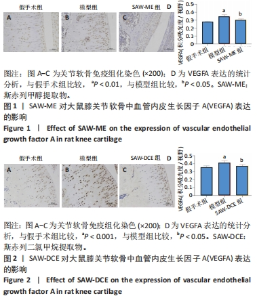
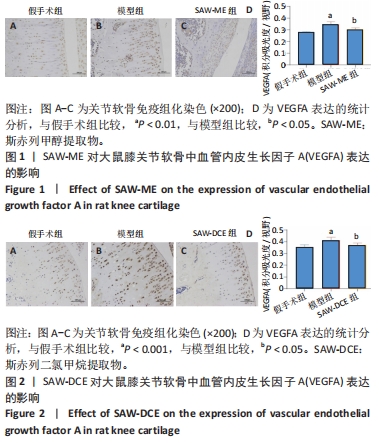
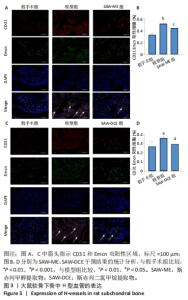
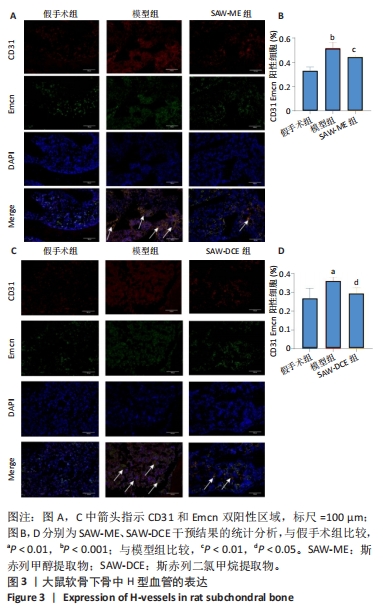
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (34): 5458-5466.doi: 10.12307/2024.808
Previous Articles Next Articles
Extracts of Sambucus adnata Wall. inhibit abnormal angiogenesis in a rat model of osteoarthritis
Jiang Zixian1, Lu Yuchun1, Li Chaomeng1, Zheng Meimei2, Li Xiufang1, Wang Wenjing1
- 1Yunnan University of Chinese Medicine, Kunming 650500, Yunnan Province, China; 2NeuroDawn Pharmaceutical, Nanjing 210000, Jiangsu Province, China
-
Received:2023-11-20Accepted:2023-12-27Online:2024-12-08Published:2024-03-14 -
Contact:Corresponding author: Wang Wenjing, MD, Professor, Doctoral supervisor, Yunnan University of Chinese Medicine, Kunming 650500, Yunnan Province, China Li Xiufang, MD, Professor, Doctoral supervisor, Yunnan University of Chinese Medicine, Kunming 650500, Yunnan Province, China -
About author:Jiang Zixian, Master candidate, Yunnan University of Chinese Medicine, Kunming 650500, Yunnan Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 82160744 (to WWJ); Song Shaojiang Expert Workstation in Yunnan Province, No. 202305AF150030 (to WWJ)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Jiang Zixian, Lu Yuchun, Li Chaomeng, Zheng Meimei, Li Xiufang, Wang Wenjing. Extracts of Sambucus adnata Wall. inhibit abnormal angiogenesis in a rat model of osteoarthritis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(34): 5458-5466.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
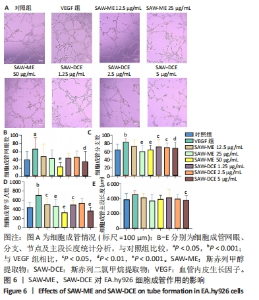
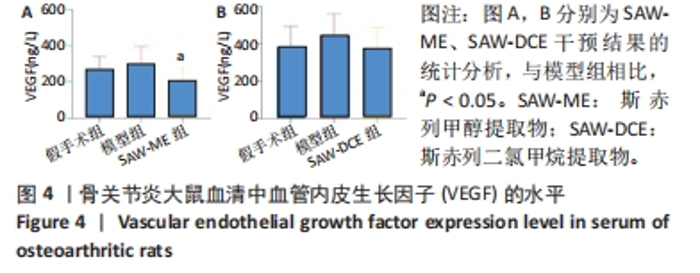
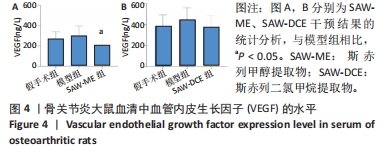
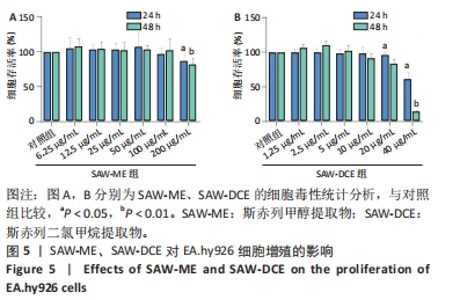
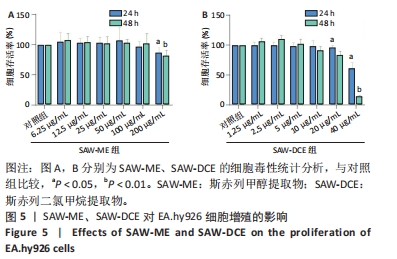
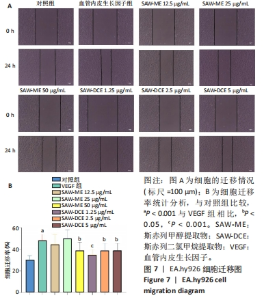
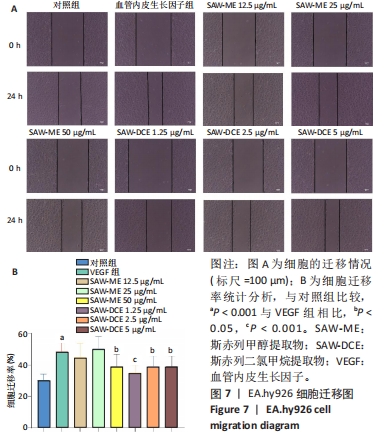
