的进步,micro-CT等其他方式提供了更高的图像质量,用于检测椎间盘本身及其周围支撑结构(如椎体和小关节)更微小的变化。近年来人工智能和深度学习的发展促进了脊柱成像,包括椎骨和椎间盘的可视化,在诊断、手术结果、康复评估、生物力学、运动分析等方面提供了更加高效且准确的评估手段。 2.4.2 组织学评价 组织学评价受大型仪器制约相对较少,绝大部分研究对椎间盘或累及神经根的组织学特征进行评价。苏木精-伊红染色、番红固绿染色、Masson 染色椎间盘切片较为常见,这些方法提供了组织学上评估椎间盘退变程度的手段[136-138],有利于观察椎间盘退变病理变化,早期发现椎间盘的细胞损伤、退变和微小的结构变化,但因受到切片层次影响,对于椎间盘总体退变进程评估不及影像学方法,这种评价方式并不能完全代替影像学评估。 2.4.3 分子生物学评价 常见的生化、基因和蛋白质分析方法在中药复方治疗腰椎间盘退变研究中依旧适用。异常应力等因素刺激下,体内炎症递质会迅速增加并分泌到髓核组织中。在分解代谢酶如基质金属蛋白酶、含Ⅰ型血小板结合蛋白基序的解聚蛋白样金属蛋白酶(A disintegrin-like and metalloproteinase with thrombospondin type-1 motifs-4,ADAMTS)的作用下,细胞外基质被加速降解,胶原蛋白和蛋白聚糖的表达下调,从而减少细胞外基质的合成,这些指标成为评估椎间盘退变程度及用药效果常用标志。腰椎间盘退变涉及分子机制繁杂,在椎间盘退变过程中,促炎细胞因子(如白细胞介素1β、肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素6、白细胞介素8)的表达显著上调,通过激活核因子κB等信号通路促进基质金属蛋白酶家族和炎症递质释放,加速细胞外基质降解,导致椎间盘脱水及结构破坏。其中,肿瘤坏死因子α和白细胞介素1β可直接诱导髓核细胞凋亡并抑制基质合成,而白细胞介素6和白细胞介素8则进一步放大炎症反应。抗炎/修复性因子转化生长因子β虽然在退变早期可能短暂上调,但在椎间盘退变表征中以下调为主。细胞凋亡标志物(如半胱天冬氨酸蛋白酶3活性增强、Bax/Bcl-2比值升高)表明线粒体凋亡通路的激活,导致髓核细胞数量锐减和功能衰竭。氧化应激标志物中,活性氧水平显著升高,超氧化物歧化酶活性下降,表明腰椎间盘退变过程会引发炎症-凋亡级联反应。这些分子变化共同驱动椎间盘退变的病理进程,检测其水平,有助于识别代谢物或蛋白质表达的变化,表征椎间盘退变的过程,为中药复方防治的靶向性研究指明方向。 2.4.4 行为学评价 实验动物在发生腰椎间盘退变时常伴随异常行为表现,通过观察或诱发这些表现,研究者能够直观地了解疾病进展及药物疗效,基于疼痛行为实验设计较为常见。张天龙等[71]研究人员使用不同强度的Von Frey细丝刺激大鼠后爪足底,观察爪子缩回反应来测定痛觉阈值。Von Frey法测量值并不连续,且操作较为繁琐。为了提高精度和简化操作,赵赫等[52]采用了电子机械测痛仪来测量大鼠后足的痛觉阈值。此外,热辐射痛测定仪常用于检测大鼠足底的热缩爪潜伏期,这是另一种常见的神经病理性疼痛行为学实验。李法杰[79]研究发现,外用海桐皮方对腰椎间盘退变大鼠的干预能够有效缓解其神经性疼痛。小鼠扭体实验则广泛应用于评估疼痛敏感性和镇痛药效,研究表明,肾着汤治疗寒湿性腰腿痛小鼠时,其扭体潜伏期延长、扭体次数减少,从而验证了该方剂在缓解疼痛方面的有效性[16]。吕游等[139]总结了刺激阈值、步态分析、脸谱疼痛评分、动态负重试验等评分标准。这类操作并不难实现,但在中药复方治疗腰椎间盘退变的动物实验中开展较少,具有进一步应用的潜力。"

| [1] ZHU L, YU C, ZHANG X, et al. The treatment of intervertebral disc degeneration using Traditional Chinese Medicine. J Ethnopharmacol. 2020;263:113117. [2] ZHOU D, SONG C, MEI Y, et al. A review of Duhuo Jisheng decoction mechanisms in intervertebral disc degeneration in vitro and animal studies. J Orthop Surg Res. 2023;18(1):436. [3] 向婷,余彧,杨利学.基于NF-κB信号通路探讨补肾活血法治疗腰椎间盘退行性变的作用机制[J].中医学报,2024,39(4):730-736. [4] 宝音,王朝鲁.蒙药索布德胶囊治疗腰椎间盘突出症的实验研究[J].中国民族医药杂志,2004,10(4):21-23. [5] 刘江涛. “腰痛定注射液”硬膜外腔注射对家兔化学性腰神经根炎的影响[D]. 武汉:湖北中医药大学,2004. [6] 谢添,章汉平,魏玉玲,等. 腰痛定对大鼠髓核自体免疫反应的影响[J]. 湖北中医杂志,2006,28(2):6-8. [7] 彭海东,魏品康,俞珊.消痰通络外用中药制剂对腰神经根性痛大鼠神经根功能和组织学的作用[J].中国临床康复,2006, 10(47):67-70+229. [8] 王智勇,王霞,张虹,等.