Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (35): 5716-5722.doi: 10.12307/2024.599
Previous Articles Next Articles
Circular RNAs are involved in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis through intracellular mechanisms
Zhou Lijun1, 2, Zhang Keyuan1, 3, Wang Xi1, 3, Yu Li1, 4, Xu Feihu1, 3, Ding Hong2, Ma Hairong1, 3, 5
- 1Institute of Clinical Medical Research, 3Orthopedic Center, 4Cardiac Center, Department of Comprehensive Cardiology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830011, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China; 2Department of Nutrition and Food Hygiene, School of Public Health, 5Department of Pharmacology, School of Pharmaceutical Science, Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830011, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2023-10-30Accepted:2023-12-28Online:2024-12-18Published:2024-03-15 -
Contact:Ma Hairong, MD, Researcher, Institute of Clinical Medical Research, The First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830011, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China; Orthopedic Center, The First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830011, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China; Department of Pharmacology, School of Pharmaceutical Science, Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830011, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China Ding Hong, MD, Associate professor, Department of Nutrition and Food Hygiene, School of Public Health, Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830011, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Zhou Lijun, Master candidate, Institute of Clinical Medical Research, The First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830011, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China; Department of Nutrition and Food Hygiene, School of Public Health, Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830011, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:Natural Science Foundation Key Project of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, No. 2021D01D21 (to MHR); National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 82060411 (to MHR)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhou Lijun, Zhang Keyuan, Wang Xi, Yu Li, Xu Feihu, Ding Hong, Ma Hairong. Circular RNAs are involved in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis through intracellular mechanisms[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(35): 5716-5722.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks

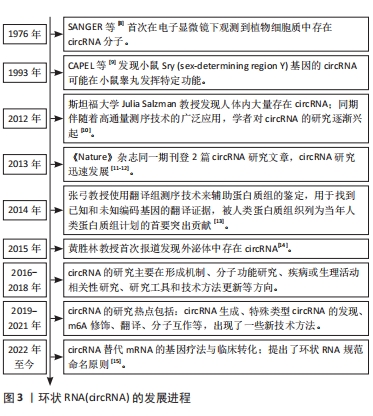
2.1 circRNA的概述、合成机制及其生物学功能 在1976年,SANGER等[8]通过电子显微镜在高等植物中首次发现了具有环状结构的RNA类病毒。从20世纪90年代末至今,其他几项研究表明,circRNA产生基因广泛存在于从果蝇到哺乳动物(包括人类)的真核细胞中[9-15],见图3。然而,在过去的30年里,由于缺乏可靠的高通量检测方法只有少数circRNA被鉴定出来,由于其结构特异性、未知功能和低丰度,circRNAs一直被认为是古老的保守分子,是剪接的错误副产物,没有得到太多关注[16]。随着RNA测序和生物信息学的发展,在植物、动物和病毒等各种生物体中发现了数千种circRNA[17],其特征为共价闭合环结构,不具有5’末端帽子和3’末端poly(A)尾,在哺乳动物中广泛表达,具有高丰度、高度保守、稳定、细胞特异性和组织特异性等特点[2]。根据外显子和内含子的基因组起源,circRNA可分为3类:全内含子型RNA(ciRNA)、全外显子型circRNA(ecircRNA)、外显子-内含子组合的circRNA(EIciRNA),全外显子型circRNA主要存在于细胞质中,全内含子型circRNA和外显子-内含子组合的circRNA主要存在于细胞核中[18]。"
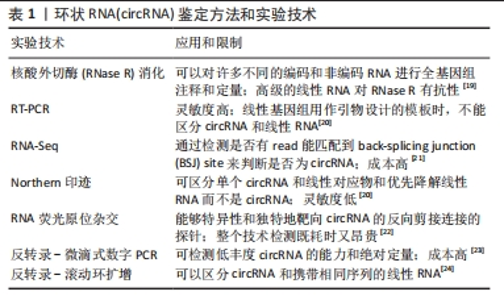
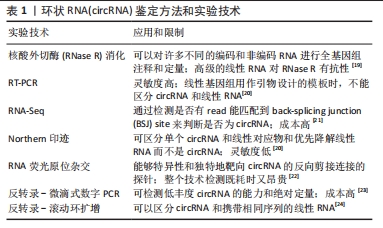
