Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (34): 5552-5557.doi: 10.12307/2024.805
Previous Articles Next Articles
Mechanism by which exercise controls uric acid level
Wu Yuwei1, 2, Zhu Jiang2, 3, Zheng Bing2, 3, Wu Zonghui1, 2, 3
- 1School of Physical Education, Southwest University, Chongqing 400715, China; 2Sports Rehabilitation Institute of Southwest University, Chongqing 400715, China; 3Southwest University Hospital, Chongqing 400715, China
-
Received:2023-11-16Accepted:2024-01-04Online:2024-12-08Published:2024-03-15 -
Contact:Wu Zonghui, Professor, Master’s supervisor, Sports Rehabilitation Institute of Southwest University, Chongqing 400715, China; Southwest University Hospital, Chongqing 400715, China -
About author:Wu Yuwei, Master candidate, School of Physical Education, Southwest University, Chongqing 400715, China; Sports Rehabilitation Institute of Southwest University, Chongqing 400715, China -
Supported by:Chongqing Municipal Chinese Medicine Key Construction Discipline Project, No. 2021-4322190044 (to WZH); Chongqing Municipal Sports Research Project, No. C202125 (to WZH)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wu Yuwei, Zhu Jiang, Zheng Bing, Wu Zonghui. Mechanism by which exercise controls uric acid level[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(34): 5552-5557.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
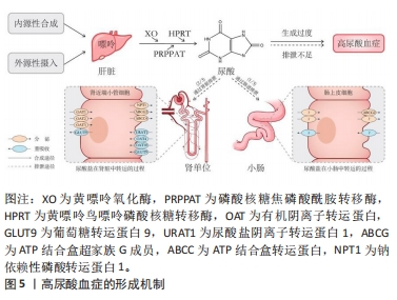
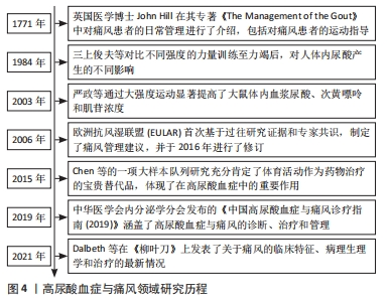
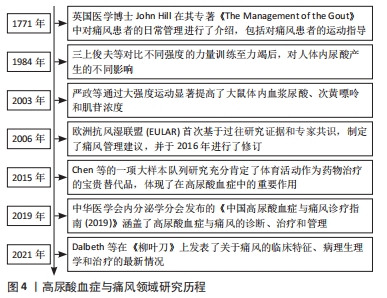
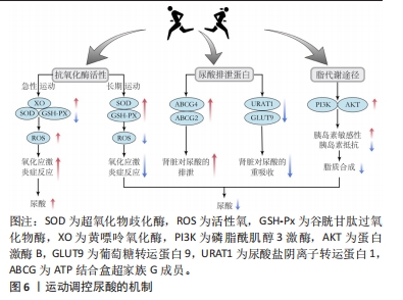
研究尿酸的历史可以追溯到18世纪,科学家首次描述了痛风(由尿酸积聚引起的疾病)的症状和特征,痛风被称为“富贵病”和“帝王病”。英国医学博士John Hill[3]于1771年在专著《The Management of the Gout》中详细介绍了痛风患者的日常管理办法,包括运动指导。20世纪后期至21世纪初期,随着对代谢过程和运动生理学的深入了解,许多学者开始探索运动如何影响嘌呤代谢及尿酸的生成和排泄[4-5]。2006年,欧洲抗风湿联盟(EULAR)首次依据历史研究证据和专家共识制定了痛风管理建议,并且于2016年进行了修订[6-7],这些建议主要涵盖非药理和药理方法、痛风急性发作的管理、长期尿酸盐降低药物治疗、预防急性发作以及合并症注意事项。2015年,CHEN等[8]的一项大样本队列研究充分肯定了体育活动作为药物治疗的宝贵替代品在高尿酸血症的治疗中发挥着关键作用。2019年,中华医学会内分泌学分会发布的《中国高尿酸血症与痛风诊疗指南(2019)》使用GRADE分级方法[9],首次提出了亚临床痛风、难治性痛风的概念和诊治意见,并且对碱化尿液相关问题和痛风常见合并症药物选择进行推荐。2021年,DALBETH等[10]在《柳叶刀》上发表了关于痛风的临床特征、病理生理学和治疗的最新情况。 2.2 高尿酸血症的机制 高尿酸血症是机体嘌呤代谢异常导致的一种代谢综合征,是痛风发病的生理基础,当正常成年人血液中尿酸浓度高于420 μmol/L时即可确诊 [9]。尿酸在体内过度积累的主要原因可分为肝脏代谢和细胞周转产生过多、肾脏和肾外排泄不足,或两者共同作用[10],见图5。"
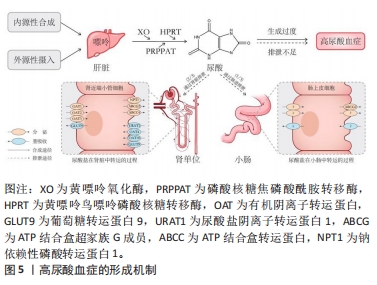
2.2.1 尿酸的形成 嘌呤代谢途径的异常活跃会导致尿酸盐过度生成,是导致尿酸水平升高的重要原因。尿酸作为人体嘌呤代谢的最终产物在肝脏、肾脏和小肠中经过一系列酶的催化作用逐步生成。黄嘌呤氧化酶、磷酸核糖焦磷酸酰胺转移酶及次黄嘌呤鸟嘌呤磷酸核糖转移酶等多种酶的缺陷可能成为原发性高尿酸血症的重要原因。黄嘌呤氧化酶作为一种铜离子依赖酶被认为是治疗高尿酸血症的重要靶点,其存在于肝脏、肾脏、骨骼肌等多种组织和器官中。在人体合成路径中约有80%的尿酸来自内源合成,20%来自高嘌呤食物。通常情况下,体内嘌呤的分解和尿酸的合成速度相对稳定,每天尿酸产量大约为700 mg。然而在极少数情况下,例如患有白血病等恶性肿瘤时,细胞的大规模无序增殖和崩解会导致DNA释放进入血液,增加嘌呤的含量并在酶的作用下导致体内尿酸合成急剧增加。尽管饮食在尿酸合成过程中占比不高,但高嘌呤饮食被认为是高尿酸血症和痛风的危险因素,同时也是不同个体尿酸水平差异的重要原因。研究表明,酒精、肉类、土豆等高嘌呤食物及含糖软饮料和能量饮料的摄入都会导致体内尿酸水平的增加[11]。 2.2.2 尿酸的排泄 尿酸排泄不足是导致尿酸浓度升高的主要原因。人体中约有1/3的尿酸通过消化道排出,其排泄机制尚不完全清楚,仅有少数研究认为与肠道菌群有关;而余下的2/3尿酸则需通过肾脏经历排泄、重吸收、再排泄、再吸收等步骤[11]。人体维持尿酸的机制使得肾脏尿酸重吸收效率极高,仅有6%-10%的尿酸最终被排出体外,其余绝大部分被重新吸收。尿酸排出量主要依赖于肾小管上皮细胞中尿酸转运蛋白家族的协同作用,它们的正常功能对于维持体内尿酸代谢平衡至关重要。