Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (24): 3858-3864.doi: 10.12307/2023.422
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effect of electroacupuncture modulation of glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta/beta-catenin signaling pathway on CD133 protein expression in rat ventricular zone cells after spinal cord injury
Duan Zhaoyuan1, Wu Mingli2, Luo Meng1, Liu Chengmei2, Gao Jing2, Li Ruiqing1, 2, Feng Xiaodong1, 2
- 1Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450000, Henan Province, China; 2Rehabilitation Center, the First Affiliated Hospital of Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450000, Henan Province, China
-
Received:2022-04-06Accepted:2022-06-20Online:2023-08-28Published:2023-01-19 -
Contact:Feng Xiaodong, Chief physician, Doctoral supervisor, Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450000, Henan Province, China; Rehabilitation Center, the First Affiliated Hospital of Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450000, Henan Province, China -
About author:Duan Zhaoyuan, Master candidate, Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450000, Henan Province, China -
Supported by:Henan Provincial Science and Technology Department Key R&D and Promotion Special Project, No. 202102311130 (to WML); 2019 Henan Provincial TCM Scientific Research Special Project, No. 2019ZY2132 (to WML); Key Scientific Research Project of Higher Education Schools in Henan Province, No. 22A360011 (to LCM)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Duan Zhaoyuan, Wu Mingli, Luo Meng, Liu Chengmei, Gao Jing, Li Ruiqing, Feng Xiaodong. Effect of electroacupuncture modulation of glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta/beta-catenin signaling pathway on CD133 protein expression in rat ventricular zone cells after spinal cord injury[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(24): 3858-3864.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
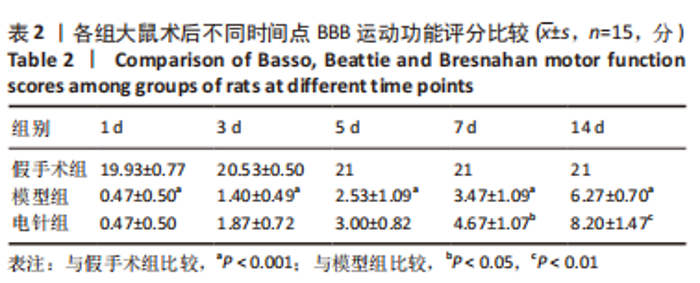
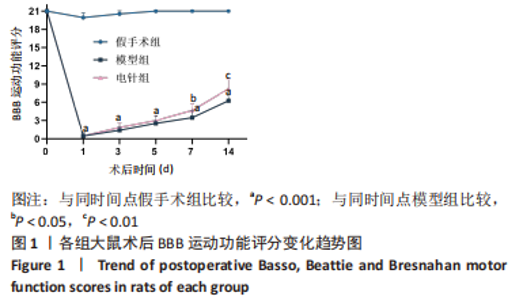
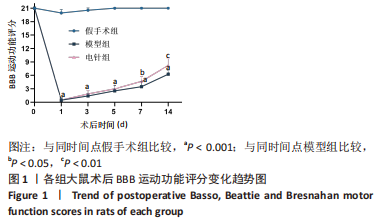
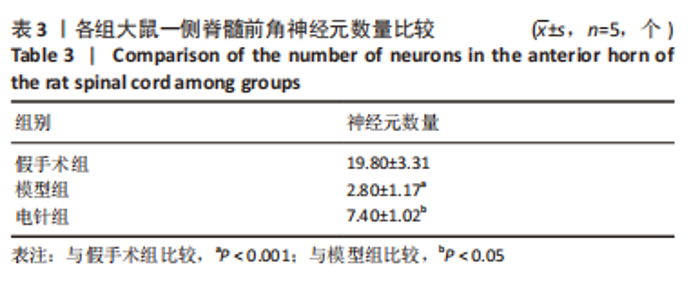
2.1 实验动物数量分析 45 只 SD 大鼠中除 15 只假手术组外,其余 30 只大鼠接受脊髓打击,造模成功率在95%以上;造模成功后干预过程中共死亡 8 只,主要死亡原因为肠道梗阻和自噬,死亡大鼠及时补充和干预。 2.2 BBB 运动功能评分结果 结果显示,与假手术组比较,模型组BBB评分在各个时间点均显著降低(P < 0.001);与模型组比较,电针组在术后 1,3,5 d 时BBB评分无显著差异(P > 0.05),在术后 7 d 时提高(P < 0.05),14 d 明显提高(P < 0.01),见表 2;由图 1 可见,模型组和电针组的 BBB 评分随时间变化有递增趋势,且电针组大鼠BBB评分较模型组增长趋势更显著。"
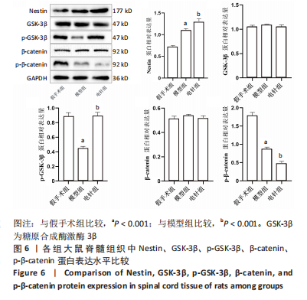
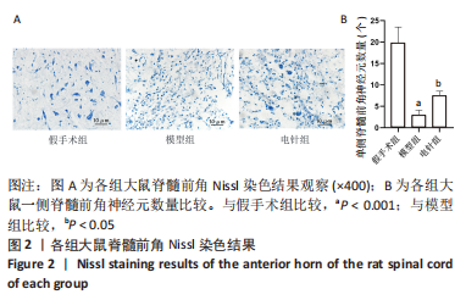
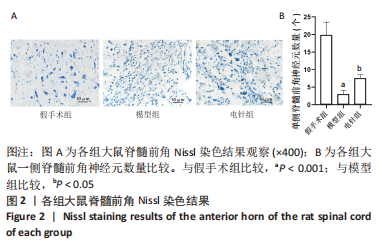
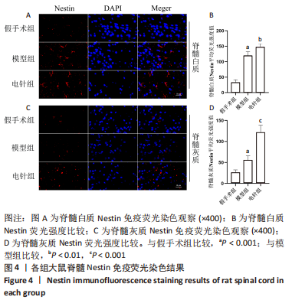
