Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (3): 609-616.doi: 10.12307/2025.130
Previous Articles Next Articles
A network meta-analysis on therapeutic effect of different types of exercise on knee osteoarthritis patients
Li Jia1, Liu Qianru1, Xing Mengnan1, Chen Bo2, Jiao Wei1, Meng Zhaoxiang2
- 1College of Sports Medicine and Rehabilitation, Beijing Sport University, Beijing 100000, China; 2Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Subei People’s Hospital of Jiangsu Province, Yangzhou 225000, Jiangsu Province, China
-
Received:2023-12-19Accepted:2024-02-18Online:2025-01-28Published:2024-06-04 -
Contact:Jiao Wei, MD, Professor, Doctoral supervisor, College of Sports Medicine and Rehabilitation, Beijing Sport University, Beijing 100000, China Co-corresponding author: Meng Zhaoxiang, MD, Chief physician, Doctoral supervisor, Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Subei People’s Hospital of Jiangsu Province, Yangzhou 225000, Jiangsu Province, China -
About author:Li Jia, Master candidate, College of Sports Medicine and Rehabilitation, Beijing Sport University, Beijing 100000, China -
Supported by:General Program of Health Commission of Jiangsu Province, No. H2023006 (to CB)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Li Jia, Liu Qianru, Xing Mengnan, Chen Bo, Jiao Wei, Meng Zhaoxiang. A network meta-analysis on therapeutic effect of different types of exercise on knee osteoarthritis patients[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(3): 609-616.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
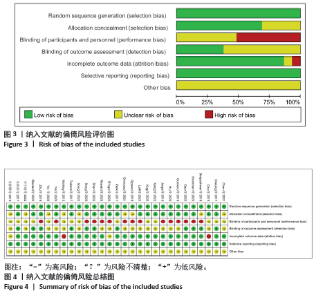
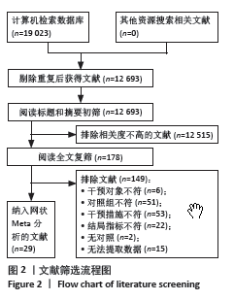
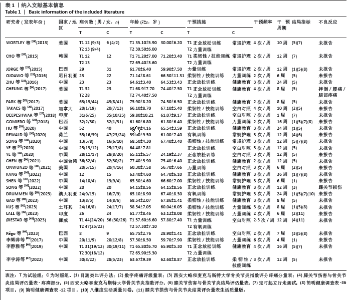
2.3 文献质量评价结果 在纳入的29篇文献中,所有文献均报告了随机序列的产生(随机数字表、计算机),评定为“低风险”;21篇文献报告了具体分配隐藏方法(密封信封、空白文件夹) [20-26,28-32,36-38,40-45],评定为“低风险”,剩余8篇文献分配隐藏方法不清楚[19,27,33-35,38,46-47];15篇文献未对参与者实施盲法[21-23,27-32,35,37,39,40,42,44],评定为“高风险”,剩余14篇文献盲法使用情况不清楚[19-20,24-26,33-34,36,38,41,43,45-47];11篇文献对评定者实施盲 法[23-27,31,38-40,43,45],评定为“低风险”,剩余18篇文献盲法使用情况不清楚[19-22,28-30,32-36,38,41-42,44,46-47];24篇文献数据完整[21-23,25-43,45,47],评定为“低风险”,2篇文献数据不完整(研究退出、失访) [19-20],评定为“高风险”,2篇文献选择性报告研究结果不清楚[44,46];所有文献均无选择性报告,评定为“低风险”,所有文献均未提到其他偏倚的来源。偏倚风险评价结果见图3,4。"


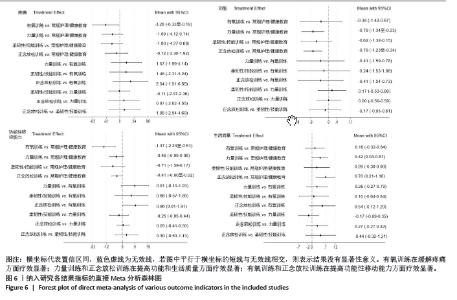
2.4 网状Meta分析结果 2.4.1 网络证据图 此次纳入的研究中,以力量训练和正念放松训练样本量居多,共有14项研究的结局指标涉及到疼痛指标[21,26,28-31,35-37,39,41-44];共有20项研究的结局指标涉及到功能指标[19,21-26,28-30,32-33,35,38-39,41,43-44,46-47];共有7项研究的结局指标涉及到功能性移动能力指标[19,27-28,36,38-39,46];共有9项研究的结局指标涉及到生活质量指标[21,24,28,36,38-39,41,43-44]。各指标总体来看,以力量训练、正念放松训练和常规护理/健康教育直接比较的数量较多,见图5。 2.4.2 不一致性检验结果 所有运动类型同时存在直接对比和间接对比称为1个闭环,文章在疼痛方面共形成2个闭环,IF介于0.972-3.720;在功能方面共形成4个闭环,IF介于0.176-0.420;在功能性移动能力方面形成1个闭环,IF=0.318;在生活质量方面形成2个闭环,IF介于0.016-0.575;以上闭环置信区间都包含0,提示各指标间无明显不一致性。不同运动类型不一致性检验结果见表2。 2.4.3 直接Meta分析结果 在疼痛方面,有氧训练(SMD=-3.26,95%CI:-6.33至-0.19)与常规护理/健康教育相比,能显著改善疼痛症状(P < 0.05),剩余运动类型的两两比较差异均无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。 在功能方面,力量训练(SMD=-0.79,95%CI:-1.34至-0.23)、正念放松训练(SMD=-0.79,95%CI:-1.23至-0.34)与常规护理/健康教育相比,能显著提高患者的膝关节功能(P < 0.05),剩余运动类型的两两比较差异均无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。 在功能性移动能力方面,有氧训练(SMD=-1.37,95%CI:-2.24至-0.51)、正念放松训练(SMD=-0.41,95%CI:-0.80至-0.02)与常规护理/健康教育相比,提高患者功能性移动能力的效果更为显著(P < 0.05)。剩余运动类型的两两比较差异均无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。 在生活质量方面,正念放松训练(SMD=0.70,95%CI:0.21-1.18)、力量训练(SMD=0.42,95%CI:0.03-0.81)与健康教育/常规护理相比,能够更有效地提高患者的生活质量(P < 0.05),剩余运动类型的两两比较,差异均无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。不同运动类型网状Meta分析结果见图6。"

