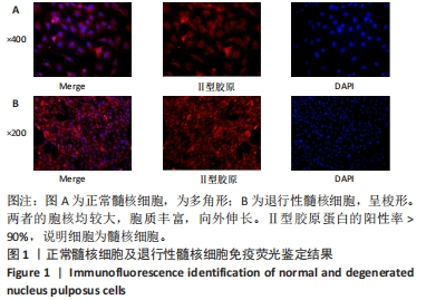
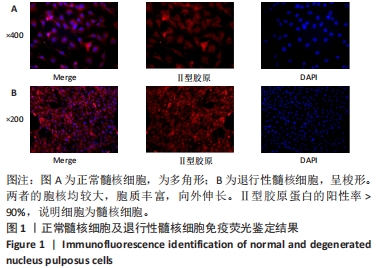
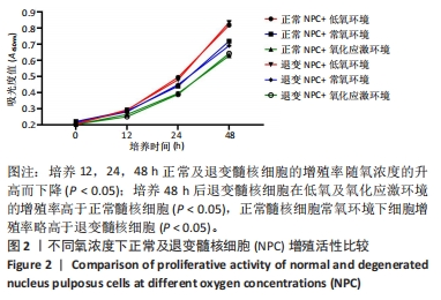
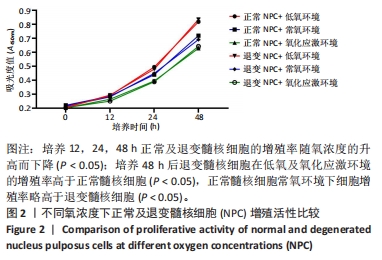
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (28): 4491-4497.doi: 10.12307/2024.469
Previous Articles Next Articles
Significance of PI3K/Akt/HIF-1α signaling pathway expression in nucleus pulposus cells at different oxygen concentrations in delaying intervertebral disc degeneration
Zhou Minghan, Zhang Hui, Zheng Xianbo, Xu Wuji
- Department of Orthopedics, the Second Affiliated Hospital of Hunan University of Chinese Medicine, Changsha 410208, Hunan Province, China
-
Received:2023-08-14Accepted:2023-09-15Online:2024-10-08Published:2023-11-27 -
Contact:Zheng Xianbo, Master, Associate chief physician, Department of Orthopedics, the Second Affiliated Hospital of Hunan University of Chinese Medicine, Changsha 410208, Hunan Province, China Xu Wuji, MD, Chief physician, Department of Orthopedics, the Second Affiliated Hospital of Hunan University of Chinese Medicine, Changsha 410208, Hunan Province, China -
About author:Zhou Minghan, Master candidate, Department of Orthopedics, the Second Affiliated Hospital of Hunan University of Chinese Medicine, Changsha 410208, Hunan Province, China Zhang Hui, Master candidate, Department of Orthopedics, the Second Affiliated Hospital of Hunan University of Chinese Medicine, Changsha 410208, Hunan Province, China -
Supported by:Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province, No. 2022JJ30449 (to XWJ); Scientific Research Key Project of Hunan Provincial Department of Education, No. 21A0249 (to XWJ); First-class Discipline Open Fund Project for Chinese Medicine of Hunan University of Chinese Medicine, No. 2022ZYX25 (to XWJ)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhou Minghan, Zhang Hui, Zheng Xianbo, Xu Wuji. Significance of PI3K/Akt/HIF-1α signaling pathway expression in nucleus pulposus cells at different oxygen concentrations in delaying intervertebral disc degeneration[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(28): 4491-4497.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
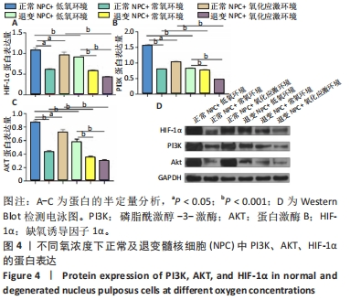
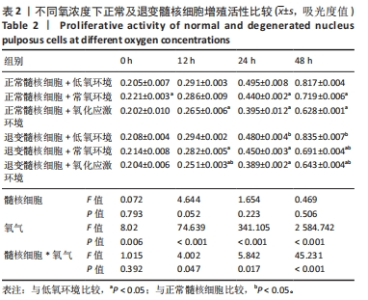
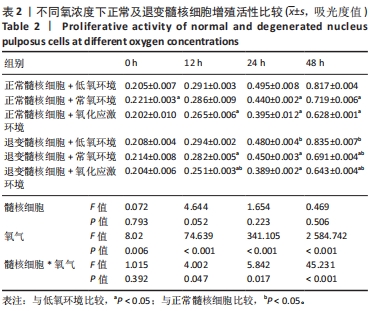
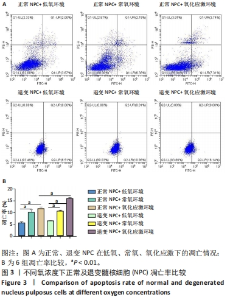
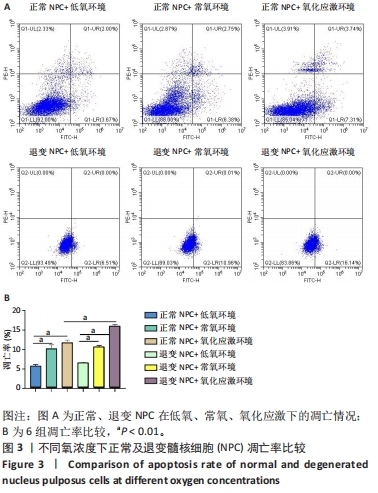
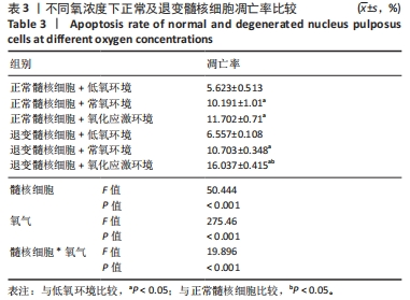
