Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (34): 5530-5537.doi: 10.12307/2023.702
Previous Articles Next Articles
Role of cuproptosis regulator in diagnosis and subtype of osteoarthritis
Xiong Bo1, Wang Bin2, Liu Jinfu1, Lu Guanyu1, Chen Cai1, Huang Yue1, Chen Lihua1
- 1Graduate School of Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530299, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; 2First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530023, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2022-09-24Accepted:2022-11-08Online:2023-12-08Published:2023-04-22 -
Contact:Wang Bin, Chief physician, First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530023, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Xiong Bo, Master candidate, Graduate School of Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530299, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:School Level Project of Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, No. YCXJ2021070 (to XB); Basic Research Ability Improvement Project of Young and Middle Aged Teachers of Guangxi Colleges and Universities, No. 2022KY0282 (to LJF); School Level Project of Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, No. YCXJ2021071 (to HY)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Xiong Bo, Wang Bin, Liu Jinfu, Lu Guanyu, Chen Cai, Huang Yue, Chen Lihua. Role of cuproptosis regulator in diagnosis and subtype of osteoarthritis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(34): 5530-5537.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
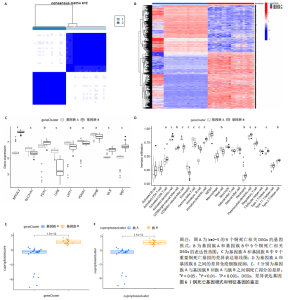
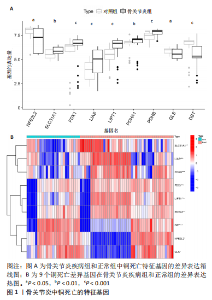
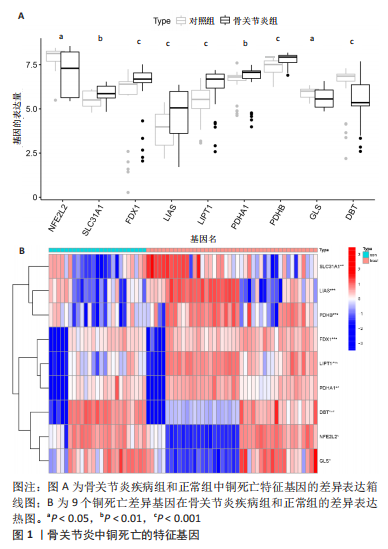
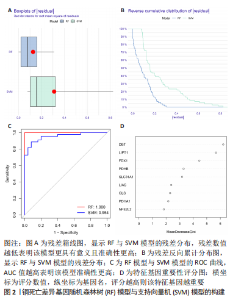
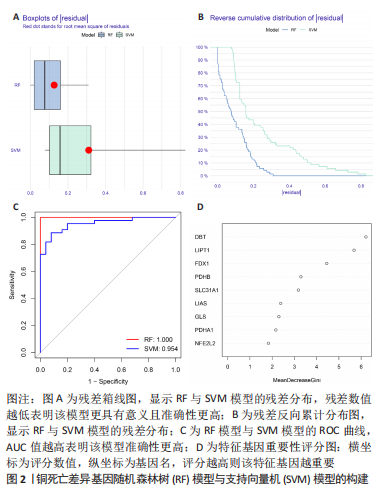
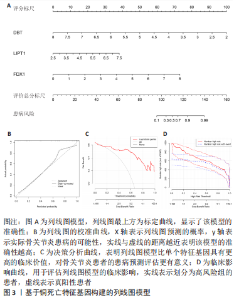
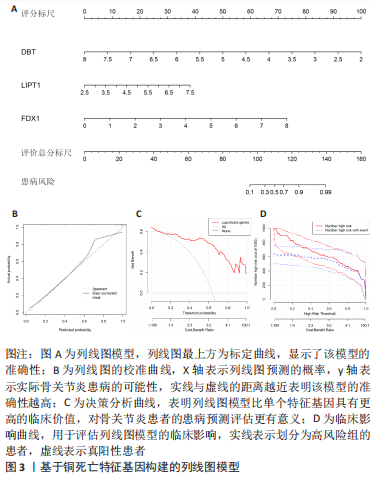
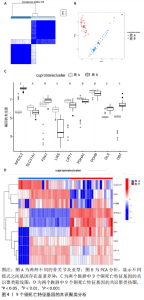
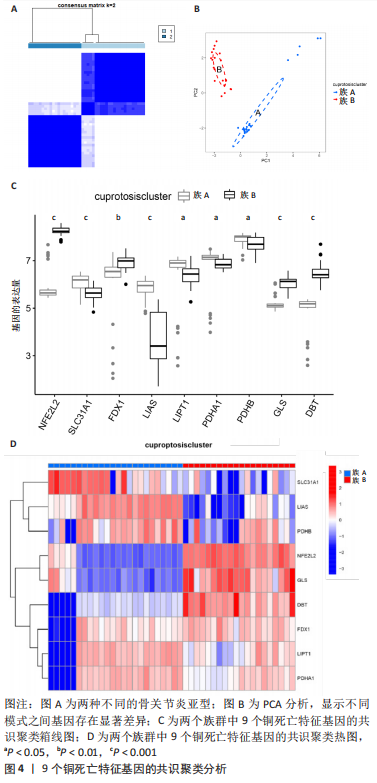
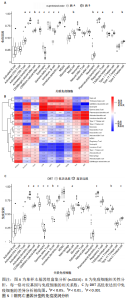
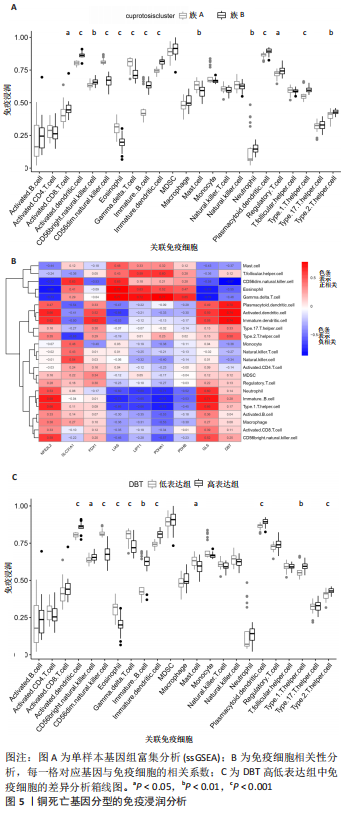
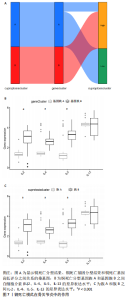
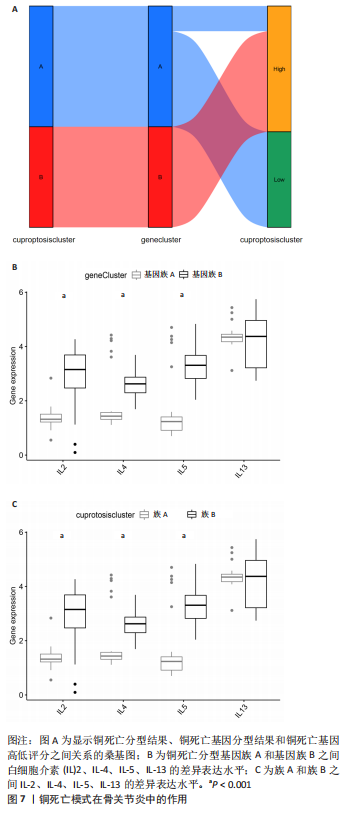
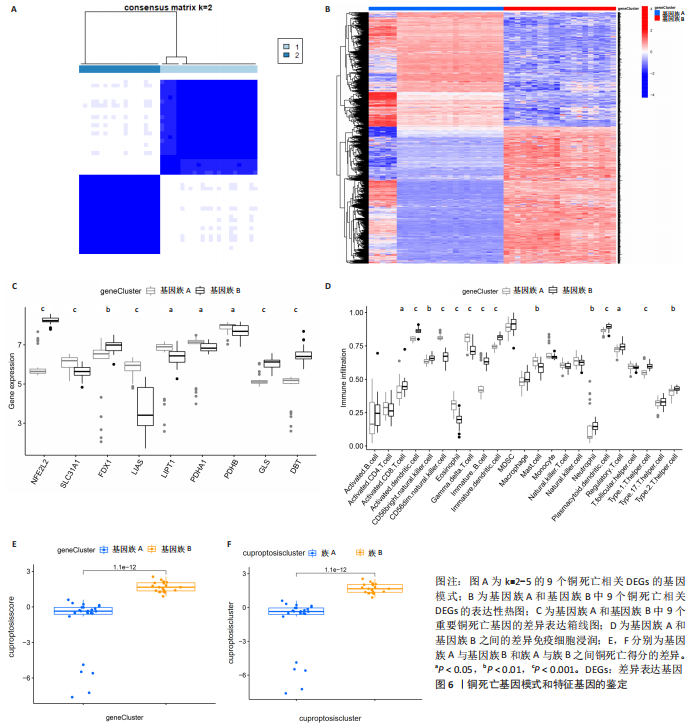
2.6 铜死亡基因模式和特征基因的鉴定 为了进一步验证铜死亡的基因模式,使用共识聚类方法根据20个铜死亡相关差异表达基因将骨关节炎患者分为不同的基因组亚型。研究发现可存在两种不同的铜死亡基因模式(基因族A和基因族B),这与铜死亡模式的分组相一致(图6A)。基因族A和基因族B中20个铜死亡相关DEGs的表达水平见图6B。图6C,D结果表明,9个铜死亡特征基因的差异表达水平及基因族A和基因族B之间的免疫细胞浸润也与铜死亡模式中的结果相近,再进一步验证了共识聚类方法分组的准确性;且为了量化铜死亡模式,利用PCA算法计算了在两种不同的铜死亡模式或铜死亡基因模式之间每个样本相应的铜死亡分数,结果显示(图6E,F),族B或基因族B的铜死亡得分高于族A和基因族A。"