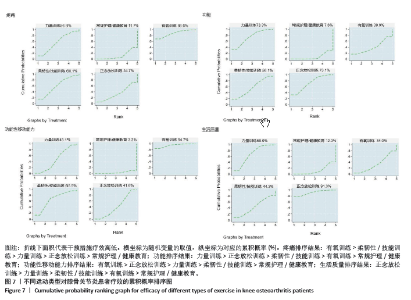
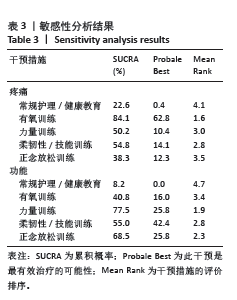
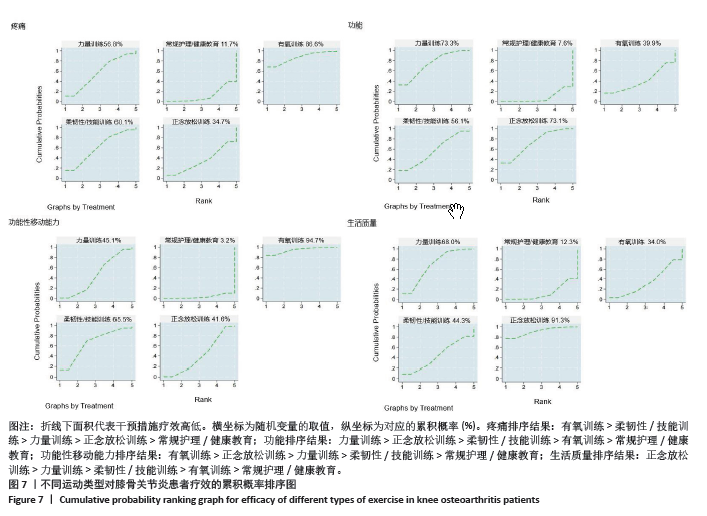
2.4.4 累积概率排序结果 SUCRA指标用来对每种运动类型的疗效进行排序,图中数字表示SUCRA 曲线下面积,面积越大,表明该运动类型的越有效。结果显示,疼痛缓解的累积概率排序依次为:有氧训练(86.6%) >柔韧性/技能训练(60.1%) >力量训练(56.8%) >正念放松训练(34.7%) >常规护理/健康教育(11.7%);功能改善的累积概率排序依次为:力量训练(73.7%) >正念放松训练(73.1%) >柔韧性/技能训练(56.1%) >有氧训练(39.9%) >常规护理/健康教育(7.6%);功能性移动能力提高的排序依次为:有氧训练(94.7%) >正念放松训练(65.5%) >力量训练(45.1%) >柔韧性/技能训练(41.6%) >常规护理/健康教育(3.2%);生活质量提高的排序依次为:正念放松训练(91.3%) >力量训练(68.0%) >柔韧性/技能训练(44.3%) >有氧训练(34.0%) >常规护理/健康教育(12.3%);不同运动类型疗效的累积概率排序图见图7。 2.5 发表偏倚评价 文章以疼痛、功能、功能性移动能力和生活质量作为结局指标,分别绘制了漏斗图以检测有无发表偏倚。从漏斗图中可以看出,漏斗图范围内散在的点分布不对称,且有部分点落在漏斗图范围外,提示文献可能存在发表偏倚和小样本效应。各结局指标发表偏倚漏斗图见图8。 2.6 敏感性分析结果 分别对疼痛、功能2个结局指标进行了敏感性分析,在剔除偏离平均值的文献[19,23,30,36,39],以及最大最小的文献后[43-44,46],网状Meta分析结果和累积排序结果并未发生明显变化,表明结果具有一定的稳健性,见表3。"
| [1] THOMAS AC, HUBBARD-TURNER T, WIKSTROM EA, et al. Epidemiology of posttraumatic osteoarthritis. J Athl Train. 2017;52(6):491-496. [2] FEJER R, RUHE A. What is the prevalence of musculoskeletal problems in the elderly population in developed countries? A systematic critical literature review. Chiropr Man Therap. 2012;20(1):31. [3] 陆艳红,石晓兵.膝骨关节炎国内外流行病学研究现状及进展[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志, 2012,20(6):81-84 [4] 梁童婧,杨晓露,黄鹏.膝关节骨性关节炎的康复治疗研究进展[J].当代体育科技,2021, 11(4):33-37. [5] 葛站勇.膝关节骨性关节炎治疗研究进展[J].中国城乡企业卫生,2023,38(11):38-41. [6] KAN HS, CHAN PK, CHIU KY, et al. Non-surgical treatment of knee osteoarthritis. Hong Kong Med J. 2019;25(2):127-133. [7] RICE D, MCNAIR P, HUYSMANS E, et al. Best evidence rehabilitation for chronic pain part 5: osteoarthritis. J Clin Med. 2019;8(11):1769. [8] ALLE DEVEZA L, BENNELL K. Management of knee osteoarthritis [EB/OL].(2022-04-05)[2022-01-08]. https://www.uptodate.cn/contents/zh-Hans/management-of-knee-osteoarthritis?search=Management%20of%20knee%20osteoarthritis&source=search_result&selectedTitle=1~127&usage_type=default&display_rank=1. [9] THOMPSON PD, ARENA R, RIEBE D, et al. ACSM’s new preparticipation health screening recommendations from ACSM’s guidelines for exercise testing and prescription, ninth edition. Curr Sports Med Rep. 2013;12(4):215-217. [10] 徐璐,唐霞珠.24式简化太极拳对老年膝关节骨性关节炎患者关节功能的影响[J].护理学报, 2016,23(11):51-53. [11] BARTELS EM, JUHL CB, CHRISTENSEN R, et al. Aquatic exercise for the treatment of knee and hip osteoarthritis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016;3(3):CD005523. [12] CEBALLOS-LAITA L, LAHUERTA-MARTÍN S, CARRASCO-URIBARREN A, et al. Strength training vs. aerobic training for managing pain and physical function in patients with knee osteoarthritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Healthcare (Basel). 