补肾健腰合剂抗大鼠椎体软骨终板老化的实验研究[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2008,16(8):40-41. [9] 宋庆慧.独活寄生汤对Hartley豚鼠椎间盘退变干预的研究[D].北京:中国中医科学院,2009. [10] 王健,严根福.补肾活血法对退变腰椎间盘动物模型NO、PG表达的影响[J].浙江中医杂志,2010,45(6):454-455. [11] LIANG QQ, XI ZJ, BIAN Q, et al. Herb formula “Fufangqishe-Pill” prevents upright posture-induced intervertebral disc degeneration at the lumbar in rats. J Pharmacol Sci. 2010; 113(1):23-31. [12] 武海兵.补肾活血汤对去势大鼠腰椎间盘组织中白介素-1干预的实验研究[D].长沙:湖南中医药大学,2013. [13] 王乐,徐无忌.灌胃给予六味地黄丸后椎间盘退变组织蛋白多糖成分的变化[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(42):6271-6277. [14] 杨届,吴官保,冯帅华,等.补肾活血汤对去势后大鼠腰椎间盘p38MAPK蛋白含量影响的研究[J].中医药导报,2017, 23(2):17-20. [15] 夏炳江,侯明生,张磊,等.五福饮对大鼠退变椎间盘聚蛋白聚糖与Ⅱ型胶原表达的影响[J].中国中医急症,2018,27(2): 276-279. [16] 孙秀玲,张靖涵. 肾着汤对寒湿性腰腿痛小鼠模型的治疗作用机制研究[J]. 大医生,2022,7(11):82-84. [17] 白雪,孙孝先,郭杨,等.益气活血方对大鼠腰椎间盘突出的影响及机制[J].中国药房,2024,35(10):1186-1192. [18] XIE Y, ZHANG J, YANG S, et al. Role of Bushen Huoxue Formula and transplanted endothelial progenitor cells play in promoting endplate microcirculation and attenuating intervertebral disc degeneration. Heliyon. 2024;10(6):e28095. [19] 王镇远,冯帅华,李泽湘,等.补肾活血汤对大鼠腰椎间盘退行性变模型Fas/FasL信号通路的影响[J].湖南中医药大学学报,2023,43(3):430-436. [20] 李明洋,冯帅华,蒋佳豪,等.补肾活血汤调控炎症小体改善大鼠椎间盘退变的实验研究[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2023, 31(1):1-6. [21] 李明洋.基于NLRP3/Caspase-1炎症小体探讨补肾活血汤干预大鼠腰椎间盘退变的机制研究[D].长沙:湖南中医药大学, 2023. [22] 李明洋,杨届,蒋佳豪,等.补肾活血汤通过调控Runt相关转录因子2基因的表达改善大鼠椎间盘退变的实验研究[J]. 河北中医,2024,46(10):1671-1675+1681. [23] 谢宏赞,张旭桥,仇湘中,等.活血健腰汤对大鼠退变椎间盘IL-6表达的影响[J].世界最新医学信息文摘,2016,16(61): 29-30+32. [24] 谢宏赞,张旭桥,仇湘中,等. 活血健腰汤对大鼠退变椎间盘TNF-a表达的影响[J]. 保健文汇,2016(2):167-169. [25] WANG D, ZHANG L, HE D, et al. Systemic pharmacology reveal the mechanism by which the Qiangjin Zhuanggu Qufeng mixture inhibits LPS-induced pyroptosis of rat nucleus pulposus cells. Phytomedicine. 2023;119:154998. [26] 仇湘中,朱承勋,张信成,等.补肝健腰方对腰椎间盘退变大鼠椎间盘TNF-α及NF-κB表达的影响[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2017,25(9):9-11+16. [27] 仇湘中,朱承勋,张信成,等.补肝健腰方对腰椎间盘退变大鼠椎间盘IL-1β、IL-6表达的影响[J].中医药导报,2017, 23(24):57-59. [28] 仇湘中,刘栋,张信成,等.补肝健腰方对腰椎间盘退变大鼠椎间盘MMP-3、TIMP-1 mRNA表达的影响[J].中医药导报, 2018,24(14):21-25. [29] 蒋盛昶,邓咪朗,仇湘中,等.不同剂量补肝健腰方对大鼠腰椎间盘退变组织bFGF mRNA表达的影响[J].湖南中医杂志, 2021,37(3):166-168. [30] 仇湘中,蒋盛昶,张信成,等.补肝健腰方对腰椎间盘退变大鼠髓核组织TNF-α、IL-1β干预作用的研究[J].湖南中医药大学学报,2015,35(4):17-19+23+73. [31] 仇湘中,张信成,严敏,等.补肝健腰方对腰椎间盘退变大鼠髓核超微结构的影响[J].