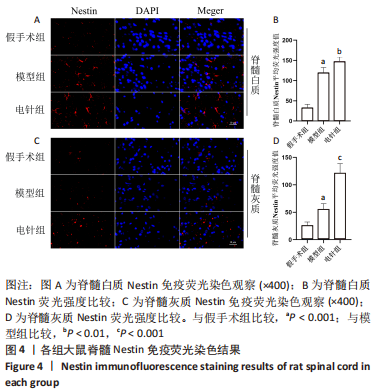
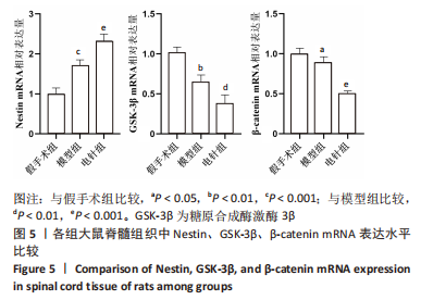
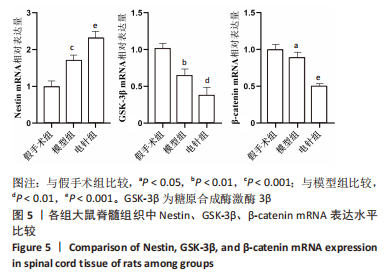
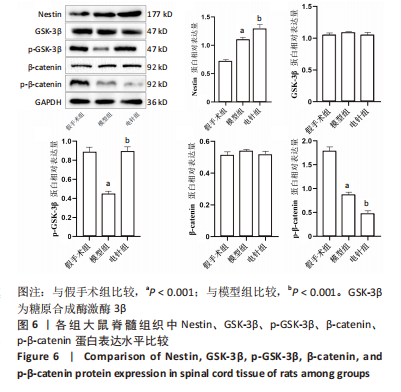
2.6 Western blot检测结果 Western blot检测结果显示,与假手术组比较,模型组Nestin蛋白表达水平显著升高(P < 0.001),p-GSK-3β蛋白表达水平显著降低(P < 0.001),p-β-catenin蛋白表达水平显著降低(P < 0.001),GSK-3β、β-catenin蛋白表达水平差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);与模型组比较,电针组Nestin蛋白表达水平显著升高(P < 0.001),p-GSK-3β蛋白表达水平显著升高(P < 0.001),p-β-catenin蛋白表达水平显著降低(P < 0.001),GSK-3β、β-catenin蛋白表达水平差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),见图6。"
| [1] YU S, YAO S, WEN Y, et al. Angiogenic microspheres promote neural regeneration and motor function recovery after spinal cord injury in rats. Sci Rep. 2016;6:33428. [2] MCDAID D, PARK AL, GALL A, et al. Understanding and modelling the economic impact of spinal cord injuries in the United Kingdom. Spinal Cord. 2019;57(9):778-788. [3] KARUSSIS D, PETROU P, KASSIS I. Clinical experience with stem cells and other cell therapies in neurological diseases. J Neurol Sci. 2013;324(1-2): 1-9. [4] MINE Y, TATARISHVILI J, OKI K, et al. Grafted human neural stem cells enhance several steps of endogenous neurogenesis and improve behavioral recovery after middle cerebral artery occlusion in rats. Neurobiol Dis. 2013;52:191-203. [5] VAN STRIEN ME, SLUIJS JA, REYNOLDS BA, et al. Isolation of neural progenitor cells from the human adult subventricular zone based on expression of the cell surface marker CD271. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2014;3(4):470-480. [6] KANNO H. Regenerative therapy for neuronal diseases with transplantation of somatic stem cells. World J Stem Cells. 2013;5(4): 163-171. [7] JENSEN MB, YAN H, KRISHNANEY-DAVISON R, et al. Survival and differentiation of transplanted neural stem cells derived from human induced pluripotent stem cells in a rat stroke model. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2013;22(4):304-308. [8] URBAN N, BLOMFIELD IM, GUILLEMOT F. Quiescence of Adult Mammalian Neural Stem Cells: A Highly Regulated Rest. Neuron. 2019; 104(5):834-848. [9] ZENG YS, DING Y, XU HY, et al. Electro-acupuncture and its combination with adult stem cell transplantation for spinal cord injury treatment: A summary of current laboratory findings and a review of literature. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2022;28(5):635-647. [10] LI SS, HUA XY, ZHENG MX, et al. Electroacupuncture treatment improves motor function and neurological outcomes after cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury. Neural Regen Res. 2022;17(7):1545-1555. [11] 吴明莉, 任亚锋, 王磊, 等. 