2023;12(1):33. [13] MO L, JIANG B, MEI T, et al. Exercise therapy for knee osteoarthritis: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. Orthop J Sports Med. 2023;11(5):23259671231172773. [14] 中华医学会骨科学分会关节外科组.骨关节炎诊疗指南(2018年版)[J].中华骨科杂志,2018, 38(12):705-715. [15] ALTMAN R, ASCH E, BLOCH D, et al. Development of criteria for the classification and reporting of osteoarthritis. classification of osteoarthritis of the knee. diagnostic and therapeutic criteria committee of the american rheumatism association. Arthritis Rheum. 1986;29(8): 1039-1049. [16] CHAIMANI A, HIGGINS JP, MAVRIDIS D, et al. Graphical tools for network meta-analysis in STATA. PLoS One. 2013;8(10):e76654. [17] CHAIMANI A, SALANTI G. Visualizing assumptions and results in network meta-analysis: the network graphs package. Stata J. 2015;15(4):905-950. [18] MAVRIDIS D, WHITE IR, HIGGINS JP, et al. Allowing for uncertainty due to missing continuous outcome data in pairwise and network meta-analysis. Stat Med. 2015;34(5): 721-741. [19] WORTLEY M, ZHANG S, PAQUETTE M, et al. Effects of resistance and Tai Ji training on mobility and symptoms in knee osteoarthritis patients. J Sport Health Sci. 2013;2(4):209-214. [20] CHO Y, KIM M, LEE W. Effect of proprioceptive training on foot posture, lower limb alignment, and knee adduction moment in patients with degenerative knee osteoarthritis: a randomized controlled trial. J Phys Ther Sci. 2015;27(2):371-374. [21] JORGE RT, SOUZA MC, CHIARI A, et al. Progressive resistance exercise in women with osteoarthritis of the knee: a randomized controlled trial. Clin Rehabil. 2015;29(3):234-243. [22] OJOAWO AO, OLAOGUN MO, HASSAN MA. Comparative effects of proprioceptive and isometric exercises on pain intensity and difficulty in patients with knee osteoarthritis: a randomised control study. Technol Health Care. 2016;24(6):853-863. [23] ZHU Q, HUANG L, WU X, et al. Effects of Tai Ji Quan training on gait kinematics in older Chinese women with knee osteoarthritis: a randomized controlled trial. J Sport Health Sci. 2016;5(3):297-303. [24] CHEUNG C, WYMAN JF, BRONAS U, et al. Managing knee osteoarthritis with yoga or aerobic/strengthening exercise programs in older adults: a pilot randomized controlled trial. Rheumatol Int. 2017;37(3):389-398. [25] PARK J, MCCAFFREY R, NEWMAN D, et al. A pilot randomized controlled trial of the effects of chair yoga on pain and physical function among community-dwelling older adults with lower extremity osteoarthritis. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2017;65(3):592-597. [26] TAKACS J, KROWCHUK NM, GARLAND SJ, et al. Dynamic balance training improves physical function in individuals with knee osteoarthritis: a pilot randomized controlled trial. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2017;98(8):1586-1593. [27] DEEPESHWAR S, TANWAR M, KAVURI V, et al. Effect of yoga based lifestyle intervention on patients with knee osteoarthritis: a randomized controlled trial. Front Psychiatry. 