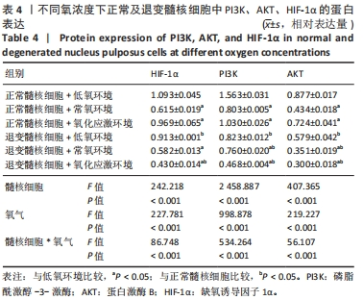
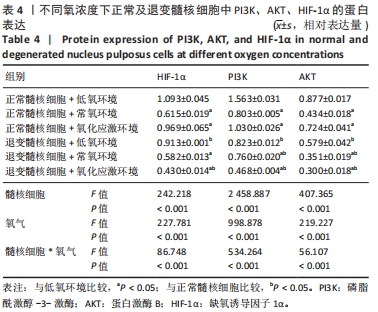
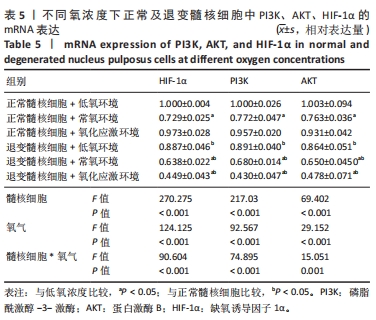
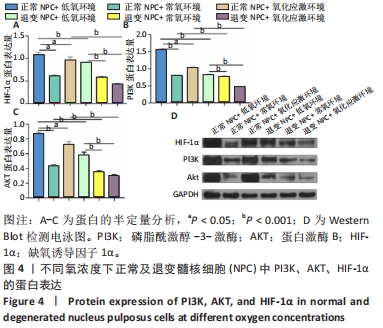
2.4 各组细胞中PI3K、AKT、HIF-1α的蛋白表达 由图4可见,不同氧浓度下正常及退变髓核细胞中PI3K、AKT、HIF-1α的蛋白表达趋势基本一致。在不同的氧浓度下,正常及退变髓核细胞中PI3K、AKT、HIF-1α的蛋白表达均有显著差异(P < 0.05),其中,正常髓核细胞中低氧环境下三者蛋白表达最高,氧化应激环境下其次,常氧环境下最低;退变髓核细胞中三者蛋白表达随氧浓度升高而下降(P < 0.05);常氧环境下,正常与退变髓核细胞中HIF-1α的蛋白表达差异无统计学意义(P > 0.05),而低氧及氧化应激环境下,正常髓核细胞HIF-1α的蛋白表达显著高于退变髓核细胞(P < 0.05);不同氧浓度下,正常髓核细胞PI3K、Akt的蛋白表达均显著高于退变髓核细胞(P < 0.05)。"
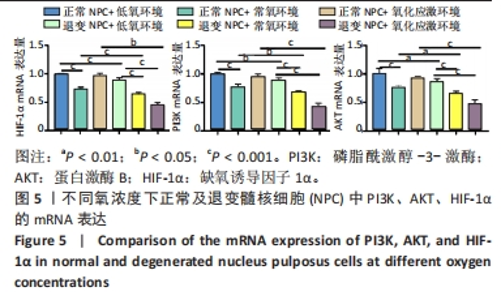
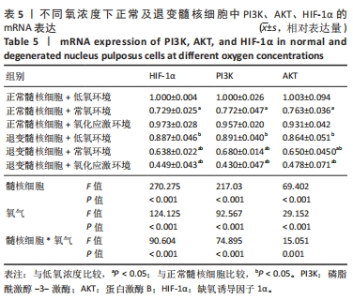
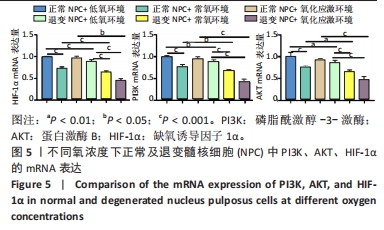
2.5 各组细胞中PI3K、AKT、HIF-1α的mRNA表达 由图5可见,不同氧浓度下正常及退变髓核细胞中PI3K、AKT、HIF-1α的mRNA表达趋势基本一致。在不同的氧浓度下,正常髓核细胞在氧化应激环境下PI3K、AKT、HIF-1α的mRNA表达与低氧环境相比差异均无显著性意义(P > 0.05),正常髓核细胞在常氧环境下PI3K、AKT、HIF-1α的mRNA表达显著低于低氧环境(P < 0.05);退变髓核细胞常氧与氧化应激环境下PI3K、AKT、HIF-1α的mRNA表达与低氧环境相比均有显著差异(P < 0.05),三者表达随氧浓度的升高而呈下降趋势。相同氧浓度下,正常髓核细胞三者mRNA表达均高于退变髓核细胞(P < 0.05)。"
| [1] PULICKAL T, BOOS J, KONIECZNY M, et al. MRI identifies biochemical alterations of intervertebral discs in patients with low back pain and radiculopathy. Eur Radiol. 2019; 29(12):6443-6446. [2] 刘鑫,胡满,赵文杰,等.镉暴露激活PI3K/Akt信号通路诱导椎间盘纤维环细胞衰老[J].中国组织工程研究,2024,28(8):1217-1222. [3] VO NV, HARTMAN RA, PATIL PR, et al. Molecular mechanisms of biological aging in intervertebral discs. J Orthop Res. 2016;34(8):1289-1306. [4] HUANG YC, LEUNG VY, LU WW, et al. The effects of microenvironment in mesenchymal stem cell-based regeneration of intervertebral disc. Spine J. 2013;13(3):352-362. [5] FENG G, JIN X, HU J, et al. Effects of hypoxias and scaffold architecture on rabbit mesenchymal stem cell differentiation towards a nucleus pulposus-like phenotype. Biomaterials. 2011;32:8182-8189. [6] 曹志鹏,石宇,李克,等.碳点-普鲁士蓝纳米酶抗氧化应激延缓椎间盘退变[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(25):4038-4044. [7] SIES H. Oxidative stress: a concept in redox biology and medicine. Redox Biol. 2015;4: 180-183. [8] WANG Y, CHENG H, WANG T, et al. Oxidative stress in intervertebral disc degeneration: Molecular mechanisms, pathogenesis and treatment. Cell Prolif. 2023;56(9):e13448. [9] 朱超,阮狄克.椎间盘退变机制研究进展[J].