Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (22): 4663-4670.doi: 10.12307/2025.447
Previous Articles Next Articles
Injectable dental pulp extracellular matrix prepared by grinding treatment for dental pulp regeneration
Yang Yuqian, Li Wenjun, Zhao Jian, Chen Gang
- Department of Stomatology, First Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Dalian 116011, Liaoning Province, China
-
Received:2024-04-07Accepted:2024-06-01Online:2025-08-08Published:2024-12-05 -
Contact:Chen Gang, MD, Associate chief physician, Department of Stomatology, First Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Dalian 116011, Liaoning Province, China -
About author:Yang Yuqian, Master candidate, Department of Stomatology, First Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Dalian 116011, Liaoning Province, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81600818 (to CG); a grant from Liaoning Provincial Department of Education, No. LJKZ0855 (to CG)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Yang Yuqian, Li Wenjun, Zhao Jian, Chen Gang. Injectable dental pulp extracellular matrix prepared by grinding treatment for dental pulp regeneration[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(22): 4663-4670.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
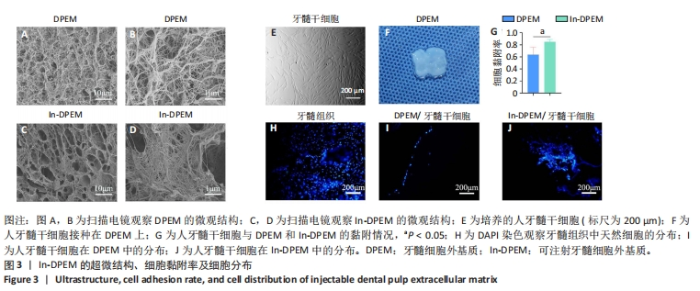
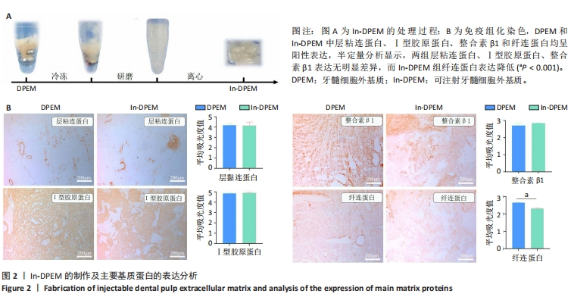
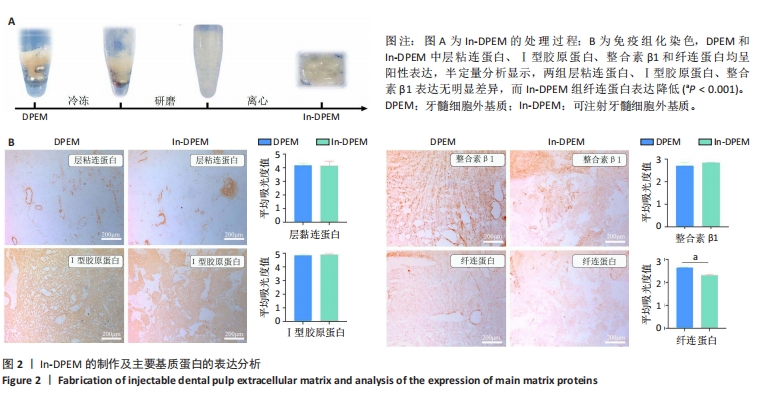
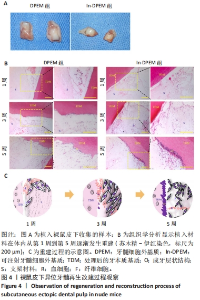
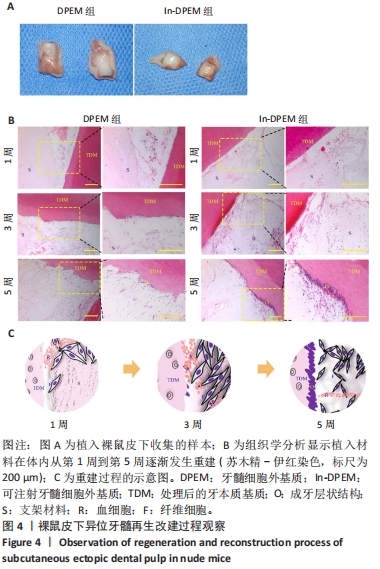
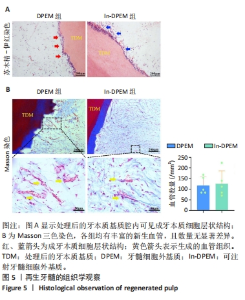
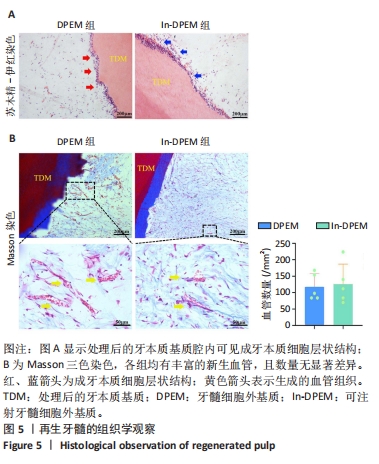
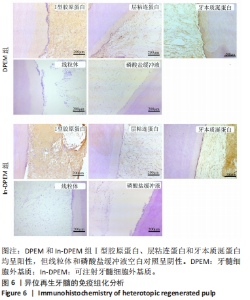
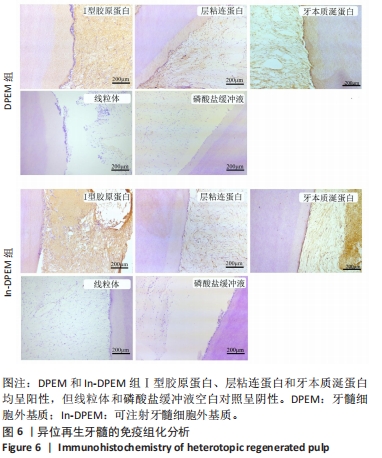
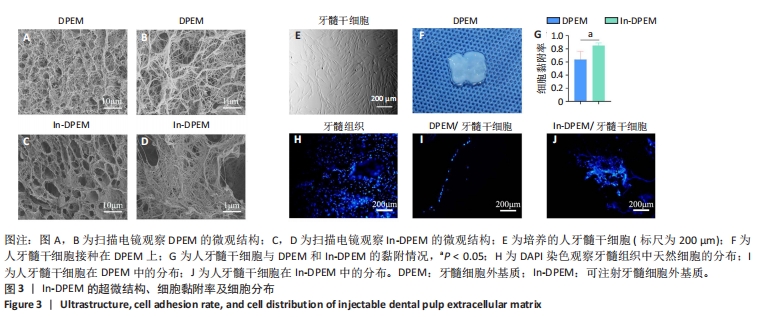
2.2 可注射牙髓细胞外基质显微结构 应用扫描电子显微镜观察到可注射牙髓细胞外基质的胶原纤维结构与牙髓细胞外基质所不同,呈被压缩状态,但仍保留了与牙髓细胞外基质相似的结构,见图3A-D。 2.3 可注射牙髓细胞外基质的生物相容性 从人类牙齿中提取的牙髓干细胞呈典型的纺锤状,在培养过程中状态良好,具有贴壁的生长特性,细胞形态稳定,具有良好的增殖能力,见图3E。制备的牙髓细胞外基质呈白色半透明,且保留了天然牙髓组织的整体形状,见图3F。为观察细胞黏附情况,将牙髓干细胞分别接种于牙髓细胞外基质和可注射牙髓细胞外基质上,得到细胞黏附率分别为(63.7±12.5)%和(85.0±4.1)%,可注射牙髓细胞外基质显著提高了细胞黏附率,见图3G。为观察细胞分布情况,制备牙髓细胞外基质/牙髓干细胞和可注射牙髓细胞外基质/牙髓干细胞切片用于DAPI染色,以正常牙髓组织的染色结果作为对照组,结果显示可注射牙髓细胞外基质中的细胞分布更均匀,且与牙髓组织中正常的细胞分布相似,而牙髓细胞外基质中的细胞主要局限于材料表面,见图3H-J。"