2018;9:180. [28] GOMIERO AB, KAYO A, ABRAÃO M, et al. Sensory-motor training versus resistance training among patients with knee osteoarthritis: randomized single-blind controlled trial. Sao Paulo Med J. 2018;136(1):44-50. [29] HU X, LAI Z, WANG L. Effects of Taichi exercise on knee and ankle proprioception among individuals with knee osteoarthritis. Res Sports Med. 2020; 28(2):268-278. [30] REWALD S, LENSSEN AFT, EMANS PJ, et al. Aquatic cycling improves knee pain and physical functioning in patients with knee osteoarthritis: a randomized controlled trial. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2020;101(8):1288-1295. [31] SONG Q, SHEN P, MAO M, et al. Proprioceptive neuromuscular facilitation improves pain and descending mechanics among elderly with knee osteoarthritis. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2020; 30(9):1655-1663. [32] YE J, ZHENG Q, ZOU L, et al. Mindful exercise (Baduanjin) as an adjuvant treatment for older adults (60 years old and over) of knee osteoarthritis: a randomized controlled trial. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020; 2020:9869161. [33] YE J, SIMPSON MW, LIU Y, et al. The effects of baduanjin qigong on postural stability, proprioception, and symptoms of patients with knee osteoarthritis: a randomized controlled trial. Front Med (Lausanne). 2020;6:307. [34] CHEN PY, SONG CY, YEN HY, et al. Impacts of tai chi exercise on functional fitness in community-dwelling older adults with mild degenerative knee osteoarthritis: a randomized controlled clinical trial. BMC Geriatr. 2021;21(1):449. [35] ONWUNZO CN, IGWE SE, UMUNNAH JO, et al. Effects of isometric strengthening exercises on pain and disability among patients with knee osteoarthritis. Cureus. 2021;13(10):e18972. [36] KANG N, WANG Y, CHEN G, et al. Functional outcomes of Tai Chi exercise prescription in women with knee osteoarthritis. Sports Med Health Sci. 2022;4(4):239-244. [37] SHEN P, LI L, SONG Q, et al. Proprioceptive neuromuscular facilitation improves symptoms among older adults with knee osteoarthritis during stair ascending: a randomized controlled trial. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2022;101(8):753-760. [38] SONG J, WEI L, CHENG K, et al. The effect of modified tai chi exercises on the physical function and quality of life in elderly women with knee osteoarthritis. Front Aging Neurosci. 2022;14:860762. [39] DRUMMEN SJJ, BALOGUN S, LAHHAM A, et al. A pilot randomized controlled trial evaluating outdoor community walking for knee osteoarthritis: walk. Clin Rheumatol. 2023;42(5): 1409-1421. [40] GAO B, LI L, SHEN P, et al. Effects of proprioceptive neuromuscular facilitation stretching in relieving pain and balancing knee loading during stepping over obstacles among older adults with knee osteoarthritis: a randomized controlled trial. PLoS One. 2023;18(2):e0280941. [41] KUŞ G, TARAKÇI E, RAZAK OZDINCLER A, et al. Sensory-motor training versus resistance training in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis: a randomized controlled trial. Clin Rehabil. 