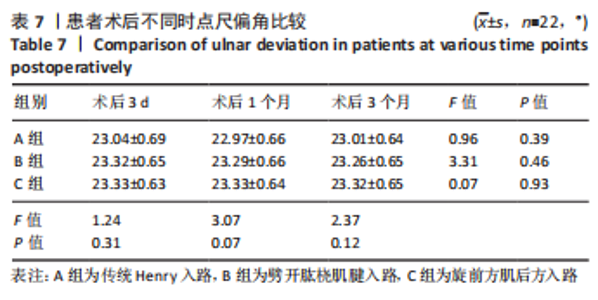
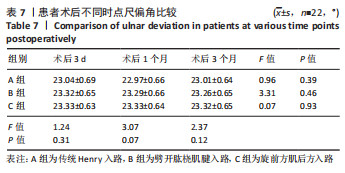
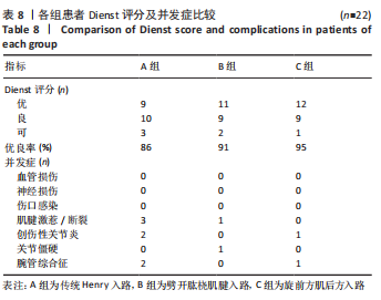
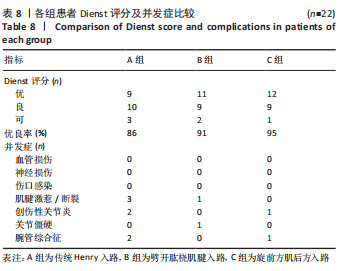
[1] DE ALENCAR NETO JB, JALES CDS, COELHO JVV, et al. Epidemiology, classification, and treatment of bilateral fractures of the distal radius. Acta Ortop Bras. 2022;30(3):e245185.
[2] 黄晓夏,贾麒钰,赵岩,等.保留旋前方肌完整性联合掌侧锁定钢板内固定治疗桡骨远端骨折[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(31): 4959-4964.
[3] YING L, CAI G, ZHU Z, et al. Does pronator quadratus repair affect functional outcome following volar plate fixation of distal radius fractures? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Med (Lausanne). 2023;10:992493.
[4] SMITH DW, HENRY MH. Volar fixed-angle plating of the distal radius. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2005;13(1):28-36.
[5] MULDERS MAM, WALENKAMP MMJ, BOS FJME, et al. Repair of the pronator quadratus after volar plate fixation in distal radius fractures: a systematic review. Strategies Trauma Limb Reconstr. 2017;12(3):181-188.
[6] HERSHMAN SH, IMMERMAN I, BECHTEL C, et al. The effects of pronator quadratus repair on outcomes after volar plating of distal radius fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2013;27(3):130-133.
[7] SEN MK, STRAUSS N, HARVEY EJ. Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis of distal radius fractures using a pronator sparing approach. Tech Hand Up Extrem Surg. 2008;12(1):2-6.
[8] JOHNSON RK, SHREWSBURY MM. The pronator quadratus in motions and in stabilization of the radius and ulna at the distal radioulnar joint. J Hand Surg Am. 1976;1(3):205-209.
[9] 黄晓夏,伊尔夏提·克力木,彭聪,等.改良Henry入路治疗桡骨远端AO B型骨折的疗效分析[J].中华骨与关节外科杂志,2022, 15(1):43-48.
[10] FEENEY MS, WENTORF F, PUTNAM MD. Simulation of altered excursion of the pronator quadratus. J Wrist Surg. 2014;3(3):198-202.
[11] HOHENDORFF B, KNAPPWERTH C, FRANKE J, et al. Pronator quadratus repair with a part of the brachioradialis muscle insertion in volar plate fixation of distal radius fractures: a prospective randomised trial. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2018;138(10):1479-1485.
[12] HUANG X, JIA Q, LI H, et al. Evaluation of sparing the pronator quadratus for volar plating of distal radius fractures: a retrospective clinical study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2022;23(1):625.
[13] KASHIR A, O’DONNELL T. A Brachioradialis Splitting Approach Sparing the Pronator Quadratus for Volar Plating of the Distal Radius. Tech Hand Up Extrem Surg. 2015;19(4):176-181.
[14] NANA AD, JOSHI A, LICHTMAN DM. Plating of the distal radius. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2005;13(3):159-171.
[15] SATAKE H, HANAKA N, HONMA R, et al. Complications of Distal Radius Fractures Treated by Volar Locking Plate Fixation. Orthopedics. 2016; 39(5):e893-e896.
