Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (28): 4484-4490.doi: 10.12307/2024.461
Previous Articles Next Articles
Electroacupuncture improves morphological structure of the detrusor muscle and bladder function in rats with spinal cord injury
Jiao Ziyuan, Zhuo Yue, Liang Roujun, Ding Qiangsheng, Zeng Xuejiu, Xu Ming, Zhang Hong
- 1School of Acupuncture, Massage and Rehabilitation, Hunan University of Chinese Medicine, Changsha 410208, China
-
Received:2023-07-12Accepted:2023-08-26Online:2024-10-08Published:2023-11-27 -
Contact:Zhang Hong, Professor, Doctoral Supervisor, School of Acupuncture, Massage and Rehabilitation, Hunan University of Chinese Medicine, Changsha 410208, China Xu Ming, Lecturer, School of Acupuncture, Massage and Rehabilitation, Hunan University of Chinese Medicine, Changsha 410208, China -
About author:Jiao Ziyuan, Master, School of Acupuncture, Massage and Rehabilitation, Hunan University of Chinese Medicine, Changsha 410208, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China (General Program), No. 82274666 (to ZH); National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 82205255 (to XM); Hunan University of Chinese Medicine Discipline Construction Project, No. 22JBZ013 (to ZH); Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine First-Class Discipline Key Project of Hunan University of Chinese Medicine, No. 2021ZXYJH15 (to ZH)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Jiao Ziyuan, Zhuo Yue, Liang Roujun, Ding Qiangsheng, Zeng Xuejiu, Xu Ming, Zhang Hong. Electroacupuncture improves morphological structure of the detrusor muscle and bladder function in rats with spinal cord injury[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(28): 4484-4490.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
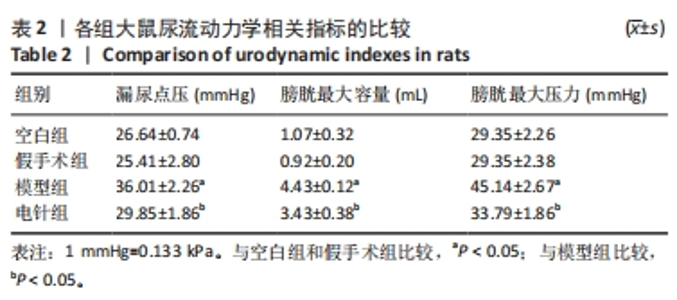
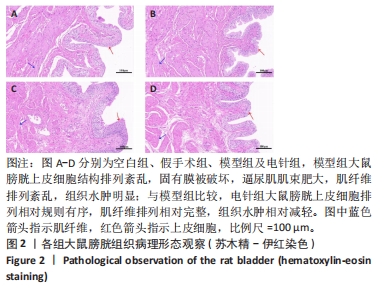
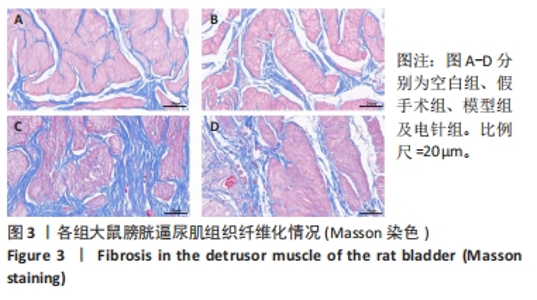
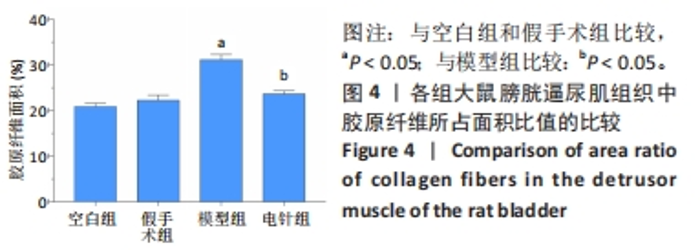
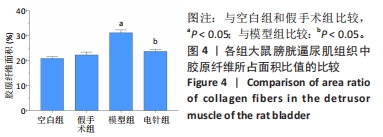
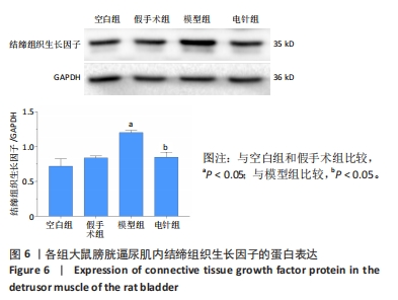
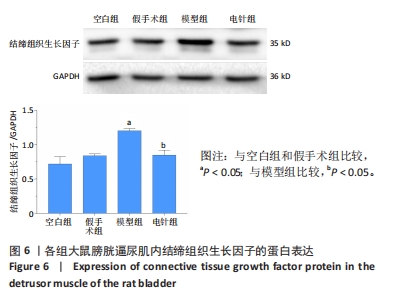
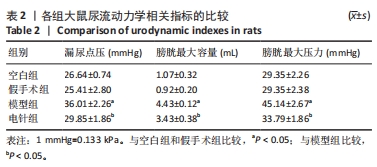
2.1 实验动物数量分析 整个实验过程中,造模大鼠因腹胀、感染及死亡等原因排除12只,剩余24只大鼠全部进入结果分析。空白组与假手术组总共24只大鼠全部进入结果分析。 2.2 各组大鼠一般情况观察 空白组和假手术组大鼠活动灵活自如,爬行正常;模型组和电针组大鼠双下肢拖曳不能行走,需每日进行手法排尿,模型组大鼠膀胱以尿潴留症状为主要表现,电针组大鼠膀胱尿量较模型组下降,膀胱肿胀情况有所减轻。 2.3 各组大鼠尿流动力学结果的比较 与空白组及假手术组比较,模型组大鼠漏尿点压、膀胱最大容量、膀胱最大压力显著增加(P < 0.05);与模型组比较,电针组大鼠漏尿点压、膀胱最大容量、膀胱最大压力均下降(P < 0.05),见表2。"