中医药导报,2015,21(19):19-22. [32] 杨柏琦,齐素兰,马金叶,等.补肝健腰方对于腰椎间盘退变模型组织中bFGF、TGF-β1、BMP-3表达影响的实验研究[J].现代生物医学进展,2023,23(22):4235-4240. [33] 仇湘中,张信成,蒋盛昶,等.补肝健腰方对腰椎退变大鼠椎间盘组织AQP1表达的影响[J].新中医,2014,46(12):191-193 [34] 邓咪朗.补肝健腰方对大鼠腰椎间盘退变组织TGF-β1、bFGF表达的影响的实验研究[D].长沙:湖南中医药大学,2019. [35] 曾奇.补肝健腰方对腰椎间盘退变大鼠髓核组织MMP-1及OP-1表达的影响[D].长沙:湖南中医药大学,2020. [36] 林一峰,张震,刘海全,等.补肾壮督方预防腰椎间盘退变的实验研究[J].中医临床研究,2016,8(13):16-18. [37] 张震.血浆miRNA与腰椎间盘退变的相关性及补肾壮督方的干预研究[D].广州:广州中医药大学,2017. [38] 周文明,林一峰,张震,等.补肾壮督方对大鼠退变椎间盘细胞线粒体凋亡通路的影响[J].中国实验方剂学杂志, 2019,25(19):25-31. [39] 周文明,林一峰,张震,等.补肾壮督方对大鼠退变髓核组织中miR-155-5p及凋亡相关蛋白的影响[J].世界科学技术-中医药现代化,2020,22(4):1354-1360. [40] 白荣飞.补肾壮督方干预大鼠退变腰椎间盘中Bcl-2和caspase-3蛋白表达的研究[D].广州:广州中医药大学,2018. [41] 邓蓉蓉,王彦超,席志鹏,等.“加味三痹汤”对大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞归巢及对椎间盘退变的影响[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2019,27(5):14-18. [42] 刘希宇.加味三痹汤介导CCL5/CCR1/NF-κB通路促进MSCs向退变椎间盘归巢的临床及其机制研究[D].南京:南京中医药大学,2023. [43] 何敢声.基于T2 mapping参数及生物力学探究三痹汤延缓椎间盘退变的机制研究[D].南京:南京中医药大学,2024. [44] 孙广达.三痹汤延缓椎间盘退变及T2 Mapping参数与椎间盘生化成分相关性的研究[D].南京:南京中医药大学,2024. [45] 王楠. 三痹汤调控炎症反应延缓椎间盘退变的作用机制研究[D].南京:南京中医药大学,2024. [46] WANG N, CHEN S, XIE Y, et al. The Sanbi Decoction alleviates intervertebral disc degeneration in rats through intestinal flora and serum metabolic homeostasis modulation. Phytomedicine. 2024;127:155480. [47] 李艺璇,姜艳玲,廖镒,等.人参固本口服液对椎间盘退变小鼠肠道菌群的影响[J].中草药,2022,53(22):7121-7128. [48] 杨光露,郭杨,马勇,等.扶阳宣痹汤对大鼠椎间盘退变及基质金属蛋白酶表达的影响[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2021,29(4):1-7. [49] 权学民. 益气化瘀中药结合BMSCs移植干预腰椎间盘退变的实验研究[D].北京:北京中医药大学,2011. [50] 李俊杰,梁舒涵,彭奇,等. 益气活血中药对大鼠退变腰椎间盘中TGF-β1、MMP-3的影响[J]. 中国中医药现代远程教育,2015,13(18):144-146. [51] 林斌,潘永亮,蔡金亮,等.益气补肾活血方对大鼠退变腰椎间盘中OP-1及IL-1的影响[J].中医药导报,2016,22(8):20-22. [52] 赵赫,高誉珊,胡振国,等.补肾壮筋汤对腰椎间盘退变大鼠椎间盘及行为学特征影响的实验研究[J].中医正骨,2017, 29(7):12-20+26. [53] GAO S, WANG C, QI L, et al. Bushen Huoxue Formula Inhibits IL-1β-Induced Apoptosis and Extracellular Matrix Degradation in the Nucleus Pulposus Cells and Improves Intervertebral Disc Degeneration in Rats. J Inflamm Res. 2024;17:121-136. [54] GUO J, YANG S, ZHAI W, et al. Network Pharmacology with Metabolomics Study to Reveal the Mechanisms of Bushen Huoxue Formula in Intervertebral Disc Degeneration Treatment. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2024;18:493-512. [55] JIN H, MA H, WU J, et al. Network Pharmacology and In Vivo Experimental Verification of the Mechanism of the Qing’e Pill for Treating Intervertebral Disc Degeneration. Curr Comput Aided Drug Des. 2024. doi: 10.2174/0115734099356426241119051916. [56] 祝坚.补肾活血舒筋方介导热休克蛋白干预椎间盘退变研究[D].南京:南京中医药大学,2016. [57] 崔海舰.身痛逐瘀汤治疗腰椎间盘突出症临床研究及延缓椎间盘退变实验研究[D].沈阳:辽宁中医药大学,2024. [58] 黄家俊,吴迪友,陶广义,等.身痛逐瘀汤调控SIRT1/Nrf2信号通路改善大鼠椎间盘退变的作用[J].中国实验方剂学杂志,2025,31(3):29-39. [59] GUO D, CHENG K, SONG C, et al. Mechanisms of inhibition of nucleus pulposus cells pyroptosis through SDF1/CXCR4-NFkB-NLRP3 axis in the treatment of intervertebral disc degeneration by Duhuo Jisheng Decoction. Int Immunopharmacol. 2023;124(Pt A):110844. [60] CHANG TK, LIU YC, CHIEN TY, et al. The effects of Elgucare in a rat model of intervertebral disc degeneration. Adv Tradit Med. 2024;24: 607-616. [61] DAI F, YU P, YU Z, et al. Yiqi Huoxue Recipe Delayed Intervertebral Disc Degeneration by Activating Autophagy. Front Pharmacol. 2021;12:705747. [62] 徐波,刘昱江,汪松林,等.枳壳甘草汤抑制巨噬细胞M1极化延缓椎间盘退变的实验研究[J].环球中医药,2023,16(12): 2421-2426. [63] 张立庄.独活寄生汤对腰椎间盘突出症小鼠纤维化坏死MMP-1表达的影响[J].中国中医基础医学杂志,2015,21(2):172-174. [64] 丁慧琴,应俊,厉驹,等.补骨壮筋汤通过调控Hedgehog信号通路延缓椎间盘退变研究[J].中华中医药杂志,2021, 36(7):4173-4177. [65] 张擎天,黄泽灵,陈华,等.枳壳甘草汤调控炎性小体改善腰椎间盘突出症痛敏的实验研究[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志, 2024,32(1):13-19. [66] 孙江涛. 枳壳甘草汤对大鼠腰椎间盘突出模型炎症及退变的实验研究[D].南京:南京中医药大学,2017. [67] 孙江涛,李宇卫,沈晓峰,等.枳壳甘草汤对腰椎间盘突出模型大鼠炎症及退变的影响[J].中国中医急症,2016,25(8):1488-1492. [68] 马智佳. 增强MRI对巨大型腰椎间盘突出症的临床转归预测及消髓化核汤促进重吸收的研究[D].南京:南京中医药大学,2022. [69] 赵继荣,张思胜,徐磊.杜仲腰痛丸对髓核非压迫性突出大鼠背根节中P物质含量的影响[J].中医正骨,2008,20(2):3-5+79. [70] 张天龙. 杜仲腰痛丸对LDH慢性下肢痛模型大鼠镇痛药效及BDNF-Trkb-CREB信号通路的调控研究[D].兰州:甘肃中医药大学,2022. [71] 张天龙,赵继荣,陈祁青,等.杜仲腰痛丸对腰椎间盘突出症慢性下肢痛模型大鼠疼痛行为学影响[J].辽宁中医药大学报,2022,24(2):20-24. [72] 陈祁青,马东,赵继荣,等.基于网络药理学及动物实验的杜仲腰痛丸治疗腰椎间盘突出症慢性下肢痛的作用研究[J].世界科学技术-中医药现代化,2023, 25(5):1702-1713. [73] 薛旭,赵继荣,陈祁青,等.基于VBM技术的杜仲腰痛丸干预腰椎间盘突出症慢性下肢痛模型大鼠的实验研究[J].中药新药与临床药理,2020,31(12):1401-1407. [74] 安娟. 基于NF-κB信号通路探讨铁包金巴布膏干预LDH的作用机制[D].长沙:湖南中医药大学,2024. [75] 邰东旭,王廷凯,房景奎.优化活血利水方对大鼠自体髓核移植后移植髓核MMP-3、TIMP-1表达的影响[J].中华中医药学刊,2011,29(5):1044-1049. [76] 邰东旭,王哲,房凌桥,等.优化活血利水方抗炎镇痛作用的实验研究[J].辽宁中医药大学学报,2009,11(9):181-183. [77] 邰东旭.活血利水方干预腰椎间盘突出症处方优化的文献与实验研究[D].沈阳:辽宁中医药大学,2009. [78] 沈晓峰,龚正丰,梁国强.吴门枳壳甘草汤对腰椎间盘突出大鼠酸敏感离子通道及相关因子影响的实验研究[J].