| [1] CHEN H, CHEN L. An integrated analysis of the competing endogenous RNA network and co-expression network revealed seven hub long non-coding RNAs in osteoarthritis. Bone Joint Res. 2020;9(3):90-98. [2] FRANK M, BWEMERO J, KALUNGA D, et al. OA60 Public health and palliative care mix; a ccpmedicine approach to reverse the overgrowing burden of non-communicable diseases in tanzania. BMJ Support Palliat Care. 2015;5 Suppl 1:A19. [3] 钱晓芬, 曾平, 刘金富, 等. 差异表达基因联合加权共表达网络分析筛选骨关节炎滑膜中的关键基因[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2022, 26(33):5342-5349. [4] SCANZELLO CR, GOLDRING SR. The role of synovitis in osteoarthritis pathogenesis. Bone. 2012;51(2):249-257. [5] HUANG YZ, XIE HQ, SILINI A, et al. Mesenchymal Stem/Progenitor Cells Derived from Articular Cartilage, Synovial Membrane and Synovial Fluid for Cartilage Regeneration: Current Status and Future Perspectives. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2017;13(5):575-586. [6] PRIETO-POTIN I, LARGO R, ROMAN-BLAS JA, et al. Characterization of multinucleated giant cells in synovium and subchondral bone in knee osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2015; 16:226. [7] HAN D, FANG Y, TAN X, et al. The emerging role of fibroblast-like synoviocytes-mediated synovitis in osteoarthritis: An update. J Cell Mol Med. 2020;24(17):9518-9532. [8] TSVETKOV P, COY S, PETROVA B, et al. Copper induces cell death by targeting lipoylated TCA cycle proteins. Science. 2022;375(6586): 1254-1261. [9] OLIVERI V. Selective Targeting of Cancer Cells by Copper Ionophores: An Overview. Front Mol Biosci. 2022;9:841814. [10] LIGHTBODY G, HABERLAND V, BROWNE F, et al. Review of applications of high-throughput sequencing in personalized medicine: barriers and facilitators of future progress in research and clinical application. Brief Bioinform. 2019;20(5):1795-1811. [11] ZHONG Y, XU F, WU J, et al. Application of Next Generation Sequencing in Laboratory Medicine. Ann Lab Med. 2021;41(1):25-43. [12] PAPPADA SM. Machine learning in medicine: It has arrived, let’s embrace it. J Card Surg. 2021;36(11):4121-4124. [13] JAMIN A, ABRAHAM P, HUMEAU-HEURTIER A. Machine learning for predictive data analytics in medicine: A review illustrated by cardiovascular and nuclear medicine examples. Clin Physiol Funct Imaging. 2021;41(2):113-127. [14] QUER G, ARNAOUT R, HENNE M, et al. Machine Learning and the Future of Cardiovascular Care: JACC State-of-the-Art Review. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2021;77(3):300-313. [15] Kokol P, Jurman J, Bogovic T, et al. Supporting Real World Decision Making in Coronary Diseases Using Machine Learning. Inquiry. 2021;58: 46958021997338. [16] 于安池. 基于改进随机森林算法的乳腺癌预测研究[D]. 鞍山:辽宁科技大学,2021. [17] 李琳. 基于优化随机森林混合模型的病症预测分析[D]. 郑州:华北水利水电大学,2022. [18] 汤胜男, 辛学刚. 机器学习在生物信息学领域的应用与研究进展[J]. 