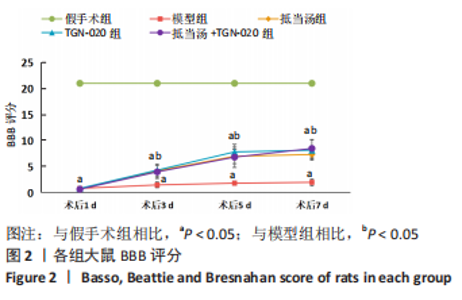
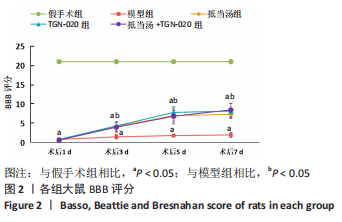
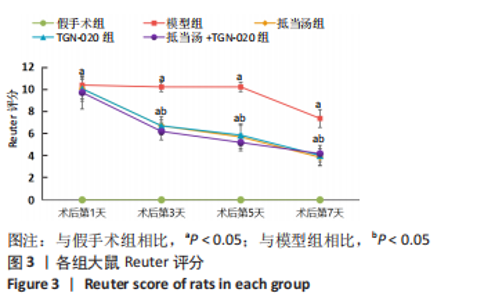
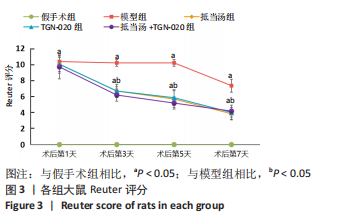
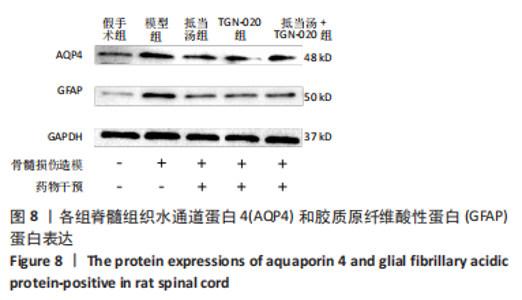
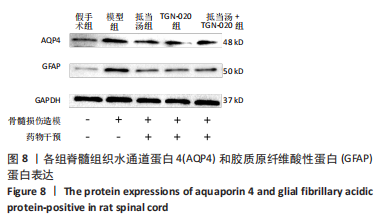
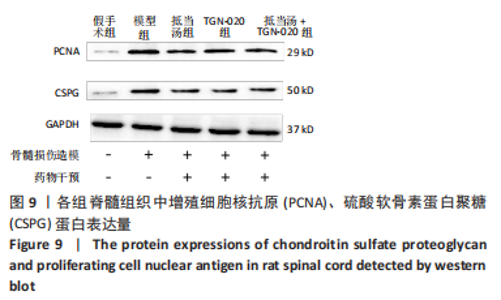
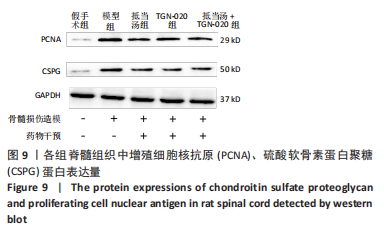
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (20): 3180-3187.doi: 10.12307/2023.529
Previous Articles Next Articles
Jiajian Didang Tang inhibits glial scar formation in rats with acute spinal cord injury under the guidance of Tongfu Zhuyu therapy
Wen Feng1, 2, 3, 4, Zhou Lei1, Li Yang2, 3, 4, Zheng Liming1, Zhang Zhiwen1, 2, 3, 4, Fan Xiao5, Wu Zijian2, 3, 4
- 1Hubei University of Chinese Medicine, Wuhan 430065, Hubei Province, China; 2Affiliated Hospital of Hubei University of Chinese Medicine, Wuhan 430061, Hubei Province, China; 3Hubei Provincial Hospital of TCM, Wuhan 430061, Hubei Province, China; 4Hubei Academy of TCM, Wuhan 430061, Hubei Province, China; 5Qingdao Municipal Hospital, Qingdao 266011, Shandong Province, China
-
Received:2022-07-11Accepted:2022-09-07Online:2023-07-18Published:2022-11-19 -
Contact:Wu Zijian, Affiliated Hospital of Hubei University of Chinese Medicine, Wuhan 430061, Hubei Province, China; Hubei Provincial Hospital of TCM, Wuhan 430061, Hubei Province, China; Hubei Academy of TCM, Wuhan 430061, Hubei Province, China -
About author:Wen Feng, MD candidate, Associate chief physician, Hubei University of Chinese Medicine, Wuhan 430065, Hubei Province, China; Affiliated Hospital of Hubei University of Chinese Medicine, Wuhan 430061, Hubei Province, China; Hubei Provincial Hospital of TCM, Wuhan 430061, Hubei Province, China; Hubei Academy of TCM, Wuhan 430061, Hubei Province, China -
Supported by:Research Project of Traditional Chinese Medicine of Hubei Provincial Health Commission, No. ZY2019M044 (to WZJ [project participant])
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wen Feng, Zhou Lei, Li Yang, Zheng Liming, Zhang Zhiwen, Fan Xiao, Wu Zijian. Jiajian Didang Tang inhibits glial scar formation in rats with acute spinal cord injury under the guidance of Tongfu Zhuyu therapy[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(20): 3180-3187.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