| [1] XU H, ZHAO W, ZHOU Y, et al. Multi-omics in Spinal Cord Injury: Diagnosis, Prognosis, and Treatment. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 2022;68(11):58-70. [2] HU X, XU W, REN Y, et al. Spinal cord injury: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic interventions. Signal Transduc Target Ther. 2023;8(1):245. [3] 胥少汀,郭世绂,陈懿.脊髓损伤基础与临床[M].北京:解放军北京军区总医院,2009. [4] JOSHI AD, SHUKLA A, CHAWATHE V, et al. Clean intermittent catheterization in long-term management of neurogenic bladder in spinal cord injury: Patient perspective and experiences. Int J Urol. 2022;29(4):317-323. [5] CHEN PC, LEE KH, LEE WC, et al. Treating Neurogenic Lower Urinary Tract Dysfunction in Chronic Spinal Cord Injury Patients-When Intravesical Botox Injection or Urethral Botox Injection Are Indicated. Toxins (Basel). 2023;15(4):288. [6] HAMID R, AVERBECK MA, CHIANG H, et al. Epidemiology and pathophysiology of neurogenic bladder after spinal cord injury. World J Urol. 2018;36(10):1517-1527. [7] KIM SJ, KIM J, NA YG, et al.Irreversible Bladder Remodeling Induced by Fibrosis. Int Neurourol J. 2021;25(Suppl 1):S3-S7. [8] DEVEAUD CM, MACARAK EJ, KUCICH U, et al. Molecular analysis of collagens in bladder fibrosis. J Urol. 1998;160(4):1518-1527. [9] AZADZOI KM, CHEN BG, RADISAVLJEVIC ZM, et al. Molecular reactions and ultrastructural damage in the chronically ischemic bladder. J Urol. 2011;186(5):2115-2122. [10] BRADHAM DM, IGARASHI A, POTTER RL, et al. Connective tissue growth factor: a cysteine-rich mitogen secreted by human vascular endothelial cells is related to the SRC-induced immediate early gene product CEF-10. J Cell Biol. 1991;114(6):1285-1294. [11] LIN F, YUAN Y, YE X, et al. Characterization and role of connective tissue growth factor gene in collagen synthesis in swim bladder of chu’s croaker (Nibea coibor). Int J Biol Macromol. 2023;227:1336-1345. [12] TRAMPUŽ SR, VAN RIET S, NORDLING Å, et al.The Role of CTGF in Liver Fibrosis Induced in 3D Human Liver Spheroids. Cells. 2023;12(2):302. [13] MILLER CA, KENNELLY MJ. Pulse article:survey of neurogenic bladder management in spinal cord injury patients around the world. Spinal Cord Ser Cases. 2021;7(1):16. [14] 王美玲.基于清洁间歇导尿术的自我护理在脊髓损伤后神经源性膀胱患者中的应用效果分析[J].中西医结合心血管病电子杂志, 2020,8(19):87,143. [15] PEREZ NE, GODBOLE NP, AMIN K, et al. Neurogenic Bladder Physiology, Pathogenesis,and Management after Spinal Cord Injury. J Pers Med. 2022;12(6):968. [16] 张胜利,赵承奇,李勇.中医综合康复治疗对脊髓损伤后神经源性膀胱尿潴留患者生活质量的改善效果分析[J].中国实用医药,2020, 15(11):141-142. [17] AI K, LIU Q, XU M, et al. Effect of electroacupuncture on urodynamics of neurogenic bladder and PACAP/cAMP/PKA signaling pathway in detrusor tissue of rats after suprasacral spinal cord injury. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2021;46(9):728-734. [18] ZHANG HT, NONG QP, WEI L, et al. Effect of thunder-fire moxibustion combined with electroacupuncture on urodynamics in patients with neurogenic bladder after spinal cord injury. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2021; 46(11):958-962. [19] 卓越,艾坤,许明,等.电针对骶上脊髓损伤后大鼠神经源性膀胱及血清外泌体miRNA差异表达的影响[J].中国康复医学杂志,2023, 38(5):577-588. [20] 张海涛,韦秋连,韦林,等.雷火灸结合电针治疗骶上脊髓损伤后神经源性膀胱的临床观察[J].中国医药导报,2020,17(28):129-132. [21] 许明,刘琼,邓石峰,等.基于PACAP-cAMP信号通路研究电针治疗骶上脊髓损伤后逼尿肌反射亢进型膀胱的效应机制[J].世界针灸杂志(英文版),2023,33(3):273-281. [22] 吕山河,胡碧浓,黄梓铭,等.电针对骶上脊髓损伤大鼠膀胱尿流动力学和逼尿肌肌电图振幅的影响[J].湖南中医药大学学报,2020, 40(11):1355-1360. [23] 卓越,许明,邓石峰,等.大鼠骶上不同节段脊髓损伤后神经源性膀胱模型比较及尿流动力学分析[J].湖南中医药大学学报,2022, 42(9):1426-1433. [24] 张雨辰,张泓,艾坤,等.大鼠脊髓损伤后神经源性膀胱模型的制备[J].中国康复医学杂志,2014,29(6):542-546. [25] SHAKER H, MOURAD MS, ELBIALY MH, et al. Urinary bladder hyperreflexia: a rat animal model. Neurourol Urodyn. 2003;22(7): 693-698. [26] SHEA VK, CAI R, CREPPS B, et al. Sensory fibers of the pelvic nerve innervating the Rat’s urinary bladder. J Neurophysiol. 2000;84(4): 1924-1933. [27] 李邦伟,周传龙,王超,等.方剑乔教授针灸治疗术后尿潴留经验探析[J].浙江中医药大学学报,2022,46(8):835-838. [28] LONG ZL, LIU ZS. Brief analysis on main indications and compatibility rules of Ciliao (BL 32) based on data mining. Zhongguo Zhen Jiu. 2022; 42(4):459-463. [29] 汪汐,龙子临,何欣,等.基于数据挖掘分析针灸改善宫颈癌术后尿潴留的选穴规律[J].针灸临床杂志,2022,38(11):39-43. [30] 孙燕,钟亮,陶林花,等.高压氧联合电针八髎穴对脊髓损伤神经源性膀胱患者尿动力学的影响[J].中国康复,2023,38(7):422-425. [31] 李慧,徐利飞.电针八髎穴联合康复治疗脊损伤患者神经源性膀胱的临床研究[J].湖北中医杂志,2023,45(7):39-41. [32] 耿丹,钟丹.电针关元穴治疗脊髓损伤患者逼尿肌反射亢进的疗效分析[J].中国社区医师,2017,33(6):57-59. [33] 韩鹏,付渊博,杨友信,等.基于数据挖掘技术探究针灸治疗脊髓损伤后神经源性膀胱选穴规律[J].中国中医药信息杂志,2022, 29(2):10-14. [34] 居诗如,尹晶,胡飞,等.电针不同穴位对脊髓损伤后神经源性膀胱大鼠作用的机制研究[J].湖北中医药大学学报,2020,22(4):10-13. [35] YU P, GAO B, XIA Y. Meta analysis of the effect of distal or local point selection on acupuncture efficacy. World J Acupunct Moxibustion. 2018;28(2):114-120. [36] WYNDAELE JJ. Investigation of the afferent nerves of the lowerurinary tract in patients with complete and incomplete spinal cord injury. Spinal Cord. 1991;29(7):490-494. [37] CHENG PT, WONG MK, CHANG PL. A therapeutic trial of acupuncture in neurogenic bladder of spinal cord injured patients--a preliminary report. Spinal Cord. 1998;36(7):476-480. [38] 韦慧麟,任亚锋,张芝兰,等.电针和艾灸治疗脊髓损伤后神经源性膀胱疗效差异:随机对照试验[J/OL].中国针灸:1-7[2023-08-10].doi:10.13703/j.0255-2930.20221027-k0005. [39] 郭宁.电针“中极”“关元”穴对骶上脊髓损伤后神经源性膀胱大鼠膀胱功能的影响及机制研究[D].郑州:河南中医药大学,2022. [40] CHANG S, MAO ST, HU SJ, et al. Studies of detrusor-sphincter synergia and dyssynergia during micturition in rats via fractional Brownian motion. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 2000;47(8):1066-1073. [41] 马源.脊髓损伤引起神经源性膀胱对膀胱-肾脏结构功能变化的影响[D].