目前circRNA并没有统一的命名,一般使用基因组位置作为名字,或者用circ-作为前缀而宿主基因符号作为后缀(例如,circ-CDR1),对于一些个别的circRNA研究,研究者对circRNA设计名字,如CDR1as[15]。而CHEN等[15]的建议是通过反向剪接产生的circRNA的名称应包括前缀“circ”,然后是宿主基因符号和外显子(如果存在的话,还有内含子)信息,一种类似的策略可以通过使用替代前缀“ci”来命名来自内含子变体的全内含子型RNA。 circRNA的临床应用主要依赖于准确的RNA表达谱分析,包括注释新的circRNA物种和量化其丰度。然而,由于circRNA的环状结构和序列与线性mRNA对应物重叠,因此检测和研究circRNA在多个水平上都存在挑战。目前最常见的circRNA鉴定方法和实验技术有核酸外切酶(RNase R)消化检测、RT-PCR检测、RNA-Seq检测、Northern印迹、RNA荧光原位杂交、反转录-微滴式数字PCR、反转录-滚动环扩增等[19-24]。但不同的方法有其自身的优点和局限性,在未来的研究中可以结合多种方法以提高circRNA检测和验证的可靠性和准确性。见表1。"
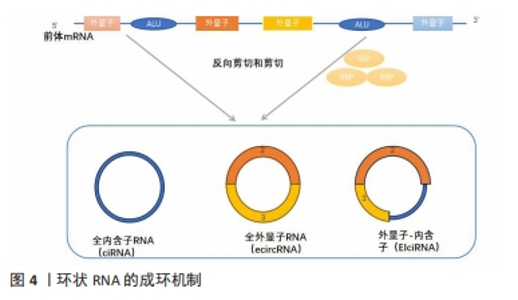
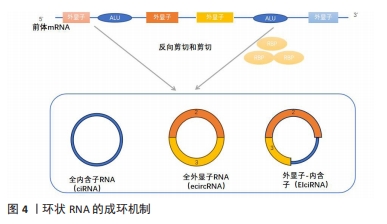
circRNA的合成机制可分为外显子环化和内含子环化,目前的主要合成机制有以下3种: ①JECK等[25]在2013年提出了2种不同的外显子环化机制模型。第一种模型是套索驱动的环化或外显子跳跃,该模型的特点是:原始的非相邻外显子通过部分折叠的前mRNA转录物靠近,并靠近其他外显子,导致外显子跳跃和重叠区域的形成,从而产生包含外显子和内部套索中间体的区域,套索中的内含子被去除,产生外显子circRNA。通常,位于环化外显子之间的内含子被剪接,并且在某些情况下,外显子-内含子circRNA不能被剪接[11-12]。第二种模式则是指由内含子配对或直接反向剪接所驱动的环化过程,不依赖于外显子跳跃,环化外显子的侧翼内含子之间能利用RNA二级结构,或内含子内丰富的ALU(限制性内切核酸酶AluI的识别序列AGCT)反向互补配对,并将下游剪接供体与上游剪接受体连接以形成环结构[26]。②由内含子自身转变成的circRNA。在特定条件下,全内含子型RNA也可直接由前体mRNA上的内含子环化所产生,但全内含子型RNA主要产生于细胞核中,与miRNAs结合的位点相对较少。③RNA结合蛋白或一类反式因子驱动的环化形成circRNA。在circRNA的生物发生过程中,该模式表明RNA结合蛋白2个侧翼内含子的紧密连接促进了circRNA的形成,然后去除内含子形成全外显子型circRNA,如RNA结合的蛋白Quaking(QKI)调节circRNA的形成[27]。见图4。"
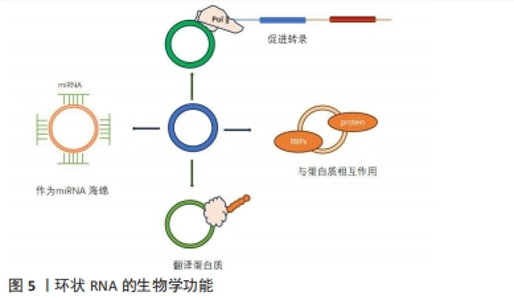
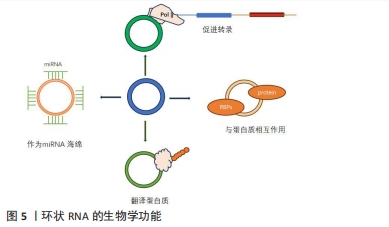
circRNA具有重要的生物学功能主要有以下几个方面:①circRNA作为miRNA的分子海绵,即circRNA上存在大量miRNA的结合位点,circRNA可用作竞争性内源性RNA(ceRNA),与miRNA结合,抑制miRNA与靶标结合,从而抑制mRNA翻译[28];②调节线性RNA转录及RNA剪切。circRNAs与mRNA结合后参与mRNA选择性剪接或转录的调控,如外显子-内含子组合的circRNA可与小核糖核蛋白互作用,再与RNA聚合酶Ⅱ结合,进而促进亲本基因的转录[29];③与RNA结合蛋白质相互作用。circRNA与RNA结合蛋白结合形成RNA-蛋白质复合物增强特定蛋白质功能并调节基因转录和翻译[30]。近年的研究发现具有IRES(Internal ribosome entry site)结构的circRNA可以作为翻译模板,翻译相应的生物功能肽段[31]。研究发现了近1 000种内源性circRNA是可翻译的,其中一半可通过滚圈翻译合成大分子蛋白质,还探索了影响circRNA翻译的因素,并通过优化相关条件,提高了circRNA蛋白的产量,在体外和体内条件下提供了更丰富、更持久的翻译蛋白产物[32]。然而,更多的研究也发现,N6-甲基腺苷依赖的翻译起始涉及起始因子eIF4G2、eIF3A以及N6-甲基腺苷读取器YTHDF3,在N6-甲基腺苷甲基化后,YTHDF3对其识别,募集eIF4G2,使circRNA翻译蛋白质[33]。见图5。"
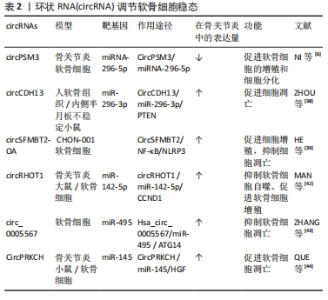
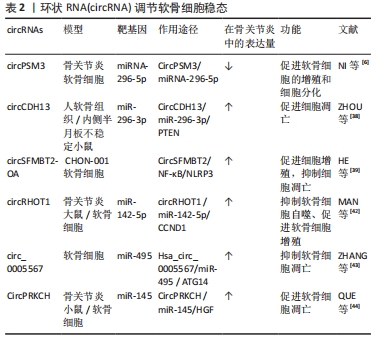
2.2 circRNA对骨关节炎的调控 目前,关于circRNA对骨关节炎的调控作用的研究主要集中在调控软骨细胞的稳态、细胞外基质的降解和软骨细胞的炎症反应等病理进程[34],影响这些病理过程的相应干预和探索circRNA在这些过程中的调节功能可以延缓骨关节炎的进展。 2.2.1 circRNA调节软骨细胞稳态 软骨细胞稳态的改变,即软骨细胞死亡和增殖之间的不平衡与骨关节炎有关[35],关节组织中异常的细胞死亡和细胞增殖是形成骨关节炎(如软骨变性)标志性特征[2,36]。cirRNA对软骨细胞稳态的调控功能主要是通过充当miRNA海绵的机制来促进或者抑制软骨细胞的凋亡[37]。对于其促进软骨细胞的凋亡的研究,肿瘤抑制因子(PTEN)是参与多种癌症并且是胚胎发育所必需的重要肿瘤抑制因子,ZHOU等[38]的研究在体内和体外人类骨关节炎模型中都证明上调的CircCDH 13参与了骨关节炎进展,circCDH13过表达后海绵miR-296-3p促进PTEN过表达,进而促进软骨细胞凋亡,这表明CircCDH 13-miR-296-3p-PTEN轴是骨关节炎中调节软骨细胞凋亡的治疗靶点。另外,NI等[6]研究表明circPSM3在骨关节炎软骨细胞中的表达显著增加,可能通过充当miRNA-296-5p的海绵促进软骨细胞的凋亡。骨关节炎中也存在对软骨细胞凋亡抑制作用的circRNA。脂多糖可以加速细胞的凋亡,在HE等[39]的研究结果中发现,circSFMBT2-OA过表达可加速脂多糖处理的 CHON-001 细胞中的细胞增殖,并抑制细胞凋亡;CircSFMBT2-OA还可以抑制NOD 样受体热蛋白结构域蛋3激活来减弱CHON-001细胞损伤。因此,circSFMBT2-O/NF-κB/NLRP3轴为骨关节炎治疗中软骨细胞凋亡的抑制提供了新的机制。 circRNA也可能是通过自噬对软骨细胞进行调控[40]。自噬对维持细胞内稳态具有重要作用,自噬功能障碍是骨关节炎发生和发展的重要驱动因素,自噬的减少导致软骨细胞中受损的细胞器和大分子的积累,从而影响软骨细胞的存活,最终导致骨关节炎,而适当水平的自噬激活可能是预防骨关节炎关节软骨退化的关键[40-41]。在骨关节炎细胞模型中,circRHOT1敲低可以抑制软骨细胞的细胞活力,但circRHOT1通过海绵化miR-1-1p来增强G1/S特异性细胞周期蛋白-D142(CCND5)的表达,以降低自噬相关基因微管相关蛋白 1A/1B-轻链 3(microtubule-associated protein 1 light 3,LC3)的表达,然后抑制细胞自噬以促进增殖[42]。ZHANG等[43]的研究结果显示,白细胞介素1β诱导的软骨细胞骨关节炎模型中,circ0005567过表达上调自噬相关标志物即LC3和beclin-1、以及LC3-Ⅱ/LC3-Ⅰ的比例;然而,自噬抑制剂3-甲基腺嘌呤逆转了由circ_0005567过表达介导的自噬促进,减弱白细胞介素1β诱导的软骨细胞凋亡。 综上,circRNA可以从多种途径调控软骨细胞的增殖、分化和凋亡,在软骨细胞中,大多数circRNA都是通过充当miRNA海绵来发挥调控作用,circRNA与miRNA结合后可以增强下游相关基因的稳定性和蛋白表达水平,还能与自噬相关蛋白相互配合调控自噬,促进软骨细胞的增殖分化。总之,在软骨细胞中,某些circRNA水平对软骨细胞是正向的,提高这些circRNA水平可以减少骨关节炎的发生。在未来的研究中可以通过靶向circRNA来控制软骨细胞凋亡和增殖之间的平衡,或调节凋亡和自噬,具有对骨关节炎治疗的潜力[44]。 调控软骨细胞稳态的部分circRNA见表2。"
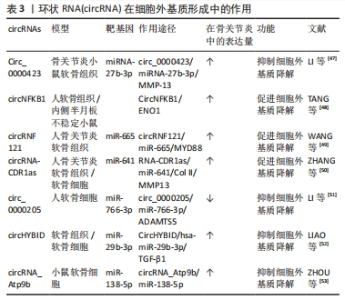
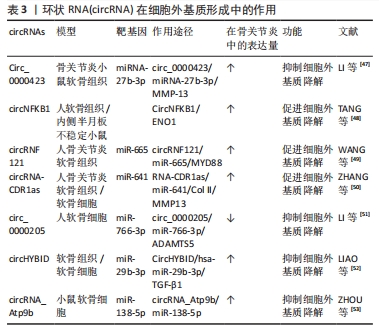