2.5 SAW-ME、SAW-DCE对EA.hy926细胞成管作用的影响 2.5.1 细胞成管网眼数和分支数分析 与对照组相比,VEGF组网眼数 (P < 0.05)、分支数 (P < 0.001)明显增加;与VEGF组相比,给予SAW-ME 50 μg/mL组网眼数 (P < 0.001)、分支数 (P < 0.001)均明显减少;给予SAW-ME 25 μg/mL和12.5 μg/mL时,分支数明显减少 (P < 0.001),网眼数具有减少的趋势,但差异无统计学意义;与VEGF组相比,给予SAW-DCE 5 μg/mL组网眼数 (P < 0.01)、分支数 (P < 0.05)明显减少;给予SAW-DCE质量浓度为2.5 μg/mL和1.25 μg/mL时,分支数均明显减少 (P < 0.05),网眼数减少,但差异无统计学意义,见图6A-C。 2.5.2 细胞成管节点数和成管主段长度分析 与对照组相比,VEGF组节点数明显增加(P < 0.001),主段长度增加,给予SAW-ME质量浓度为50,25和12.5 μg/mL时,节点数明显减少 (P < 0.001或P < 0.05),主段长度减少,但各组的差异均无统计学意义;给予SAW-DCE质量浓度为5 μg/mL时,节点数明显减少 (P < 0.001),段长度明显减少 (P < 0.05),给予SAW-DCE质量浓度为2.5 μg/mL和1.25 μg/mL时,节点数减少,主段长度减少,差异无统计学意义,见图6A,D,E。 "
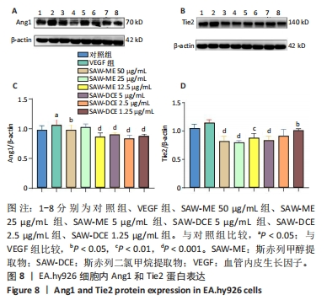
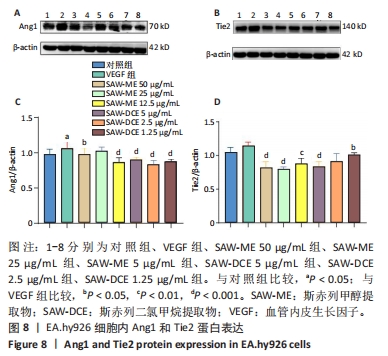
2.7 SAW-ME、SAW-DCE对EA.hy926细胞内Ang1和Tie2蛋白表达的影响 2.7.1 Ang1的蛋白表达 与对照组比较,VEGF组中Ang1的蛋白表达水平明显升高 (P < 0.05);与VEGF组相比,给予SAW-ME的质量浓度为50,12.5 μg/mL时,Ang1蛋白表达水平明显降低 (P < 0.001或P < 0.05);与VEGF组相比,给予SAW-DCE的质量浓度为5,2.5,1.25 μg/mL时,Ang1蛋白表达水平均显著降低 (P < 0.001) ,见图8A,B。提示斯赤列这两种提取物均可以抑制Ang1的蛋白表达水平。 2.7.2 Tie2的蛋白表达 与对照组比较,VEGF组中Tie2的蛋白表达水平有升高的趋势,但无统计学意义。与VEGF组相比,给予SAW-ME质量浓度为50,25,12.5 μg/mL时,Tie2蛋白表达水平明显降低 (P < 0.001或P < 0.01);与VEGF组相比,给予SAW-DCE质量浓度为5,1.25 μg/mL时,Tie2蛋白表达水平均显著降低 (P < 0.001或P < 0.05),见图8C,D。在蛋白水平上说明了斯赤列这两种提取物可以抑制Tie2的表达水平。 "
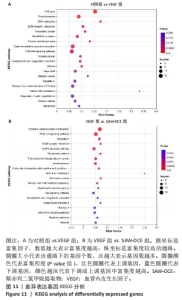
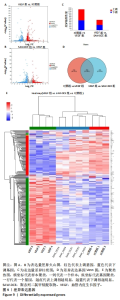
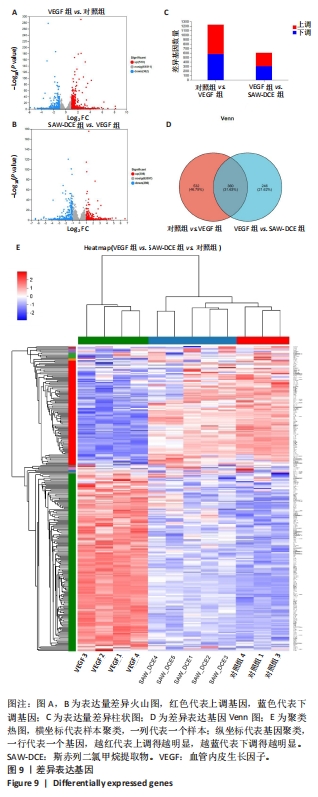
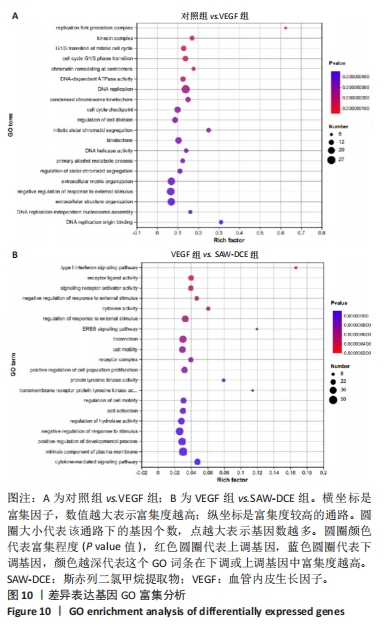
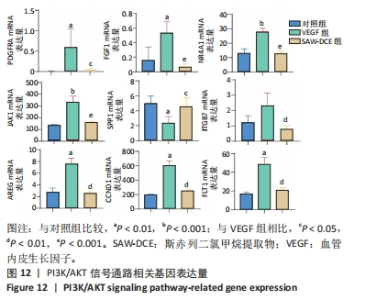
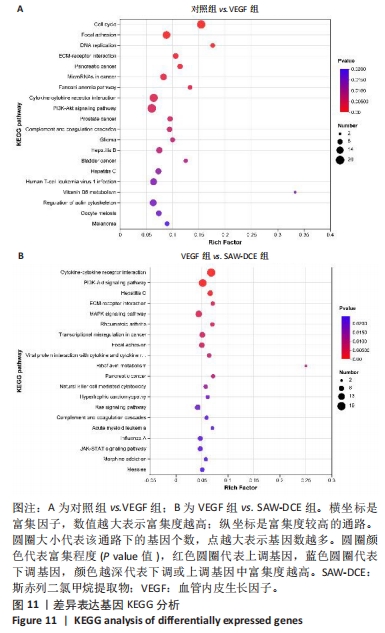
2.8.3 对差异表达基因进行KEGG富集分析 对照组和VEGF组比较的差异基因,富集到了细胞周期、黏着斑、DNA复制、ECM-receptor相互作用、Fanconi anemia通路、PI3K-Akt信号通路等;VEGF组与SAW-DCE组比较的差异基因,富集到了细胞因子-细胞因子受体相互作用、PI3K/Akt信号通路、MAPK信号通路、风湿性关节炎、Ras信号通路、JAK/STAT信号通路等。综合以上KEGG通路富集结果,对富集到的PI3K/Akt信号通路进行分析,对照组与VEGF组比较,在PI3K/Akt信号通路上富集到了20个差异基因;VEGF组与SAW-DCE组比较,在该信号通路上富集到了17个差异基因,见图11。若将两个基因集放在一起比较,在该通路上主要富集到了:PDGFRA;FGF1;NR4A1;JAK1;SPP1;ITGB7;AREG;CCND1;FLT1等基因,生信分析发现,经过SAW-DCE干预之后,这些基因mRNA表达水平都明显下调,推测SAW-DCE可能通过抑制PI3K/AKT信号通路,抑制血管新生和迁移,见图12。 通过转录组分析,对PI3K/AKT信号通路中富集到的差异基因的表达量采用柱状图进行展示,见图12。"
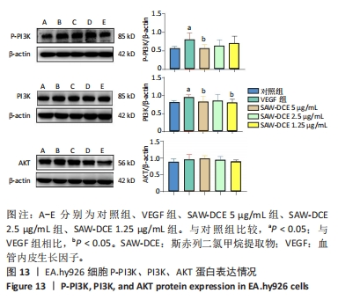
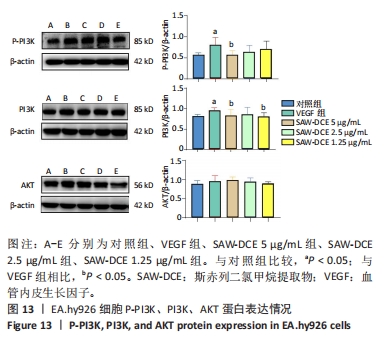
