Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (32): 5104-5109.doi: 10.12307/2024.506
Previous Articles Next Articles
Syringin inhibits intervertebral disc degeneration in rats
Zhang Yunxin1, Zhang Cunxin2, Wang Qian2, Xu Xinliang3, Lyu Chaoliang2, Ni Yong2
- 1School of Clinical Medicine, Jining Medical University, Jining 272067, Shandong Province, China; 2Department of Spine Surgery, 3Department of Pain, Jining No. 1 People’s Hospital, Jining 272000, Shandong Province, China
-
Received:2023-08-16Accepted:2023-10-12Online:2024-11-18Published:2023-12-28 -
Contact:Ni Yong, Master, Associate chief physician, Department of Spine Surgery, Jining No. 1 People’s Hospital, Jining 272000, Shandong Province, China Lyu Chaoliang, MD, Chief physician, Department of Spine Surgery, Jining No. 1 People’s Hospital, Jining 272000, Shandong Province, China -
About author:Zhang Yunxin, Master candidate, School of Clinical Medicine, Jining Medical University, Jining 272067, Shandong Province, China -
Supported by:Shandong Province Medical and Health Science and Technology Development Plan Projects, Nos. 202204070552 (to WQ) and 2021M079 (to XXL); Jining Key Research and Development Plan Project, Nos. 2021YXNS050 (to WQ) and 2020JKNS008 (to ZCX)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhang Yunxin, Zhang Cunxin, Wang Qian, Xu Xinliang, Lyu Chaoliang, Ni Yong. Syringin inhibits intervertebral disc degeneration in rats[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(32): 5104-5109.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
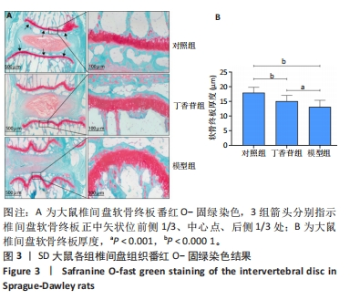
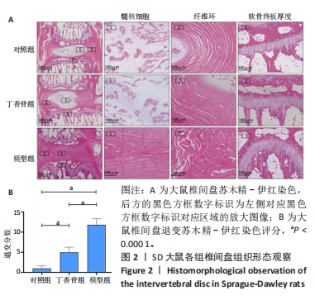
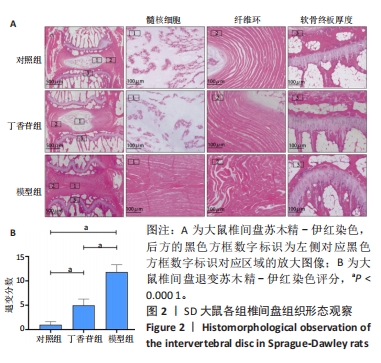
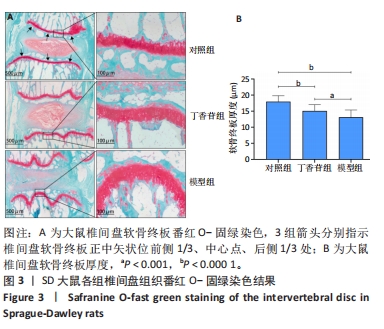
苏木精-伊红染色显示,对照组大鼠椎间盘形态良好,椎间盘高度正常,纤维环呈环状分层排列整齐,无纤维环断裂或紊乱迹象,髓核中心部分呈椭圆形、体积饱满,无明显炎症细胞浸润,上下软骨终板厚度一致,连续性好。模型组大鼠椎间盘组织染色不均匀,椎间盘高度降低,软骨终板变薄、连续性差且有裂隙出现,纤维环结构紊乱、呈现玻璃样变,纤维环内存在裂隙,髓核皱缩或消失,胶原含量明显减少,可见大量类软骨细胞坏死,核碎裂或溶解,胞质嗜酸性增强,没有内部细胞结构,无细胞外基质染色,如Ⅱ型胶原和聚集物。丁香苷组大鼠椎间盘组织中纤维环排列较模型组相对规整,椎间盘高度正常或略低于对照组,软骨终板厚度与模型组相比均匀且连续性较好,未出现裂隙,髓核部分皱缩,但中央透明空腔仍存在,可见少量类软骨细胞坏死,部分核碎裂或溶解,少量胞质嗜酸性增强。这些研究结果提示与对照组对比,模型组大鼠椎间盘在组织结构、形态方面发生明显病理学变化;穿刺联合丁香苷药物注射处理后,大鼠椎间盘组织病理形态学较模型组明显改善。所以基于该实验结果,推测丁香苷可能具有抑制大鼠椎间盘退变的作用。 椎间盘退变组织学评分结果显示,对照组、丁香苷组、模型组的评分分别为(1.00±0.64),(5.00±1.27),(11.83±1.47)分,组间比较差异有非常显著性意义(P < 0.000 1)。 2.3 大鼠椎间盘组织番红O-固绿染色结果 见图3。"

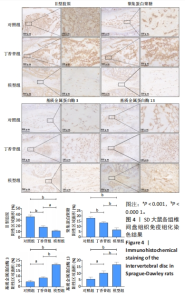
免疫组化染色显示,对照组大鼠椎间盘中Ⅱ型胶原、聚集蛋白聚糖高度表达,主要位于软骨组织和髓核区域,反映了健康的软骨结构;基质金属蛋白酶3,13的表达较低,反映了正常椎间盘中的细胞活动和降解过程有限。模型组大鼠椎间盘中Ⅱ型胶原、聚集蛋白聚糖的表达显著减少,基质金属蛋白酶3,13的表达显著增加,表明椎间盘发生了退变。相较于模型组,丁香苷组大鼠椎间盘中Ⅱ型胶原、聚集蛋白聚糖的表达增加,基质金属蛋白酶3,13的表达减少,表明丁香苷对椎间盘退变有一定的抑制作用。 免疫组化染色定量分析结果显示,对照组、丁香苷组及模型组大鼠椎间盘中Ⅱ型胶原阳性区域面积分别为(35.88±2.80)%,(18.01±2.28)%,(11.61±1.30)%,组间比较差异有非常显著性意义(P < 0.001,P < 0.000 1);对照组、丁香苷组及模型组大鼠椎间盘中聚集蛋白聚糖阳性区域面积分别为(18.04±1.04)%,(13.65±0.92)%,(6.98±1.74)%,组间比较差异有非常显著性意义(P < 0.000 1);对照组、丁香苷组及模型组大鼠椎间盘中基质金属蛋白酶3阳性区域面积分别为(4.93±1.38)%,(8.53±1.00)%,(21.15±1.34)%,组间比较差异有非常显著性意义(P < 0.001,P < 0.000 1);对照组、丁香苷组及模型组大鼠椎间盘中基质金属蛋白酶13阳性区域面积分别为(5.69±1.44)%,(10.22±1.62)%,(16.73±1.77)%,组间比较差异有非常显著性意义(P < 0.001,P < 0.000 1)。"