郑州:郑州大学,2021. [42] BUSHNELL JY, CATES LN, HYDE JE, et al. Early Detrusor Application of Botulinum Toxin A Results in Reduced Bladder Hypertrophy and Fibrosis after Spinal Cord Injury in a Rodent Model. Toxins (Basel). 2022;14(11):777. [43] JHANG JF, JIANG YH, HSU YH, et al. Pathogenesis evidence from human and animal models of detrusor underactivity. Tzu Chi Med J. 2021;34(3):287-296. [44] 刘倩,王军锋,马楠,等.结缔组织生长因子在神经源性膀胱纤维化过程中的影响因素研究[J].中华小儿外科杂志,2018,39(7): 539-545. [45] REBOLLEDO DL, LIPSON KE, BRANDAN E. Driving fibrosis in neuromuscular diseases: Role and regulation of Connective tissue growth factor (CCN2/CTGF). Matrix Biol Plus. 2021;11:100059. [46] SHIEH JM, TSAI YJ, CHI JC, et al. TGFβ mediates collagen production in human CRSsNP nasal mucosa-derived fibroblasts through Smad2/3-dependent pathway and CTGF induction and secretion. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234(7):10489-10499. [47] 宋晨,诸靖宇,吴金星,等.骶3神经电调节对脊髓损伤早期大鼠逼尿肌细胞凋亡及膀胱纤维化影响的实验研究[J].浙江中西医结合杂志,2015,25(5):439-442,529. |
| [1] | Huang Xiarong, Hu Lizhi, Sun Guanghua, Peng Xinke, Liao Ying, Liao Yuan, Liu Jing, Yin Linwei, Zhong Peirui, Peng Ting, Zhou Jun, Qu Mengjian. Effect of electroacupuncture on the expression of P53 and P21 in articular cartilage and subchondral bone of aged rats with knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1174-1179. |
| [2] | Li Longyang, Zhang Songjiang, Zhao Xianmin, Zhou Chunguang, Gao Jianfeng. Electroacupuncture intervention on the proliferation and differentiation of hippocampal neurons and oligodendrocytes in Alzheimer’s disease model mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1029-1035. |
| [3] | Ma Sicong, Chen Jing, Li Yunqing. Functions and roles of connective tissue growth factor in nervous systems [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 615-620. |
| [4] | Zhan Lifen, Ai Kun, Zeng Xuejiu, Liang Rouyun, Ding Qiangsheng, Zhang Hong. Application and prospect of reconstructing bladder micturition reflex in neurogenic bladder after spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(18): 2925-2931. |
| [5] | Luo Fu, Shu Xiangzhong, Liu Danni, Tan Jinqu, Peng Ting, Huang Xiarong, Sun Guanghua, Peng Xinke, Wang Jinling, Zhou Jun. Electroacupuncture reduces inflammatory factor expression by suppressing Toll-like receptor 4/nuclear factor-kappa B signaling in rats with cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(14): 2186-2190. |
| [6] | Guo Shuhui, Yang Ye, Jiang Yangyang, Xu Jianwen. Screening and validation of neurogenic bladder miRNA-mRNA regulatory network [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(在线): 1-8. |
