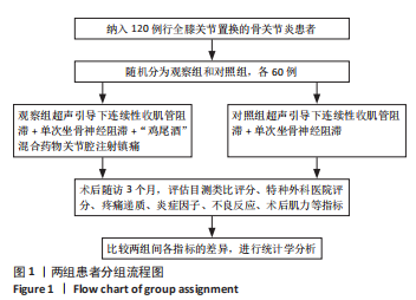
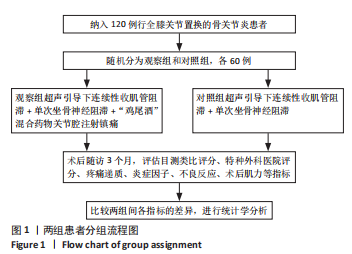
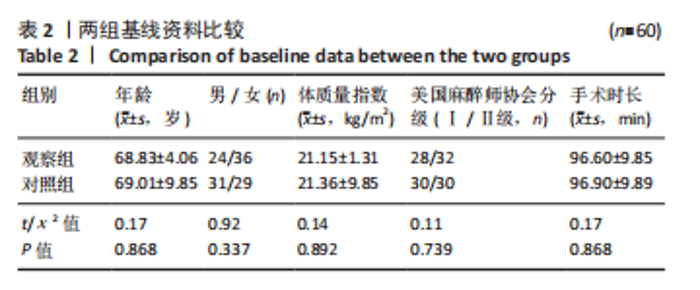
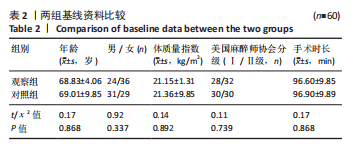
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (24): 3833-3838.doi: 10.12307/2024.606
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effect of adductor canal block and single sciatic nerve block combined with analgesic drugs on pain after total knee arthroplasty
Geng Haoyang1, Liu Wenping1, Wang Guorui1, Liu Bin1, Wang Wei2, Ma Zhanqiao1, Wang Jianhua1
- 1Department of Anesthesiology, Hebei Province Cangzhou Hospital of Integrated Traditional and Western Medicine, Cangzhou 061000, Hebei Province, China; 2Department of Orthopedics, Zhengding County People’s Hospital, Shijiazhuang 050899, Hebei Province, China
-
Received:2023-04-18Accepted:2023-07-08Online:2024-08-28Published:2023-11-21 -
Contact:Wang Jianhua, Master, Associate chief physician, Department of Anesthesiology, Hebei Province Cangzhou Hospital of Integrated Traditional and Western Medicine, Cangzhou 061000, Hebei Province, China -
About author:Geng Haoyang, Attending physician, Department of Anesthesiology, Hebei Province Cangzhou Hospital of Integrated Traditional and Western Medicine, Cangzhou 061000, Hebei Province, China -
Supported by:2022 Medical Science Research Project Plan of Hebei Province, No. 20220689 (to LWP)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Geng Haoyang, Liu Wenping, Wang Guorui, Liu Bin, Wang Wei, Ma Zhanqiao, Wang Jianhua. Effect of adductor canal block and single sciatic nerve block combined with analgesic drugs on pain after total knee arthroplasty[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(24): 3833-3838.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
| [1] 欧德阳,区国集,黄朝荣,等.全膝关节置换术治疗晚期膝骨性关节炎[J].临床骨科杂志,2021,24(3):358-361. [2] ROBBINS SM, RASTOGI R, MCLAUGHLIN TL. Predicting acute recovery of physical function following total knee joint arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2014;29(2):299-303. [3] CONNELLY JW, GALEA VP, ROJANASOPONDIST P, et al. Which preoperative factors are associated with not attaining acceptable levels of pain and function after TKA? Findings from an international multicenter study. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2020; 478(5):1019. [4] 吴绪才,高子军,卢志方,等.徒手法收肌管阻滞用于人工全膝关节置换术的效果[J].临床麻醉学杂志,2019,35(3):270-274. [5] 张力,李继勇,陈治军.超声引导下连续收肌管阻滞用于老年患者全膝置换术对术后认知功能的影响[J].中国老年学杂志,2020, 40(12):2565-2567. [6] 胡玲,康路,王瑞婷,等.超声引导下收肌管联合IPACK阻滞在老年患者全膝关节置换术中的应用[J].实用医学杂志,2020,36(7): 950-953. [7] NIESEN AD, HARRIS DJ, JOHNSON CS, et al. Interspace between Popliteal Artery and posterior Capsule of the Knee (IPACK) Injectate Spread: A Cadaver Study. J Ultrasound Med. 2019;38(3):741-745. [8] SALWAN A, PISULKAR GL, TAYWADE S, et al. A Review on the Efficacy of Extraosseous Local Infiltration of Multimodal Drug Cocktail for Pain Management After Total Knee or Hip Arthroplasty. Cureus. 2022;14(10):e30451. [9] GERVAIS HW. The ASA Classification - solid like a rock in anesthesiology. Anaesthesist. 2017;66(1):3-4. [10] LAMPLOT JD, WAGNER ER, MANNING DW. Multimodal pain management in total knee arthroplasty: a prospective randomized controlled trial. J Arthroplasty. 2014;29(2):329-334. [11] SONG B, LI Y, TENG X, et al. Comparison of morning and evening operation under general anesthesia on intraoperative anesthetic requirement, postoperative sleep quality, and pain: a randomized controlled trial. Nature and Science of Sleep. 2020;12:467-475. [12] SŁUPIK A, BIAŁOSZEWSKI D. A comparative analysis of the clinical utility of the Staffelstein-score and the hospital for special surgery knee score (HSS) in monitoring physiotherapy of total knee replacement patients--preliminary study. Ortop Traumatol Rehabil. 2009;11(1):37-45. [13] 中华医学会骨科学分会关节外科学组. 骨关节炎诊疗指南(2018年版)[J]. 