| [1] AHMED GM, ABOUAUF EA, ABUBAKR N, et al. Tissue Engineering Approaches for Enamel, Dentin, and Pulp Regeneration: An Update. Stem Cells Int. 2020;2020:5734539. [2] HASHEMI-BENI B, KHOROUSHI M, FOROUGHI MR, et al. Tissue engineering: Dentin - pulp complex regeneration approaches (A review). Tissue Cell. 2017;49(5):552-564. [3] WOLF MT, DALY KA, REING JE, et al. Biologic scaffold composed of skeletal muscle extracellular matrix. Biomaterials. 2012;33(10):2916-2925. [4] YIN H, WANG Y, SUN X, et al. Functional tissue-engineered microtissue derived from cartilage extracellular matrix for articular cartilage regeneration. Acta Biomater. 2018;77:127-141. [5] TAVELLI L, MCGUIRE MK, ZUCCHELLI G, et al. Extracellular matrix-based scaffolding technologies for periodontal and peri-implant soft tissue regeneration. J Periodontol. 2020;91(1):17-25. [6] HYNES RO. The extracellular matrix: not just pretty fibrils. Science. 2009;326(5957):1216-1219. [7] ZHU M, LI W, DONG X, et al. In vivo engineered extracellular matrix scaffolds with instructive niches for oriented tissue regeneration. Nat Commun. 2019;10(1):4620. [8] LIN X, PATIL S, GAO YG, et al. The Bone Extracellular Matrix in Bone Formation and Regeneration. Front Pharmacol. 2020; 11:757. [9] NEVINS M, NEVINS ML, CAMELO M, et al. The clinical efficacy of DynaMatrix extracellular membrane in augmenting keratinized tissue. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 2010;30(2):151-161. [10] BRAGA-VILELA AS, PIMENTEL ER, MARANGONI S, et al. Extracellular matrix of porcine pericardium: biochemistry and collagen architecture. J Membr Biol. 2008;221(1):15-25. [11] SHIRAKATA Y, SCULEAN A, SHINOHARA Y, et al. Healing of localized gingival recessions treated with a coronally advanced flap alone or combined with an enamel matrix derivative and a porcine acellular dermal matrix: a preclinical study. Clin Oral Investig. 2016;20(7):1791-1800. [12] 王柯柯,蔡俊,刘子钰,等.心房颤动患者胶原蛋白和弹性蛋白的表达[J].中国心脏起搏与心电生理杂志,2024,38(2):90-95. [13] 赵永杰,尹刚,杜瑞,等.不同长骨制备的脱矿骨基质中BMP-2含量测定及其成骨性能的体外研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2023, 37(8):945-951. [14] 金渝瑜,罗飞宏.软骨细胞外基质基因调控与遗传缺陷研究新进展[J].临床儿科杂志,2024,42(2):164-170. [15] CHEN G, CHEN J, YANG B, et al. Combination of aligned PLGA/Gelatin electrospun sheets, native dental pulp extracellular matrix and treated dentin matrix as substrates for tooth root regeneration. Biomaterials. 2015;52:56-70. [16] SONG JS, TAKIMOTO K, JEON M, et al. Decellularized Human Dental Pulp as a Scaffold for Regenerative Endodontics. J Dent Res. 2017;96(6): 640-646. [17] HU J, CAO Y, XIE Y, et al. Periodontal regeneration in swine after cell injection and cell sheet transplantation of human dental pulp stem cells following good manufacturing practice. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2016; 7(1):130. [18] DISSANAYAKA WL, HARGREAVES KM, JIN L, et al. The interplay of dental pulp stem cells and endothelial cells in an injectable peptide hydrogel on angiogenesis and pulp regeneration in vivo. Tissue Eng Part A. 2015;21(3-4):550-563. [19] CHREPA V, AUSTAH O, DIOGENES A. Evaluation of a Commercially Available Hyaluronic Acid Hydrogel (Restylane) as Injectable Scaffold for Dental Pulp Regeneration: An In Vitro Evaluation. J Endod. 2017; 43(2):257-262. [20] SILVA CR, BABO PS, GULINO M, et al. Injectable and tunable hyaluronic acid hydrogels releasing chemotactic and angiogenic growth factors for endodontic regeneration. Acta Biomater. 2018;77:155-171. [21] SARRIGIANNIDIS SO, REY JM, DOBRE O, et al. A tough act to follow: collagen hydrogel modifications to improve mechanical and growth factor loading capabilities. Mater Today Bio. 2021;10:100098. [22] 黄长瑾,雷桓,唐晓军.EDC/NHS交联重组胶原蛋白水凝胶修复关节软骨缺损[J].中国材料进展,2024,43(4):344-354. [23] 赵红霞,孙政伟,韩阳,等.富血小板纤维蛋白复合甲基丙烯酰化明胶水凝胶的促成骨性能[J].中国组织工程研究,2025,29(4):809-817. [24] 王斐昊,许波,王平,等.纤维素/海藻酸钠/明胶复合水凝胶的制备与性能[J].高分子材料科学与工程,2024,40(3):133-142. [25] 王慧斌,赵东东,张璐,等.基于多肽水凝胶材料的肿瘤类器官培养体系的建立[J/OL].生物工程学报,1-20[2024-05-20].https://doi.org/10.13345/j.cjb.240135. [26] 祁凤英,王蕾,李东东,等.可缓释富血小板血浆生长因子的新型自组装多肽水凝胶制备及性能表征[J].中国组织工程研究,2024, 28(15):2364-2370. [27] HAUGEN HJ, BASU P, SUKUL M, et al. Injectable Biomaterials for Dental Tissue Regeneration. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(10):3442. [28] LI J, RAO Z, ZHAO Y, et al. A Decellularized Matrix Hydrogel Derived from Human Dental Pulp Promotes Dental Pulp Stem Cell Proliferation, Migration, and Induced Multidirectional Differentiation In Vitro. J Endod. 2020;46(10):1438-1447.e5. [29] TRAPHAGEN SB, FOURLIGAS N, XYLAS JF, et al. Characterization of natural, decellularized and reseeded porcine tooth bud matrices. Biomaterials. 2012;33(21):5287-5296. [30] LI R, GUO W, YANG B, et al. Human treated dentin matrix as a natural scaffold for complete human dentin tissue regeneration. Biomaterials. 2011;32(20):4525-4538. [31] YANG B, CHEN G, LI J, et al. Tooth root regeneration using dental follicle cell sheets in combination with a dentin matrix - based scaffold. Biomaterials. 2012;33(8):2449-2461. [32] HU L, GAO Z, XU J, et al. Decellularized Swine Dental Pulp as a Bioscaffold for Pulp Regeneration. Biomed Res Int. 2017;2017:9342714. [33] MAURER T, STOFFEL MH, BELYAEV Y, et al. Structural characterization of four different naturally occurring porcine collagen membranes suitable for medical applications. PLoS One. 2018;13(10):e0205027. [34] OTT HC, MATTHIESEN TS, GOH SK, et al. Perfusion-decellularized matrix: using nature’s platform to engineer a bioartificial heart. Nat Med. 2008;14(2):213-221. [35] BASSAT E, MUTLAK YE, GENZELINAKH A, et al. The extracellular matrix protein agrin promotes heart regeneration in mice. Nature. 