在肾脏中,尿酸经肾小球自由过滤,排泄则由近端小管中的一系列尿酸转运蛋白控制。在细胞表面,介导尿酸进入细胞的有尿酸阴离子交换蛋白,包括尿酸盐转运蛋白、有机阴离子转运蛋白4、有机阴离子转运蛋白10和葡萄糖转运蛋白9,而分泌转运蛋白包括ATP结合盒超家族G成员2、ATP结合盒转运蛋白4和钠依赖性磷酸转运蛋白1 [12]。另外,细胞的外膜还有其他转运蛋白控制尿酸盐的运输,其中有机阴离子转运蛋白1、有机阴离子转运蛋白2和有机阴离子转运蛋白3负责将尿酸盐运输至近端小管细胞,而葡萄糖转运蛋白9则调节尿酸盐的再吸收[13]。在肠道中,分泌转运蛋白ATP结合盒超家族G成员2与肠道尿酸盐排泄密切相关,其遗传变异可能导致肾外尿酸盐分泌不足和高尿酸血症[14],其他尿酸盐转运体也可能影响肠道尿酸盐排泄,但目前尚未确证[15]。基因内遗传多态性编码的肾脏和肠道跨膜转运体强调了其在影响尿酸盐浓度方面的重要性,全基因组关联研究已确定183个位点与血清尿酸盐浓度高低相关,解释了约7.7%的血清尿酸盐浓度变异率,其中55个与痛风风险相关[11]。葡萄糖转运蛋白9、ATP结合盒超家族G成员2和尿酸盐转运蛋白1的变异与全球多个人群的血清尿酸盐和痛风关联最为密切[16]。尽管遗传因素在高尿酸血症形成中起着重要作用,但仅具有高风险基因并不一定导致高尿酸血症的发生,基因和环境相互作用、转录生长因子及细胞骨架等因素也会影响尿酸水平。 2.3 运动对尿酸的调控 运动可以促进脂肪和嘌呤代谢、减轻炎症反应、降低脂肪含量,从而调节尿酸的合成与排泄,达到预防和治疗高尿酸血症的目的。高尿酸血症为痛风和尿酸性肾病的主要原因之一,运动可以降低痛风的发病率和症状严重程度并减少尿酸结晶的形成,因此,国内外相关的高尿酸血症或痛风治疗指南均将运动作为一种重要的非药物治疗手段[9]。现有研究表明,不同类型和强度的运动对尿酸的调控效果有所差异,需要根据个体情况选择合适的运动方式。 2.3.1 有氧耐力运动对尿酸的调控 肥胖被认为是高尿酸血症的独立危险因子 [17],其导致体内脂肪堆积,影响肝脏代谢尿酸的能力,从而使尿酸水平升高。此外,肥胖还可能引发胰岛素抵抗,加重尿酸的代谢负担。研究表明,有氧运动对于全身脂肪和下肢脂肪的改善效果明显优于其他运动方式[18]。谢舟煜等[19]对肥胖大鼠进行了8周的跑台训练,发现脂肪堆积程度和脂代谢功能均得到改善。曲静等[20]和潘丽英等[21]对不同程度肥胖的青年进行了4-6周的40%心率储备+安静心率和60%-75%最大心率的慢跑、游泳等有氧运动训练,结果显示,训练后的青少年在基础生理功能、肥胖程度、糖脂代谢和炎症反应等方面均有所改善;此外,尿酸浓度与体质量指数和腰围呈正相关 [22]。以上研究表明,有氧运动可以通过降低肥胖高尿酸血症患者的身体形态指标来改善糖脂代谢,从而降低高尿酸血症风险。老年人群是高尿酸血症的高发人群,随着年龄的增长,身体对尿酸的代谢能力逐渐下降,同时伴随着代谢产生的尿酸增加,导致尿酸上升。一项多中心研究表明,每周锻炼不足1 h的高尿酸血症患者死亡率增加了27%,而每周(≥7.5代谢当量/h)进行锻炼的高尿酸血症患者死亡率降低11%,寿命延长了4-6年[8]。此外,黄秀兰等 [23]对老年慢性病患者进行每周三四次的40%-50%最大心率的运动后,患者糖脂水平、24 h尿酸等指标明显改善。刘振华等 [24]将高龄[(83±4)岁]老人根据其不同的运动习惯进行对比后发现,高运动组(有氧运动> 2年,每次> 30 min)患者高尿酸血症患病率显著低于低运动组(有氧运动< 2年,每次< 30 min),说明良好的运动习惯不仅可以帮助老年人预防高尿酸血症,还能降低死亡风险、延长寿命。 不同运动强度、运动频次、运动形式的有氧运动会对尿酸产生不同的影响。HOU等 [25]对比了12个月无运动组、57%-63%最大心率的轻度步行组和64%-76%最大心率的慢跑组的尿酸水平,运动组尿酸水平均得到了改善,并且中等强度慢跑组效果最好,提示运动强度是调控尿酸的重要参数,但目前缺乏长期大强度有氧运动对尿酸影响的相关研究。在运动频次上,辛东岭等 [26]将高尿酸血症患者分为高运动频次组(5次/周)和低运动频次组(3次/周),进行3个月30-45 min/次、强度为64%-76%最大心率的慢跑运动,结果显示两组的尿酸水平均有改善,并且高运动频次组效果更加明显。因此,各个组织机构都建议采用中等强度运动,运动时间不低于150 min/周的运动方案。但值得注意的是,日常运动时即使无法达到建议运动量和运动强度,如每天锻炼15 min而不是30 min以上,或选择快走而不是慢跑,也可以减少由高尿酸导致的死亡率增加 [27]。 2.3.2 力量训练对尿酸的调控 骨骼肌质量和密度是反映力量素质的主要标志。近年来,大量横断面研究认为血尿酸浓度与肌肉质量和抓地力之间存在密切联系。一项针对500名成年人的研究发现,较高的尿酸水平与更高的骨骼肌脂肪指数存在相关性,并且与体质量指数无关[28],这与LUSTGARTEN等 [29]的研究结果间接一致。然而一些研究结果存在争议,例如HUANG等[30]的研究认为成年男性高尿酸血症人群的握力和伸膝力量显著低于健康人群,并且尿酸浓度与肌肉力量呈倒“J”形关系。目前,尚不清楚尿酸与肌肉质量和力量之间的确切联系机制,这可能与尿酸强大的抗氧化能力有关,尿酸可能保护骨骼肌功能免受活性氧诱导的蛋白质氧化损伤。力量训练对尿酸的影响比有氧运动更加敏感,三上俊夫等[5]对比了不同初始强度(30%,60%和80%的最大肌力)急性力量训练至力竭后受试者的尿酸水平,发现30%和60%最大肌力组的受试者尿酸显著升高,而80%最大肌力组尿酸上升不明显。然而,对于长期力量训练对尿酸的影响目前仍存在争议。成晓翠等[31]对痛风患者进行55%-70%最大摄氧量的有氧慢跑和8-12次最大重复次数负荷的弹力带抗阻训练,延续管理24周后发现两者均有助于降低尿酸和血脂水平。但KRAEMER 等[32]在对力量项目运动员进行4周超量负荷全身抗阻训练的研究中发现,除第1周血尿酸浓度显著上升,后续周期均无明显变化。FAELLI等 [33]对男性青年进行8周50%-60%最大肌力到65%-75%最大肌力的抗阻训练,尽管尿酸水平在第一次和最后一次训练后都有所增加,但最后一次增加的幅度明显降低,这表明单独的力量训练方案存在提高尿酸水平的风险,但通过长期坚持、控制强度或与有氧运动结合训练能够达到更好的效果。 2.3.3 高强度间歇训练对尿酸的调控 与传统的中等强度连续训练模式相比,高强度间歇训练具有省时(≤4 min)/高效(80%-100%最大心率)的特点。苗晶晶[34]对成年痛风患者进行了为期1个月的有氧高强度间歇训练,以85%的心肺运动试验峰值功率为功率踏车起始运动负荷量,持续训练3 min、间歇1 min,患者血清尿酸、身体骨骼肌、脂肪含量均有所改善,同时降低了痛风发作频次。史锦伟 [35]对单纯性肥胖青少年进行4周20%-40%储备心率有氧运动(快走、椭圆机等)结合40%-60%储备心率高强度间歇性力量训练(自重训练、杠铃操等),结果显示各项指标显著降低,同时减少了痛风发作的风险并提高了肝功能。