中国骨与关节杂志,2022,11(9):700-706. [10] ZHAN D, LIN M, CHEN J, et al. Hypoxia-inducible factor-1α regulates PI3K/AKT signaling through microRNA-32-5p/PTEN and affects nucleus pulposus cell proliferation and apoptosis. Exp Ther Med. 2021;21(6):646. [11] RIDER SM, MIZUNO S, KANG JD. Molecular Mechanisms of Intervertebral Disc Degeneration. Spine Surg Relat Res. 2018;3(1):1-11. [12] CHEN J, BAI M, NING C, et al. Gankyrin facilitates follicle-stimulating hormone-driven ovarian cancer cell proliferation through the PI3K/ AKT/HIF-1α/cyclin D1 pathway. Oncogene. 2015;35(19):2506-2517. [13] 陈江,肖辉灯,孙旗,等.人椎间盘髓核细胞增殖活性与益肾活血通络方的干预调控[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(8):1200-1206. [14] BRIDGEN DT, FEARING BV, JING L, et al. Regulation of human nucleus pulposus cells by peptide-coupled substrates. Acta Biomater. 2017;55:100-108. [15] OUYANG ZH, WANG WJ, YAN YG, et al. The PI3K/Akt pathway: a critical player in intervertebral disc degeneration. Oncotarget. 2017;8(34):57870-57881. [16] WU J, YU L, LIU Y, et al. Hypoxia regulates adipose mesenchymal stem cells proliferation, migration, and nucleus pulposus-like differentiation by regulating endoplasmic reticulum stress via the HIF-1α pathway. J Orthop Surg Res. 2023;18(1):339. [17] 谢文冠,刘宇涛,崔文波,等.褪黑素抑制过氧化氢诱导人髓核细胞的损伤[J].中国组织工程研究,2024,28(14):2180-2185. [18] 高小新. 低氧条件下髓核细胞外泌体诱导骨髓间充质干细胞向髓核样细胞分化的作用研究[D].重庆:中国人民解放军陆军军医大学,2022. [19] LE MC, POCKERT A, BUTTLE DJ, et al. Matrix synthesis and degradation in human intervertebral disc degeneration. Biochem Soc Trans. 2007;35(Pt4):652-655. [20] ZOU YP, ZHANG QC, ZHANG QY, et al. Procyanidin B2 alleviates oxidative stress-induced nucleus pulposus cells apoptosis through upregulating Nrf2 via PI3K-Akt pathway. J Orthop Res. 2023;41(7):1555-1564. [21] HUANG YC, LEUNG VY, LU WW, et al. The effects of microenvironment in mesenchymal stem cell- based regeneration of intervertebral disc. Spine J. 2013;13(3):352-362. [22] LOTZ JC, CHIN JR. Intervertebral Disc Cell Death Is Dependent on the Magnitude and Duration of Spinal Loading. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2000;25(12):1477-1483. [23] RANNOU F, LEE TS, ZHOU RH, et al. Intervertebral disc degeneration: the role of the mitochondrial pathway in annulus fibrosus cell apoptosis induced by overload. Am J Pathol. 2004;164(3):915-924. [24] DIMOZI A, MAVROGONATOU E, SKLIROU A, et al. Oxidative stress inhibits the proliferation, induces premature senescence and promotes a catabolic phenotype in human nucleus pulposus intervertebral disc cells. Eur Cell Mater. 