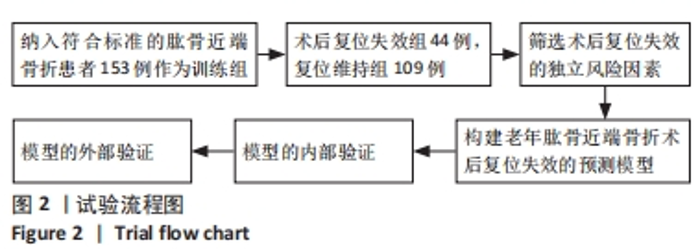
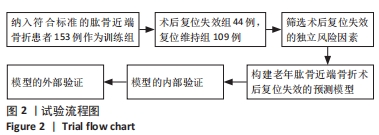
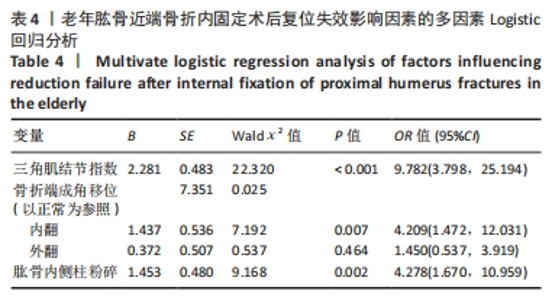
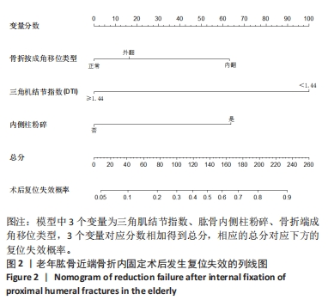
[1] 司元龙,冯康虎,申建军,等. 老年肱骨近端骨折的诊治现状与进展[J]. 中国骨与关节杂志,2021,10(12):904-908.
[2] MIN KS, SHERIDAN B, WARYASZ GR, et al. Predicting reoperation after operative treatment of proximal humerus fractures. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2021;31(6): 1105-1112.
[3] MAIER D, JAEGER M, IZADPANAH K, et al. Proximal humeral fracture treatment in adults. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2014;96(3):251-261.
[4] WANG M, WANG X, CAI P, et al. Locking plate fixation versus intramedullary nail fixation for the treatment of multifragmentary proximal humerus fractures (OTA/AO type 11C): a preliminary comparison of clinical efficacy. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2023;24(1):461.
[5] 蒙敏峰, 陈茂峰, 王玉乐, 等. 老年肱骨近端骨折分型和治疗的研究进展[J]. 中医正骨,2020,32(11):33-36.
[6] 梁乐乐, 王凯, 邢浩, 等. 老年肱骨近端骨折内固定强化措施的研究进展[J]. 医学综述,2020,26(21):4283-4287.
[7] 陈冰, 罗金金. 肱骨近端锁定钢板治疗肱骨近端骨折术后继发性螺钉穿出[J]. 临床骨科杂志,2021,24(3):412.
[8] LAUX CJ, GRUBHOFER F, WERNER C, et al. Current concepts in locking plate fixation of proximal humerus fractures. J Orthop Surg Res. 2017;12(1):137.
[9] CHEN H, YIN P, WANG S, et al. The Augment of the Stability in Locking Compression Plate with Intramedullary Fibular Allograft for Proximal Humerus Fractures in Elderly People. Biomed Res Int. 2018;2018:3130625.
[10] BARLOW JD, LOGLI AL, STEINMANN SP, et al. Locking plate fixation of proximal humerus fractures in patients older than 60 years continues to be associated with a high complication rate. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2020;29(8):1689-1694.
[11] 管宏,胡钢锋,李珍楠,等. 骨水泥在老年骨质疏松性肱骨近端骨折治疗中的应用进展[J]. 中医正骨,2021,33(9):47-51.
[12] 梁志军,沈圣兵.老年人肱骨近端骨折治疗的进展[J]. 贵州医药,2021,45(7): 1041-1043.
[13] 黄淑纾, 林华, 朱秀芬, 等. 骨质量与骨质疏松性骨折[J]. 中华骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病杂志,2012,5(4):285-291.
[14] 张玺, 胡永成, 耿欣, 等. 老年肱骨近端骨折患者皮质骨厚度与骨密度相关性分析[J]. 中华老年骨科与康复电子杂志,2015,1(1):16-21.