然而,高强度间歇训练对高尿酸血症影响的直接研究尚不充分,大多数研究侧重于通过调节可能导致尿酸升高的因素(如脂肪、糖脂代谢和胰岛素敏感性等)来探索高强度间歇训练对高尿酸血症的影响。HAYES 等[36]对久坐老年男性进行为期6周40%峰值功率的高强度间歇冲刺训练,结果表明训练可略微改善空腹血糖、胰岛素和胰岛素抵抗,但对规律运动的老年人影响不明显。李抒等[18]对肥胖儿童采用了100%-120%最大有氧速度(使最大心率保持在80%以上)的冲刺跑和往返跑训练,发现内脏脂肪显著减少,效果比中等强度连续训练更好。 总体而言,运动对尿酸调控的效果因运动类型、强度及个体差异而异。有氧运动对降低高尿酸血症风险有正面作用,但需根据个体情况选择合适的运动方式。力量训练对尿酸水平影响尚不确定,可通过结合有氧运动达到更佳效果。高强度间歇训练显示了一定潜力,但仍需更深入的研究验证其有效性。未来需要更多关于不同运动方式对尿酸影响的深入研究,以更精准地指导高尿酸血症的预防和管理。 2.4 运动调控尿酸的机制 近年来,学者们广泛关注运动作为非药物手段对尿酸调控的潜在机制。研究指出,运动可以通过调节抗氧化酶活性、尿酸排泄蛋白表达及脂质代谢途径来影响尿酸水平,从而降低高尿酸血症和痛风发作的风险,见图6。"
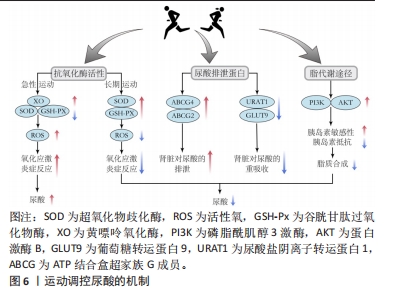
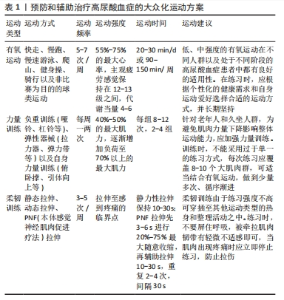
2.4.1 运动通过调节抗氧化酶的活性来改善尿酸水平 尿酸在机体中具有氧化-还原的双重作用,当尿酸水平正常时,其表现为抗氧化作用,有助于增强免疫功能和抗衰老;然而当尿酸水平过高时,表现为促氧化作用,导致内皮细胞损伤、促炎因子产生,引发氧化应激,从而诱发肾病综合征、代谢综合征等疾病 [37]。在急性运动过程中肾脏中的活性氧水平增加,导致暂时性炎症反应;同时,骨骼肌内腺嘌呤核苷酸发生降解,生成大量次黄嘌呤,从而增加黄嘌呤氧化酶活性。黄嘌呤氧化酶作为嘌呤代谢的重要酶在尿酸生成的最后步骤中催化次黄嘌呤和氧化黄嘌呤,其活性增加被认为是高尿酸血症的主要原因之一 [38]。研究发现,长时间有氧运动至力竭会导致大鼠心肌组织活性氧和心肌线粒体丙二醛显著升高[39],暗示力竭运动后机体的自由基产生和清除平衡被破坏,诱发氧化应激反应。另一研究表明,对代谢综合征人群进行单次30 min恒定65%-70%最大心率强度的训练后,黄嘌呤氧化酶活性增加,超氧化物歧化酶活性显著降低[40]。因此,运动引发尿酸暂时性升高可能与尿酸合成增多和肾脏氧化性损伤密切相关。然而,长期运动可使机体产生运动适应性,提高抗氧化酶的活性和表达水平,降低氧化损伤的风险。针对糖尿病肾病小鼠的研究也表明,长期有氧跑步训练能显著降低丙二醛含量,增加谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶及超氧化物歧化酶活性[41-43]。另外,有氧运动后老年女性体内的总抗氧化物参数显著提高[44]。因此,不同强度的急性运动可导致体内尿酸升高,主要是由于机体出现抗氧化保护,减少活性氧引起的氧化应激和调节黄嘌呤氧化酶活性,而长期规律运动(无论何种类型)能减轻机体氧化损伤程度,在尿酸的调控中发挥重要作用。 2.4.2 运动通过调节尿酸排泄蛋白的表达来改善尿酸水平 肾脏是尿酸排泄的主要器官,通过肾小球滤过和肾小管重吸收来调节尿酸的水平。临床上90%的高尿酸患者都是尿酸排泄能力下降所致,而运动可通过调节尿酸排泄蛋白的表达、减轻炎症反应等途径促进尿酸的排泄。现有研究认为,尿酸转运蛋白主要属于溶质载体转运蛋白和ATP结合盒转运蛋白2个转运蛋白超家族,而目前前者转运体数量相对更多。溶质载体转运蛋白成员是二级活性转运体或利用其他过程产生的电化学梯度促进转运体,而ATP结合盒转运蛋白成员则利用ATP的直接结合和水解 [45]。ATP结合盒转运蛋白4和ATP结合盒超家族G成员2是肾细胞排泄尿酸的重要途径,当它们的表达被抑制时,肾脏尿酸排泄减少,体内尿酸水平增加。核因子κB和核因子E2相关因子2作为调控ATP结合盒转运蛋白家族蛋白表达的上游因子,在高尿酸血症发病机制和临床病理表型中起着至关重要的作用。有研究表明,具有抗氧化作用的药物会通过调节核因子E2相关因子2和核因子κB的表达来增加ATP结合盒转运蛋白4和ATP结合盒超家族G成员2的表达,而有氧运动具有抗氧化作用,可以通过调节肾脏中核因子κB和核因子E2相关因子2的表达来提高身体的抗氧化能力,从而削弱氧化应激损伤和减少炎症反应,进而缓解肾脏损伤和改善肾功能,达到与药物相似的效果 [46-47]。目前,有氧运动对身体各种组织和器官中的核因子E2相关因子2表达有积极作用已被证明,但运动通过核因子κB途径上调ATP结合盒超家族G成员2表达的机制尚不明确,仅有一项12周中等强度跑台运动显示大鼠海马体中的ATP结合盒超家族G成员2表达增加,但对肾脏中 ATP结合盒转运蛋白4和ATP结合盒超家族G成员2表达的影响尚未报告 [48]。尿酸盐阴离子转运蛋白1和葡萄糖转运蛋白9 主要负责肾脏对尿酸的重吸收,当它们的表达减少时体内尿酸水平降低 [49-50]。其中,尿酸盐阴离子转运蛋白1位于肾皮质近端小管的管腔膜上,是一种具有12跨膜结构域的蛋白质,对其他有机阴离子(如乳酸)有亲和力,这也是尿酸盐吸收的强大跨刺激作用的原因(一侧的乳酸盐刺激另一侧的尿酸盐运输)。葡萄糖转运蛋白9则主要存在于近曲小管的顶端和基底外侧膜上,与葡萄糖转运蛋白葡萄糖转运蛋白1和葡萄糖转运蛋白5具有显著的同源性,但在功能上主要是负责尿酸转运 [51]。近期的一项大鼠实验显示,长期有氧运动能够通过核因子E2相关因子2调节ATP结合盒转运蛋白4、尿酸盐阴离子转运蛋白1和葡萄糖转运蛋白9,通过核因子κB调节ATP结合盒超家族G成员2,降低大鼠尿酸水平,对调节肾尿酸转运蛋白表达发挥了重要作用[52]。然而,运动后血清中的哪些循环因子最终影响核因子E2相关因子2和核因子κB仍不清楚。 综上所述,有氧运动对尿酸排泄蛋白表达具有益处,但力量训练、高强度间歇运动以及大强度急性运动对不同尿酸排泄蛋白机制的影响仍需进一步研究探讨。 2.4.3 运动通过调节脂代谢途径来改善尿酸水平 脂质是嘌呤合成的前体,外界热量的摄入为嘌呤合成提供充足的能量基础,使得尿酸升高 [53]。在肥胖人群中,内脏脂肪堆积过多会产生过量游离脂肪酸,刺激脂肪酸合成,增加嘌呤代谢量,导致尿酸合成增加 [54]。肥胖还会引发胰岛素抵抗、水钠潴留和尿液酸化,增加肾近端小管对尿酸的重吸收,进一步减少尿酸的排泄[55]。当体内尿酸升高时,不仅会引起脂肪细胞炎症反应的发生,还会使脂蛋白酶活性下降影响脂质代谢,导致高血压、肥胖、2型糖尿病等相关合并症的发生。葡萄糖转运蛋白4是一种跨膜己糖转运蛋白,其在脂肪组织中的选择性缺失可能导致肌肉和肝脏胰岛素抵抗,加重尿酸代谢的负担 [56]。运动能有效促进葡萄糖转运蛋白4表达,但其潜在因素、起源组织和生理相关性仍需进一步研究 [57]。