督脉穴、夹脊穴电针联合电子生物反馈治疗脊髓损伤后神经源性膀胱临床观察[J]. 中国康复医学杂志, 2020,35(7):843-846. [12] 吴明莉, 冯晓东, 王永福. 夹脊穴、督脉穴电针治疗脊髓损伤患者的疗效观察[J]. 中华物理医学与康复杂志,2016,38(11):858-859. [13] 常文涛. 基于PI3K自噬信号通路探讨督脉穴电针促进脊髓损伤大鼠功能恢复的机制研究[D]. 郑州:河南中医药大学,2021. [14] LEE MY, LIM HW, LEE SH, et al. Smad, PI3K/Akt, and Wnt-dependent signaling pathways are involved in BMP-4-induced ESC self-renewal. Stem Cells. 2009;27(8):1858-1868. [15] COSKUN V, WU H, BLANCHI B, et al. CD133+ neural stem cells in the ependyma of mammalian postnatal forebrain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008;105(3):1026-1031. [16] SCHEFF SW, RABCHEVSKY AG, FUGACCIA I, et al. Experimental modeling of spinal cord injury: characterization of a force-defined injury device. J Neurotrauma. 2003;20(2):179-193. [17] 王玲洁, 陈显兵. 基于“瘀阻经络”病机探讨自噬与脊髓损伤修复的关系[J]. 中国康复理论与实践,2017,23(6):654-656. [18] 阮传亮, 陈若蓝, 黄梅, 等. 苏稼夫温经通督外治方结合督脉铺灸对脊髓损伤后神经源性膀胱尿流动力学的影响[J]. 中国针灸,2019, 39(11):1177-1180. [19] 卫彦, 朱久宇, 寇吉友, 等. 电针夹脊穴配合艾灸治疗肌萎缩侧索硬化17例[J]. 中国针灸,2018,38(6):613-615. [20] SHMELKOV SV, ST CR, LYDEN D, et al. AC133/CD133/Prominin-1. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2005;37(4):715-719. [21] CAVE JW, WANG M, BAKER H. Adult subventricular zone neural stem cells as a potential source of dopaminergic replacement neurons. Front Neurosci. 2014;8:16. [22] BECKERVORDERSANDFORTH R, TRIPATHI P, NINKOVIC J, et al. In vivo fate mapping and expression analysis reveals molecular hallmarks of prospectively isolated adult neural stem cells. Cell Stem Cell. 2010; 7(6):744-758. [23] MELETIS K, BARNABE-HEIDER F, CARLEN M, et al. Spinal cord injury reveals multilineage differentiation of ependymal cells. PLoS Biol. 2008;6(7):e182. [24] COSKUN V, WU H, BLANCHI B, et al. CD133+ neural stem cells in the ependyma of mammalian postnatal forebrain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008;105(3):1026-1031. [25] WENZEL HJ, HUNSAKER MR, GRECO CM, et al. Ubiquitin-positive intranuclear inclusions in neuronal and glial cells in a mouse model of the fragile X premutation. Brain Res. 2010;1318:155-166. [26] WANG J, HU J, CHEN X, et al. Traditional Chinese Medicine Monomers: Novel Strategy for Endogenous Neural Stem Cells Activation After Stroke. Front Cell Neurosci. 2021;15:628115. [27] BERNAL A, ARRANZ L. Nestin-expressing progenitor cells: function, identity and therapeutic implications. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2018;75(12): 2177-2195. [28] YANG Z, WANG KK. Glial fibrillary acidic protein: from intermediate filament assembly and gliosis to neurobiomarker. Trends Neurosci. 