2023; 37(5):636-650. [42] LALL S, PREM V, KARVANNAN H. Comparison of neuromuscular joint facilitation and quadriceps strengthening exercise in knee osteoarthritis: a randomized controlled trial. Int J Ther Massage Bodywork. 2023;16(3):10-19. [43] ØIESTAD BE, ÅRØEN A, RØTTERUD JH,et al. The efficacy of strength or aerobic exercise on quality of life and knee function in patients with knee osteoarthritis. A multi-arm randomized controlled trial with 1-year follow-up. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2023;24(1):714. [44] RÊGO TAM, FERREIRA APL, VILLELA DW, et al. Effects of mat Pilates on older adult women with knee osteoarthritis: a randomized controlled trial. J Bodyw Mov Ther. 2023;33:136-141. [45] 李辉萍,宋涛,邓景贵,等.本体感觉神经肌肉促进技术对膝骨关节炎患者本体感觉及平衡能力的影响[J].中华物理医学与康复杂志, 2017,39(6):456-459. [46] 李静雅,程亮.太极拳和抗阻训练对膝关节骨性关节炎老人症状及运动能力的影响[J].中国康复医学杂志,2019,34(11):1304-1309. [47] 李宇涛,叶银燕,牛晓敏,等.易筋经功法对膝骨关节炎患者下肢肌群协调激活能力的影响[J].中华中医药杂志,2022,37(4):2380-2385. [48] GOH SL, PERSSON MSM, STOCKS J, et al. Relative efficacy of different exercises for pain, function, performance and quality of life in knee and hip osteoarthritis: systematic review and network meta-analysis. Sports Med. 2019;49(5):743-761. [49] ETTINGER WH JR, BURNS R, MESSIER SP, et al. A randomized trial comparing aerobic exercise and resistance exercise with a health education program in older adults with knee osteoarthritis. The Fitness Arthritis and Seniors Trial (FAST). JAMA. 1997;277(1):25-31. [50] MESSIER SP, LOESER RF, MILLER GD, et al. Exercise and dietary weight loss in overweight and obese older adults with knee osteoarthritis: the arthritis, diet, and activity promotion trial. Arthritis Rheum. 2004;50(5):1501-1510. [51] MESSIER SP, GUTEKUNST DJ, DAVIS C, et al. Weight loss reduces knee-joint loads in overweight and obese older adults with knee osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2005;52(7): 2026-2032. [52] WANG C, BANNURU R, RAMEL J, et al. Tai Chi on psychological well-being: systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2010;10:23. [53] LI JX, HONG Y, CHAN KM. Tai chi: physiological characteristics and beneficial effects on health. Br J Sports Med. 2001;35(3):148-156. [54] ESCH T, DUCKSTEIN J, WELKE J, et al. Mind/body techniques for physiological and psychological stress reduction: stress management via Tai Chi training - a pilot study. Med Sci Monit. 2007; 13(11):CR488-CR497. |
| [1] | Li Jiagen, Chen Yueping, Huang Keqi, Chen Shangtong, Huang Chuanhong. The construction and validation of a prediction model based on multiple machine learning algorithms and the immunomodulatory analysis of rheumatoid arthritis from the perspective of mitophagy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(在线): 1-15. |
| [2] | Ma Chi, Wang Ning, Chen Yong, Wei Zhihan, Liu Fengji, Piao Chengzhe. Application of 3D-printing patient-specific instruments combined with customized locking plate in opening wedge high tibial osteotomy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1863-1869. |
