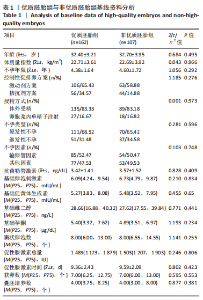
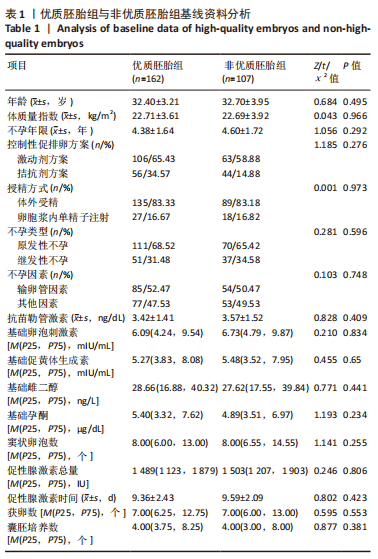
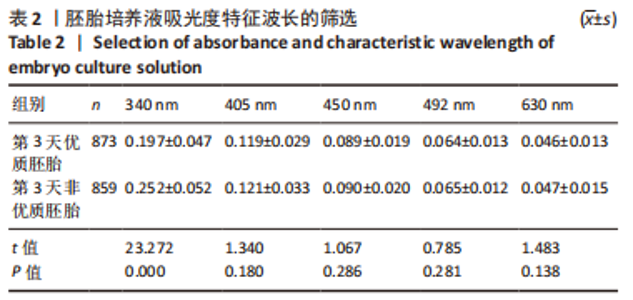
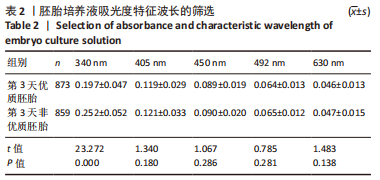
[1] DE MOUZON J, CHAMBERS GM, ZEGERS-HOCHSCHILD F, et al. International Committee for Monitoring Assisted Reproductive Technologies world report: assisted reproductive technology 2012. Hum Reprod. 2020;35(8):1900-1913.
[2] 石玉华,王秋敏,戚丹.辅助生殖技术前沿研究热点及进展[J].山东大学学报,2021,59(9):97-102.
[3] DEANGELIS AM, MARTINI AE, OWEN CM. Assisted Reproductive Technology and Epigenetics. Semin Reprod Med. 2018;36(3-04): 221-232.
[4] NIU Y, SUN N, LI C, et al. Dissecting primate early post-implantation development using long-term in vitro embryo culture. Science. 2019; 366(6467):eaaw5754.
[5] ESHRE SPECIAL INTEREST GROUP OF EMBRYOLOGY AND ALPHA SCIENTISTS IN REPRODUCTIVE MEDICINE. The Vienna consensus: report of an expert meeting on the development of ART laboratory performance indicators. Reprod Biomed Online. 2017;35(5):494-510.
[6] 李蕾,范英英,李净羽,等.优质单囊胚移植早期妊娠丢失的影响因素分析及预测模型建立[J].中华实用诊断与治疗杂志,2021, 35(10):1007-1012.
[7] 王珺,王晓红.胚胎染色体非整倍性来源[J].中国优生与遗传杂志, 2021,29(12):1786-1790.
[8] 黄鑫.代谢组学评估胚胎发育潜能的研究进展[J].世界临床药物, 2021,42(2):87-91.
[9] BERNILLON S, MAUCOURT M, DEBORDE C, et al. Characterization of GMO or glyphosate effects on the composition of maize grain and maize-based diet for rat feeding. Metabolomics. 2018;14(3):36.
[10] THOMPSON JG, BROWN HM, SUTTON-MCDOWALL ML. Measuring embryo metabolism to predict embryo quality. Reprod Fertil Dev. 2016; 28(1-2):41-50.
[11] 耿蒙慧,张璨,邢阿英,等.胚胎质量评估方法的研究进展[J].中华妇幼临床医学杂志,2018,14(5):612-616.
[12] LEESE HJ, BRISON DR, STURMEY RG. The Quiet Embryo Hypothesis: 20 years on. Front Physiol. 2022;13:899485.