2015;38(6):364-374. [29] MCDONOUGH A, HOANG AN, MONTERRUBIO AM, et al. Compression injury in the mouse spinal cord elicits a specific proliferative response and distinct cell fate acquisition along rostro-caudal and dorso-ventral axes. Neuroscience. 2013;254:1-17. [30] CAWSEY T, DUFLOU J, WEICKERT CS, et al. Nestin-Positive Ependymal Cells Are Increased in the Human Spinal Cord after Traumatic Central Nervous System Injury. J Neurotrauma. 2015;32(18):1393-1402. [31] LEE JY, CHOI DC, OH TH, et al. Analgesic effect of acupuncture is mediated via inhibition of JNK activation in astrocytes after spinal cord injury. PLoS One. 2013;8(9):e73948. [32] DEMA A, SCHROTER MF, PERETS E, et al. The A-Kinase Anchoring Protein (AKAP) Glycogen Synthase Kinase 3beta Interaction Protein (GSKIP) Regulates beta-Catenin through Its Interactions with Both Protein Kinase A (PKA) and GSK3beta. J Biol Chem. 2016;291(37): 19618-19630. [33] KIM J, CHOI KW, LEE J, et al. Wnt/β-catenin Signaling Inhibitors suppress the Tumor-initiating properties of a CD44+CD133+ subpopulation of Caco-2 cells. Int J Biol Sci. 2021;17(7):1644-1659. [34] BEHROOZ AB, SYAHIR A. Could We Address the Interplay Between CD133, Wnt/β-Catenin, and TERT Signaling Pathways as a Potential Target for Glioblastoma Therapy? Front Oncol. 2021;11:642719. [35] ZHOU L, XU M, YANG Y, et al. Activation of β-Catenin Signaling in CD133-Positive Dermal Papilla Cells Drives Postnatal Hair Growth. PLoS One. 2016;11(7):e0160425. |
| [1] | Guo Shuhui, Yang Ye, Jiang Yangyang, Xu Jianwen. Screening and validation of neurogenic bladder miRNA-mRNA regulatory network [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(在线): 1-8. |
| [2] | Yang Jiujie, Li Zhi, Wang Shujie, Tian Ye, Zhao Wei. Intraoperative neurophysiological monitoring of functional changes following durotomy with decompression for acute spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1232-1236. |
| [3] | Hao Liufang, Duan Hongmei, Wang Zijue, Hao Fei, Hao Peng, Zhao Wen, Gao Yudan, Yang Zhaoyang, Li Xiaoguang. Spatiotemporal dynamic changes of ependymal cells after spinal cord injury in transgenic mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 883-889. |
| [4] | Li Xiaoyin, Yang Xiaoqing, Chen Shulian, Li Zhengchao, Wang Ziqi, Song Zhen, Zhu Daren, Chen Xuyi. Collagen/silk fibroin scaffold combined with neural stem cells in the treatment of traumatic spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 890-896. |
| [5] | Zhang Qijian, Xu Ximing. Acquisition and application of ectodermal mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 928-934. |