2.2.2 circRNA在细胞外基质形成中的作用 细胞外基质主要由胶原蛋白、糖胺聚糖和蛋白聚糖组成,细胞外基质中分解代谢和合成代谢之间的平衡对于维持细胞外基质稳态特别重要[45-46]。细胞外基质降解是骨关节炎中进行性软骨损失的关键特征,主要是由于基质降解酶的上调,负责细胞外基质降解的主要基质降解酶包括基质金属蛋白酶和具有血小板反应蛋白1型基序的去整合素和金属蛋白酶(a disvolin and metallo-proteinase with thrombospondin motifs,ADAMTS)[47]。circRNA充当miRNA海绵来调节下游靶标的表达,促进基质金属蛋白酶3、基质金属蛋白酶13、ADAMTS4和ADAMTS5的表达,并抑制Ⅱ型胶原和聚集蛋白聚糖的表达,促进细胞外基质降解[44]。如Circ_0000423也被证明通过海绵吸附miRNA-27b-3p促进细胞外基质降解,从而降低Ⅱ型胶原并提高基质金属蛋白酶13表达[47]。circNFKB1与 α-烯醇化酶相互作用后,调控其亲本基因 NFKB1 的表达,并维持软骨细胞中核因子κB信号通路的激活。且过表达的circNFKB1显著增加基质金属蛋白酶3和基质金属蛋白酶13蛋白水平,促进白细胞介素1β诱导的人软骨细胞细胞外基质降解以及缓解受损的细胞外基质合成代谢[48]。circRNF121的过表达增加了基质金属蛋白酶13和ADAMTS5的水平,降低了聚集蛋白和Ⅱ型胶原的水平,表明circRNF121过表达促进了细胞外基质降解[49]。据报道,小脑变性相关蛋白1反义转录物 circRNA-CDR1as在骨关节炎软骨细胞中上调,降低了Ⅱ型胶原并增加了基质金属蛋白酶13的表达[50]。 在骨关节炎发生过程中也存在抑制细胞外基质降解的circRNA,如在体外骨关节炎模型中,circ_0000205的敲低可以下调原代软骨细胞中金属蛋白酶和基质金属蛋白酶13的表达,并上调Ⅱ型胶原α1的表达,敲低的circ_0000205通过海绵 miR-766-3p 抑制白细胞介素1β诱导的骨关节炎样软骨细胞的细胞外基质降解过程[51],因此,通过 circ_0000205/miR-766-3p/ADAMTS5轴可能是调节骨关节炎细胞外基质降解的治疗靶点。CircHYBID表达在白细胞介素1β刺激的软骨细胞中显著下调,并降低透明质酸的水平,功能获得实验显示,在软骨细胞中过表达的circHYBID通过调节透明质酸合酶2和HYBID表达来增加透明质酸的积累,进一步减轻细胞外基质降解,即CircHYBID通过hsa-miR-29 b-3p/TGF-β1轴调节软骨细胞中透明质酸代谢参与细胞外基质代谢过程[52]。此外,在白细胞介素1β诱导的小鼠软骨细胞中,circRNA_Atp9b基因表达显著上调,敲低circRNA_Atp9b显著增加了Ⅱ型胶原的水平,并降低了基质金属蛋白酶13、白细胞介素6和环氧化酶2的水平,防止白细胞介素1β诱导的细胞外基质降解[53]。因此,靶向上述circRNA可能增强细胞外基质稳态,从而缓解骨关节炎。 综上,细胞外基质在组织中起到支撑作用,同时也含有大量信号分子,参与细胞增殖、分化和代谢等活动。circRNA在软骨细胞外基质形成中发挥着积极作用,作用于不同的信号分子以促进软骨细胞外基质降解,进而加速骨关节炎的进程。细胞外基质降解严重时,无法为组织提供营养物质、结构支撑和柔韧性,会引起软骨机制退化及关节结构变形扭曲,进而加重关节疾病的发生发展。circRNA在软骨细胞中的作用并不仅是调节软骨细胞外基质降解酶和其组成成分相关基因的表达,还可能直接或间接调控的下游分子影响细胞外基质的降解过程,因此,circRNA/miRNA/mRNA轴可能是预防骨关节炎软骨中细胞外基质降解的潜在靶点,其具体功能及作用机制仍需进一步研究。 调控细胞外基质的部分circRNA见表3。"
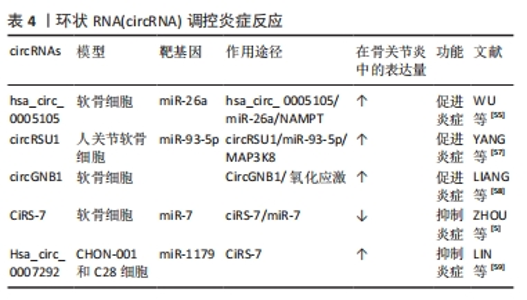
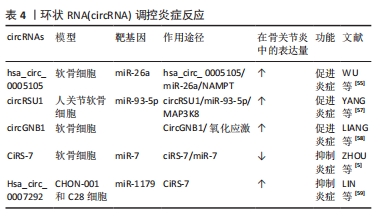
2.2.3 circRNA调控炎症反应 骨关节炎是一种炎症性疾病。近年来,越来越多的实验结果表明,低度炎症是骨关节炎病理进展的重要驱动因素之一,骨关节炎关节组织和滑液中存在多种促炎递质,如肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素6、趋化因子、前列腺素和白三烯[53],circRNA介导的炎症过程在骨关节炎中也起着至关重要的作用[54]。白细胞介素1β诱导的软骨细胞是炎性软骨细胞的适用模型,WU等[55]在白细胞介素1β诱导的软骨细胞中检测到hsa_circ_0005105的表达显著增加,hsa_circ_0005105的增加有助于前列腺素E2、白细胞介素6和白细胞介素8的表达,而miR-26a抑制了这些因子的表达,下调烟酰胺磷酸核糖基转移酶可逆转hsa_circ_0005105的这种功能,即hsa_circ_0005105通过与miR-26a靶标烟酰胺磷酸核糖基转移酶结合来增强炎性因子的表达,从而加重骨关节炎进展。氧化应激激活促炎途径也可能引发炎症反应[56],circRNA还可以通过氧化应激途径促进骨关节炎的进展,circRSU1在H2O2处理的软骨细胞和老年人骨关节炎关节软骨中显著上调,通过核因子κB途径和MEK/ERK1/2上调环氧化酶2和诱导型一氧化氮合酶表达以响应活性氧物质的变化来促进骨关节炎的炎症进展[57]。LIANG等[58]的研究结果发现circGNB1海绵化 miR-152-3p,从而阻断其与其下游 mRNA 靶标无名指蛋白219(RNF219)的相互作用,后者通过阻止其在 K47 残基处的泛素化来稳定caveolin-1(CAV1)。CircGNB1通过拮抗 miR-152-3p 介导的 RNF219和CAV1抑制来抑制白细胞介素10信号传导。circGNB1过表达时会增强分解代谢因子表达和氧化应激以及抑制体外和体内合成代谢基因,进而促进骨关节炎进展。此外,circGNB1 敲低减轻了骨关节炎的严重程度,而circGNB1过表达在骨关节炎的内侧半月板不稳定小鼠模型中具有相反的效果。因此,circGNB1/miR-152-3p/RNF219/CAV1轴可能是预防骨关节炎炎症治疗的潜在靶点。 部分circRNA也可抑制炎症因子释放。CiRS-7,也称为Cdr1as,被认为是miR-7的内源性竞争性RNA抑制剂,并且充当miR-7的“超级海绵”,在骨关节炎软骨细胞中,ciRS-7的表达显著下调,miR-7被上调[5]。转染ciRS-7siRNA和miR-7模拟物可促进炎症因子的释放,这可被ciRS-7cDNA和miR-7抑制剂逆转,间接表明ciRS-7/miR-7轴有助于抑制骨关节炎软骨细胞中的炎症。Hsa_circ_0007292表达在骨关节炎组织和白细胞介素1β诱导的软骨细胞中上调,增强炎症因子(肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素6和白细胞介素8)水平[59]。这些研究表明,circRNAs可以通过miRNA参与炎症因子的调节从而参与骨关节炎的发生与发展。因此,消除促炎因子的circRNA是骨关节炎相关炎症的潜在治疗靶点。 骨关节炎是以关节疼痛为主要症状。炎症反应是骨关节炎发展过程中的一个重要环节,炎症和关节软骨的磨损会加重关节痛感,这种疼痛可能会持续并加重,严重影响患者的生活质量。软骨损伤后促炎细胞因子释放,诱导多种分解代谢反应,导致软骨细胞的激活和炎症细胞的浸润,最终炎症导致软骨修复和再生能力下降,并加重疼痛反应。当炎性细胞因子的异常增加时会导致细胞外基质的破坏和降解,还会抑制软骨细胞的合成和修复。部分circRNA可以通过抑制炎症因子的释放来减缓骨关节炎的发生发展和缓解疼痛,但目前已发现的具有抑制炎症因子释放的circRNA种类少,其功能和机制也尚处于探索阶段,进一步研究骨关节炎疼痛的原因和开发应对策略是至关重要的。调控炎症反应的部分circRNA见表4。"

