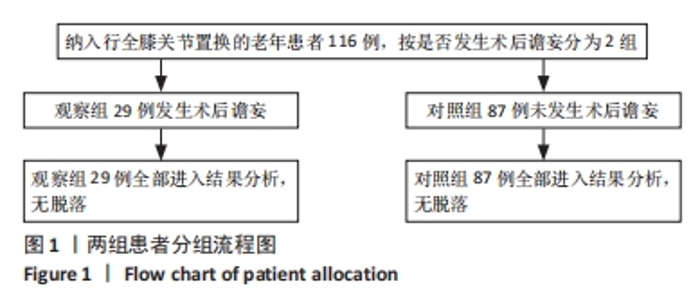
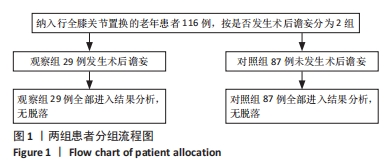
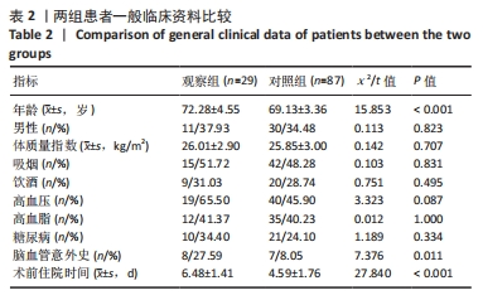
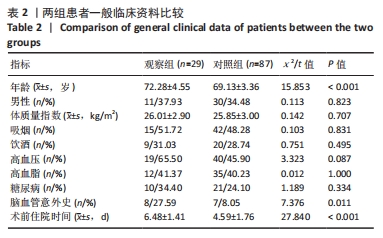
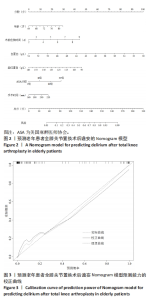
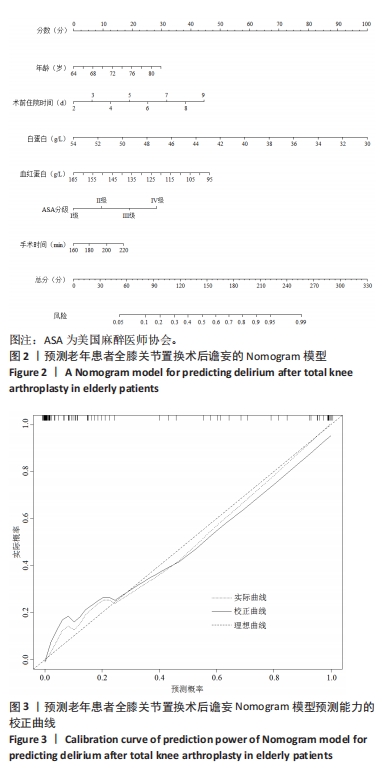
[1] WANG YY, YUE JR, XIE DM, et al. Effect of the tailored,family-involved hospital elder life program on postoperative delirium and function in older adults:a randomized clinical trial.JAMA Intern Med. 2020;180(1):17-25.
[2] ZHANG Y, SHAN GJ, ZHANG YX, et al. Propofol compared with sevoflurane general anaesthesia is associated with decreased delayed neurocognitive recovery in older adults.Br J Anaesth. 2018;121(3): 595-604.
[3] DE LA VARGA-MARTÍNEZ O, GÓMEZ-PESQUERA E, MUÑOZ-MORENO MF, et al. Development and validation of a delirium risk prediction preoperative model for cardiac surgery patients (DELIPRECAS): An observational multicentre study. J Clin Anesth. 2021;69:110158.
[4] 谭刚,郭向阳,罗爱伦,等.老年非心脏手术患者术后谵妄的流行病学调查[J].协和医学杂志,2011,2(4):319-325.
[5] 李丽琴,孙艳丽,王聪,等.老年患者术后谵妄防治的研究进展[J].国际老年医学杂志,2019,40(1):59-64.
[6] GREENE NH, ATTIX DK, WELDON BC, et al. Measures of executive function and depression identify patients at risk for postoperative delirium. Anesthesiology. 2009;110(4):788-795.
[7] 周建雄,胥明哲,王蕊,等.老年患者术后谵妄的研究进展[J].临床麻醉学杂志,2019,35(9):920-924.
[8] HELWANI MA, AVIDAN MS, BEN AA, et al. Effects of regional versus general anesthesia on outcomes after total hip arthroplasty: a retrospective propensity-matched cohort study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2015;97(3):186-193.
[9] 杨娜瑜,姜丽华.老年患者术后谵妄的研究进展[J].临床麻醉学杂志,2013,29(10):1039-1040.
[10] ZHANG J, PAN Z, ZHAO F, et al.Development and validation of a nomogram containing the prognostic determinants of chondrosarcoma based on the surveillance, epidemiology,and end results database.Int J Clin Oncol. 2019;24(11):1459-1467.