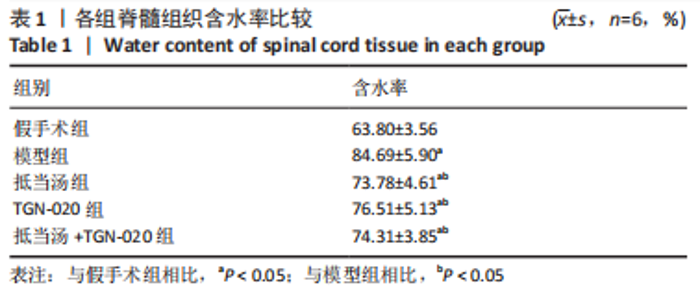
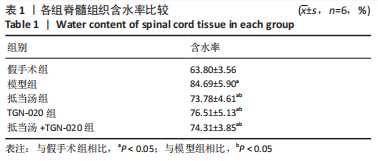
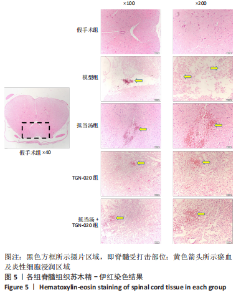
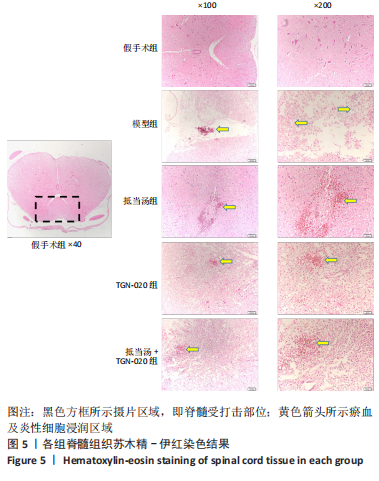
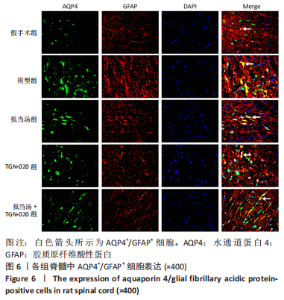
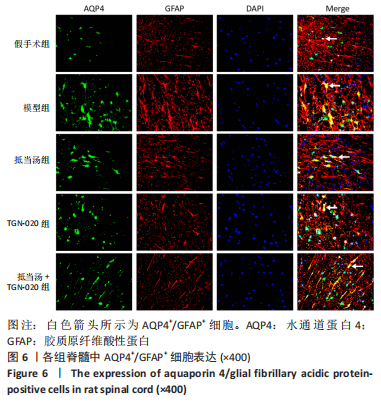
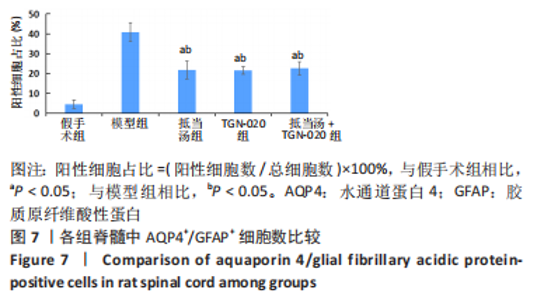
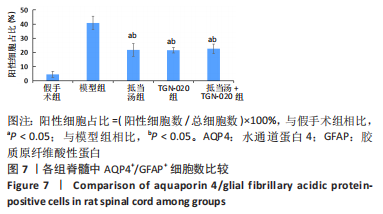
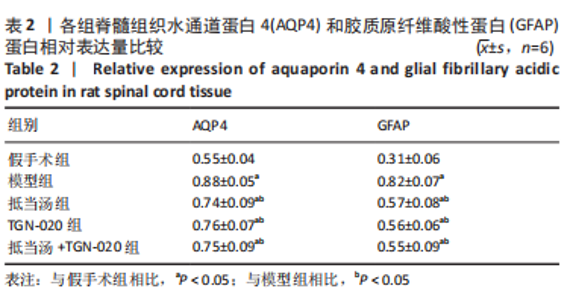
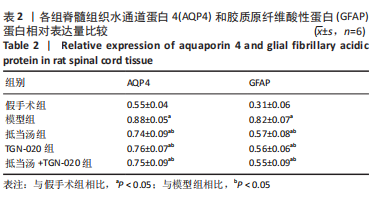
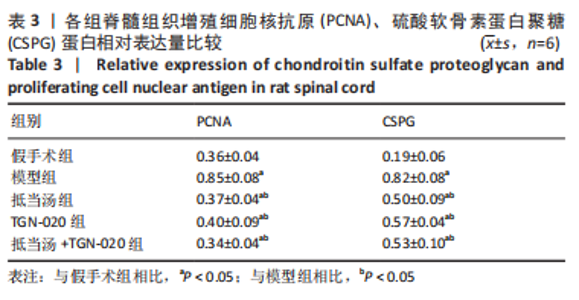
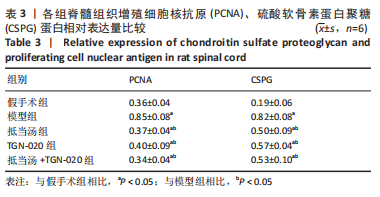
| [1] 苏义基. 红景天苷干预NF-κB及MAPK信号通路影响大鼠脊髓损伤模型运动功能的研究[D] . 南宁:广西医科大学,2017. [2] SAADOUN S, PAPADOPOULOS MC. Aquaporin-4 in brain and spinal cord oedema. Neuroscience. 2010;168(4):1036-1046. [3] 张姣姣, 于石成, 么鸿雁,等. 1990-2017年中国创伤性脊髓损伤疾病负担特点分析[J]. 中华创伤杂志,2020,36(11):1004-1009. [4] 陈星月, 陈栋, 陈春慧,等. 中国创伤性脊髓损伤流行病学和疾病经济负担的系统评价[J]. 中国循证医学杂志,2018,18(2):143-150. [5] 刘俊, 高峰, 李建军. 创伤性脊髓损伤患者的流行病学及住院费用影响因素研究[J]. 中国康复,2020,35(3):139-142. [6] Li YN, Gao ZW, Li R, et al. Aquaporin 4 regulation by ginsenoside Rb1 intervenes with oxygen-glucose deprivation/reoxygenation-induced astrocyte injury. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019;98(42):e17591. [7] HARAT M, RADEK A, KOCHANOWSKI J. The physiopathology of acute spinal cord injury and a hope for a successful treatment. Neurol Neurochir Pol. 1996;30(1):123-135. [8] 王富贵. 大鼠脊髓损伤后早期PAR2通过p38MAPK调控胶质瘢痕的形成[D].重庆:重庆医科大学,2016. [9] 张振东. 脊髓损伤后促红细胞生成素对神经营养因子及神经细胞凋亡的影响[D].苏州:苏州大学,2007. [10] ZHU YM, GAO X, NI Y, et al. Sevoflurane postconditioning attenuates reactive astrogliosis and glial scar formation after ischemia-reperfusion brain injury. Neuroscience. 2017;356:125-141. [11] KWIECIEN JM. Barriers to axonal regeneration after spinal cord injury: a current perspective. Neural Regen Res. 2022;17(1):85-86. [12] 许静芬, 黄芝瑛. 用Excel软件计算动物的体表面积及对用药剂量的换算[J]. 上海实验动物科学,1999(1):58-59. [13] LI J, JIA Z, XU W, et al. TGN-020 alleviates edema and inhibits astrocyte activation and glial scar formation after spinal cord compression injury in rats. Life Sci. 2019;222:148-157. [14] 赵亮, 李丹, 刘囡,等. 抑制水通道蛋白4可降低脊髓后角胶质细胞细胞外调节蛋白激酶信号的活化改善坐骨神经损伤导致的神经病理性疼痛[J]. 解剖学报,2019,50(1):35-39. [15] GRUNER JA. A monitored contusion model of spinal cord injury in the rat. J Neurotrauma. 1992;9(2):123-126; discussion 126-128. [16] 吴杨鹏. 活血通督汤对大鼠急性脊髓损伤的修复作用及机制[D].福州:福建中医药大学,2018. [17] 吕静. 大鼠脊髓损伤模型的建立及行为学评分[D].