2015;30:89-102. [25] NASTO LA, ROBINSON AR, NGO K, et al. Mitochondrial-derived reactive oxygen species (ROS) play a causal role in aging-related intervertebral disc degeneration. J Orthop Res. 2013;31(7):1150-1157. [26] JING D, WU W, DENG X, et al. FoxO1a mediated cadmium-induced annulus fibrosus cells apoptosis contributes to intervertebral disc degeneration in smoking. J Cell Physiol. 2021;236(1):677-687. [27] NI BB, LI B, YANG YH, et al. The effect of transforming growth factor β1 on the crosstalk between autophagy and apoptosis in the annulus fibrosus cells under serum deprivation. Cytokine. 2014;70(2):87-96. [28] FRUMAN DA, CHIU H, HOPKINS BD, et al. The PI3K Pathway in Human Disease. Cell. 2017;170(4):605-635. [29] XIAO Q, TENG Y, XU C, et al. Role of PI3K/AKT Signaling Pathway in Nucleus Pulposus Cells. Biomed Res Int. 2021;2021:9941253. [30] BEITNER-JOHNSON D, RUST RT, HSIEH TC, et al. Hypoxia activates Akt and induces phosphorylation of GSK-3 in PC12 cells. Cell Signal. 2001;13(1):23-27. [31] CHENG X, ZHANG G, ZHANG L, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells deliver exogenous miR-21 via exosomes to inhibit nucleus pulposus cell apoptosis and reduce intervertebral disc degeneration. J Cell Mol Med. 2018;22(1):261-276. [32] ZHENG J, CHANG L, BAO X, et al. TRIM21 drives intervertebral disc degeneration induced by oxidative stress via mediating HIF-1α degradation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2021;555:46-53. [33] LIU Z, LI C, MENG X, et al. Hypoxia-inducible factor-lαmediates aggrecan and collagen Π expression via NOTCH1 signaling in nu cleus pulposus cells during intervertebral disc degeneration. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2017;488(3):554-561. [34] KARAR J, MAITY A. PI3K/AKT/mTOR Pathway in Angiogenesis. Front Mol Neurosci. 2011; 4:51. [35] HOSFORD GEOLSON DM. Effects of hyperoxia on VEGF, its receptors, and HIF-2alpha in the newborn rat lung.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2003;285(1):L161-168. [36] DUAN S, SHAO G, YU L, et al. Angiogenesis contributes to the neuroprotection induced by hyperbaric oxygen preconditioning against focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Int J Neurosci. 2015;125(8):625-634. [37] KANG L, XIANG Q, ZHAN S, et al. Restoration of Autophagic Flux Rescues Oxidative Damage and Mitochondrial Dysfunction to Protect against Intervertebral Disc Degeneration. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019;2019:7810320. [38] DING F, SHAO ZW, XIONG LM. Cell death in intervertebral disc degeneration.Apoptosis. 2013;18(7):777-785. [39] HE F, LI Q, SHENG B, et al. SIRT1 Inhibits Apoptosis by Promoting Autophagic Flux in Human Nucleus Pulposus Cells in the Key Stage of Degeneration via ERK Signal Pathway. Biomed Res Int. 2021;2021:8818713. [40] SONG P, JO HS, SHIM WS, et al. Emodin induces collagen type I synthesis in Hs27 human dermal fibroblasts. Exp Ther Med. 2021;21(5):420. [41] Chen MM, Li Y, Deng SL, et al. Mitochondrial Function and Reactive Oxygen/Nitrogen Species in Skeletal Muscle. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022;10:826981. [42] KAUFMAN B, SCHARF O, ARBEIT J, et al. Proceedings of the Oxygen Homeostasis/Hypoxia Meeting. Cancer Res. 2004;64(9):3350-3356. [43] YANG SH, HU MH, SUN YH, et al. Differential phenotypic behaviors of human degenerative nucleus pulposus cells under normoxic and hypoxic conditions: influence of oxygen concentration during isolation, expansion, and cultivation. Spine J. 2013;13(11):1590-1596. [44] 朱超,阮狄克.椎间盘退变机制研究进展[J].中国骨与关节杂志,2022,11(9):700-706. [45] 李欣怡,王洪伸,谭傲威,等.氯化钴诱导体外人髓核细胞缺氧模型的建立[J].广东医学,2023,44(6):729-734. |
| [1] | Yang Yifeng, Ye Nan, Wang Lin, Guo Shuaicheng, Huang Jian. Signaling pathway of dexmedetomidine against ischemia-reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1464-1469. |
| [2] | Wei Juan, Li Ting, Huan Mengting, Xie Ying, Xie Zhouyu, Wei Qingbo, Wu Yunchuan. Mechanism by which static exercise improves insulin resistance in skeletal muscle of type 2 diabetes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1271-1276. |
| [3] | Lou Guo, Zhang Yan, Fu Changxi. Role of endothelial nitric oxide synthase in exercise preconditioning-induced improvement of myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1283-1288. |
| [4] | Yue Yun, Wang Peipei, Yuan Zhaohe, He Shengcun, Jia Xusheng, Liu Qian, Li Zhantao, Fu Huiling, Song Fei, Jia Menghui. Effects of croton cream on JNK/p38 MAPK signaling pathway and neuronal apoptosis in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1186-1192. |
| [5] | Liu Xin, Hu Man, Zhao Wenjie, Zhang Yu, Meng Bo, Yang Sheng, Peng Qing, Zhang Liang, Wang Jingcheng. Cadmium promotes senescence of annulus fibrosus cells via activation of PI3K/Akt signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1217-1222. |