人工智能,2020(1):84-93. [19] WANG L, WEI S, ZHOU B, et al. A nomogram model to predict the venous thromboembolism risk after surgery in patients with gynecological tumors. Thromb Res. 2021;202:52-58. [20] TSVETKOV P, COY S, PETROVA B, et al. Copper induces cell death by targeting lipoylated TCA cycle proteins. Science. 2022;375(6586):1254-1261. [21] Kaminska JA. A random forest partition model for predicting NO2 concentrations from traffic flow and meteorological conditions. Sci Total Environ. 2019;651(Pt 1):475-483. [22] Huang S, Cai N, Pacheco PP, et al. Applications of Support Vector Machine (SVM) Learning in Cancer Genomics. Cancer Genomics Proteomics. 2018;15(1):41-51. [23] ZHANG Y, LIU N, WANG S. A differential privacy protecting K-means clustering algorithm based on contour coefficients. PLoS One. 2018; 13(11):e206832. [24] AHN SH, YANG HY, TRAN GB, et al. Interaction of peroxiredoxin V with dihydrolipoamide branched chain transacylase E2 (DBT) in mouse kidney under hypoxia. Proteome Sci. 2015;13:4. [25] ABDUL SZ, CERO C, PIERCE AE, et al. Combining a beta3 adrenergic receptor agonist with alpha-lipoic acid reduces inflammation in male mice with diet-induced obesity. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2022;30(1): 153-164. [26] MAYR JA, FEICHTINGER RG, TORT F, et al. Lipoic acid biosynthesis defects. J Inherit Metab Dis. 2014;37(4):553-563. [27] FROMMER KW, HASSELI R, SCHAFFLER A, et al. Free Fatty Acids in Bone Pathophysiology of Rheumatic Diseases. Front Immunol. 2019;10:2757. [28] STRUSHKEVICH N, MACKENZIE F, CHERKESOVA T, et al. Structural basis for pregnenolone biosynthesis by the mitochondrial monooxygenase system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011;108(25):10139-10143. [29] ZHANG Z, MA Y, GUO X, et al. FDX1 can Impact the Prognosis and Mediate the Metabolism of Lung Adenocarcinoma. Front Pharmacol. 2021;12:749134. [30] BELLUZZI E, STOCCO E, POZZUOLI A, et al. Contribution of Infrapatellar Fat Pad and Synovial Membrane to Knee Osteoarthritis Pain. Biomed Res Int. 2019;2019:6390182. [31] 陈龑, 薛艳, 蒋鼎, 等. T淋巴细胞在骨关节炎中作用的研究进展[J]. 医学综述,2021,27(5):833-838. [32] 叶小康, 白自然, 金敏丽, 等. 滑膜细胞在骨关节炎中的研究进展[J]. 生物化学与生物物理进展,2021,48(11):1282-1289. [33] ZHANG Y, ZHANG Y, GU W, et al. Th1/Th2 cell’s function in immune system. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2014;841:45-65. [34] MONASTERIO G, CASTILLO F, ROJAS L, et al. Th1/Th17/Th22 immune response and their association with joint pain, imagenological bone loss, RANKL expression and osteoclast activity in temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis: A preliminary report. J Oral Rehabil. 