| [7] | Duan Zhaoyuan, Wu Mingli, Luo Meng, Liu Chengmei, Gao Jing, Li Ruiqing, Feng Xiaodong. Effect of electroacupuncture modulation of glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta/beta-catenin signaling pathway on CD133 protein expression in rat ventricular zone cells after spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(24): 3858-3864. |
| [8] | Yao Haihua, Min Youjiang, Hong Dongying, Wang Li, Lu Xiuyun, Yang Yihua. Effects of Santong electroacupuncture on the activity of cytoplasmic phospholipase A2 in rats with spinal cord injury via the Rho/Rho kinase and MEK/ERK signaling pathways [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(20): 3158-3166. |
| [9] | Guo Shuhui, Yang Ye, Jiang Yangyang, Xu Jianwen. Screening and validation of neurogenic bladder miRNA-mRNA regulatory network [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(20): 3143-3150. |
| [10] | Ma Munan, Xie Jun, Sang Yuchao, Huang Lei, Zhang Guodong, Yang Xiaoli, Fu Songtao. Electroacupuncture combined with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of chemotherapy-induced premature ovarian insufficiency in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(1): 1-7. |
| [11] | LIU Danni, SUN Guanghua, ZHOU Guijuan, LIU Hongya, ZHOU Jun, TAN Jinqu, HUANG Xiarong, PENG Ting, FENG Wei-bin, LUO Fu. Effect of electroacupuncture on apoptosis of neurons in cerebral cortex of rats with cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury at "Shuigou" and "Baihui" points [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(在线): 1-6. |
| [12] | Xiao Yang, Gong Liqiong, Fei Jing, Li Leiji. Effect of electroacupuncture on nerve growth factor and its receptor expression in facial nerve nucleus after facial nerve injury in rabbits [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1253-1259. |
| [13] | Fan Jianchao, Xu Paidi, Han Yongli, Wen Caiyuzhu, Zhang Hongxing, Pan Xiaoli. Effects of electroacupuncture at Zusanli acupoint on visceral hypersensitivity in rats with functional dyspepsia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 663-668. |
| [14] | Dong Miaomiao, Lai Han, Li Manling, Xu Xiuhong, Luo Meng, Wang Wenhao, Zhou Guoping. Effect of electroacupuncture on expression of nucleotide binding oligomerization domain-like receptor protein 3/cysteinyl aspartate specific proteinase 1 in rats with cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 749-755. |
| [15] | Wang Nan, Qian Yuzhang, Xie Lin. Network Meta-analysis of different acupuncture methods for the treatment of lumbar disc herniation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 813-820. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||