过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体γ是重要的细胞分化转录因子,在抑制炎症反应和炎症因子的产生、改善脂肪肝方面发挥重要作用 [58],活化的过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体γ可促进磷脂酰肌醇3激酶/蛋白激酶 B信号通路增强胰岛素敏感性,加速三酰甘油在外周组织的分解,抑制胰高血糖素的产生,从而改善糖脂代谢紊乱[59]。研究表明,长期中等强度有氧运动能增加过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体γ、磷脂酰肌醇3激酶、蛋白激酶 B的蛋白表达 [60]。此外,运动还可以作用于骨骼肌组织、外周组织间接改善改善肝脏胰岛素抵抗,减少脂肪堆积。近年来运动对脂代谢的研究认为,中等强度急性运动会使肝脏三酰甘油增加并于24 h内恢复原有水平 [61],高强度急性运动会使肝脏组织发生炎症反应,出现氧化应激,释放肝脏转氨酶等产生消极影响[62]。而长期运动干预有助于改善肝脏代谢,促进肝脏脂肪酸,提高胰岛素敏感性等 [63]。因此,运动通过调节脂代谢途径来调节尿酸水平,对高尿酸血症及其他心血管、糖尿病等合并症患者具有重要意义。 2.5 运动预防和治疗高尿酸血症的实践 流行病学、临床研究以及各种实验已经确证了运动在预防和治疗高尿酸血症及减少痛风发作中的有效性。一项涉及46万个样本的观察性研究发现,相较于尿酸水平正常但不进行运动的人群,无症状高尿酸血症患者若进行适度运动预期寿命可增加4-6年,并且可消除高尿酸带来的死亡风险[8]。因此,世界卫生组织、美国运动医学会等组织机构都建议通过建立运动处方来预防和治疗高血尿酸症和痛风[64]。针对高血尿酸症或痛风患者的综合性运动处方通常包括每天持续运动20-30 min或一周累计运动90-150 min,主要以低、中强度为主,避免长时间剧烈运动,运动类型包括有氧运动、柔韧性运动、神经肌肉训练及轻度高重复次数的力量练习。然而,鉴于年龄、个体运动能力、健康状况以及疾病阶段的差异,需因人而异地制定运动方案。因此在相关研究的基础上,为高血尿酸症患者制定合适的大众化运动方案,并且针对不同阶段的患者提出执行运动方案的注意事项。为方便实行,运动强度采用大众易获取的最大心率百分比、代谢当量和0-20级主观疲劳感觉等指标。 在运动方式上,有氧运动可采取快走、慢跑、慢速游泳、爬山、健身操、骑行以及进行一些非比赛为目的的球类运动,力量训练可采取负重训练(哑铃、杠铃等)、弹性器械(拉力器、弹力带等)以及自身力量训练(俯卧撑、引体向上等)。在运动频率、强度和时间上,应根据不同人群的特点进行个性化安排。对于成年人,有氧运动建议每周5-7次,强度控制在55%-75%的最大心率,主观疲劳感觉保持在12-13级之间,每天20-30 min;而力量训练则建议每周一两次,强度控制在40%-50%的最大肌力逐渐增加至80%的最大肌力,每组8-12次,2-4组。老年人有氧运动每周5-7次,强度为55%-75%最大心率,主观疲劳感觉保持在11-13级,每天20-30 min;力量训练每周一两次,强度从40%-50%的最大肌力逐渐增加至60%-70%的最大肌力,每组10-15次重复,一两组;在每次练习之后需进行10-20 s的拉伸训练,2-4次重复,间隔30 s,见表1。"
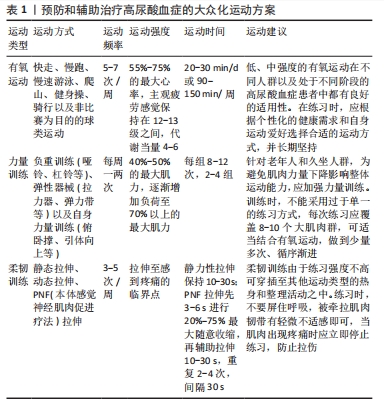

对于处在不同阶段的高尿酸血症患者进行运动时,应注意以下事项:①在无症状高尿酸阶段,由于痛风尚未发作,有氧耐力运动和高强度间歇训练是降低尿酸并促进脂肪代谢的良好选择,过于专注于长期单一的力量训练可能会导致尿酸水平升高。然而在老年人和久坐人群中,肌肉力量下降可能会显著影响整体运动能力,因此对于这些患者适当增加力量训练是有益的。由于高强度间歇训练需要更高的运动能力和身体素质,最好在专业人士的监督下进行。②在慢性痛风阶段,需要注意2种情况:一种是痛风急性发作期间,为避免增加关节损伤,应避免剧烈运动,当痛风发作时应立即停止运动,冰敷20 min;另一种情况是痛风发作的间歇期,运动时应注意不能诱发过度的应激,如出现脱水、寒冷等情况可能再次诱发痛风。③最后是痛风性关节炎阶段,人们通常担心关节受损、害怕疼痛而逃避运动,反而加重了高尿酸、痛风症状。现有研究认为规律运动可以像药物一样缓解关节炎疼痛,因此在这个阶段的患者参考上述运动方案时,应注意在运动方式上应选择关节容易活动的运动,如步行、自行车、水中的有氧运动等,既避免了受伤的风险,同时也不会因为过度扭曲而损伤关节。在运动强度上应循序渐进,尤其是无运动习惯者,做到少量多次。在运动类型上,应注重身体主要肌肉群的力量训练,每周训练频次由一两次逐渐增加至四五次,每次一两组,每组重复8-10次,随着力量的增大,不仅能够为关节提供更大的支撑、减轻关节负荷,还能有效缓解疼痛。同时,为保持关节的活动度,进行每周四五次的柔韧性训练,拉伸单个动作至轻微不适状态,保持10-15 s,重复5-10次。值得注意的是,运动处方制定应建立在准确测量和评估个体健康状况和运动能力的基础之上,针对不同人群及潜在的基础疾病进行差异化处理,以满足个性化的健康需求和运动偏好。"

| [1] DEHLIN M, JACOBSSON L, RODDY E. Global epidemiology of gout: prevalence, incidence, treatment patterns and risk factors. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2020;16(7):380-390. [2] ZHANG T, GU Y, MENG G, et al. Genetic Risk, Adherence to a Healthy Lifestyle, and Hyperuricemia: The TCLSIH Cohort Study. Am J Med. 2023;136(5):476-483.e5. [3] JOHN H. The Management of the Gout: In Diet, Exercise, and Temperc. R. Baldwin, 1771. [4] 严政,于文兵,马继政.大强度运动对大鼠嘌呤核苷酸代谢的影响及运动模型研究[J].体育与科学,2003(5):66-68. [5] 三上俊夫,中山正幸,丹信介,等.运动性高尿酸现象的研究[J].