[15] KIM DM, PARK D, KIM H, et al. Risk Factors for Severe Proximal Humerus Fracture and Correlation Between Deltoid Tuberosity Index and Bone Mineral Density. Geriatr Orthop Surg Rehabil. 2020;11:1864664671.
[16] SPROSS C, KAESTLE N, BENNINGER E, et al. Deltoid Tuberosity Index: A Simple Radiographic Tool to Assess Local Bone Quality in Proximal Humerus Fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2015;473(9):3038-3045.
[17] 林浩东, 傅慧超, 吴晓明. 《2021版老年肱骨近端骨折治疗指南》解读[J]. 中华创伤杂志,2022,38(9):834-839.
[18] 汪秋柯,陈云丰.浅谈肱骨近端骨折的分型[J]. 国际外科学杂志,2017,44(11):727-730.
[19] WANG JQ, JIANG BJ, GUO WJ, et al. Serial changes in the head-shaft angle of proximal humeral fractures treated by placing locking plates: a retrospective study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2018;19(1):420.
[20] HERTEL R, HEMPFING A, STIEHLER M, et al. Predictors of humeral head ischemia after intracapsular fracture of the proximal humerus. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2004;13(4): 427-433.
[21] 高永祥, 张晋昕. Logistic回归分析的样本量确定[J]. 循证医学,2018,18(2):122-124.
[22] VAN SMEDEN M, MOONS KG, DE GROOT JA, et al. Sample size for binary logistic prediction models: Beyond events per variable criteria. Stat Methods Med Res. 2019; 28(8):2455-2474.
[23] HENKELMANN R, THEOPOLD J, KITSCHE J, et al. Comorbidities, substance abuse, weight and age are independent risk factors for postoperative complications following operation for proximal humerus fractures: a retrospective analysis of 1109 patients. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2022;142(10):2701-2709.
[24] 姜献, 周红云, 许超, 等. 肱骨近端骨折钢板内固定术后常见并发症的研究进展[J]. 中医正骨,2018,30(5):34-36.
[25] NEWTON AW, SELVARATNAM V, PYDAH SK, et al. Simple radiographic assessment of bone quality is associated with loss of surgical fixation in patients with proximal humeral fractures. Injury. 2016;47(4):904-908.
[26] TINGART MJ, APRELEVA M, VON STECHOW D, et al. The cortical thickness of the proximal humeral diaphysis predicts bone mineral density of the proximal humerus. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2003;85(4):611-617.
[27] JUNG SW, SHIM SB, KIM HM, et al. Factors that Influence Reduction Loss in Proximal Humerus Fracture Surgery. J Orthop Trauma. 2015;29(6):276-282.
[28] BAI L, FU ZG, WANG TB, et al. Radiological evaluation of reduction loss in unstable proximal humeral fractures treated with locking plates. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2014;100(3):271-274.
[29] HAWS BE, SAMBORSKI SA, KARNYSKI S, et al. Risk factors for loss of reduction following locked plate fixation of proximal humerus fractures in older adults. Injury. 2023;54(2):567-572.
[30] 汪秋柯, 张明, 陈云丰. 肱骨近端骨折锁定钢板内固定术后螺钉穿出的影响因素及处理研究进展[J]. 中华创伤骨科杂志,2017,19(7):641-644.
[31] 张玉富,蒋协远. 肱骨近端骨折手术治疗的进展与思考[J]. 中国骨伤,2023,36(2): 99-102.
[32] 常祖豪, 张伟, 唐佩福, 等. 内侧支撑重建增强固定技术在肱骨近端骨折治疗中的研究进展[J]. 中国修复重建外科杂志,2021,35(3):375-380.
[33] 韦财. 成人肱骨近端骨折治疗进展[J]. 中外医学研究,2020,18(9):177-179.
[34] 龚冠亦, 许苏梁, 骆川, 等. 老年肱骨近端骨折非手术治疗研究进展[J]. 中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2022,37(11):1227-1229.
[35] SOLBERG BD, MOON CN, FRANCO DP, et al. Locked plating of 3- and 4-part proximal humerus fractures in older patients: the effect of initial fracture pattern on outcome. J Orthop Trauma. 2009;23(2):113-119.
[36] 何继业, 张家红, 蔡贵泉, 等. 锁定钢板治疗不稳定肱骨近端骨折术后内翻的危险因素分析[J]. 中华创伤杂志,2020,36(5):448-454.
|