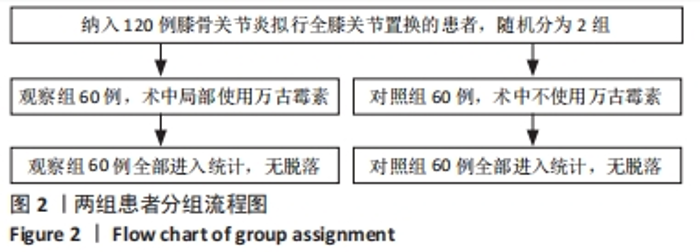
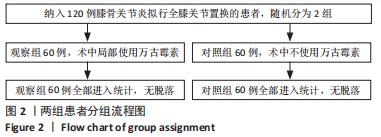
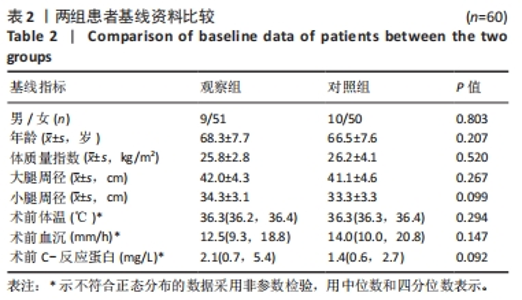
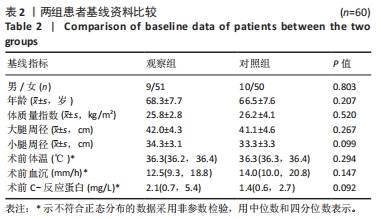
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (33): 5346-5350.doi: 10.12307/2024.668
Previous Articles Next Articles
Topical application of vancomycin in prevention of early incision infection in total knee arthroplasty
Li Zhengyuan, Hao Lin, Chen Shenghong, Peng Kai, Wang Jun, Yin Zongsheng
- Department of Joint Surgery, First Affiliated Hospital of Anhui Medical University, Hefei 230022, Anhui Province, China
-
Received:2023-07-19Accepted:2023-09-22Online:2024-11-28Published:2024-01-30 -
Contact:Yin Zongsheng, MD, Chief physician, Professor, Department of Joint Surgery, First Affiliated Hospital of Anhui Medical University, Hefei 230022, Anhui Province, China -
About author:Li Zhengyuan, Master candidate, Department of Joint Surgery, First Affiliated Hospital of Anhui Medical University, Hefei 230022, Anhui Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Li Zhengyuan, Hao Lin, Chen Shenghong, Peng Kai, Wang Jun, Yin Zongsheng. Topical application of vancomycin in prevention of early incision infection in total knee arthroplasty[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(33): 5346-5350.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
| [1] HAWKER GA, BOHM E, DUNBAR MJ, et al. The Effect of Patient Age and Surgical Appropriateness and Their Influence on Surgeon Recommendations for Primary TKA: A Cross-Sectional Study of 2,037 Patients. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2022;104(8): 700-708. [2] DOWSEY MM, BROWN WA, COCHRANE A, et al. Effect of Bariatric Surgery on Risk of Complications After Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Netw Open. 2022;5(4):e226722. [3] RAJPUT V, MEEK R, HADDAD FS. Periprosthetic joint infection: what next? Bone Joint J. 2022;104-B(11):1193-1195. [4] KHEIR MM, TAN TL, AZBOY I, et al. Vancomycin Prophylaxis for Total Joint Arthroplasty: Incorrectly Dosed and Has a Higher Rate of Periprosthetic Infection Than Cefazolin. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2017;475(7):1767-1774. [5] JONES R, QUARTUCCIO KS, STERN JL, et al. Antibiotic Stewardship Interventions Improve Choice of Antibiotic Prophylaxis in Total Joint Arthroplasty in Patients with Reported Penicillin Allergies. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2021;479(7):1484-1494. [6] LI M, LYU C, FANG Y, et al. Characteristics and risk factors of fever after total joint arthroplasty: a single-center retrospective study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2022;23(1):979. [7] LU X, JIN J, LIN J, et al. Course of fever and potential infection after total joint replacement. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2015;23(6):1870-1876. [8] KOLZ JM, RAINER WG, WYLES CC, et al. Lymphedema: A Significant Risk Factor for Infection and Implant Failure After Total Knee Arthroplasty. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2020;28(23):996-1002. [9] DATTILO J, GITTINGS D, SLOAN M, et al. ‘Hot Joints’ infection protocol reduces unnecessary post-operative re-admissions following total hip and knee arthroplasty. Bone Joint J. 2017;99-B(12):1603-1610. [10] UVODICH ME, DUGDALE EM, OSMON DR, et al. The effectiveness of laboratory tests to predict early postoperative periprosthetic infection after total knee arthroplasty. Bone Joint J. 2021;103-B(6 Supple A):177-184. [11] CASENAZ A, PIROTH L, LABATTUT L, et al. Epidemiology and antibiotic resistance of prosthetic joint infections according to time of occurrence, a 10-year study. J Infect. 