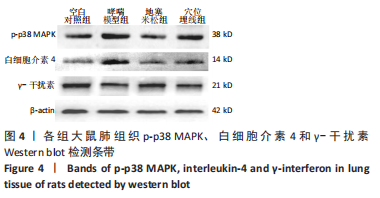
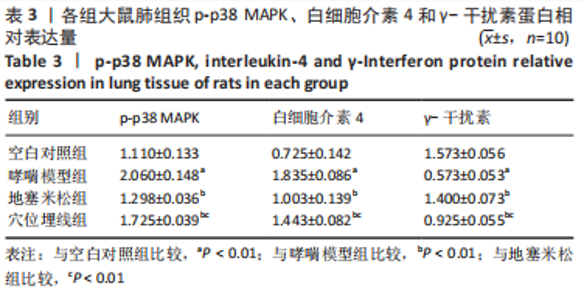
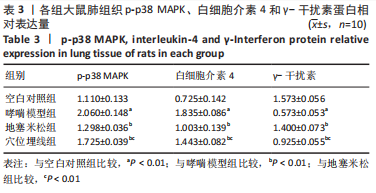
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (35): 5688-5694.doi: 10.12307/2023.869
Previous Articles Next Articles
Acupoint catgut embedding regulates the role of type II alveolar epithelial cells in airway inflammation in asthmatic rats
Tang Xuyun1, Chen Panbi1, Du Dijia2, Qin Zhongyin1, Long Runjin1
- 1College of Acupuncture and Tuina, Guizhou University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Guiyang 550025, Guizhou Province, China; 2Department of Acupuncture, Zhijin County Hospital of TCM, Zhijin 552100, Guizhou Province, China
-
Received:2022-10-20Accepted:2022-12-09Online:2023-12-18Published:2023-06-05 -
Contact:Chen Panbi, Professor, College of Acupuncture and Tuina, Guizhou University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Guiyang 550025, Guizhou Province, China -
About author:Tang Xuyun, Master, Assistant teacher, College of Acupuncture and Tuina, Guizhou University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Guiyang 550025, Guizhou Province, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81760894 (to CPB); Guizhou Science and Technology Plan Project, No. QKHJ[2019]1018 (to CPB); 2017 High-level Innovative Talents Project in Guizhou Province, No. ZQ2017004 (to CPB)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Tang Xuyun, Chen Panbi, Du Dijia, Qin Zhongyin, Long Runjin. Acupoint catgut embedding regulates the role of type II alveolar epithelial cells in airway inflammation in asthmatic rats[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(35): 5688-5694.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
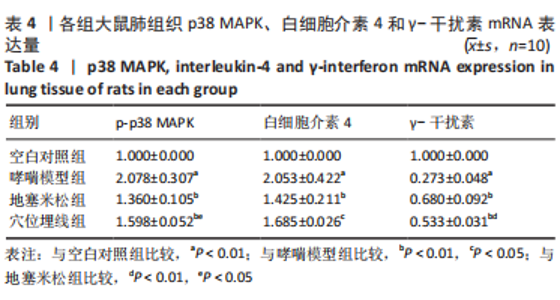
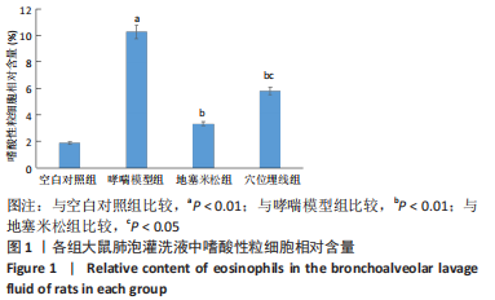
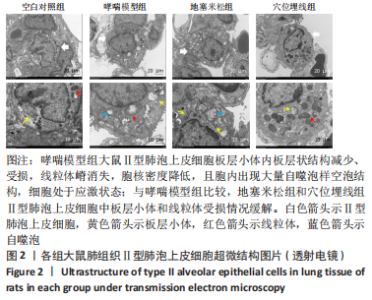
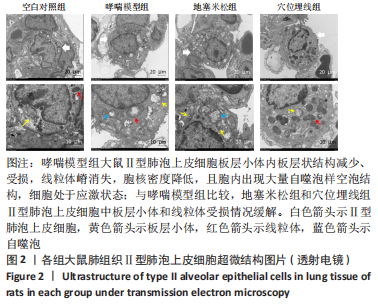
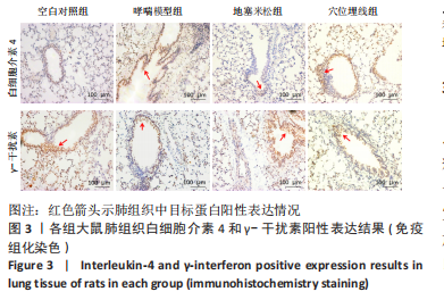
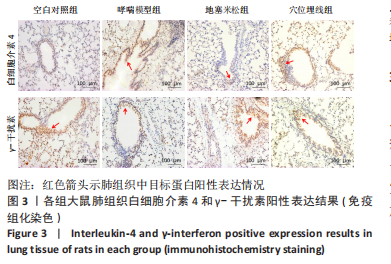