长沙:中南大学,2011. [18] LIU X, WANG Y, YANG J, et al. Anti-edema effect of melatonin on spinal cord injury in rats. Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2015;159(2):220-226. [19] FAN ZK, WANG YF, CAO Y, et al. The effect of aminoguanidine on compression spinal cord injury in rats. Brain Res. 2010;1342:1-10. [20] 王雅欣, 林一璨, 郭伊诺,等. 中医药调控细胞自噬治疗脊髓损伤的方法、技术及未来[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2023,27(13):2116-2123. [21] WILSON JR, ARNOLD PM, SINGH A, et al. Clinical prediction model for acute inpatient complications after traumatic cervical spinal cord injury: a subanalysis from the Surgical Timing in Acute Spinal Cord Injury Study. J Neurosurg Spine. 2012;17(1 Suppl):46-51. [22] FEHLINGS MG, VACCARO A, WILSON JR, et al. Early versus delayed decompression for traumatic cervical spinal cord injury: results of the Surgical Timing in Acute Spinal Cord Injury Study (STASCIS). PLoS One. 2012;7(2):e32037. [23] FURLAN JC, NOONAN V, CADOTTE DW, et al. Timing of decompressive surgery of spinal cord after traumatic spinal cord injury: an evidence-based examination of pre-clinical and clinical studies. J Neurotrauma. 2011;28(8):1371-1399. [24] FLACK JA, SHARMA KD, XIE JY. Delving into the recent advancements of spinal cord injury treatment: a review of recent progress. Neural Regen Res. 2022;17(2):283-291. [25] 崔河泉,高体三. 《伤寒论》蓄血证方析疑[J]. 国医论坛,1995(1):1-4. [26] 孙琛琛,孙西庆. “阳明蓄血,其人喜忘”诌议[J]. 中医药临床杂志, 2014,26(5):509-510. [27] 太史春,邰东梅,邹晓明. 肾主水液与水通道蛋白内在关系探讨[J]. 实用中医内科杂志,2007,21(8): 7-8. [28] ZHANG H, GONG M, LUO X. Methoxytetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl)methyl benzoate inhibits spinal cord injury in the rat model via PPAR-γ/PI3K/p-Akt activation. Environ Toxicol. 2020;35(6):714-721. [29] 武亮, 李建军, 陈亮,等. 抑制脊髓损伤后星形胶质细胞增殖和胶质瘢痕形成的研究进展[J]. 中国康复理论与实践,2010,16(3): 201-204. [30] PAPADOPOULOS MC, VERKMAN AS. Potential utility of aquaporin modulators for therapy of brain disorders. Prog Brain Res. 2008;170: 589-601. [31] XU M, SU W, XU QP. Aquaporin-4 and traumatic brain edema. Chin J Traumatol. 2010;13(2):103-110. [32] ENG LF, GHIRNIKAR RS, LEE YL. Glial fibrillary acidic protein: GFAP-thirty-one years (1969-2000). Neurochem Res. 2000;25(9-10):1439-1451. [33] SAADOUN S, PAPADOPOULOS MC, DAVIES DC, et al. Aquaporin-4 expression is increased in oedematous human brain tumours. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2002;72(2):262-265. [34] SAADOUN S, PAPADOPOULOS MC, KRISHNA S. Water transport becomes uncoupled from K+ siphoning in brain contusion, bacterial meningitis, and brain tumours: immunohistochemical case review. J Clin Pathol. 2003;56(12):972-975. [35] LI G, CAO Y, SHEN F, et al. Mdivi-1 Inhibits Astrocyte Activation and Astroglial Scar Formation and Enhances Axonal Regeneration after Spinal Cord Injury in Rats. Front Cell Neurosci. 2016;10:241. [36] SAADOUN S, PAPADOPOULOS MC, WATANABE H, et al. Involvement of aquaporin-4 in astroglial cell migration and glial scar formation. J Cell Sci. 2005;118(Pt 24):5691-5698. [37] CUI D, JIA S, LI T, et al. Alleviation of brain injury by applying TGN-020 in the supraoptic nucleus via inhibiting vasopressin neurons in rats of focal ischemic stroke. Life Sci. 2021;264:118683. [38] 李坚. TGN-020促进大鼠脊髓损伤后运动功能恢复的机制研究[D]. 锦州: 锦州医科大学,2019. |
| [1] | He Xi, Wan Yu, Tang Yuting, Yang Anning, Wu Kai, Jiao Yun, Bai Zhigang, Jiang Yideng, Shen Jiangyong. Erastin inhibits proliferation of hypertrophic scar fibroblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(在线): 1-. |
| [2] | Yang Jiujie, Li Zhi, Wang Shujie, Tian Ye, Zhao Wei. Intraoperative neurophysiological monitoring of functional changes following durotomy with decompression for acute spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1232-1236. |
| [3] | Gao Yu, Han Jiahui, Ge Xin. Immunoinflammatory microenvironment after spinal cord ischemia-reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1300-1305. |
| [4] | Hao Liufang, Duan Hongmei, Wang Zijue, Hao Fei, Hao Peng, Zhao Wen, Gao Yudan, Yang Zhaoyang, Li Xiaoguang. Spatiotemporal dynamic changes of ependymal cells after spinal cord injury in transgenic mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 883-889. |
| [5] | Chen Guodong, Zheng Meiyan, Zhang Peng, Wang Zhenchao, Jin Lixin. Changes in sensory neurons and astrocytes and the expression of interleukin 1beta and glial fibrillary acidic protein in the rat spinal cord after selective dorsal rhizotomy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(5): 726-731. |
| [6] | Lu Huixiu, Cao Haiyu, Lou Dan, Li Jianying, Liu Hongyuan, Sun Jing. Imiquimod combined with photodynamic therapy for hypertrophic scars: immune response and prognosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(5): 690-694. |