2018;45(8): 589-597. [35] WANG J, JIANG H, QIU Y, et al. Effector memory regulatory T cells were most effective at suppressing RANKL but their frequency was downregulated in tibial fracture patients with delayed union. Immunol Lett. 2019;209:21-27. [36] NACHER-JUAN J, TERENCIO MC, ALCARAZ MJ, et al. Osteostatin Inhibits Collagen-Induced Arthritis by Regulation of Immune Activation, Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines, and Osteoclastogenesis. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(16): 3845. [37] CASTROGIOVANNI P, DI ROSA M, RAVALLI S, et al. Moderate Physical Activity as a Prevention Method for Knee Osteoarthritis and the Role of Synoviocytes as Biological Key. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(3):511. [38] ROSSHIRT N, HAGMANN S, TRIPEL E, et al. A predominant Th1 polarization is present in synovial fluid of end-stage osteoarthritic knee joints: analysis of peripheral blood, synovial fluid and synovial membrane. Clin Exp Immunol. 2019;195(3):395-406. [39] HE Z, LEONG DJ, XU L, et al. CITED2 mediates the cross-talk between mechanical loading and IL-4 to promote chondroprotection. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2019;1442(1):128-137. [40] CHEN K, KOLLS JK. T cell-mediated host immune defenses in the lung. Annu Rev Immunol. 2013;31:605-633. [41] RAPHAEL I, NALAWADE S, EAGAR TN, et al. T cell subsets and their signature cytokines in autoimmune and inflammatory diseases. Cytokine. 2015;74(1):5-17. [42] ALAHDAL M, ZHANG H, HUANG R, et al. Potential efficacy of dendritic cell immunomodulation in the treatment of osteoarthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2021;60(2):507-517. [43] KULKARNI P, MARTSON A, VIDYA R, et al. Pathophysiological landscape of osteoarthritis. Adv Clin Chem. 2021;100:37-90. |
| [1] | Li Xiaomin, Tian Xiangdong, Tan Yetong, Zhu Guangyu, Wang Rongtian, Wang Jian, Xue Zhipeng, Ma Sheng, Hu Yuanyi, Huang Ye, Ding Tiansong. Changes of lower limb force line and knee function after high tibial osteotomy in osteoporotic medial ventricular knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1325-1329. |
| [2] | Yu Wenqiang, Ren Fuchao, Shi Guohong, Xu Yuanjing, Liu Tongyou, Xie Youzhuan, Wang Jinwu, . Methods and application of gait analysis of lower limbs after stroke [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1257-1263. |
| [3] | Shen Lianwei, Zhu Hongliu, Wang Wei. Risk factor analysis of metabolic syndrome and construction of a nomogram prediction model in middle-aged and elderly people [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(5): 657-662. |
| [4] | Li Long, Li Guangdi, Shi Hao, Deng Keqi. Circular RNA as a competing endogenous RNA is involved in the regulation of osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(5): 751-757. |