[11] SKOLARIKI K, TERRERA GM, DANSO SO. Predictive models for mild cognitive impairment to Alzheimer’s disease conversion. Neural Regen Res. 2021;16(9):1766-1767.
[12] 崔凡,赵伟,李春晶,等.修正衰弱指数与人工关节置换术后老年病人谵妄发生的关系[J]. 中华麻醉学杂志,2019,39(10):1158-1161.
[13] 李呈凯,白树财,宋秀钢,等.老年髋部骨折患者术后谵妄相关危险因素的回顾性研究[J]. 中华骨科杂志,2018,38(4):250-256.
[14] NEUFELD KJ, LEOUTSAKOS JM, SIEBER FE, et al. Outcomes of early delirium diagnosis after general anesthesia in the elderly. Anesth Analg. 2013;117(2):471-478.
[15] 韩向真,董江涛,张运清,等.全膝关节置换术后患者谵妄的危险因素分析及围手术期管理[J].河北医科大学学报,2016,37(2):207-209.
[16] MROWKA P, GLODKOWSKA-MROWKA E. PPARγagonists in combination cancer therapies. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2020;20:197-215.
[17] TAKADA I, MAKISHIMA M. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor agonists and antagonists:a patent review(2014-present). Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2020;30:10-13.
[18] 李国威,杨建军.老年髋关节置换术后谵妄的进展研究[J].贵州医药,2017,41(2):212-213.
[19] 薄晗,刘玥,马正良.术后谵妄诊断方法的研究进展[J].实用老年医学,2020,34(4):410-414.
[20] 胡川,田少奇,张驰,等.高龄患者全膝关节置换术后1个月内急性合并症[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2019,27(13):1176-1180.
[21] ARNOLD JB, WALBERS JL, FERRAR KE. Does physical activity increase after total hip or knee arthroplasty for osteoarthritis a systematic review. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2016;46(6):431-442.
[22] 王昕,胡龙,王雄,等.同期或分期全膝关节置换术治疗高龄双膝关节骨关节炎的疗效[J].中国老年学杂志,2017;37(5):1201-1203.
[23] BIN AH, YUNG WY. Postoperative delirium in patients undergoing total joint arthroplasty:a systematic review. J Arthroplasty. 2015;30(8):1414-1417.
[24] 杨钦烽,王健,张洋,等.美国住院病人髋膝关节置换术后谵妄发生率及危险因素[J].中华关节外科杂志(电子版),2021,15(1):57-63.
[25] WANG L, SEOK S, KIM S, et al. The risk factors of postoperative delirium after total knee arthroplasty. J Knee Surg. 2017;30(6):600-605.
[26] 吕晓春,周雁.膝关节置换患者术后谵妄的危险因素分析[J].临床麻醉学杂志,2017,33(3):264-268.
[27] GUO Y, JIA P, ZHANG J, et al. Prevalence and risk factors of postoperative delirium in elderly hip fracture patients. J Int Med Res. 2016;44(2): 317-327.
[28] 赵立本,杨国敬,张雷.人工关节置换术后谵妄的风险因子评估及临床分析[J].实用骨科杂志,2019,25(12):1077-1080+1088.
[29] GAO F, ZHANG Q, LI Y, et al. Transcutaneous electrical acupoint stimulation for prevention of postoperative delirium in geriatric patients with silent lacunar infarction: a preliminary study. Clin Interv Aging. 2018;13:2127-2134.
[30] 陈红,胡军,周娟,等.全麻术后谵妄在苏醒期的识别与护理进展[J].麻醉安全与质控,2021,5(4):242-247.
[31] 张翠琴,金乾坤.老年髋部骨折患者术后谵妄的危险因素分析及护理策略[J].中华全科医学,2019,17(8):1427-1429.
[32] 冯旭,陈辉,蔡宁宇,等.老年髋部骨折患者术后谵妄发生的危险因素分析 [J]. 中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2017,32(2):2135-2138.
[33] 朱姣,桂潇,李文迁,等. 丙泊酚麻醉与老龄大鼠术后谵妄及炎症反应的关系[J]. 中华麻醉学杂志,2018,38(10):1198-1200.
[34] 孙珣,胡小义,周健,等.营养控制状况评分与老年非心脏手术患者术后谵妄的相关性研究[J].医学研究杂志,2021,50(4):37-42.
[35] STANYON HF, VILES JH. Human serum albumin can regulate amyloid-β peptide fiber growth in the brain interstitium: implications for alzheimer disease. J Biol Chem. 2012;287(33):28163-28168.
[36] WEINSTEIN SM, POULTSIDES L, BAAKLINI LR, et al.Postoperative delirium in total knee and hip arthroplasty patients: a study of perioperative modifiable risk factors. Br J Anaesth. 2018;120(5):999-1008. |