| [6] | Li Zhichao, Tan Guoqing, Su Hui, Xu Zhanwang, Xue Haipeng. Regulatory role of non-coding RNAs as potential therapeutic targets in spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(5): 758-764. |
| [7] | Tao Xin, Xu Yi, Song Zhiwen, Liu Jinbo. Hippo signaling pathway in the regulation of spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 619-625. |
| [8] | Cai Chuang, Huang Yonghui, Cao Xingbing, Sun Haitao, Guan Shihao, Huang Wenkang, Han Bo. Astrocyte-derived extracellular vesicles promote the differentiation of rat neural stem cells into neurons [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(24): 3845-3851. |
| [9] | Wang Liping, Li Jisheng, Deng Li, Wang Zhiqiang, Liu Jinming, Deng Chen, Sun Lin. Effects of high-mobility group box 1 on different subtypes of rat spinal reactive astrocytes after oxygen-glucose deprivation/restoration in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(24): 3831-3837. |
| [10] | Fan Xiao, Tao Jingwei, Jiang Shengyuan, Deng Bowen, Mu Xiaohong. Effect of tetramethylpyrazine on iron metabolism after spinal cord injury in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(22): 3561-3566. |
| [11] | Jiang Shengyuan, Deng Bowen, Liu Gang, Fan Xiao, Bai Huizhong, Tao Jingwei, Zhao Yi, Ren Jingpei, Xu Lin, Mu Xiaohong. Safety evaluation of electroactive hydrogel in the treatment of complete spinal cord transection in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(21): 3314-3319. |
| [12] | Guo Shuhui, Yang Ye, Jiang Yangyang, Xu Jianwen. Screening and validation of neurogenic bladder miRNA-mRNA regulatory network [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(20): 3143-3150. |
| [13] | Yao Haihua, Min Youjiang, Hong Dongying, Wang Li, Lu Xiuyun, Yang Yihua. Effects of Santong electroacupuncture on the activity of cytoplasmic phospholipase A2 in rats with spinal cord injury via the Rho/Rho kinase and MEK/ERK signaling pathways [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(20): 3158-3166. |
| [14] | Wen Feng, Zhou Lei, Li Yang, Zheng Liming, Zhang Zhiwen, Fan Xiao, Wu Zijian. Jiajian Didang Tang inhibits glial scar formation in rats with acute spinal cord injury under the guidance of Tongfu Zhuyu therapy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(20): 3180-3187. |
| [15] | Liu Gang, Deng Bowen, Jiang Shengyuan, Xu Lin, Fan Xiao, Tao Jingwei, Zhang Houjun, He Feng, Zhao Yi, Mu Xiaohong. Tetramethylpyrazine improves hemorheological indexes in rats with complete spinal cord transection: a dynamic observation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(2): 282-286. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||