2.9 Western bolt验证测序结果 为进一步验证RNA-seq筛选出基因的表达水平,实验选择了与骨关节炎相关度较高的PI3K/AKT信号通路采用Western bolt进行验证。与对照组比较,VEGF组中内皮细胞P-PI3K、PI3K的表达明显升高 (P < 0.05);与VEGF组相比,SAW-DCE干预后P-PI3K、PI3K的表达均降低,SAW-DCE在5 μg/mL的质量浓度下,P-PI3K、PI3K降低的趋势较为明显 (P < 0.05);在1.25 μg/mL的质量浓度下,PI3K下降趋势较为明显 (P < 0.05);与对照组比较,VEGF组中内皮细胞内AKT的表达有升高的趋势,在SAW-DCE的干预质量浓度为2.5,1.25 μg/mL时,AKT的蛋白表达水平有降低的趋势,但差异没有统计学意义,见图13。"
| [1] SU W, LIU G, LIU X, et al. Angiogenesis stimulated by elevated PDGF-BB in subchondral bone contributes to osteoarthritis development.JCI Insight. 2020;5(8):e135446-e135462. [2] HUNTER DJ, BIERMA-ZEINSTRA S. Osteoarthritis. Lancet. 2019;393 (10182):1745-1759. [3] ZHANG H, WANG L, CUI J, et al. Maintaining hypoxia environment of subchondral bone alleviates osteoarthritisprogression. SCI ADV. 2023; 9(14):7868-7885. [4] WANG YH, KUO SJ, LIU SC, et al. Apelin Affects the Progression of Osteoarthritis by Regulating VEGF-Dependent Angiogenesis and miR-150-5p Expression in Human Synovial Fibroblasts. Cells. 2020;9(3): 594-610. [5] BAGGIO C, BOSCARO C, OLIVIERO F, et al. Gender differences and pharmacological regulation of angiogenesis induced by synovial fluids in inflammatory arthritis. Biomed Pharmacother. 2022;152:113181-113192. [6] ACHUDHAN D, LIU SC, LIN YY, et al. Antcin K inhibits VEGF-dependent angiogenesis in human rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts.J Food Biochem. 2022;46(1):e14022-e14034. [7] CUI Z, WU H, XIAO Y, et al. Endothelial PDGF-BB/PDGFR-beta signaling promotes osteoarthritis by enhancing angiogenesis-dependent abnormal subchondral bone formation.Bone Res. 2022;10(1):58-73. [8] PENG Y, WU S, LI Y, et al. Type H blood vessels in bone modeling and remodeling. Theranostics. 2020;10(1):426-436. [9] LIN C, CHEN Z, GUO D, et al. Increased expression of osteopontin in subchondral bone promotes bone turnover and remodeling, and accelerates the progression of OA in a mouse model. Aging (Albany NY). 2022;14(1):253-271. [10] DING W, XU C, ZHANG Y, et al. Advances in the understanding of the role of type-H vessels in the pathogenesis of osteoporosis. Arch Osteoporos. 