辽宁中医药大学学报,2020,22(1):36-39. [79] 李法杰.海桐皮方外用治疗腰椎间盘突出症的临床疗效评价及其缓解神经病理性疼痛的机制研究[D].北京:中国中医科学院,2024. [80] 汤小康,肖可,王攀,等.寒湿阻滞型腰痛大鼠模型构建及独活寄生汤干预效果的实验研究[J].湖南中医药大学学报, 2024,44(6):976-981. [81] 王裕祥,杨应忠,秦卫春,等.舒筋祛痹汤对腰椎间盘突出症大鼠PLA2活性、IL-6、TNF-α水平和椎间盘退变的影响[J].颈腰痛杂志,2018,39(5):543-546. [82] 罗琳.蛭龙活血通瘀血胶囊在腰椎间盘突出症大鼠模型髓核中PLA2影响程度的实验研究[D].泸州:泸州医学院,2013. [83] 高春鹏,朱宇,姜宏,等.益气活血方介导P38MAPK信号通路促进突出椎间盘组织重吸收的机制研究[J].江苏中医药,2018,50(6):75-78. [84] 师振予.龙丹腰痹丸对腰椎间盘突出症的抗炎镇痛作用及分子机制研究[D].长沙:湖南中医药大学,2012. [85] HUANG Z, LU B, ZHANG X, et al. Zhiqiao Gancao Decoction Ameliorates Hyperalgesia in Lumbar Disc Herniation via the CCL2/CCR2 Signaling Pathway. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2023;17:2239-2257. [86] 刘汝专,刘金浪,郭艳军,等.溶髓方对大鼠椎间盘软骨终板细胞凋亡的影响[J].河南中医,2014,34(1):79-81. [87] 刘汝专,刘金浪,郭艳军,等.溶髓方对大鼠椎间盘退变中软骨终板IL-1β的影响[J].辽宁中医杂志,2014,41(6):1284-1287. [88] 潘建西,张思胜,谈明顺,等.腰腿理痛散对大鼠硬膜外移植自体髓核脊神经节损伤的组织学研究[J].中国中医药科技, 2008,15(5):331-332+320. [89] 姜承华.腰腿痛宁胶囊治疗腰椎间盘突出症(肾虚血瘀型)的临床及实验研究[D].长春:长春中医药大学,2018. [90] 姜劲挺,安文博.腰腿痛胶囊对髓核移植型腰椎间盘突出症大鼠模型背根神经节中P物质和降钙素基因相关肽含量的影响[J].中医正骨,2012,24(6):18-20. [91] 李晨光,崔学军,侯莉娟,等.腰痛宁对腰椎间盘突出症模型大鼠神经根损伤的保护作用[J].中医杂志,2009,50(11):1026-1028. [92] 李晨光,侯莉娟,王拥军.腰痛宁对腰椎间盘突出模型大鼠比目鱼肌BDNF和NT-3蛋白表达的影响[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2009,17(4):8-10. [93] 侯莉娟,郝银丽,王拥军.腰神经根压迫性损伤及药物干预后BDNF和NT-3含量的研究[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志, 2008,16(9):23-25. [94] 唐朝辉,曹亮,丁岗,等.腰痹通胶囊对大鼠腰椎神经根压迫致腰椎间盘突出模型药效及炎性因子的影响[J].中国实验方剂学杂志,2015,21(5):155-158. [95] 唐朝辉,李娜,曹亮,等.腰痹通胶囊改善大鼠腰椎间盘突出及其机制研究[J].现代药物与临床,2014,29(10):1086-1091. [96] 姜国成.中药栓剂治疗腰椎间盘突出症的机理研究[D].成都:成都中医药大学,2008. [97] 罗才贵,张冲,罗建,等.大鼠炎性神经根髓鞘形态学变化及复方中药栓剂对神经根损伤的修复[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2007,11(19):3748-3751. [98] 刘洋,王东风,黄娜.复方南星蠲瘀软膏对大鼠神经根炎和足趾肿胀的药理作用研究[J].中国药房,2011,22(11):977-979. [99] 徐继禧.六味地黄丸对糖尿病大鼠椎间盘组织退变的影响[D].广州:广州中医药大学,2022. [100] 谢芳,吴官保,姚红艳,等.补肾活血汤干预衰老大鼠退变椎间盘模型中经典WNT信号通路β-catenin蛋白含量的研究[J].湖南中医药大学学报,2018,38(3):275-279. [101] 刘仁,吴官保,冯帅华,等.补肾活血汤对腰椎间盘退变大鼠TNF-α表达的影响[J].湖南中医杂志,2017,33(3):144-145+156. [102] 冯帅华,刘仁,吴官保,等.补肾活血汤对D-半乳糖致腰椎间盘退变大鼠模型IL-1β、TGF-β1表达的影响[J].中医药导报,2018,24(4):11-13+17. [103] 孙凯,魏戌,朱立国,等.壮腰通络方对腰椎间盘退行性病变大鼠病理变化及血清炎症因子表达的影响[J].中国中医药信息杂志,2022,29(7):93-98. [104] 肖可. 独活寄生汤对腰椎间盘退变大鼠模型的干预效果研究[D].长沙:湖南中医药大学,2024. [105] 冯帅华,姚红艳,吴官保,等.补肾活血法对去势大鼠腰椎间盘组织中TNF-α影响的实验研究[J].