| [1] 陈莎,王诗忠,邓德万.大鼠腰椎间盘退变模型的建立及其形态学观察[J].福建中医药,2021,52(9):39-40. [2] 康小彪,李鹏飞,滕元平,等.淫羊藿苷通过核转录因子KappaB通路减轻大鼠椎间盘退变[J].广州中医药大学学报,2022,39(8):1878-1885. [3] JENSEN CE, RIIS A, PETERSEN KD, et al. Economic evaluation of an implementation strategy for the management of low back pain in general practice. Pain. 2017;158(5): 891-899. [4] 方未晶.髓核靶向性纳米给药系统的构建及在椎间盘退变中的应用[D].杭州:浙江大学,2020. [5] ROH EJ, DARAI A, KYUNG JW, et al. Genetic Therapy for Intervertebral Disc Degeneration. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(4):1579. [6] 马振,李延坤,翟凯,等.基质金属蛋白酶-1在椎间盘退变中的表达与调节机制的研究进展[J].湖北民族学院学报(医学版),2019,36(1):72-74. [7] 许大勇,李云朋,魏景梅,等.芸香苷改善大鼠椎间盘退变的机制[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(14):2139-2145. [8] 王啸华,何敢声,谢林.氧化应激在椎间盘退变中的作用进展[J].中医正骨,2023, 35(5):44-48. [9] WANG G, HUANG K, DONG Y, et al. Lycorine Suppresses Endplate-Chondrocyte Degeneration and Prevents Intervertebral Disc Degeneration by Inhibiting NF-kappaB Signalling Pathway. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;45(3):1252-1269. [10] 杨青志,毛碧峰.腰椎间盘突出症的治疗进展[J].实用中医内科杂志,2023,37(6): 66-70. [11] 代守前.丹酚酸B调节氧化应激缓解椎间盘退变的体内体外实验研究[D].苏州:苏州大学,2021. [12] KEOROCHANA G, JOHNSON JS, TAGHAVI CE, et al. The effect of needle size inducing degeneration in the rat caudal disc: evaluation using radiograph, magnetic resonance imaging, histology, and immunohistochemistry. Spine J. 2010;10(11):1014-1023. [13] HAN B, ZHU K, LI FC, et al. A simple disc degeneration model induced by percutaneous needle puncture in the rat tail. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2008;33(18):1925-1934. [14] SUZUKI S, FUJITA N, HOSOGANE N, et al. Excessive reactive oxygen species are therapeutic targets for intervertebral disc degeneration. Arthritis Res Ther. 2015;17:316. [15] WANG Y, CHENG H, WANG T, et al. Oxidative stress in intervertebral disc degeneration: Molecular mechanisms, pathogenesis and treatment. Cell Prolif. 2023;56(9):e13448. [16] 王倩,卢子昂,李利和,等.青藤碱可有效抑制白细胞介素1β介导的髓核细胞凋亡[J].中国组织工程研究,2024,28(2):224-230. [17] KANG L, LIU S, LI J, et al. The mitochondria-targeted anti-oxidant MitoQ protects against intervertebral disc degeneration by ameliorating mitochondrial dysfunction and redox imbalance. Cell Prolif. 2020;53(3):e12779. [18] YU H, HOU G, CAO J, et al. Mangiferin Alleviates Mitochondrial ROS in Nucleus Pulposus Cells and Protects against Intervertebral Disc Degeneration via Suppression of NF-kappaB Signaling Pathway. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021;2021:6632786. [19] GONG X, ZHANG L, JIANG R, et al. Hepatoprotective effects of syringin on fulminant hepatic failure induced by D-galactosamine and lipopolysaccharide in mice. J Appl Toxicol. 2014;34(3):265-271. [20] ZHANG H, GU H, JIA Q, et al. Syringin protects against colitis by ameliorating inflammation. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2020;680:108242. [21] 石雅倩,李鑫,黄思源,等.紫丁香苷调控PI3K/Akt/mTOR诱导乳腺癌细胞凋亡的研究(英文)[J].生物化学与生物物理进展,2023:1-16. doi:10.16476/j.pibb.2023.0061 [22] 宋媛媛,周越,孙守兵,等.丁香苷对免疫功能低下小鼠的免疫调节作用[J].中药药理与临床,2013,29(2):44-47. [23] 石美晶,师幸伟,石珍,等.丁香苷对H/R心肌细胞的保护作用及其机制研究[J].西部医学,2019,31(3):364-369. [24] 宋媛媛,李媛,张洪泉.丁香苷对大鼠佐剂性关节炎的治疗作用及其机制[J].药学学报,2010,45(8):1006-1011. [25] 谭俊毅.丁香苷通过FOXO3a/NF-κB途径对大鼠脑缺血再灌注损伤的神经保护作用[D].重庆:重庆医科大学,2021. [26] ZHANG B, ZHAO Q, LI Y, et al. Moxibustion alleviates intervertebral disc degeneration via activation of the HIF-1alpha/VEGF pathway in a rat model. Am J Transl Res. 2019; 11(9):6221-6231. [27] 廖瑶,涂婷,曾惜羽,等.瑞芬太尼对椎间盘退变模型大鼠椎间盘的影响及机制[J].重庆医科大学学报,2023,48(7):760-764. [28] LAI A, GANSAU J, GULLBRAND SE, et al. Development of a standardized histopathology scoring system for intervertebral disc degeneration in rat models: An initiative of the ORS spine section. JOR Spine. 2021;4(2):e1150. [29] 吴靖平,朱斌,丁磊,等.大鼠椎间盘软骨终板退变与细胞凋亡的形态计量学研究[J].复旦学报(医学版),2010,37(2):140-145. [30] BASSO M, CAVAGNARO L, ZANIRATO A, et al. What is the clinical evidence on regenerative medicine in intervertebral disc degeneration? Musculoskelet Surg. 2017; 101(2):93-104. [31] 陈江,肖辉灯,孙旗,等.人椎间盘髓核细胞增殖活性与益肾活血通络方的干预调控[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(8):1200-1206. [32] ZHANG Y, HE F, CHEN Z, et al. Melatonin modulates IL-1beta-induced extracellular matrix remodeling in human nucleus pulposus cells and attenuates rat intervertebral disc degeneration and inflammation. Aging (Albany NY). 2019;11(22):10499-10512. [33] XIE T, PAN R, HUANG W, et al. Myricetin alleviates H2O2-induced senescence and apoptosis in rat nucleus pulposus-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Folia Histochem Cytobiol. 2023;61(2):98-108. [34] VO N, NIEDERNHOFER LJ, NASTO LA, et al. An overview of underlying causes and animal models for the study of age-related degenerative disorders of the spine and synovial joints. J Orthop Res. 2013;31(6):831-837. [35] KIM KW, CHUNG HN, HA KY, et al. Senescence mechanisms of nucleus pulposus chondrocytes in human intervertebral discs. Spine J. 2009;9(8):658-666. [36] FINKEL T. Signal transduction by reactive oxygen species. J Cell Biol. 2011;194(1):7-15. [37] 刘祺,杨舟,朱青安.氧化应激与椎间盘退变的研究进展[J].中国临床解剖学杂志, 2020,38(3):363-366. [38] JOHNSON ZI, SHAPIRO IM, RISBUD MV. Extracellular osmolarity regulates matrix homeostasis in the intervertebral disc and articular cartilage: evolving role of TonEBP. Matrix Biol. 2014;40:10-16. [39] 陶红平,张觅,游长江,等.IL-13抑制剂在损伤大鼠尾椎间盘退变中的作用研究[J].生物技术进展,2021,11(3):369-377. [40] ZHOU T, LIN H, CHENG Z, et al. Mechanism of microRNA-146a-mediated IL-6/STAT3 signaling in lumbar intervertebral disc degeneration. Exp Ther Med. 2017;14(2):1131-1135. [41] HSU HT, YUE CT, TENG MS, et al. Immuohistochemical score of matrix metalloproteinase-1 may indicate the severity of symptomatic cervical and lumbar disc degeneration. Spine J. 2020;20(1):124-137. [42] 赵继荣,杨正汉,马俊飞,等.