2020;15(1):5-14. [11] LU J, ZHANG H, CAI D, et al. Positive-Feedback Regulation of Subchondral H-Type Vessel Formation by Chondrocyte Promotes Osteoarthritis Development in Mice. J Bone Miner Res. 2018;33(5):909-920. [12] ZHU S, BENNETT S, KUEK V, et al. Endothelial cells produce angiocrine factors to regulate bone and cartilage via versatile mechanisms.Theranostics. 2020;10(13):5957-5965. [13] HU W, CHEN Y, DOU C, et al. Microenvironment in subchondral bone: predominant regulator for the treatment of osteoarthritis.Ann Rheum Dis. 2021;80(4):413-422. [14] LIU Y, XIE HQ, SHEN B.Type H vessels-a bridge connecting subchondral bone remodelling and articular cartilage degeneration in osteoarthritis development.Rheumatology (Oxford). 2023;62(4):1436-1444. [15] 云南省食品药品监督管理局.云南省中药材标准2005年版第一册[M].昆明:云南美术出版社,2005. [16] 杨本雷.中国彝族药学[M].昆明:云南民族出版社,2004. [17] 云南省食品药品监督管理局.云南省中药材标准2005版第六册·彝族药(Ⅲ)[M].昆明:云南科技出版社,2010. [18] 云南省卫生局革命委员会.云南中草药[M].昆明:云南人民出版社,1971. [19] 郑梅梅,郑俭彬,江自鲜,等.两种斯赤列提取物促进成骨细胞的增殖与分化[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(11):1677-1682. [20] 郑俭彬,陆玉春,江自鲜,等.彝药斯赤列甲醇提取物对骨关节炎模型大鼠的治疗作用及靶点预测[J].中国组织工程研究,2024, 28(23):3627-3635. [21] 樊孝俊,林景雄,叶海程.虎力散片联合塞来昔布治疗膝骨关节炎的临床研究[J].现代药物与临床,2022,37(12):2855-2859. [22] LIU X, ZHANG P, GU Y, et al. Type H vessels: functions in bone development and diseases. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023;11:1236545-1236555. [23] 林军,郑秋坚,臧学慧,等.膝骨关节炎患者血清IL-2、IL-6与血管内皮生长因子的相关性[J].海南医学,2021,32(5):577-579. [24] 黄鑫,王扬生,薛祖军,等.关节滑液炎性细胞因子白细胞介素-8、白细胞介素-17、血管内皮生长因子检测在膝骨性关节炎临床诊断中的应用价值分析[J].中国卫生检验杂志,2019,29(11):1328-1330. [25] MA K, SINGH G, WANG J, et al. Targeting Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptors as a Therapeutic Strategy for Osteoarthritis and Associated Pain. INT J BIOL SCI. 2023;19(2):675-690. [26] LUDIN A, SELA JJ, SCHROEDER A, et al. Injection of vascular endothelial growth factor into knee joints induces osteoarthritis in mice.Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2013;21(3):491-497. [27] NAGAO M, HAMILTON JL, KC R, et al. Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor in Cartilage Development and Osteoarthritis. Sci Rep. 2017; 7(1):13027-13043. [28] ROMEO SG, ALAWI KM, RODRIGUES J, et al. Endothelial proteolytic activity and interaction with non-resorbing osteoclasts mediate bone elongation. Nat Cell Biol. 2019;21(4):430-441. [29] ZUO Q, LU S, DU Z, et al.Characterization of nano-structural and nano-mechanical properties of osteoarthritic subchondral bone. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2016;17(1):367-380. [30] 黄丽嫣,唐蕾,朱晓琳,等.基于Ang1/Tie2信号通路研究周细胞调控腹膜血管新生的作用机制[J].中国病理生理杂志,2023,39(5): 884-892. [31] 汪元,刘健,黄传兵,等.佐剂关节炎大鼠滑膜血管新生与VEGF/PI3K/AKT信号通路相关性研究[J].山西中医,2022,38(7):56-59. |
| [1] | Li Yongjie, Fu Shenyu, Xia Yuan, Zhang Dakuan, Liu Hongju. Correlation of knee extensor muscle strength and spatiotemporal gait parameters with peak knee flexion/adduction moment in female patients with knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1354-1358. |
| [2] | Qi Haodong, Lu Chao, Xu Hanbo, Wang Mengfei, Hao Yangquan. Effect of diabetes mellitus on perioperative blood loss and pain after primary total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1383-1387. |
| [3] | Du Changling, Shi Hui, Zhang Shoutao, Meng Tao, Liu Dong, Li Jian, Cao Heng, Xu Chuang. Efficacy and safety of different applications of tranexamic acid in high tibial osteotomy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1409-1413. |
| [4] | Yang Yufang, Yang Zhishan, Duan Mianmian, Liu Yiheng, Tang Zhenglong, Wang Yu. Application and prospects of erythropoietin in bone tissue engineering [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1443-1449. |
| [5] | Huang Xiarong, Hu Lizhi, Sun Guanghua, Peng Xinke, Liao Ying, Liao Yuan, Liu Jing, Yin Linwei, Zhong Peirui, Peng Ting, Zhou Jun, Qu Mengjian. Effect of electroacupuncture on the expression of P53 and P21 in articular cartilage and subchondral bone of aged rats with knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1174-1179. |
| [6] | Zhao Garida, Ren Yizhong, Han Changxu, Kong Lingyue, Jia Yanbo. Mechanism of Mongolian Medicine Erden-uril on osteoarthritis in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1193-1199. |