[13] FIGOLI CB, GARCEA M, BISIOLI C, et al. A robust metabolomics approach for the evaluation of human embryos from in vitro fertilization. Analyst. 2021;146(20):6156-6169.
[14] 曹羽明,张元珍,罗孟成.代谢组学预测人卵母细胞质量与胚胎体外发育潜能的研究现状[J].生殖医学杂志,2021,30(3):400-404.
[15] 孙青,黄国宁,孙海翔,等.胚胎实验室关键指标质控专家共识[J].生殖医学杂志,2018,27(9):836-851.
[16] GARDNER DK, LANE M, STEVENS J, et al. Blastocyst score affects implantation and pregnancy outcome: towards a single blastocyst transfer. Fertil Steril. 2000;73(6):1155-1158.
[17] 胡琳莉,黄国宁,孙海翔,等.辅助生殖技术临床关键指标质控专家共识[J].生殖医学杂志,2018,27(9):828-835.
[18] ZHU Q, ZHU J, WANG Y, et al. Live birth rate and neonatal outcome following cleavage-stage embryo transfer versus blastocyst transfer using the freeze-all strategy. Reprod Biomed Online. 2019;38(6):892-900.
[19] BERGH C, KAMATH MS, WANG R, et al. Strategies to reduce multiple pregnancies during medically assisted reproduction. Fertil Steril. 2020; 114(4):673-679.
[20] 王浩原,王崴然,白春梅,等.人类辅助生殖技术中评估胚胎发育潜能的四种方法[J].生殖医学杂志,2022,31(6):850-856.
[21] MUNNÉ S, WEIER HU, GRIFO J, et al. Chromosome mosaicism in human embryos. Biol Reprod. 1994;51(3):373-379.
[22] ALMEIDA PA, BOLTON VN. The relationship between chromosomal abnormality in the human preimplantation embryo and development in vitro. Reprod Fertil Dev. 1996;8(2):235-241.
[23] BAUMANN CG, MORRIS DG, SREENAN JM, et al. The quiet embryo hypothesis: molecular characteristics favoring viability. Mol Reprod Dev. 2007;74(10):1345-1353.
[24] SCHINI SA, BAVISTER BD. Two-cell block to development of cultured hamster embryos is caused by phosphate and glucose. Biol Reprod. 1988;39(5):1183-1192.
[25] CONAGHAN J, HARDY K, HANDYSIDE AH, et al. Selection criteria for human embryo transfer: a comparison of pyruvate uptake and morphology. J Assist Reprod Genet. 1993;10(1):21-30.
[26] 赵海静,邱绮,区颂邦,等.胚胎形态学评分联合培养液铵离子浓度有助于预测低质量卵裂期胚胎的种植结局[J].生殖医学杂志, 2022,31(6):758-764.
[27] KASHIR J, HEINDRYCKX B, JONES C, et al. Oocyte activation, phospholipase C zeta and human infertility. Hum Reprod Update. 2010;16(6):690-703.
[28] SCOTT R, SELI E, MILLER K, et al. Noninvasive metabolomic profiling of human embryo culture media using Raman spectroscopy predicts embryonic reproductive potential: a prospective blinded pilot study. Fertil Steril. 2008;90(1):77-83.
[29] GARDNER DK, HAMILTON R, MCCALLIE B, et al. Human and mouse embryonic development, metabolism and gene expression are altered by an ammonium gradient in vitro. Reproduction. 2013;146(1):49-61.
[30] LIANG B, GAO Y, XU J, et al. Raman profiling of embryo culture medium to identify aneuploid and euploid embryos. Fertil Steril. 2019;111(4): 753-762.
[31] BOYAMA BA, CEPNI I, IMAMOGLU M, et al. Homocysteine in embryo culture media as a predictor of pregnancy outcome in assisted reproductive technology. Gynecol Endocrinol. 2016;32(3):193-195.
[32] LEE YS, THOUAS GA, GARDNER DK. Developmental kinetics of cleavage stage mouse embryos are related to their subsequent carbohydrate and amino acid utilization at the blastocyst stage. Hum Reprod. 2015; 30(3):543-552.
|