中华骨科杂志,2018,38(12):705-715. [14] SARDANA V, BURZYNSKI JM, SCUDERI GR. Adductor Canal Block or Local Infiltrate Analgesia for Pain Control After Total Knee Arthroplasty? A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. J Arthroplasty. 2019;34(1):183-189. [15] VORA MU, NICHOLAS TA, KASSEL CA, et al. Adductor canal block for knee surgical procedures: review article. J Clin Anesth. 2016;35:295-303. [16] LAN F, SHEN Y, MA Y, et al. Continuous Adductor Canal Block used for postoperative pain relief after medial Unicondylar Knee Arthroplasty: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. BMC Anesthesiol. 2019;19(1):1-9. [17] SCHNABEL A, REICHL SU, WEIBEL S, et al. Adductor canal blocks for postoperative pain treatment in adults undergoing knee surgery. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019;2019(10):CD012262. [18] 叶久敏,卿忠,易双强,等. 超声引导下膝关节囊后间隙联合收肌管阻滞对全膝关节置换术患者的镇痛效果分析[J]. 中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2020,35(6):573-576. [19] 叶久敏,卿忠,杨光,等.超声引导下腘动脉与膝关节后囊间隙不同入路阻滞对全膝关节置换患者围术期镇痛效果观察[J].陕西医学杂志,2020,49(11):1408-1411+1425. [20] 徐露,胡玲,魏昕,等.超声引导下连续收肌管阻滞联合膝关节后囊间隙阻滞在老年患者全膝关节置换术中应用价值[J].临床军医杂志,2021,49(8):876-879. [21] 陈思凯,邢金明,叶承锋,等. 鸡尾酒式药物在全膝关节置换术中的应用现状及研究进展[J]. 浙江医学,2021,43(6):683-686. [22] RANGASAMI VK, SAMANTA S, PARIHAR VS, et al. Harnessing hyaluronic acid-based nanoparticles for combination therapy: A novel approach for suppressing systemic inflammation and to promote antitumor macrophage polarization. Carbohydr Polym. 2021;254:117291. [23] 李涛,裴建祥,宋奇志,等. 鸡尾酒疗法对全膝关节置换术后患者疼痛及肿胀控制研究[J]. 陕西医学杂志,2018,47(12):1609-1611. [24] EYIGÖR H, EYIGÖR M, EROL B, et al. Changes in substance P levels of inferior turbinate in patients with mucosal contact headache. Braz J Otorhinolaryngol. 2020;86(4):450-455. [25] PATTERSON ME, VITTER J, BLAND K, et al. The effect of the IPACK block on pain after primary TKA: a double-blinded, prospective, randomized trial. J Arthroplasty. 2020;35(6):S173-S177. [26] SULLIVAN B, STONE AV, CONLEY CEW, et al. Human synovial fluid interleukinain after primary TKA: a double-blinded, prospective, randomized trial. J Arthroplastyation. alysis of Randomized Controlleduction. J Orthop Res. 2023;41(2):300-306. [27] HUANG Z, CAI Y, YANG Y, et al. Effects of ultrasound-guided lumbar-sciatic nerve block and epidural anesthesia on the levels of IL-6, IL-8, TNF-α and coagulation factors in peripheral blood of elderly patients after hip joint surgery. J Med Biochem. 2022;41(4):433-440. [28] LANGKILDE A, JAKOBSEN TL, BANDHOLM TQ, et al. Inflammation and post-operative recovery in patients undergoing total knee arthroplasty-secondary analysis of a randomized controlled trial. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2017;25(8):1265-1273. [29] LEI YT, XIE JW, HUANG Q, et al. The antifibrinolytic and anti-inflammatory effects of a high initial-dose tranexamic acid in total knee arthroplasty: a randomized controlled trial. Int Orthop. 2020;44(3): 477-486. [30] ZHAO HY, YEERSHENG R, KANG XW, et al. The effect of tourniquet uses on total blood loss, early function, and pain after primary total knee arthroplasty: a prospective, randomized controlled trial. Bone Joint Res. 2020;9(6):322-332. [31] ZHAO C, WANG L, CHEN L, et al. Effects of magnesium sulfate on periarticular infiltration analgesia in total knee arthroplasty: a prospective, double-blind, randomized controlled trial. J Orthop Surg Res. 2023;18(1):301. [32] LI D, WANG Q, ZHAO X, et al. Comparison of intravenous and topical dexamethasone for total knee arthroplasty: a randomized double-blinded controlled study of effects on dexamethasone administration route and enhanced recovery. J Arthroplasty. 2021;36(5):1599-1606. |
| [1] | Zhi Fang, Zhu Manhua, Xiong Wei, Lin Xingzhen. Analgesic effect of acupuncture in a rat model of lumbar disc herniation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 936-941. |