| [5] | Wan Guoli, Shi Chenhui, Wang Weishan, Li Ang, Shi Xunda, Cai Yi. Retrospective analysis of the influencing factors of chronic pain after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 558-564. |
| [6] | Guo Yingqi, Gong Xianxu, Zhang Yan, Xiao Han, Wang Ye, Gu Wenguang. Meniscus extrusion and patellofemoral joint cartilage injury and bone marrow lesions: MRI semi-quantitative score [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 600-605. |
| [7] | Zhu Xunpeng, Xu Hui, Wang Lin, Wang Jun, Zhang Hui. Relationship of preoperative sleep quality and early rehabilitation after unicompartmental knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(36): 5806-5811. |
| [8] | Alimujiang•Yusufu, Abuduwupuer•Haibier, Qin Qi, Liu Yuzhe, Zhang Qianlong, Ran Jian. Efficacy and safety of tranexamic acid and aminocaproic acid in perioperative period of total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(36): 5812-5817. |
| [9] | Yu Jian, Zhou Bingqian, Wang Zhao, Li Yue, Chang Yaru, Cao Hong. Comparison of random forest model and logistic regression model in predicting the prolonged length of stay of hip fracture patients [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(34): 5413-5420. |
| [10] | Tang Li, Pan Yao, Zhu Guochen. Epidermal neural crest stem cells of hair follicles regulate the local expression of inflammatory factors after facial nerve injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(33): 5249-5255. |
| [11] | Xie Na, Ma Run, Wang Lian, Shu Yuanhui, He Ping, Zhou Yan, Xiang Yining, Wang Yuping. Effect of formononetin on glucose oxidase-induced oxidative stress in rat hepatic stellate cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(33): 5309-5313. |
| [12] | Zhang Huiyu, Yu Jingwen, Bai Zhenjun, Li Liang, Mu Bingtao, Zhang Jinfeng, Xie Jiawei. Triptolide protects damaged neurons by regulating microglial polarization [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(33): 5342-5347. |
| [13] | Feng Ruibing, Huang Yong, Hu Hao, Wu Gang, Duan Xiaofeng, Li Chaowen. Analgesic effect and mechanism of icariin in a rat model of post-traumatic knee arthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(32): 5108-5113. |
| [14] | Niu Feng, Su Baotong, Chen Yulin, Xie Yajuan, Xu Yilang, Li Cong, Cheng Zhian. Establishment of Nomogram prediction model for postoperative blood transfusion in elderly hip fractures using R software [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(31): 4932-4936. |
| [15] | Zhu Hongliu, Wang Wei. Correlation analysis of low back pain in middle-aged and elderly people in China and construction of a linear graph prediction mode [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(31): 4937-4942. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||