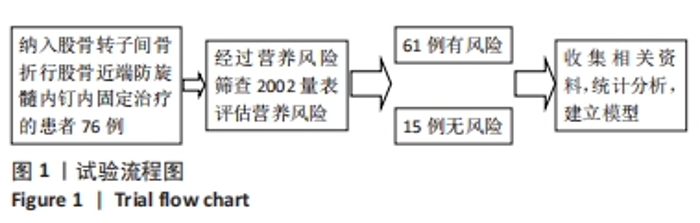
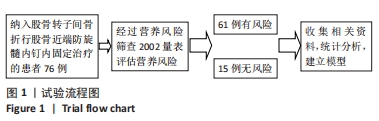
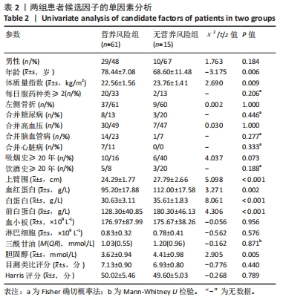
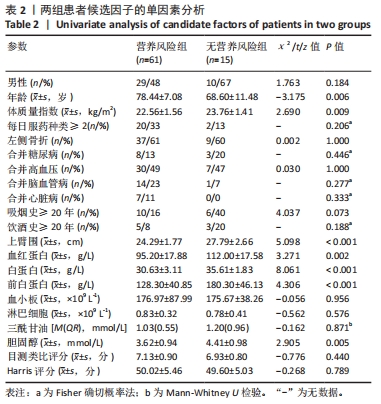
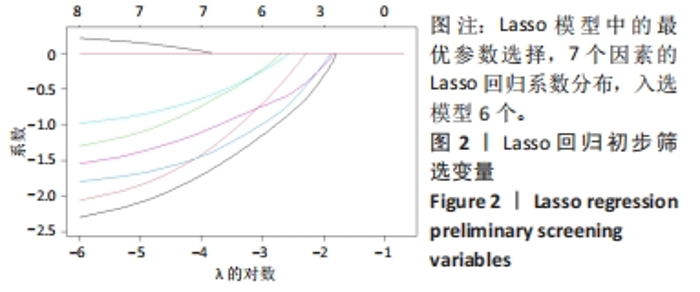
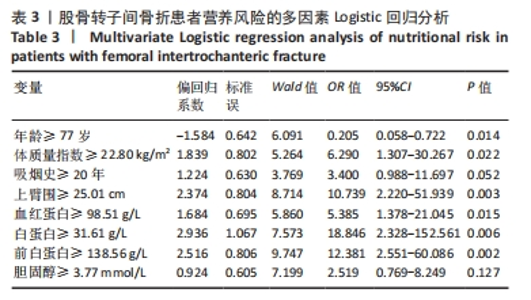
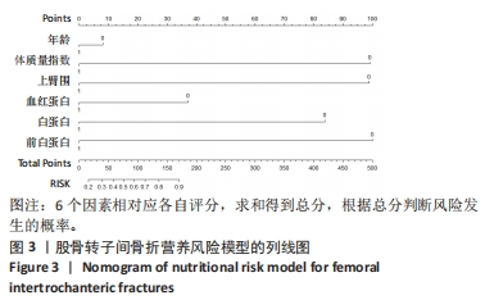
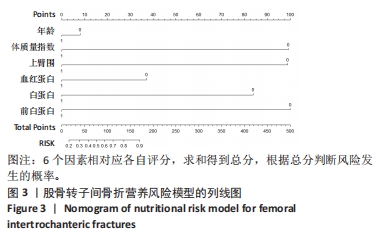
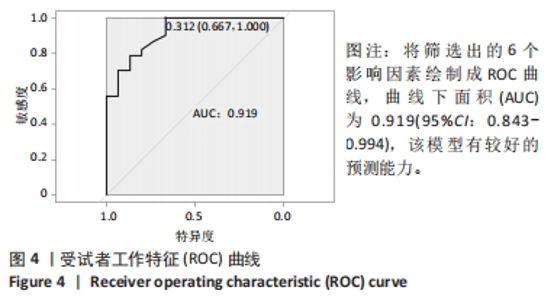
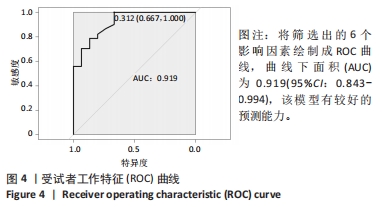
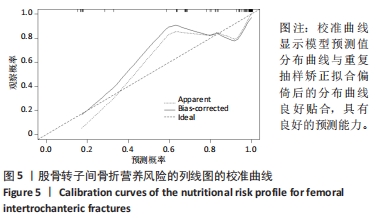
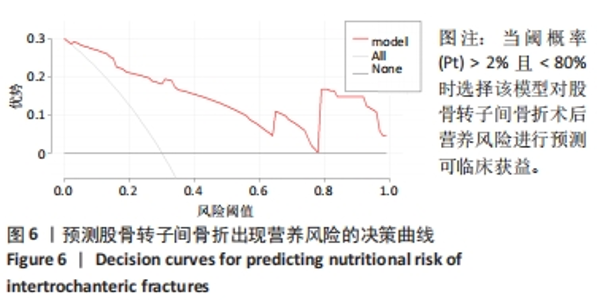
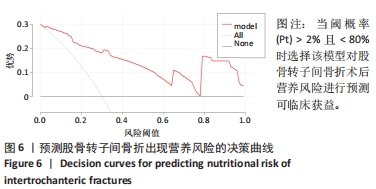
[1] 张世民,胡孙君,杜守超,等.股骨转子间骨折一种新的综合分类法[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2022,36(9):1056-1063.