| [2] | Wang Jianlei, He Peiliang, Sun Yongjian. A meta-analysis of clinical efficacy and safety of intravenous glucocorticoids before lower limb joint arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(3): 599-607. |
| [3] | Li Jia, Liu Qianru, Xing Mengnan, Chen Bo, Jiao Wei, Meng Zhaoxiang. A network meta-analysis on therapeutic effect of different types of exercise on knee osteoarthritis patients [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(3): 609-616. |
| [4] | Su Dejun, Dong Wanpeng, Dong Yuefu, Zhang Jichao, Zhang Zhen. Design of asymmetric prosthesis and mechanical analysis of total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(3): 510-516. |
| [5] | Zheng Xiang, Zhang Mingxing, Huang Ya, Shan Sharui. Improvement of lower limb walking function in patients with chronic non-specific low back pain by biofeedback assisted electrical stimulation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(3): 547-553. |
| [6] | Cao Zhengpei, Lu Shengsheng, Zhang Jiahuan, Wang Xiaoying. Effects of silver needle comprehensive therapy on the ultrasonographic morphology of multifidus muscles in patients with lumbar disc herniation: an ultrasound morphologic assessment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(11): 2261-2267. |
| [7] | Zhang Jiale, Wang Fusen, Qiu Zhenrui, Fan Xinming, Zou Jilong, Bi Zhenggang, Sun Jiabing. Exercise therapy for the treatment of chronic nonspecific lower back pain through mechanical-chemical coupling [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(11): 2377-2384. |
| [8] | Zhao Wenqi, Yu Haichi, Song Yiru, Yuan Tianyang, Liu Qinyi. Platelet-rich plasma and hydrogel for spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(10): 2189-2200. |
| [9] | Wu Jing, Yao Yingce, Yang Xiaowei, Xue Boshi, Zhao Jianbin, Yang Chen, Luan Tianfeng, Zhou Zhipeng. Intervention of muscle strength training combined with neuromuscular electrical stimulation on lower limb function and biomechanical changes in patients with patellofemoral pain [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1365-1371. |
| [10] | Shan Jiaxin, Zhang Yilong, Wu Hongtao, Zhang Jiayuan, Li Anan, Liu Wengang, Xu Xuemeng, Zhao Chuanxi. Changes in muscle strength and pain in patients receiving Jianpi Yiqi Huoxue Formula after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1378-1382. |
| [11] | Qi Haodong, Lu Chao, Xu Hanbo, Wang Mengfei, Hao Yangquan. Effect of diabetes mellitus on perioperative blood loss and pain after primary total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1383-1387. |
| [12] | Li Xiaoqiang, Chen Wei, Li Mingyue, Shan Tianchi, Shen Wen. Value of preoperative quantitative ultrasound analysis of quadriceps femoris in predicting chronic post-surgical pain after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1388-1393. |
| [13] | Feng Tianxiao, Bu Hanmei, Wang Xu, Zhu Liguo, Wei Xu. Interpretation of key points of International Framework for Examination of the Cervical Region for potential of vascular pathologies of the neck prior to Orthopaedic Manual Therapy (OMT) Intervention: International IFOMPT Cervical Framework [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1420-1425. |
| [14] | Chen Zhiling, Huang Xuecheng, Pan Min, Huang Ying, Wu Yuntian. Evaluation of the relationship between neck and shoulder pain and scalene muscles based on shear wave elastography [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1265-1270. |
| [15] | Han Bing, Liu Hongbin, Wang Hehong, Zhao Hanqing, Zhao Riguang, Sun Yiyan, Zhang Yu. Correlation between lower limb alignment and risk factors of patellofemoral pain syndrome in young men [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1211-1216. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||