2.3 circRNA在骨关节炎中的临床应用前景 2.3.1 诊断性生物标志物 由于circRNA有较强的组织表达特异性,一些研究表明,某些circRNA可以作为骨关节炎的潜在生物标志物,具有潜在的诊断和预测疾病进展的价值[28]。人外周血中的许多circRNA比它们的线性对应物更丰富和更稳定,表明它们作为诊断标志物的潜力,对来自患有大骨节病和骨关节炎患者的5对膝关节软骨样本进行circRNA测序,结果显示hsa_circRNA_0020014具有区分大骨节病和骨关节炎的潜力[60]。LIU等[61]通过转录组高通量测序检查了骨关节炎患者滑膜中的circRNA,生物信息学分析和生物学功能预测表明,hsa_circ_0072697可以充当hsa_miR_6736-5p海绵,并且具有早期骨关节炎的诊断潜力。在辐射诱导骨骼损伤恢复的研究中,进行RT-qPCR以检测所有参与者血浆样品中circRNA-016901的RNA积累,结果显示,与健康对照组相比,骨关节炎组中circRNA-016901的表达水平增加1.77倍,可用于提高骨关节炎的诊断准确性[62]。circSCAPER上调白细胞介素1β模型化的C28/I2 细胞中的凋亡标志物Bcl-2和半胱氨酸天冬氨酸蛋白酶3[63]。 血液、滑液等这些人体样品中包含着许多潜在的疾病发生信息,通过检测和评估这些信息就能够预测一些疾病的发生。证据表明,许多circRNA在血液、滑液等体液中能够被检测到,且与疾病紧密相关,因此,通过circRNA来预测疾病是可能的,即circRNA及其上游或下游调控分子可能是骨关节炎诊断的潜在生物标志物。随着对circRNA的深入研究和生物技术的发展,在未来的骨关节炎早期临床诊断时,可通过对circRNA在体内(外周血和滑液)的分布及含量分析(如细胞内、组织、体液及细胞间经外泌体的交换等)来提高诊断的准确性。 2.3.2 治疗靶点 circRNA已被证明是骨关节炎临床策略的潜在治疗靶点[28]。间充质干细胞作为骨关节炎的一种潜在治疗选择手段,在间充质干细胞的软骨分化过程中,有多种circRNA的表达水平发生变化[36],其中circRNA-CDR1as已被验证可维持人脐带间充质干细胞的分化和增殖[64]。因此,circRNA可用作调节因子来确定间充质干细胞治疗期间的分化趋势和速度,这为定制骨关节炎治疗提供了新的参考依据。细胞外囊泡也是软骨稳态和骨关节炎的重要调节因子,细胞外囊泡被分为外泌体和微囊泡等[65]。细胞外囊泡通过直接结合靶细胞表面上的受体或通过胞吞作用将内容物释放到受体细胞中来介导细胞间联系,携带circRNA的细胞外囊泡可以有效地改善骨关节炎微环境,如MSCs-circHIPK3-EVs(源自过表达circHIPK3的间充质干细胞的细胞外囊泡)通过 miR-124-3p/MYH9 轴参与了间充质干细胞-细胞外囊泡介导的软骨细胞增殖和迁移以及抑制诱导的软骨细胞凋亡,这为治疗骨关节炎提供了一种有潜力的新型无细胞疗法[66]。随着circRNA的深入研究和生物技术的发展,未来可能通过恢复下调circRNA的表达或敲低异常上调的circRNA来实现对骨关节炎的治疗。有研究表明,T4 RNA连接酶合成的circRNA不会引起细胞内先天免疫应答[67],且人工制造circRNA技术也已成功应用于药物开发[68],从2022年开始,人工circRNAs表达相关抗原被用来触发适应性免疫反应,在难以治疗的黑色素瘤恶性肿瘤中显示出治疗和预防效果[69]。 circRNA具有非常广阔的应用前景,它不仅与骨关节炎相关,还与感染性疾病、罕见病、血液病、自身免疫病、肿瘤等多种疾病相关。内源性circRNA在未来临床上可作为药物新靶点或疾病诊断的标志物,并且人工制备的circRNA可针对多种靶点在细胞内发挥作用。circRNA因其共价闭合的环状结构能够抵抗核酸酶的切割,从而获得更强的稳定性和更长的使用期限,从理论上来讲,即使在低剂量水平下,也可以增强其治疗潜力。自2020年以来,科研领域和生物产业领域认识到circRNA既可作为药物新靶点或疾病诊断的标志物,又可以将人工合成circRNA导入体内作为疫苗或治疗癌症等疾病的核酸药物。因此,通过实现circRNA疫苗的完整性和增强体外制作circRNA技术,基于circRNA的新兴治疗技术将为骨关节炎的治疗和预防开辟新的方向。"

| [1] ZHOU ZB, HUANG GX, FU Q, et al. circRNA.33186 Contributes to the Pathogenesis of Osteoarthritis by Sponging miR-127-5p. Mol Ther. 2019; 27(3):531-541. [2] WANG H, ZHAO J, WANG J. Role of circular RNAs in osteoarthritis: update on pathogenesis and therapeutics. Mol Genet Genomics. 2023;298(4):791-801. [3] JIN Z, WANG D, ZHANG H, et al. Incidence trend of five common musculoskeletal disorders from 1990 to 2017 at the global, regional and national level: results from the global burden of disease study 2017. Ann Rheum Dis. 2020;79(8):1014-1022. [4] 任薄霖. sa_circ_0032472对骨关节炎软骨细胞凋亡、增殖、ECM代谢的作用研究[D].长沙:中南大学,2022. [5] ZHOU X, JIANG L, FAN G, et al. Role of the ciRS-7/miR-7 axis in the regulation of proliferation, apoptosis and inflammation of chondrocytes induced by IL-1β. Int Immunopharmacol. 2019;71:233-240. [6] NI JL, DANG XQ, Shi ZB. CircPSM3 inhibits the proliferation and differentiation of OA chondrocytes by targeting miRNA-296-5p. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020;24(7):3467-3475. [7] LI HZ, LIN Z, Xu XH, et al. The potential roles of circRNAs in osteoarthritis: a coming journey to find a treasure. Biosci Rep. 2018;38(5):BSR20180542. [8] SANGER HL, KLOTZ G, RIESNER D, et al. Viroids are single-stranded covalently closed circular RNA molecules existing as highly base-paired rod-like structures. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976;73(11):3852-3856. [9] CAPEL B, SWAIN A, NICOLIS S, et al. Circular transcripts of the testis-determining gene Sry in adult mouse testis. Cell. 1993;73(5):1019-1030. [10] SALZMAN J, GAWAD C, WANG PL, et al. Circular RNAs are the predominant transcript isoform from hundreds of human genes in diverse cell types. PLoS One. 2012;7(2):e30733. [11] HANSEN TB, JENSEN TI, CLAUSENl BH, et al. Natural RNA circles function as efficient microRNA sponges. Nature. 