| [7] | Liu Xin, Hu Man, Zhao Wenjie, Zhang Yu, Meng Bo, Yang Sheng, Peng Qing, Zhang Liang, Wang Jingcheng. Cadmium promotes senescence of annulus fibrosus cells via activation of PI3K/Akt signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1217-1222. |
| [8] | Li Rui, Zhang Guihong, Wang Tao, Fan Ping. Effect of ginseng polysaccharide on the expression of prostaglandin E2/6-keto-prostaglandin 1alpha in traumatic osteoarthritis model rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1235-1240. |
| [9] | Wei Juan, Li Ting, Huan Mengting, Xie Ying, Xie Zhouyu, Wei Qingbo, Wu Yunchuan. Mechanism by which static exercise improves insulin resistance in skeletal muscle of type 2 diabetes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1271-1276. |
| [10] | Zhang Kefan, Shi Hui. Research status and application prospect of cytokine therapy for osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 961-967. |
| [11] | Zhang Zeyi, Yang Yimin, Li Wenyan, Zhang Meizhen. Effect of foot progression angle on lower extremity kinetics of knee osteoarthritis patients of different ages: a systematic review and meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 968-975. |
| [12] | Zhang Ya, Mu Qiuju, Wang Zilin, Liu Hongjie, Zhu Lili. Hydrogel loaded with platelet-rich plasma promotes wound healing in diabetic rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(5): 690-696. |
| [13] | Wang Yeyuan, Du Yilang, Yu Dehao, Ning Fengting, Bai Bing. Effect of micro-arc oxidation treatment on biological activity of medical metals [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(5): 771-776. |
| [14] | Wang Jiani, Chen Junyu. Angiogenesis mechanism of metal ions and their application in bone tissue engineering [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(5): 804-812. |
| [15] | Shen Feiyan, Yao Jixiang, Su Shanshan, Zhao Zhongmin, Tang Weidong. Knockdown of circRNA WD repeat containing protein 1 inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis of chondrocytes in knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 499-504. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||