[2] 李亚伟,沈雪梅,邵明强,等.股骨转子间骨折内固定失败因素的荟萃分析[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2022,30(8):1-5
[3] 曹发奇,闫晨晨,薛航,等.中国老年髋部骨折病人行微创手术治疗专家共识[J].临床外科杂志,2022,30(4):394-400.
[4] 高卉,吕蓓蓓,李琳,等.围手术期口服营养补充对老年股骨转子间骨折术后营养状况及生活质量的影响[J].肠外与肠内营养,2018,25(5):296-300.
[5] 袁媛,喻博,焦竞,等.加速康复外科理念在老年股骨粗隆间骨折围术期中的应用[J].中国康复医学杂志,2022,37(9):1214-1218.
[6] 曹磊,瞿萍,方传勤,等.急性缺血性脑卒中病人营养风险预测模型的建立和验证[J].肠外与肠内营养,2021,28(4):193-198.
[7] COLLINS GS, REITSMA JB, ALTMAN DG, et al. Transparent reporting of a multivariable prediction model for individual prognosis or diagnosis (TRIPOD): the TRIPOD statement. BMJ. 2015;350:g7594.
[8] LHA I, LBA I, ABA I, et al. Nutritional risk screening (NRS 2002) is a strong and modifiable predictor risk score for short-term and long-term clinical outcomes: secondary analysis of a prospective randomised trial. Clin Nutr. 2020;39(9): 2720-2729.
[9] DAHL H, WARZ SI, WELLAND NL, et al. Factors associated with nutritional risk in patients receiving haemodialysis assessed by Nutritional Risk Screening 2002 (NRS2002). J Ren Care. 2022;48(2):112-118.
[10] MALAFARINA V, REGINSTER JY, CABRERIZO S, et al. Nutritional Status and Nutritional Treatment Are Related to Outcomes and Mortality in Older Adults with Hip Fracture. Nutrients. 2018;10(5):555.
[11] SAHLI L, HAGENBUCH N, BALLMER PE, et al. NRS-2002 components, nutritional score and severity of disease score, and their association with hospital length of stay and mortality. Swiss Med Wkly. 2021;151:w20517.
[12] 沈彬,翁习生,廖刃,等.中国髋、膝关节置换术加速康复——围术期疼痛与睡眠管理专家共识[J].中华骨与关节外科杂志,2016,9(2):91-97.
[13] 刘斌,邱贵兴,裴福兴,等.骨科加速康复围手术期疼痛管理专家共识[J].中华骨与关节外科杂志,2022,15(10):739-745.
[14] TABERNA DJ, NAVAS-CARRETERO S, MARTINEZ JA. Current nutritional status assessment tools for metabolic care and clinical nutrition. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2019;22(5):323-328.
[15] RABITO EI, MARCADENTI A, DA SILVA FINK J, et al. Nutritional Risk Screening 2002, Short Nutritional Assessment Questionnaire, Malnutrition Screening Tool, and Malnutrition Universal Screening Tool Are Good Predictors of Nutrition Risk in an Emergency Service. Nutr Clin Pract. 2017;32(4):526-532.
[16] RINNINELLA E, RUGGIERO A, MAURIZI P, et al. Clinical tools to assess nutritional risk and malnutrition in hospitalized children and adolescents. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2017;21(11):2690-2701.
[17] 于健,周冰倩,王朝,等.随机森林模型和Logistic回归模型预测髋部骨折患者住院时间延长的效能比较[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(34):5413-5420.
[18] 杨昌凤,何永琴,易德坤,等.老年髋部骨折患者术后1年内死亡的影响因素分析及列线图预测模型构建[J].陆军军医大学学报,2023,45(1):60-66.
[19] BARCELÓ M, TORRES OH, MASCARÓ J, et al. Hip fracture and mortality: study of specific causes of death and risk factors [published correction appears in Arch Osteoporos. 2021 Mar 4;16(1):53]. Arch Osteoporos. 2021;16(1):15.
[20] INOUE T, MISU S, TANAKA T, et al. Acute phase nutritional screening tool associated with functional outcomes of hip fracture patients: A longitudinal study to compare MNA-SF, MUST, NRS-2002 and GNRI. Clin Nutr. 2019;38(1):220-226.
[21] KOREN-HAKIM T, WEISS A, HERSHKOVITZ A, et al. Comparing the adequacy of the MNA-SF, NRS-2002 and MUST nutritional tools in assessing malnutrition in hip fracture operated elderly patients. Clin Nutr. 2017;36(3):912.
[22] GÜRBÜZ Ş, EKMEKYAPAR M, DURAK MA, et al. Nutritional evaluation of non-traumatic patients admitted to the hospital from Emergency Department. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2022;26(10):3593-3598.
[23] LAMBERT C, NÜSSLER A, BIESALSKI HK, et al. Age-dependent risk factors for malnutrition in traumatology and orthopedic patients. Nutrition. 2017;37:60-67.
[24] TOBARI M, HASHIMOTO E. Characteristic Features of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Japan with a Focus on the Roles of Age, Sex and Body Mass Index. Gut Liver. 2020;14(5):537-545.
[25] 李长润编译. GOMEZ M, MARC C.股骨粗隆间骨折的加速康复外科治疗:如何影响住院时间和并发症[J].中华医学杂志,2020,100(37):2888.
[26] ZHU W, YAN Y, SUN Y, et al. Implementation of Enhanced Recovery After Surgery (ERAS) protocol for elderly patients receiving surgery for intertrochanteric fracture: a propensity score-matched analysis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2021;16(1):469.
[27] 胡雯,邱贵兴,裴福兴,等.骨科大手术加速康复围手术期营养管理专家共识[J].中华骨与关节外科杂志,2022,15(10):763-767. |