2017;547(7662):179-184. [36] YASSIN MA, LEKNES KN, PEDERSEN TO, et al. Cell seeding density is a critical determinant for copolymer scaffolds-induced bone regeneration. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2015;103(11):3649-3658. [37] LI X, MA C, XIE X, et al. Pulp regeneration in a full-length human tooth root using a hierarchical nanofibrous microsphere system. Acta Biomater. 2016;35:57-67. [38] HUANG GT, LIU J, ZHU X, et al. Pulp/Dentin Regeneration: It Should Be Complicated. J Endod. 2020;46(9S):S128-S134. [39] DUNCAN HF, KOBAYASHI Y, SHIMIZU E. Growth Factors and Cell Homing in Dental Tissue Regeneration. Curr Oral Health Rep. 2018;5(4):276-285. [40] MENG H, HU L, ZHOU Y, et al. A Sandwich Structure of Human Dental Pulp Stem Cell Sheet, Treated Dentin Matrix, and Matrigel for Tooth Root Regeneration. Stem Cells Dev. 2020;29(8):521-532. [41] FU J, CHEN J, LI W, et al. Laminin-Modified Dental Pulp Extracellular Matrix for Dental Pulp Regeneration. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2021; 8:595096. [42] SMITH AJ, SCHEVEN BA, TAKAHASHI Y, et al. Dentine as a bioactive extracellular matrix. Arch Oral Biol. 2012;57(2):109-121. |
| [1] | Lai Pengyu, Liang Ran, Shen Shan. Tissue engineering technology for repairing temporomandibular joint: problems and challenges [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(在线): 1-9. |
| [2] | Shui Jing, He Yu, Jiang Nan, Xu Kun, Song Lijuan, Ding Zhibin, Ma Cungen, Li Xinyi. Astrocytes regulate remyelination in central nervous system [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(36): 7889-7897. |
| [3] | Shi Tongtong, Deng Rongxia, Zhang Jianguang. Differences in physicochemical properties and collagen secretion stimulation of natural and synthetic hydroxyapatite particles [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(34): 7278-7285. |
| [4] | Zhang Xiaoyu, Wei Shanwen, Fang Jiawei, Ni Li. Prussian blue nanoparticles restore mitochondrial function in nucleus pulposus cells through antioxidation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(34): 7318-7325. |
| [5] | Wang Wanchun, , Yi Jun, Yan Zhangren, Yang Yue, Dong Degang, Li Yumei. 717 Jiedu Decoction remodels homeostasis of extracellular matrix and promotes repair of local injured tissues in rats after Agkistrodon halys bite [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(30): 6457-6465. |