| [3] | Zhang Xinxin, Gao Ke, Xie Shidong, Tuo Haowen, Jing Feiyue, Liu Weiguo. Network meta-analysis of non-surgical treatments for foot and ankle ability and dynamic balance in patients with chronic ankle instability [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1931-1944. |
| [4] | Sun Yundi, Cheng Lulu, Wan Haili, Chang Ying, Xiong Wenjuan, Xia Yuan. Effect of neuromuscular exercise for knee osteoarthritis pain and function: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1945-1952. |
| [5] | Liu Yan, Wang Kai, Wu Min. Relationship between coronal angle fluctuation of ankle point and recovery of joint function after ankle fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1820-1826. |
| [6] | Wang Peiguang, Zhang Xiaowen, Mai Meisi, Li Luqian, Huang Hao. Generalized equation estimation of the therapeutic effect of floating needle therapy combined with acupoint embedding on different stages of human knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1565-1571. |
| [7] | Wang Juan, Wang Guanglan, Zuo Huiwu. Efficacy of exercise therapy in the treatment of anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction patients: #br# a network meta-analysis #br# [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1714-1726. |
| [8] | Zheng Huakun, Yin Mingyue, Liu Qian. Effects of interval and continuous training on the quality of life in physically inactive adults: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1727-1740. |
| [9] | He Guanghui, Yuan Jie, Ke Yanqin, Qiu Xiaoting, Zhang Xiaoling. Hemin regulates mitochondrial pathway of oxidative stress in mouse chondrocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1183-1191. |
| [10] |
Liang Xiaoxiao, Zheng Jiejiao, Duan Linru, Chen Xi, Zhang Tingyu.
Characterization of postural stability in elderly patients with idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus #br#
#br#
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1208-1213.
|
| [11] | Ma Haoyu, Qiao Hongchao, Hao Qianqian, Shi Dongbo. Causal effects of different exercise intensities on the risk of osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1305-1311. |
| [12] | Li Jiatong, Jin Yue, Liu Runjia, Song Bowen, Zhu Xiaoqian, Li Nianhu . Association between thyroid function levels and phenotypes associated with sarcopenia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1312-1320. |
| [13] | Li Shuai, Liu Hua, Shang Yonghui, Liu Yicong, Zhao Qihang, Liu Wen. Stress distribution on the maxilla when wearing the Twin-block appliance for Class II malocclusion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 881-887. |
| [14] | Zhi Fang, Zhu Manhua, Xiong Wei, Lin Xingzhen. Analgesic effect of acupuncture in a rat model of lumbar disc herniation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 936-941. |
| [15] | Liu Zan, An Ran, Li Baocheng. Effect of pravastatin on functional recovery from sciatic nerve crush injury in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 942-950. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||