| [6] | Pan Xiaolong, Fan Feiyan, Ying Chunmiao, Liu Feixiang, Zhang Yunke. Effect and mechanism of traditional Chinese medicine on inhibiting the aging of mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1091-1098. |
| [7] | Zhang Kefan, Shi Hui. Research status and application prospect of cytokine therapy for osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 961-967. |
| [8] | Chen Zepeng, Hou Yonghui, Chen Shudong, Hou Yu, Lin Dingkun. Tauroursodeoxycholic acid treats spinal cord injury by reducing apoptosis of spinal cord neurons under glucose and oxygen deprivation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 528-534. |
| [9] | Wei Yuanxun, Chen Feng, Lin Zonghan, Zhang Chi, Pan Chengzhen, Wei Zongbo. The mechanism of Notch signaling pathway in osteoporosis and its prevention and treatment with traditional Chinese medicine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 587-593. |
| [10] | Cao Sheng, Kong Lingwei, Xu Kun, Sun Zhijie. Effect of gelatin methacryloyl hydrogel loaded with salvianolic acid B on intervertebral disc degeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(3): 380-386. |
| [11] | Qian Longjie, Su Wenli, Zhu Wenxian, Wang Yixin. SRT1720, an activator of silent information regulator 1, alleviates acute traumatic brain injury in a rat model [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(28): 4447-4454. |
| [12] | Zhai Sheng, Aikeremujiang • Aerken, Zhang Zheng, Rixiati • Paerhati, Hao Feihu. CircCDR1as/miR-7-5p/RAF1 axis promotes autophagy levels in steroid-induced necrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(28): 4455-4460. |
| [13] | Zhang Tiandong, Peng Qingping, Liu Huan, Feng Jianguo, Yi Qian, Huang Wenhua. Semen cuscutae in the treatment of osteoarthritis: network pharmacology analysis and experimental validation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(28): 4516-4521. |
| [14] | Chen Chen, Zheng Runquan, Zhang Guichun. Effects of emodin on the proliferation, apoptosis and oxidative stress of chondrocytes in osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(28): 4528-4534. |
| [15] | Ma Jianglei, Zhang Huijie, Zhang Chenfang, Yang Xitong, Cheng Jianjie, Wang Guangming. Neuroprotective mechanism by which fenofibrate regulates superoxide dismutase 2 expression in transgenic C57BL/6J mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(28): 4547-4552. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||