湖南中医杂志,2015, 31(11):158-161. [106] 姚啸生,王禹,荆涛,等. 活血补肾方对大鼠退变腰椎间盘mTOR通路依赖性自噬的影响[J]. 世界科学技术-中医药现代化,2019,21(7):1384-1392. [107] 荆涛. 活血补肾方对大鼠退变椎间盘mTOR通路介导下自噬的影响的实验研究[D].沈阳:辽宁中医药大学,2020. [108] 戴锋.益气活血方治疗破裂型腰椎间盘突出症的疗效观察及基于细胞自噬影响重吸收的机制研究[D].南京:南京中医药大学,2021 [109] 朱立国,张平,宋庆慧,等.补肾活血方对沙鼠增龄过程中腰椎软骨终板钙化干预作用的初步研究[J].中国骨伤,2017, 30(10):926-932. [110] 付远飞. 补肾通络方调控淋巴管系统促进髓核突出重吸收机制研究[D].广州:广州中医药大学,2022. [111] 许勇,薛彬,孟祥超,等.伸筋活血汤对低氧诱导因子-1α缺失小鼠椎间盘退变的影响[J].中医正骨,2018,30(1):12-17. [112] 谢晚晴.从Wnt/β-catenin信号通路解析腰椎退行性骨关节病“肾-督-骨失常”的分子机制[D].沈阳:辽宁中医药大学, 2018. [113] 何升华,赖居易,王业广,等.腰突颗粒调节腰椎间盘退变模型兔Fas/FasL基因的表达[J].中国组织工程研究,2017, 21(32):5140-5145. [114] 李凯明. 补肾活血方治疗椎间盘源性腰痛的临床研究及对人髓核细胞活性与功能的影响[D].北京:中国中医科学院,2022. [115] 李玲慧,李凯明,龚浩,等.补肾活血方对兔退变椎间盘血管内皮生长因子表达影响[J].辽宁中医药大学学报,2020, 22(10):31-34. [116] 李玲慧,魏戌,朱立国,等.补肾活血方对兔退变椎间盘模型MMP-3表达影响[J].辽宁中医药大学学报,2020,22(8): 8-11+221. [117] 李凯明,朱立国,李玲慧,等.补肾活血方对兔退变椎间盘模型经典Wnt/β-catenin信号通路的影响[J].中华中医药杂志,2020,35(12):6001-6005. [118] 刘岩路,黄异飞,董振宇.中药对兔退变椎间盘内TNF-α的影响[J].山西中医, 2011,27(3):41-43. [119] 李彪.基于JAK2/STAT3信号通路研究腰痹舒治疗腰椎间盘突出症的作用机制[D].长沙:湖南师范大学,2020. [120] 夏铎.腰痹舒对兔椎间盘退变髓核组织TNF-α、MMP-1及TIMP-1表达的影响[D].衡阳:南华大学,2013. [121] 王宁科.腰痹舒对兔椎间盘退变髓核组织中水通道蛋白AQP1、AQP3mRNA及蛋白质表达的影响[D].衡阳:南华大学,2014. [122] 谭财福.腰痹舒对兔退变腰椎间盘IL-1α含量及Sox9基因mRNA表达的影响[D].衡阳:南华大学,2011. [123] 孙湘云. 独活寄生汤对兔退变腰椎间盘中Ⅱ型胶原及MMP-13表达的影响[D].长沙:湖南中医药大学,2020. [124] 肖强兵,何承建,曾俊华,等.风湿骨痛药酒药槌外治法对兔退变腰椎间盘内TNF-α表达的影响[J].时珍国医国药, 2013,24(3):759-761. [125] 肖强兵,叶劲立,邹季.风湿骨痛药酒药槌外治法对兔退变腰椎间盘内磷脂酶A2活性的影响[C]//中国中西医结合学会,中国中西医结合学会骨伤科专业委员会.第十八届全国中西医结合骨伤科学术研讨会论文汇编.湖北中医学院附属医院;仙桃市中医院,2011. [126] 杜佳林,包玉龙,李显石,等.腰痛贴膏对家兔腰椎间盘突出症模型的影响[J].实验动物科学,2014,31(4):32-35+40. [127] 郑先波,徐无忌.六味地黄丸对兔退变椎间盘髓核细凋亡的影响[J].内蒙古中医药,2017,36(4):130-131. [128] 陈祖彦,江健宁,杨勇,等.独活寄生汤提取物治疗椎间盘退变性疾病机理实验研究[J].新中医,2012,44(9):118-121. [129] 蔡楚豪.补肾活血方对韧带损伤型“筋伤”腰椎失稳动物模型的影响[D].北京:北京中医药大学,2023. [130] 吕存贤,吴永琴.益气活血法对兔退变髓核中Fas/FasL的表达及基质代谢的影响[J].中华中医药学刊,2013,31(1):77-80+228. [131] 刘奕,陈晓峰,刘逸,等.补肾活血方对兔NPMSCs移植治疗退变椎间盘P38MAPK信号通路的影响[J].环球中医药,2020,13(6):958-963. [132] WOJCIKOWSKI K, GOBE G. Animal studies on medicinal herbs: predictability, dose conversion and potential value. Phytother Res. 2014;28(1):22-27. [133] PFIRRMANN CW, METZDORF A, ZANETTI M, et al. Magnetic resonance classification of lumbar intervertebral disc degeneration. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2001;26(17):1873-1878. [134] GRIFFITH JF, WANG YX, ANTONIO GE, et al. Modified Pfirrmann grading system for lumbar intervertebral disc degeneration. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2007; 32(24):E708-E712. [135] 许浩然. 髓核基质硬化通过激活MRTF-A减弱糖酵解进而促进椎间盘退变机制研究[D].武汉:华中科技大学,2023. [136] HAN B, ZHU K, LI FC, et al. A simple disc degeneration model induced by percutaneous needle puncture in the rat tail. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2008;33(18): 1925-1934. [137] KEOROCHANA G, JOHNSON JS, TAGHAVI CE, et al. The effect of needle size inducing degeneration in the rat caudal disc: evaluation using radiograph, magnetic resonance imaging, histology, and immunohistochemistry. Spine J. 2010; 10(11):1014-1023. [138] LAI A, GANSAU J, GULLBRAND SE, et al. Development of a standardized histopathology scoring system for intervertebral disc degeneration in rat models: An initiative of the ORS spine section. JOR Spine. 2021;4(2):e1150. [139] 吕游,侯树勋.腰痛动物模型研究进展[J].中国骨与关节杂志,2018,7(2):146-149. |
| [1] | Zhu Xiaolong, Zhang Wei, Yang Yang. Visualization analysis of research hotspots and cutting-edge information in the field of intervertebral disc regeneration and repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(9): 2391-2402. |
| [2] | Cai Ziming, Yu Qinghe, Ma Pengfei, Zhang Xin, Zhou Longqian, Zhang Chongyang, Lin Wenping. Heme oxygenase-1 alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory response in nucleus pulposus mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(7): 1624-1631. |
| [3] | Yang Jing, Wang Houmei, Wang Yi, Song Min, Ren Jie, Dai Lujun, Xiao Ziwen. Constructing a rat animal model of pelvic organ prolapse: a comparison of three modeling methods [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 864-872. |
| [4] | Wang Peng, Li Zhijun, Zhang Shaojie, Wu Yimin. Intervertebral disc rehydration after posterior lumbar dynamic internal fixation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(3): 711-720. |
| [5] | Jiang Chao, Che Yanjun. Biological mechanisms and future research trends of cartilaginous endplate degeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(23): 5915-5924. |
| [6] | Zhou Tianle, Wang Wei, Zhang Zhiwen, Liu Ximing. Application and progress of transcriptomics and proteomics techniques in the study of intervertebral disc degeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(23): 5925-5933. |