尿酸,1984, 8(2):151-158. [6] ZHANG W, DOHERTY M, BARDIN T, et al. EULAR Standing Committee for International Clinical Studies Including Therapeutics. EULAR evidence based recommendations for gout. Part II: Management. Report of a task force of the EULAR Standing Committee for International Clinical Studies Including Therapeutics (ESCISIT). Ann Rheum Dis. 2006;65(10):1312-1324. [7] RICHETTE P, DOHERTY M, PASCUAL E, et al. 2016 updated EULAR evidence-based recommendations for the management of gout. Ann Rheum Dis. 2017;76(1):29-42. [8] CHEN JH, WEN CP, WU SB, et al. Attenuating the mortality risk of high serum uric acid: the role of physical activity underused. Ann Rheum Dis. 2015;74(11):2034-2042. [9] 中华医学会内分泌学分会.中国高尿酸血症与痛风诊疗指南(2019)[J].中华内分泌代谢杂志,2020,36(1):1-13. [10] DALBETH N, MERRIMAN TR, STAMP LK. Gout. Lancet. 2016;388(10055):2039-2052. [11] LONG T, LIU L. Research Progress on the Relationship between Dietary Patterns and Hyperuricemia. Appl Bionics Biomech. 2022;2022:5658423. [12] DALBETH N, GOSLING AL, GAFFO A, et al. Gout. Lancet. 2021;397(10287):1843-1855. [13] MANDAL AK, MOUNT DB. The molecular physiology of uric acid homeostasis. Annu Rev Physiol. 2015;77:323-345. [14] ICHIDA K, MATSUO H, TAKADA T, et al. Decreased extra-renal urate excretion is a common cause of hyperuricemia. Nat Commun. 2012;3:764. [15] XU X, LI C, ZHOU P, et al. Uric acid transporters hiding in the intestine. Pharm Biol. 2016;54(12):3151-3155. [16] TIN A, MARTEN J, HALPERIN KUHNS V L, et al. Target genes, variants, tissues and transcriptional pathways influencing human serum urate levels. Nat Genet. 2019;51(10):1459-1474. [17] 薛政昊,陈德明.运动防治肥胖合并高尿酸血症患者研究现状与展望[J].哈尔滨体育学院学报,2022,40(5):82-90. [18] 李抒,曹甍,邹昱,等.高强度间歇训练对肥胖儿童内脏脂肪和心肺适能的影响[J].体育学刊,2023,30(3):138-144. [19] 谢舟煜,何艾舟,李婷,等.有氧运动对肥胖大鼠内皮功能障碍和内脂素的影响[J].中国实验动物学报,2022,30(4):533-539. [20] 曲静,林小晶,王业玲,等.4周结合饮食控制的有氧运动降低肥胖青年血清炎症因子chemerin水平及其应用价值[J].中国体育科技,2022,58(7):76-82. [21] 潘丽英,马春莲,谷涌泉.6周有氧运动改善不同程度肥胖青少年体质健康的研究[J].武汉体育学院学报,2022,56(7):76-83. [22] 安亚琼,傅松波,汤旭磊,等.兰州市居民高尿酸血症现状及相关因素分析[J].中国预防医学杂志,2020,21(8):841-845. [23] 黄秀兰,于金芝,李春霞.有氧运动对老年慢性病患者健康管理效果分析[J].中国卫生标准管理,2022,13(8):60-62. [24] 刘振华,严鹏飞,刘陪沛,等.高龄老人有氧运动与血脂及尿酸关系的研究[J].人民军医,2014,57(8):840-841. [25] HOU Y, MA R, GAO S, et al. The Effect of Low and Moderate Exercise on Hyperuricemia: Protocol for a Randomized Controlled Study. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021;12:716802. [26] 辛东岭,刘淑文,戴剑松.不同剂量运动对高尿酸血症影响的试验研究[J].科技资讯,2020,18(13):204-206. [27] VILLEGAS R, XIANG YB, CAI Q, et al. Prevalence and determinants of hyperuricemia in middleaged,urban Chinese men. Metab Syndr Relat Disord. 2010;8(3):263-270. [28] CHEN N, HAN T, LIU H, et al. Muscle Fat Content Is Strongly Associated With Hyperuricemia: A Cross-Sectional Study in Chinese Adults. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022;13:935445. [29] LUSTGARTEN MS, FIELDING RA. Metabolites related to renal function, immune activation, and carbamylation are associated with muscle composition in older adults. Exp Gerontol. 2017;100:1-10. [30] HUANG C, NIU K, KOBAYASHI Y, et al. An inverted J-shaped association of serum uric acid with muscle strength among Japanese adult men: a cross-sectional study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2013;14:258. [31] 成晓翠,孙明艳,孙巧云,等.