2022;85(5):492-498. [12] FROSCHEN FS, RANDAU TM, FRANZ A, et al. Microbiological Trends and Antibiotic Susceptibility Patterns in Patients with Periprosthetic Joint Infection of the Hip or Knee over 6 Years. Antibiotics (Basel). 2022;11(9):1244. [13] BUCHALTER DB, NDUAGUBA A, TEO GM, et al. Cefazolin remains the linchpin for preventing acute periprosthetic joint infection following primary total knee arthroplasty. Bone Jt Open. 2022;3(1):35-41. [14] SHAHI A, PARVIZI J. Prevention of Periprosthetic Joint Infection. Arch Bone Jt Surg. 2015;3(2):72-81. [15] URISH KL, DEMUTH PW, KWAN BW, et al. Antibiotic-tolerant Staphylococcus aureus Biofilm Persists on Arthroplasty Materials. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2016; 474(7):1649-1656. [16] RAVI S, ZHU M, LUEY C, et al. Antibiotic resistance in early periprosthetic joint infection. ANZ J Surg. 2016;86(12):1014-1018. [17] VILLA JM, PANNU TS, RIESGO AM, et al. Dual Antibiotic Prophylaxis in Total Knee Arthroplasty: Where Do We Stand? J Knee Surg. 2020;33(2):100-105. [18] LANE MK, KEENEY JA. Dual Antibiotic Prophylaxis in Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty-No Benefit for Extremely Obese Patients. J Knee Surg. 2022;35(11): 1209-1213. [19] 汪萧和, 王志文, 陆鸣, 等. 两种止血带使用方式对150例全膝关节置换术患者失血量和术后康复影响的前瞻性随机对照研究[J]. 中华骨与关节外科杂志,2020,13(9): 736-740. [20] 吴晓飞. 发热诊断的临床思路与急诊处理[J]. 中华全科医学,2021,19(12): 1989-1990. [21] 李程,ANDREJ T. 人工关节置换术后假体周围感染的临床诊断[J]. 中华关节外科杂志(电子版),2019,13(6):715-723. [22] SPRINGER BD. The Diagnosis of Periprosthetic Joint Infection. J Arthroplasty. 2015;30(6):908-911. [23] YOUNG SW, ZHANG M, FREEMAN JT, et al. Higher cefazolin concentrations with intraosseous regional prophylaxis in TKA. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2013;471(1):244-249. [24] PENG Z, LIN X, KUANG X, et al. The application of topical vancomycin powder for the prevention of surgical site infections in primary total hip and knee arthroplasty: A meta-analysis. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2021;107(4):102741. [25] SLIEPEN J, CORRIGAN RA, DUDAREVA M, et al. Does the Use of Local Antibiotics Affect Clinical Outcome of Patients with Fracture-Related Infection? Antibiotics (Basel). 2022;11(10):1330. [26] LEE SH, TAI CL, CHEN SY, et al. Elution and Mechanical Strength of Vancomycin-Loaded Bone Cement: In Vitro Study of the Influence of Brand Combination. PLoS One. 2016;11(11):e166545. [27] TAILAITI A, SHANG J, SHAN S, et al. Effect of intrawound vancomycin application in spinal surgery on the incidence of surgical site infection: a meta-analysis. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2018;14:2149-2159. [28] BOKHARI R, YOU E, ZEILER FA, et al. Effect of Intrawound Vancomycin on Surgical Site Infections in Nonspinal Neurosurgical Procedures: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. World Neurosurg. 2019;123:409-417. [29] DEVIN CJ, CHOTAI S, MCGIRT MJ, et al. Intrawound Vancomycin Decreases the Risk of Surgical Site Infection After Posterior Spine Surgery: A Multicenter Analysis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2018;43(1):65-71. [30] YAVUZ IA, OKEN OF, YILDIRIM AO, et al. No effect of vancomycin powder to prevent infection in primary total knee arthroplasty: a retrospective review of 976 cases. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2020;28(9):3055-3060. [31] HANADA M, NISHIKINO S, HOTTA K, et al. Intrawound vancomycin powder increases post-operative wound complications and does not decrease periprosthetic joint infection in primary total and unicompartmental knee arthroplasties. Knee Surg Sport Tr A. 2019;27(7):2322-2327. [32] XU X, ZHANG X, ZHANG Y, et al. Role of intra-wound powdered vancomycin in primary total knee arthroplasty. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2020;106(3):417-420. [33] PROBASCO WV, CEFALU CJ, LEE R, et al. Prevalence of idiopathically elevated ESR and CRP in patients undergoing primary total knee arthroplasty as a function of body mass index. J Clin Orthop Trauma. 2020;11(Suppl 5):S722-S728. [34] FELDMAN M, AZIZ B, KANG GN, et al. C-reactive protein and erythrocyte sedimentation rate discordance: frequency and causes in adults. Transl Res. 2013; 161(1):37-43. [35] UVODICH ME, DUGDALE EM, OSMON DR, et al. The effectiveness of laboratory tests to predict early postoperative periprosthetic infection after total knee arthroplasty. Bone Joint J. 2021;103-B(6 Supple A):177-184. [36] KAINTH MK, GIGLIOTTI F. Simultaneous testing of erythrocyte sedimentation rate and C-reactive protein: increased expenditure without demonstrable benefit. J Pediatr. 2014;165(3):625-627. [37] MAGRO F, SOUSA P, MINISTRO P. C-reactive protein in Crohn’s disease: How informative is it? Expert Rev Gastroent. 2014;8(4):393-408. [38] LEE SA, KANG S, YOON C, et al. Temporal Value of C-Reactive Protein and Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate after Total Knee Arthroplasty in Patients with Elevated Preoperative C-Reactive Protein: A Matched-Pair Analysis. Indian J Orthop. 2019;53(3):437-441. [39] ASCIONE T, BALATO G, BOCCIA G, et al. Predictive value of fever following arthroplasty in diagnosing an early infection. Infez Med. 2017;25(1):3-7. [40] WEINBERG L, LI M, CHURILOV L, et al. Associations of fluid amount, type, and balance and acute kidney injury in patients undergoing major surgery. Anaesth Intensive Care. 2018;46(1):79-87. [41] SHOHAT N, GOSWAMI K, TAN TL, et al. Fever and Erythema are Specific Findings in Detecting Infection Following Total Knee Arthroplasty. J Bone Jt Infect. 2019;4(2):92-98. [42] ULGER F, PEHLIVANLAR KM, OZTURK CE, et al. Non-infectious Fever After Acute Spinal Cord Injury in the Intensive Care Unit. J Spinal Cord Med. 2019;42(3):310-317. [43] MAYO BC, HAWS BE, BOHL DD, et al. Postoperative Fever Evaluation Following Lumbar Fusion Procedures. Neurospine. 2018;15(2):154-162. [44] 付志强,夏长所,李志杰,等,全膝关节置换后早期夹闭引流管对失血量的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2016,20(13):1852-1858. [45] 王笑欢,郭凯,牛子健,等,万古霉素致非霍奇金淋巴瘤患儿免疫性溶血及凝血功能障碍分析[J]. 中华实用儿科临床杂志,2021,36(20):1568-1571. [46] SZOTS K, PEDERSEN PU, HORDAM B, et al. Physical health problems experienced in the early postoperative recovery period following total knee replacement. Int J Orthop Trauma Nurs. 2015;19(1):36-44. |
| [1] | Shan Jiaxin, Zhang Yilong, Wu Hongtao, Zhang Jiayuan, Li Anan, Liu Wengang, Xu Xuemeng, Zhao Chuanxi. Changes in muscle strength and pain in patients receiving Jianpi Yiqi Huoxue Formula after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1378-1382. |