2013;495(7441):384-388. [12] MEMCZAK S, ENSM, ELEFSINIOTI A, et al. Circular RNAs are a large class of animal RNAs with regulatory potency. Nature. 2013;495(7441):333-338. [13] LIAN X, GUO J, GU W, et al. Genome-Wide and Experimental Resolution of Relative Translation Elongation Speed at Individual Gene Level in Human Cells. PLoS Genet. 2016;12(2):e1005901 [14] LI S, LI Y, CHEN B, et al. exoRBase: a database of circRNA, lncRNA and mRNA in human blood exosomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018;46(D1):D106-D112. [15] CHEN LL, BINDEREIF A, BOZZONII, et al. A guide to naming eukaryotic circular RNAs. Nat Cell Biol. 2023;25(1):1-5. [16] HAN B, CHAO J, YAO H. Circular RNA and its mechanisms in disease: From the bench to the clinic. Pharmacol Ther. 2018;187:31-44. [17] WANGJ, YANG B, WU C, et al. Role of circular RNAs in osteoarthritis (Review). Exp Ther Med. 2021;22(5):1279. [18] REN S, LIN P, WANG J, et al. Circular RNAs: Promising Molecular Biomarkers of Human Aging-Related Diseases via Functioning as an miRNA Sponge. Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev. 2020;18:215-229. [19] GERSTEIN MB, ROZOWSKY J, YAN KK, et al. Comparative analysis of the transcriptome across distant species. Nature. 2014;512(7515):445-448. [20] PISGNANO G, MICHAEL DC, VISAL TH, et al.. Going circular: history, present, and future of circRNAs in cancer. Oncogene. 2023;42(38):2783-2800. [21] MERCER TR, GERHARDT DJ, DINGER ME, et al. Targeted RNA sequencing reveals the deep complexity of the human transcriptome. Nat Biotechnol. 2011;30(1):99-104. [22] LIM AS, LIM TH. Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization on Tissue Sections. Methods Mol Biol. 2017;1541:119-125. [23] LI T, SHAO Y, FU L, et al. Plasma circular RNA profiling of patients with gastric cancer and their droplet digital RT-PCR detection. J Mol Med (Berl). 2018;96(1): 85-96. [24] ZHANG P, GAO K, LIANG Y, et al. Ultrasensitive detection of circular RNA by accurate recognition of the specific junction site using stem-loop primer induced double exponential amplification. Talanta. 2020;217:121021. [25] JECK WR, SORRENTINO JA, WANGK, et al. Circular RNAs are abundant, conserved, and associated with ALU repeats. RNA. 2013;19(2):141-157. [26] LI Z, HUANG C, BAO C, et al. Exon-intron circular RNAs regulate transcription in the nucleus. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2015;22(3):256-264. [27] CONN SJ, PILLMAN KA, TOUBIA J, et al. The RNA binding protein quaking regulates formation of circRNAs. Cell. 2015;160(6):1125-1134. [28] LI Z, LU J. circRNAs in osteoarthritis: research status and prospect. Front Genet. 2023;14:1173812. [29] CONN VM, HUGOUVIEUX V, NAYAK AYAK A, et al. A circRNA from SEPALLATA3 regulates splicing of its cognate mRNA through R-loop formation. Nat Plants. 2017;3:17053. [30] ZANG J, LU D, XU A. The interaction of circRNAs and RNA binding proteins: An important part of circRNA maintenance and function. J Neurosci Res. 2020;98(1): 87-97. [31] LIANG WC, WONGCW, LIANG PP, et al. Translation of the circular RNA circβ-catenin promotes liver cancer cell growth through activation of the Wnt pathway. Genome Biol. 2019;20(1):84. [32] FAN X, YANG Y, CHEN C, et al. Pervasive translation of circular RNAs driven by short IRES-like elements. Nat Commun. 