| [7] | Niu Zihan, Yu Yang, Ai Jiang, Bu Panpan, Li Wenbo, Suriye·Reheman, Ma Shaolin. Total flavonoids of Hippophae rhamnoides L. interfere with the regression of hypertrophic scar tissue blocks in a rabbit ear model [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(2): 258-263. |
| [8] | Ming Jiang, Liao Yidong, Song Wenxue, Mu Deyong, Liu Zongwei, Xu Kaya. Experimental method of simultaneous culture of primary cortical neurons and astrocytes of Sprague-Dawley suckling rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(15): 2339-2343. |
| [9] | He Xi, Ma Fang, Wan Yu, Tang Yuting, Ma Shengchao, Jiang Yideng, Shen Jiangyong. miR-382-3p inhibits the proliferation of human hypertrophic scar fibroblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(11): 1758-1764. |
| [10] | Liu Qing, Wang Xiao, Gu Chengxu, Guo Qixuan, Li Xikai, Zhang Luping, Huang Fei. Apelin promotes locomotor recovery and spinal cord morphology repair in rats with spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(11): 1744-1749. |
| [11] | Li Xialin, Hu Guangxun, Pan Dayu. Schwann cell-derived exosomes attenuate angiogenesis and fibrotic scar formation and promote nerve repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(10): 1567-1571. |
| [12] | Wang Xinxin, Wang Jingxin. Mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes in treatment of secondary lymphedema [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(10): 1603-1609. |
| [13] | Zhang Lichuang, Xu Hao, Ma Yinghui, Xiong Mengting, Han Haihui, Bao Jiamin, Zhai Weitao, Liang Qianqian. Mechanism and prospects of regulating lymphatic reflux function in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1459-1466. |
| [14] | Zhang Yujie, Yang Jiandong, Cai Jun, Zhu Shoulei, Tian Yuan. Mechanism by which allicin inhibits proliferation and promotes apoptosis of rat vascular endothelial cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1080-1084. |
| [15] | Zhang Lili, Ou Ya, Yuan Xiaodong, Zhang Pingshu. Bax/Bcl-2 protein and apoptosis during adipose-derived stromal cell differentiation into astrocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(31): 4982-4987. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||