中医药干预基质金属蛋白酶表达治疗椎间盘退变研究进展[J].中国实验方剂学杂志,2023,29(5):272-282. [43] 李陆虎.腰椎间盘突出症中医证型与退变椎间盘组织中MMP-2、MMP-13相关性研究[D].咸阳:陕西中医药大学,2017. [44] 李熙阳.HOTAIR与COLⅡ、MMP3在椎间盘退变中的表达及相关性研究[D].衡阳:南华大学,2020. [45] WANG Q, SUN CT. Characteristics and correlation analysis of spino-pelvic sagittal parameters in elderly patients with lumbar degenerative disease. J Orthop Surg Res. 2019;14(1):127. [46] LI W, ZHOU P, YAN B, et al. Disc regeneration by injectable fucoidan-methacrylated dextran hydrogels through mechanical transduction and macrophage immunomodulation. J Tissue Eng. 2023;14:1778670354. [47] LIU J, ZHANG Z, GUO Q, et al. Syringin prevents bone loss in ovariectomized mice via TRAF6 mediated inhibition of NF-kappaB and stimulation of PI3K/AKT. Phytomedicine. 2018;42:43-50. [48] SUN S, ZHANG Y, XU W, et al. Mitochondrial dysfunction is involved in the cellular activity inhibition by eleutheroside B in SMMC-7721 and HeLa cells. Hum Exp Toxicol. 2022;41:774860050. [49] DENG Z, REN C, TANG C, et al. Syringin alleviates hepatic fibrosis by enhancing autophagic flux and attenuating ER stress-TRIB3/SMAD3 in diabetic mice. Tissue Cell. 2023;83:102159. [50] 罗力文,简秀英,周跃.GATA4调控NF-κB信号通路促进椎间盘髓核细胞发生炎症和衰老[J].免疫学杂志,2021,37(7):553-559. [51] 李敬超.红景天苷通过Nrf2/ARE信号通路缓解椎间盘退变的研究[D].天津:天津医科大学,2020. [52] 刘志超,张帆,祝永刚,等.身痛逐瘀汤方对椎间盘退变中PI3K/AKT通路影响的研究[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2018,26(10):14-19. [53] 罗明秀,马海江,张甜,等.TGF-β对C-28/I2人软骨细胞聚集蛋白聚糖硫酸化修饰的影响[J].宁夏医学杂志,2021,43(6):481-484. [54] 姚思琦,黎文正,汪虹.转化生长因子β/Smad信号通路与瘢痕疙瘩的靶向治疗[J].中国组织工程研究,2024,28(16):2619-2624. |
| [1] | Huang Xiarong, Hu Lizhi, Sun Guanghua, Peng Xinke, Liao Ying, Liao Yuan, Liu Jing, Yin Linwei, Zhong Peirui, Peng Ting, Zhou Jun, Qu Mengjian. Effect of electroacupuncture on the expression of P53 and P21 in articular cartilage and subchondral bone of aged rats with knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1174-1179. |
| [2] | Liu Xin, Hu Man, Zhao Wenjie, Zhang Yu, Meng Bo, Yang Sheng, Peng Qing, Zhang Liang, Wang Jingcheng. Cadmium promotes senescence of annulus fibrosus cells via activation of PI3K/Akt signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1217-1222. |
| [3] | Li Longyang, Zhang Songjiang, Zhao Xianmin, Zhou Chunguang, Gao Jianfeng. Electroacupuncture intervention on the proliferation and differentiation of hippocampal neurons and oligodendrocytes in Alzheimer’s disease model mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1029-1035. |
| [4] | Li Yang, Ma Fei, Leng Yebo, Xu Shicai, He Baoqiang, Zhou Jiajun, Liao Yehui, Tang Qiang, Tang Chao, Wang Qing, Zhong Dejun. Correlation between intervertebral disc degeneration and hyperuricemia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(32): 5091-5096. |