有氧运动和抗阻运动在痛风患者延续管理中的应用效果比较[J].山东医药,2021,61(35):72-75. [32] KRAEMER WJ, RATAMESS NA, VOLEK JS, et al. The effects of amino acid supplementation on hormonal responses to resistance training overreaching. Metabolism. 2006;55(3):282-291. [33] FAELLI E, BISIO A, CODELLA R, et al. Acute and Chronic Catabolic Responses to CrossFit((R)) and Resistance Training in Young Males. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020;17(19):71-72. [34] 苗晶晶.高强度间歇训练对青年高尿酸血症痛风患者血清尿酸水平和痛风发作频次的影响[J].中国疗养医学,2021,30(1):78-80. [35] 史锦伟.有氧运动结合高强度间歇性力量训练对单纯性肥胖青少年的减肥效果研究[D].上海:上海体育学院,2020. [36] HAYES LD, HERBERT P, SCULTHORPE N, et al. High intensity interval training (HIIT) produces small improvements in fasting glucose, insulin, and insulin resistance in sedentary older men but not masters athletes. Exp Gerontol. 2020;140:111074. [37] 苏志燕,刘薇,史婷婷.老年2型糖尿病患者血尿酸浓度与代谢综合征的相关性分析[J].首都医科大学学报,2023,44(1):137-142. [38] WANG F, ZHAO X, SU X, et al. Isorhamnetin, the xanthine oxidase inhibitor from Sophora japonica, ameliorates uric acid levels and renal function in hyperuricemic mice. Food Funct. 2021;12(24):12503-12512. [39] 谢文杰,周刚,谢金美,等.一次性力竭运动模型大鼠心肌氧化损伤的作用途径[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(2):247-252. [40] FEOLI AM, MACAGNAN FE, PIOVESAN CH, et al. Xanthine oxidase activity is associated with risk factors for cardiovascular disease and inflammatory and oxidative status markers in metabolic syndrome: effects of a single exercise session. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2014;2014:587083. [41] 刘晓晨,王改凤,张社峰.有氧运动可改善糖尿病肾病模型小鼠肾脏的氧化应激损伤[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(17):2712-2717. [42] 周中源,史媛媛,王梦,等.有氧运动抑制NLRP3炎性小体活化减轻2型糖尿病小鼠肾脏损伤[J].中国运动医学杂志,2021,40(12):962-969. [43] 朱凤林,闫会萍,陆一帆,等.运动和2,3,7,8-四氯二苯并二噁英(TCDD)持续暴露对大鼠肾脏氧化应激指标的影响[J].生态毒理学报,2023,18(2):366-372. [44] PADILHA CS, RIBEIRO AS, FLECK SJ, et al. Effect of resistance training with different frequencies and detraining on muscular strength and oxidative stress biomarkers in older women. Age. 2015;37(5):104. [45] ADOMAKO EA, MOE OW. Uric acid transport, transporters, and their pharmacological targeting. Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2023;238(2):e13980. [46] CARNEY EF. Prevention: Intensive exercise associated with reduced risk of diabetic nephropathy in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2015;11(4):198. [47] REYNA SM, TANTIWONG P, CERSOSIMO E, et al. Short-term exercise training improves insulin sensitivity but does not inhibit inflammatory pathways in immune cells from insulin-resistant subjects. J Diabetes Res. 2013;2013:107805. [48] 何标,梁艳,徐波,等.跑台运动对TgAPP/PS1小鼠海马Aβ转运清除的影响[J].体育学刊,2018,25(4):134-139. [49] ERALY SA, VALLON V, RIEG T, et al. Multiple organic anion transporters contribute to net renal excretion of uric acid. Physiol Genomics. 