| [2] | Qi Haodong, Lu Chao, Xu Hanbo, Wang Mengfei, Hao Yangquan. Effect of diabetes mellitus on perioperative blood loss and pain after primary total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1383-1387. |
| [3] | Li Xiaoqiang, Chen Wei, Li Mingyue, Shan Tianchi, Shen Wen. Value of preoperative quantitative ultrasound analysis of quadriceps femoris in predicting chronic post-surgical pain after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1388-1393. |
| [4] | Wang Tihui, Wang Xu, Wu Jinqing, Chen Jiliang, Wang Xiaolu, Miao Juan. Application of three-dimensional simulated osteotomy of the distal femur in total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 905-910. |
| [5] | Chen Zan, Lei Fei, Ye Fei, Zhou Qingzhong, Yuan Hao, Zheng Lipeng, Zha Xian, Feng Daxiong. Relationship between drainage time and early efficacy after short-segment lumbar fusion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 927-933. |
| [6] | Yang Yifeng, Huang Jian, Ye Nan, Wang Lin. Ischemia-reperfusion injury in total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 955-960. |
| [7] | Sun Jinghua, Qi Zhiming, Ruan Wenli, Zhang Jiaguo, Yang Zhitong. Application advantages of Brainlab Knee 3 navigation combined with gap balance in total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(33): 5333-5339*. |
| [8] | Lin Ying, Liao Qi, Yan Laixiu, Lai Jianhong. Risk factors of delirium after total knee arthroplasty in elderly patients and establishment of nomogram prediction model [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(33): 5340-5345. |
| [9] | Wang Tihui, Wang Xu, Wu Jinqing, Chen Jiliang, Wang Qijin, Xu Hongwei, Lin Jianguo. Moderate and severe valgus knee by total knee arthroplasty through medial and lateral parapatellar approach [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(30): 4825-4830. |
| [10] | Huang Xueli, Luo Ruiqin, Chen Sheng, Li Xiaowu, Chen Haibo, Zeng Qingqiang, Zheng Zhihui. Application of balance technique and measurement osteotomy technique under Offset Repo-Tensor in total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(24): 3822-3826. |
| [11] | Geng Haoyang, Liu Wenping, Wang Guorui, Liu Bin, Wang Wei, Ma Zhanqiao, Wang Jianhua. Effect of adductor canal block and single sciatic nerve block combined with analgesic drugs on pain after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(24): 3833-3838. |
| [12] | Li Xingyu, Zhou Jie, Li Shasha, Zhang Tianxi, Guo Guoning, Yu Anyong, Deng Jiang, Ye Peng. Repair of infected osteochondral defect with sustained release vancomycin three-dimensional scaffold in rabbits [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(22): 3509-3516. |
| [13] | Chen Jiahao, Feng Shuo, Wang Hu, Zhang Qiang, Chen Xiangyang. Value of mean platelet volume combined with thromboelastography in predicting thrombosis after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(21): 3334-3338. |
| [14] | Yang Yongze, Cheng Qinghao, Zhang Anren, Yang Xin, Zhang Zhuangzhuang, Fan Hua, Zhang Fukang, Guo Hongzhang. Advantages and disadvantages of trauma effects during robot-assisted total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(21): 3413-3417. |
| [15] | Li Bowei, Pan Wenjie, Xu Chao, Huang Yuanchi, Ma Jianbing. Effect analysis of a modified topical application of tranexamic acid in primary total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(18): 2852-2858. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||