| [5] | Wen Huaneng, Lin Run, Wang Yixiao, Wang Bingshui, Liu Lu, Liu Chuanyao, Cai Canxin, Cui Shaoyang, Xu Mingzhu. Effects of electroacupuncture with “Zhi San Zhen” on Notch signaling pathway and synaptic plasticity in 5xFAD mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(32): 5148-5153. |
| [6] | Cao Sheng, Kong Lingwei, Xu Kun, Sun Zhijie. Effect of gelatin methacryloyl hydrogel loaded with salvianolic acid B on intervertebral disc degeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(3): 380-386. |
| [7] | Jiao Ziyuan, Zhuo Yue, Liang Roujun, Ding Qiangsheng, Zeng Xuejiu, Xu Ming, Zhang Hong. Electroacupuncture improves morphological structure of the detrusor muscle and bladder function in rats with spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(28): 4484-4490. |
| [8] | Zhou Minghan, Zhang Hui, Zheng Xianbo, Xu Wuji. Significance of PI3K/Akt/HIF-1α signaling pathway expression in nucleus pulposus cells at different oxygen concentrations in delaying intervertebral disc degeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(28): 4491-4497. |
| [9] | Liu Jing, Liang Fangyuan, Li Jia, Wang Hua. Mechanisms of acupuncture in the treatment of irritable bowel syndrome with diarrhea based on proteomics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(26): 4129-4136. |
| [10] | Guo Zehua, Li Zhaoyong, Chen Long, Duan Jiahao, Jiang Haobo, Chen Guangxue, Su Youxian, Liu Enxu, Yang Shaofeng. Action mechanism of Bushenhuoxue decoction on promoting nucleus pulposus-like differentiation of adipose-derived stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(25): 3974-3980. |
| [11] | Huang Jie, Jiang Qiang, Han Jiaheng, Liu Jiang, Zhang Yan, Lu Zhencao, Ding Yu. Mechanism by which interleukin-1beta regulates the expression of Semaphorin 3A to induce intervertebral disc degeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(23): 3680-3685. |
| [12] | Xie Yue, Zhai Weifeng, Guo Ji, Jia Yongwei. Integrative analyses of pyroptosis-related genes associated with intervertebral disc degeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(21): 3438-3444. |
| [13] | Liu Yuhang, Sun Ruifen, Mu Rigen Jiya, Wang Xing, Li Zhijun, Liu Yanan, Hao Yunteng, Cai Yongqiang, Zhang Shaojie, Li Kun. Development of a three-dimensional digital children’s acupuncture point visualization system of Mongolian medicine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(20): 3223-3228. |
| [14] | Zhou Shuliang, Xu Liang, Qian Xuefeng, Zeng Jincai, Zhu Lifan. Correlation between the expression of miRNA-142-3p, mixed lineage kinase 3 and interleukin-1beta in nucleus pulposus and the degree of lumbar intervertebral disc degeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(2): 165-171. |
| [15] | Wang Qian, Lu Ziang, Li Lihe, Lyu Chaoliang, Wang Meng, Zhang Cunxin. Sinomenine effectively inhibits interleukin-1beta-induced apoptosis in nucleus pulposus cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(2): 224-230. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||