2008;33(2):180-192. [50] LIU S, YUAN Y, ZHOU Y, et al. Phloretin attenuates hyperuricemia-induced endothelial dysfunction through co-inhibiting inflammation and GLUT9-mediated uric acid uptake. J Cell Mol Med. 2017;21(10):2553-2562. [51] MANOLESCU AR, AUGUSTIN R, MOLEY K, et al. A highly conserved hydrophobic motif in the exofacial vestibule of fructose transporting SLC2A proteins acts as a critical determinant of their substrate selectivity. Mol Membr Biol. 2007;24(5-6): 455-463. [52] JIANG Z, CAO J, SU H, et al. Exercise serum regulates uric acid transporters in normal rat kidney cells. Sci Rep. 2022;12(1):18086. [53] MA Z, WANG Y, XU C, et al. Obesity-Related Genetic Variants and Hyperuricemia Risk in Chinese Men. Front Endocrinol(Lausanne). 2019;10:230. [54] LI Q, LI X, WANG J, et al. Diagnosis and treatment for hyperuricemia and gout: a systematic review of clinical practice guidelines and consensus statements. BMJ Open. 2019;9(8):e026677. [55] BEN-DOV IZ, Bursztyn M. Associations of arterial stiffness indices with measures of insulin resistance and renal sodium reabsorption. Am J Hypertens. 2019;32(9): 810-812. [56] KOESTER AM, GEISER A, BOWMAN PRT, et al. GLUT4 translocation and dispersal operate in multiple cell types and are negatively correlated with cell size in adipocytes. Sci Rep. 2022;12(1):20535. [57] FLORES-OPAZO M, RAAJENDIRAN A, WATT MJ, et al. Exercise serum increases GLUT4 in human adipocytes. Exp Physiol. 2019;104(5):630-634. [58] WANG N, KONG R, LUO H, et al. Peroxisome proliferator- activated receptors associated with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. PPAR Res. 2017;2017:6561701. [59] TANG H, ZENG Q, TANG T, et al. Kaempferide improves glycolipid metabolism disorder by activating PPARgamma in high-fat-diet-fed mice. Life Sci. 2021;270: 119133. [60] 宋燕娟,马春莲,肖笑.中等强度有氧运动调节PPARγ/PI3K/AKT通路改善2型糖尿病大鼠肝脏糖脂代谢紊乱及炎症[J].中国运动医学杂志,2023,42(1): 48-56. [61] MCGEE SL, HARGREAVES M. Exercise adaptations: molecular mechanisms and potential targets for therapeutic benefit. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2020;16(9):495-505. [62] 祝锴烨,吴秋雪,罗海静,等.紫云英苷对急性力竭运动小鼠肝脏组织中miR-155表达的影响[J].动物营养学报,2021,33(12):7062-7069. [63] BELLAR A, WELCH N, DASARATHY S. Exercise and physical activity in cirrhosis: opportunities or perils. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2020;128(6):1547-1567. [64] 美国运动医学学会.ACSM运动测试与运动处方指南(第十版)[M].王正珍,译.北京:北京体育大学出版社,2019. |
| [1] | Wu Jing, Yao Yingce, Yang Xiaowei, Xue Boshi, Zhao Jianbin, Yang Chen, Luan Tianfeng, Zhou Zhipeng. Intervention of muscle strength training combined with neuromuscular electrical stimulation on lower limb function and biomechanical changes in patients with patellofemoral pain [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1365-1371. |
| [2] | Wei Juan, Li Ting, Huan Mengting, Xie Ying, Xie Zhouyu, Wei Qingbo, Wu Yunchuan. Mechanism by which static exercise improves insulin resistance in skeletal muscle of type 2 diabetes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1271-1276. |