2022;13(1):3751. [33] PRATS AC, DAVIA F, DIALLO LH, et al. Circular RNA, the Key for Translation. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(22):8591. [34] MAO X, CAO Y, GUO Z, et al. Biological roles and therapeutic potential of circular RNAs in osteoarthritis. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2021;24:856-867. [35] WENG PW, YADAV VK, PIKATANi NW, et al. Novel NFκB Inhibitor SC75741 Mitigates Chondrocyte Degradation and Prevents Activated Fibroblast Transformation by Modulating miR-21/GDF-5/SOX5 Signaling. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(20):11082. [36] DELLA BELLA E, MNELLEl U, BASOLI V, et al. Stoddart MJ. Differential Regulation of circRNA, miRNA, and piRNA during Early Osteogenic and Chondrogenic Differentiation of Human Mesenchymal Stromal Cells. Cells. 2020;9(2):398. [37] 申飞燕, 姚吉祥, 苏珊珊, 等. 敲低环状RNA WD重复含蛋白1抑制膝骨关节炎软骨细胞增殖并诱导凋亡[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2024,28(4): 499-504. [38] ZHOU Z, MA J, LU J, et al. Circular RNA CircCDH13 contributes to the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis via CircCDH13/miR-296-3p/PTEN axis. J Cell Physiol. 2021;236(5):3521-3535. [39] HE A, LIU Y, ZHANG R, et al. CircSFMBT2-OA alleviates chondrocyte apoptosis and extracellular matrix degradation through repressing NF-κB/NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Heliyon. 2023;9(6):e17312. [40] JIA Z, LIU J, Wang J. circRNA-MSR regulates the expression of FBXO21 to inhibit chondrocyte autophagy by targeting miR-761 in osteoarthritis. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2022;38(12):1168-1177. [41] LVX, ZHAO T, DAI Y, et al. New insights into the interplay between autophagy and cartilage degeneration in osteoarthritis. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022;10: 1089668. [42] MAN G, YANG H, SHEN K, et al. Circular RNA RHOT1 Regulates miR-142-5p/CCND1 to Participate in Chondrocyte Autophagy and Proliferation in Osteoarthritis. J Immunol Res. 2022;2022:4370873. [43] ZHANG J, CHENG F, RONG G, et al. Hsa_circ_0005567 Activates Autophagy and Suppresses IL-1β-Induced Chondrocyte Apoptosis by Regulating miR-495. Front Mol Biosci. 2020;7:216. [44] QUE W, LIU H, YANG Q. CircPRKCH modulates extracellular matrix formation and metabolism by regulating the miR-145/HGF axis in osteoarthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2022;24(1):216. [45] 聂江波,金明超,方添顺,等.环状RNA在骨关节炎调控的研究进展[J]. 中国现代医生,2022,60(16):148-151. [46] LIN S, LI H, WU B, et al. TGF-β1 regulates chondrocyte proliferation and extracellular matrix synthesis via circPhf21a-Vegfa axis in osteoarthritis. Cell Commun Signal. 2022;20(1):75. [47] LI X, XIE C, XIAO F, et al. Circular RNA circ_0000423 regulates cartilage ECM synthesis via circ_0000423/miRNA-27b-3p/MMP-13 axis in osteoarthritis. Aging (Albany NY). 2022;14(8):3400-3415. [48] TANG S, NIE X, RUAN J, et al. Circular RNA circNFKB1 promotes osteoarthritis progression through interacting with ENO1 and sustaining NF-κB signaling. Cell Death Dis. 2022;13(8):695. [49] WANG T, HAO Z, LIU C, et al. LEF1 mediates osteoarthritis progression through circRNF121/miR-665/MYD88 axis via NF-кB signaling pathway [published correction appears in Cell Death Dis. 2020;11(8):689]. Cell Death Dis. 2020;11(7):598. [50] ZHANG W, ZHANG C, HU C, et al. Circular RNA-CDR1as acts as the sponge of microRNA-641 to promote osteoarthritis progression. J Inflamm (Lond). 