| [7] | Xu Peng, Jiang Wei, Yu You, Lei Zhengliang, Tian Yang, Zhang Jie, Liu Luchang. Cobalt chloride-induced hypoxic environment accelerates knee cartilage degeneration in New Zealand rabbits [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(22): 5650-5658. |
| [8] | Wang Xinyue, Li Hongli, Guo Chunhui, Chen Jibing, Yu Hua. Changes in the expression of six microRNAs in ovarian tissue from animal models of premature ovarian failure and in peripheral blood of patients with premature ovarian failure [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(18): 4675-4684. |
| [9] | Li Feifan, Zhang Yibo, Wang Jing, Zhu Jinqiang, Zheng Wenke. Comparison and evaluation of three methods for preparing insomnia mouse models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(18): 4685-4693. |
| [10] | Fu Jingyue, Zhou Qinfeng, Li Muzhe, Ma Yong, Pan Yalan, Sun Jie, Huang Xiangyang, Guo Yang. Preparation and evaluation of an animal model of osteoporosis and osteoarthritis comorbidity in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(17): 4299-4308. |
| [11] | Peng Hao, Jiang Yang, Song Yanping, Wu Quan, Yao Na, Chen Qigang, Shen Zhen. H-type angiogenesis and its role in various skeletal disease animal models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(16): 4154-4165. |
| [12] | Lai Pengyu, Liang Ran, Shen Shan. Tissue engineering technology for repairing temporomandibular joint: problems and challenges [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(在线): 1-9. |
| [13] | Zhou Panpan, Cui Yinglin, Zhang Wentao, Wang Shurui, Chen Jiahui, Yang Tong . Role of cellular autophagy in cerebral ischemic injury and the regulatory mechanism of traditional Chinese medicine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1650-1658. |
| [14] | Qian Kun, Li Ziqing, Sun Shui . Endoplasmic reticulum stress in the occurrence and development of common degenerative bone diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1285-1295. |
| [15] | Xiang Pan, Che Yanjun, Luo Zongping. Compressive stress induces degeneration of cartilaginous endplate cells through the SOST/Wnt/beta-catenin pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 951-957. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||