| [3] | Lou Guo, Zhang Yan, Fu Changxi. Role of endothelial nitric oxide synthase in exercise preconditioning-induced improvement of myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1283-1288. |
| [4] | Lin Zeyu, Xu Lin. Research progress in gout-induced bone destruction mechanism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1295-1300. |
| [5] | Cheng Jie, Wang Jihong, Zhang Pei. Functional exercise for tendon adhesion in a model of deep flexor tendon II injury of the third toe [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1161-1167. |
| [6] | Wang Ji, Zhang Min, Li Wenbo, Yang Zhongya, Zhang Long. Effect of aerobic exercise on glycolipid metabolism, skeletal muscle inflammation and autophagy in type 2 diabetic rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1200-1205. |
| [7] | Ruan Rong, Lou Xujia, Jin Qiguan, Zhang Libing, Xu Shang, Hu Yulong. Effect of resveratrol on gluconeogenesis in exercise-induced fatigue rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1229-1234. |
| [8] | Liu Zhiyang, Fu Zeting, Xia Yu, Ding Haili. The role of BMAL1 and MyoD in exercise-induced skeletal muscle damage [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 510-515. |
| [9] | Zhu Xiaofeng, Chen Weiwei, Huang Jian. Effects of maternal high-fat diet and exercise intervention on insulin sensitivity and the hypothalamic arcuate nucleus in male offspring mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 556-561. |
| [10] | Wang Shijie, Wen Dengtai, Wang Jingfeng, Gao Yinghui. Mammalian target of rapamycin in relation to exercise, high fat/high salt diet, and aging [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 574-580. |
| [11] | Yang Yuqing, Chen Zhiyu. Role and application of early transient presence of M1 macrophages in bone tissue engineering [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 594-601. |
| [12] | Wu Zixuan, Sun Shiyi, Zhang Cheng, Zhang Guangyi, Yang Tongjie, He Haijun. Relationship between blood indicators and course of nontraumatic osteonecrosis of femoral head in different stages: multiple logistic regression analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(36): 5865-5871. |
| [13] | Chang Ying, Xia Yuan, Sun Yundi, Cheng Lulu, Xiong Wenjuan, Zhao Xianghu. Effectiveness of different specific exercise therapies in treatment of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: a network meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(36): 5899-5904. |
| [14] | Dong Gengxin, Li Yiting, Hong Yinglu, Bao Dapeng. Effect of hydrogen-rich gas on proprioception and muscle endurance after high-intensity exercise [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(34): 5413-5418. |
| [15] | Xu Zheng, Zhao Xiaoqin, Chen Xiaodan, Wang Jiapu, Bao Fenmiao, Yu Liang, Li Junping, Wei Yan. Aerobic exercise upregulates the thioredoxin system and inhibits cardiomyocyte apoptosis in aging rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(34): 5508-5515. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||