2020;17:8. [51] LI G, LUO H, DING Z, et al. Silencing of circ_0000205 mitigates interleukin-1β-induced apoptosis and extracellular matrix degradation in chondrocytes via targeting miR-766-3p/ADAMTS5 axis. Innate Immun. 2022;28(2):79-90. [52] LIAO HX, ZHANG ZH, CHEN HL, et al. CircHYBID regulates hyaluronan metabolism in chondrocytes via hsa-miR-29b-3p/TGF-β1 axis. Mol Med. 2021;27(1):56. [53] ZHOU ZB, DU D, HUANG GX, et al. Circular RNA Atp9b, a competing endogenous RNA, regulates the progression of osteoarthritis by targeting miR-138-5p. Gene. 2018;646:203-209. [54] ROBINSON WH, LEPUS CM, WANG Q, et al. Low-grade inflammation as a key mediator of the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2016;12(10): 580-592. [55] WU Y, ZHANG Y, ZHANG Y, et al. circRNA hsa_circ_0005105 upregulates NAMPT expression and promotes chondrocyte extracellular matrix degradation by sponging miR-26a. Cell Biol Int. 2017;41(12):1283-1289. [56] ARRA M, SWARNKAR G, ALIPPE Y, et al. IκB-ζ signaling promotes chondrocyte inflammatory phenotype, senescence, and erosive joint pathology. Bone Res. 2022;10(1):12. [57] YANG Y, SHEN P, YAO T, et al. Novel role of circRSU1 in the progression of osteoarthritis by adjusting oxidative stress. Theranostics. 2021;11(4):1877-1900. [58] LIANG Y, SHENL, NI W, et al. CircGNB1 drives osteoarthritis pathogenesis by inducing oxidative stress in chondrocytes. Clin Transl Med. 2023;13(8): e1358. [59] LIN Z, LI P, TANG Y, et al. Hsa_circ_0007292 promotes chondrocyte injury in osteoarthritis via targeting the miR-1179/HMGB1 axis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2023; 18(1):544. [60] WANG Y, WU C, ZHANG Y, et al. Screening for differentially expressed circRNA between Kashin-Beck disease and osteoarthritis patients based on circRNA chips. Clin Chim Acta. 2020;501:92-101. [61] LIU P, GAO G, ZHOU X, et al. Circular RNA profiles of osteoarthritic synovium. Mol Omics. 2022;18(5):439-448. [62] DU M, FAN S, LIU Y, et al. The Application of circRNA-016901 in Improving the Diagnostic Accuracy of Osteoarthritis. Biomed Res Int. 2022;2022: 1158562. [63] LUOBU Z, WANG L, JIANG D, et al. CircSCAPER contributes to IL-1β-induced osteoarthritis in vitro via miR-140-3p/EZH2 axis. Bone Joint Res. 2022;11(2):61-72. [64] YANG L, BIN Z, HUI S, et al. The Role of CDR1as in Proliferation and Differentiation of Human Umbilical Cord-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Stem Cells Int. 2019; 2019:2316834. [65] MIYAKI S,LOTZ MK. Extracellular vesicles in cartilage homeostasis and osteoarthritis. J Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2018;30(1):129-135. [66] LI S, LIU J, LIU S, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles prevent the development of osteoarthritis via the circHIPK3/miR-124-3p/MYH9 axis. J Nanobiotechnol. 2021;19(1):194. [67] LIU CX, GUO SK, NAN F, et al. RNA circles with minimized immunogenicity as potent PKR inhibitors. Mol Cell. 2022;82(2):420-434.e6. [68] LU D, CHATTERJEE S, XIAO K, et al. A circular RNA derived from the insulin receptor locus protects against doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity. Eur Heart J. 2022;43(42):4496-4511. [69] NIU D, WU Y, LIAN J. Circular RNA vaccine in disease prevention and treatment. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023;8(1):341. |
| [1] | Yang Junliang, Lu Tan, Xu Biao, Jiang Yaqiong, Wang Fucheng. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of effects of partial anterior cruciate ligament rupture on knee joint stress [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1347-1353. |