[16] SATO K, MURAKAMI K, MIMATA Y, et al. Incidence of tendon rupture following volar plate fixation of distal radius fractures: A survey of 2787 cases. J Orthop. 2018;15(1):236-238.
[17] CHIANG PP, ROACH S, BARATZ ME. Failure of a retinacular flap to prevent dorsal wrist pain after titanium Pi plate fixation of distal radius fractures. J Hand Surg Am. 2002;27(4):724-728.
[18] VIA GG, ROEBKE AJ, JULKA A. Dorsal Approach for Dorsal Impaction Distal Radius Fracture-Visualization, Reduction, and Fixation Made Simple. J Orthop Trauma. 2020;34 Suppl 2:S15-S16.
[19] 彭聪,黄晓夏,孔维奇,等.两种术中透视方法在桡骨远端骨折掌侧接骨板固定时的应用价值对比[J].中华骨与关节外科杂志, 2022,15(5):341-347.
[20] STUART PR. Pronator quadratus revisited. J Hand Surg Br. 1996;21(6): 714-722.
[21] HAERLE M, SCHALLER HE, MATHOULIN C. Vascular anatomy of the palmar surfaces of the distal radius and ulna: its relevance to pedicled bone grafts at the distal palmar forearm. J Hand Surg Br. 2003;28(2):131-136.
[22] MCCONKEY MO, SCHWAB TD, TRAVLOS A, et al. Quantification of pronator quadratus contribution to isometric pronation torque of the forearm. J Hand Surg Am. 2009;34(9):1612-1617.
[23] SWIGART CR, BADON MA, BRUEGEL VL, et al. Assessment of pronator quadratus repair integrity following volar plate fixation for distal radius fractures: a prospective clinical cohort study. J Hand Surg Am. 2012;37(9):1868-1873.
[24] TOSTI R, ILYAS AM. Prospective evaluation of pronator quadratus repair following volar plate fixation of distal radius fractures. J Hand Surg Am. 2013;38(9):1678-1684.
[25] SONNTAG J, WOYTHAL L, RASMUSSEN P, et al. No effect on functional outcome after repair of pronator quadratus in volar plating of distal radial fractures: a randomized clinical trial. Bone Joint J. 2019;101-B(12):1498-1505.
[26] HÄBERLE S, SANDMANN GH, DEILER S, et al. Pronator quadratus repair after volar plating of distal radius fractures or not? Results of a prospective randomized trial. Eur J Med Res. 2015;20:93.
[27] ATESCHRANG A, STUBY F, WERDIN F, et al. Irritation der Beugesehnen nach palmarer winkelstabiler Plattenosteosynthese des distalen Radius mit der 3,5-mm-T-Platte: Erarbeitung von Risikofaktoren [Flexor tendon irritations after locked plate fixation of the distal radius with the 3.5 mm T-plate: identification of risk factors]. Z Orthop Unfall. 2010;148(3): 319-325.
[28] 李彦宇,赵岩,李孟杰. 改良Henry入路治疗不稳定桡骨远端骨折疗效分析[J]. 中国骨与关节杂志,2020,9(9):654-660.
[29] MAUCK BM, SWIGLER CW. Evidence-Based Review of Distal Radius Fractures. Orthop Clin North Am. 2018;49(2):211-222.
[30] MIRARCHI AJ, NAZIR OF. Minimally Invasive Surgery: Is There a Role in Distal Radius Fracture Management? Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med. 2021;14(1):95-100.
[31] FAN J, CHEN K, ZHU H, et al. Effect of fixing distal radius fracture with volar locking palmar plates while preserving pronator quadratus. Chin Med J (Engl). 2014;127(16):2929-2933.
[32] TOSTI R, ILYAS AM. Prospective evaluation of pronator quadratus repair following volar plate fixation of distal radius fractures. J Hand Surg Am. 2013;38(9):1678-1684.
[33] ITOH S, YUMOTO M, KANAI M, et al. Significance of a Pronator Quadratus-Sparing Approach for Volar Locking Plate Fixation of Comminuted Intra-articular Fractures of the Distal Radius. Hand (N Y). 2016;11(1):83-87.
[34] 方盛,余伟林,孙晓亮. 不切开旋前方肌对桡骨远端骨折掌侧接骨板内固定术后疗效的影响[J]. 中华骨与关节外科杂志,2016,9(2): 153-156. |