| [6] | Song Yuting, Wen Chunlei, Li Yi, Bai Xue, Gao Hong, Hu Tingju, Wang Zijun, Yan Xu. Effects of myocardial extracellular matrix remodeling on connexin 43 and its Ser368 phosphorylation and electrical conduction [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(29): 6212-6218. |
| [7] | Sun Yahui, Wang Yufeng, Guo Chao, Yao Junjie, Ji Yuanyuan, Li Zhongxu, Lou Huijuan, Jiang Jinglei, Sun Yiping, Xu Jing, Cong Deyu. Effect of massage on extracellular matrix collagen deposition in skeletal muscle of type 2 diabetic rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(26): 5549-5555. |
| [8] | Ji Yaqiong, Ning Zhongping. Protective effect of paeoniflorin on angiotensin II-induced fibrosis in cardiac fibroblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(25): 5382-5389. |
| [9] | Zhou Lijun, Zhang Keyuan, Xu Feihu, Wang Xi, Yu Li, Dong Shiming, Xu Junyu, Guo Yufeng, Ma Hairong, Ding Hong. Effect and mechanism of circular RNA SEC24A on proliferation and apoptosis of synovial fibroblasts in osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(24): 5086-5092. |
| [10] | Wang Dan, Zhu Xiaojun, Li Zhicheng, Li Na. Construction of tissue engineered urethra by combining acellular matrix with exosomes in small intestinal submucosa [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(23): 4907-4914. |
| [11] | Kong Xiaojuan, Ma Zhengjiao, Tan Zhenyu, Liu Peng. Amniotic and bladder extracellular matrix materials in repairing rat endometrial injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(22): 4731-4739. |
| [12] | Lai Pengyu, Liang Ran, Shen Shan. Tissue engineering technology for repairing temporomandibular joint: problems and challenges [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(22): 4804-4812. |
| [13] | Wu Lijuan, Wang Zhenfei, Tan Xiaohui, Wu Yingcai, Zheng Yanling, Dai Fengxue. Effect of extracellular matrix stiffness on tumor progression and treatment strategies [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(20): 4286-4294. |
| [14] | Yu Yangyi , Song Zhuoyue, Lian Qiang, Ding Kang, Li Guangheng . AAV-mediated expression of p65shRNA and bone morphogenetic protein 4 synergistically enhances chondrocyte regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(17): 3537-3547. |
| [15] | Israrguli · Maimeti, Jia Sen, Liu Jia. Bone morphogenetic protein 2-loaded hydrogel induces osteogenic differentiation of dental pulp stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(16): 3301-3310. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||