| [2] | Li Yongjie, Fu Shenyu, Xia Yuan, Zhang Dakuan, Liu Hongju. Correlation of knee extensor muscle strength and spatiotemporal gait parameters with peak knee flexion/adduction moment in female patients with knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1354-1358. |
| [3] | Qi Haodong, Lu Chao, Xu Hanbo, Wang Mengfei, Hao Yangquan. Effect of diabetes mellitus on perioperative blood loss and pain after primary total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1383-1387. |
| [4] | Du Changling, Shi Hui, Zhang Shoutao, Meng Tao, Liu Dong, Li Jian, Cao Heng, Xu Chuang. Efficacy and safety of different applications of tranexamic acid in high tibial osteotomy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1409-1413. |
| [5] | Huang Xiarong, Hu Lizhi, Sun Guanghua, Peng Xinke, Liao Ying, Liao Yuan, Liu Jing, Yin Linwei, Zhong Peirui, Peng Ting, Zhou Jun, Qu Mengjian. Effect of electroacupuncture on the expression of P53 and P21 in articular cartilage and subchondral bone of aged rats with knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1174-1179. |
| [6] | Zhao Garida, Ren Yizhong, Han Changxu, Kong Lingyue, Jia Yanbo. Mechanism of Mongolian Medicine Erden-uril on osteoarthritis in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1193-1199. |
| [7] | Li Rui, Zhang Guihong, Wang Tao, Fan Ping. Effect of ginseng polysaccharide on the expression of prostaglandin E2/6-keto-prostaglandin 1alpha in traumatic osteoarthritis model rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1235-1240. |
| [8] | Liu Jianhong, Liao Shijie, Li Boxiang, Tang Shengping, Wei Zhendi, Ding Xiaofei. Extracellular vesicles carrying non-coding RNA regulate the activation of osteoclasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1076-1082. |
| [9] | Zhang Kefan, Shi Hui. Research status and application prospect of cytokine therapy for osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 961-967. |
| [10] | Zhang Zeyi, Yang Yimin, Li Wenyan, Zhang Meizhen. Effect of foot progression angle on lower extremity kinetics of knee osteoarthritis patients of different ages: a systematic review and meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 968-975. |
| [11] | Shen Feiyan, Yao Jixiang, Su Shanshan, Zhao Zhongmin, Tang Weidong. Knockdown of circRNA WD repeat containing protein 1 inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis of chondrocytes in knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 499-504. |
| [12] | Maisituremu·Heilili, Zhang Wanxia, Nijiati·Nuermuhanmode, Maimaitituxun·Tuerdi. Effect of intraarticular injection of different concentrations of ozone on condylar histology of rats with early temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 505-509. |
| [13] | Qiao Hujun, Wang Guoxiang. Evaluation of rat osteoarthritis chondrocyte models induced by interleukin-1beta [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 516-521. |
| [14] | Liu Yuhan, Fan Yujiang, Wang Qiguang. Comparison of protocols for constructing animal models of early traumatic knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 542-549. |
| [15] | Zhang Yaru, Chen Yanjun, Zhang Xiaodong, Chen Shenghua, Huang Wenhua. Effect of ferroptosis mediated by glutathione peroxidase 4 in the occurrence and progression of synovitis in knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 550-555. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||