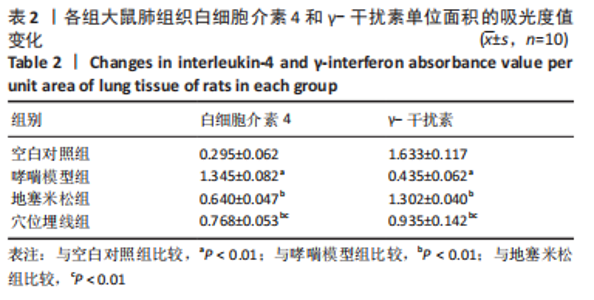
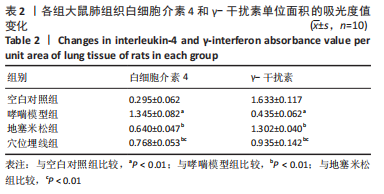
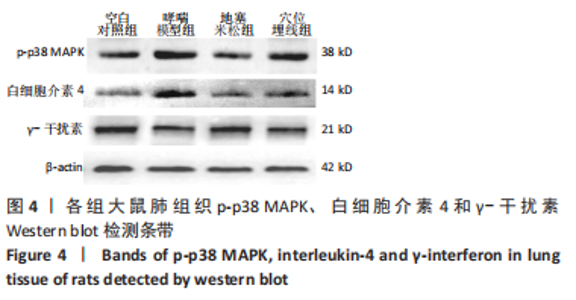
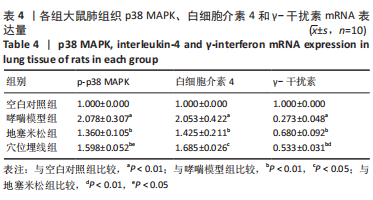
2.7 各组大鼠肺组织p38 MAPK、白细胞介素4和γ-干扰素mRNA表达 与空白对照组比较,哮喘模型组大鼠肺组织p38 MAPK和白细胞介素4 mRNA相对表达升高(P < 0.01),γ-干扰素mRNA相对表达降低(P < 0.01);与哮喘模型组比较,地塞米松组和穴位埋线组大鼠肺组织p38 MAPK和白细胞介素4 mRNA相对表达降低(P < 0.01,P < 0.05),γ-干扰素mRNA相对表达显著升高(P < 0.01);与地塞米松组比较,穴位埋线组大鼠肺组织p38 MAPK mRNA相对表达升高(P < 0.05),白细胞介素4 mRNA相对表达无明显变化(P > 0.05),γ-干扰素mRNA相对表达降低(P < 0.01),见表4。"
| [1] KURUVILLA ME, ANIJCHAROENKARN K, SHIH JA, et al. Epidemiology and risk factors for asthma. Respir Med. 2019;149:16-22. [2] BONTINCK A, MAES T, JOOS G. Asthma and air pollution: recent insights in pathogenesis and clinical implications. Curr Opin Pulm Med. 2020;26(1):10-19. [3] HELLINGS PW, STEELANT B. Epithelial barriers in allergy and asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2020;145(6):1499-1509. [4] FREY A, LUNDING LP, EHLERS JC, et al. More Than Just a Barrier: The Immune Functions of the Airway Epithelium in Asthma Pathogenesis. Front Immunol. 2020;11:761. [5] NELSON RK, BUSH A, STOKES J, et al. Eosinophilic Asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2020;8(2):465-473. [6] 常春,孙永昌.2022版《全球哮喘管理和预防策略》更新解读[J].中国全科医学,2022,25(35):4355-4362. [7] GANS MD, GAVRILOVA T. Understanding the immunology of asthma: Pathophysiology, biomarkers, and treatments for asthma endotypes. Paediatr Respir Rev. 2020;36:118-127. [8] RUARO B, SALTON F, BRAGA L, et al. The History and Mystery of Alveolar Epithelial Type II Cells: Focus on Their Physiologic and Pathologic Role in Lung. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(5):2566. [9] DO DC, ZHANG Y, TU W, et al. Type II alveolar epithelial cell-specific loss of RhoA exacerbates allergic airway inflammation through SLC26A4. JCI Insight. 2021;6(14):e148147. [10] ABONYO BO, ALEXANDER MS, HEIMAN AS. Autoregulation of CCL26 synthesis and secretion in A549 cells: a possible mechanism by which alveolar epithelial cells modulate airway inflammation. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2005;289(3):L478-488. [11] WANG J, ZHAO YL, ZHANG X, et al. Type II alveolar epithelial cell aryl hydrocarbon receptor protects against allergic airway inflammation through controlling cell autophagy. Front Immunol. 2022;13:964575. [12] LYNN MC, CHRISTOPHER MW. Epithelial repair mechanisms in the lung. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2010;298(6):L715-731. [13] AHDIEH M, VANDENBOS T, YOUAKIM A. Lung epithelial barrier function and wound healing are decreased by IL-4 and IL-13 and enhanced by IFN-gamma. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2001;281(6):C2029-2038. [14] HURST SM, MCGHIE TK, COONEY JM, et al. Blackcurrant proanthocyanidins augment IFN-gamma-induced suppression of IL-4 stimulated CCL26 secretion in alveolar epithelial cells. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2010;54 Suppl 2:S159-170. [15] COLEMAN SL, KRUGER MC, SAWYER GM, et al. Procyanidin A2 Modulates IL-4-Induced CCL26 Production in Human Alveolar Epithelial Cells. Int J Mol Sci. 2016;17(11):1888. [16] 张琳.穴位埋线对哮喘大鼠Th1/Th2的影响[J].贵阳中医学院学报, 2008,30(3):46-47. [17] 唐徐韵,陈盼碧,杜狄佳,等.穴位埋线对哮喘大鼠肺组织中p38MAPK信号通路及细胞间黏附分子-1、白细胞介素-4和嗜酸性粒细胞的影响[J].针刺研究,2022,47(2):129-134. [18] 李泳兴,钟鸣,王勇,等.常用哮喘动物模型的建立[J].中国比较医学杂志,2020,30(11):97-101. [19] 崔瑾,陈盼碧,杨孝芳,等.简易穴位埋线对哮喘大鼠ICAM-1和NF-κB表达及气道炎症的影响[J].中国针灸,2010,30(2):141-145. [20] 黄继汉,黄晓晖,陈志扬,等.药理试验中动物间和动物与人体间的等效剂量换算[J].中国临床药理学与治疗学,2004,9(9): 1069-1072. [21] 中国针灸学会.实验动物常用穴位名称与定位第2部分:大鼠[J].针刺研究,2021,46(4):351-352. [22] 赵文翰,许坚,符丽.基于痰饮理论治疗支气管哮喘气道黏液高分泌的思路探索[J].辽宁中医杂志,2021,48(5):68-70. [23] YANG M, CHEN JY, WEI W. Dimerization of glucocorticoid receptors and its role in inflammation and immune responses. Pharmacol Res. 2021;166:105334. [24] ZDZIARSKI P, PASCIAK M, GAMIAN A. Microbiome Analysis and Pharmacovigilance After Inhaled Glucocorticoid: Oral Dysbiosis With the Isolation of ThreeRothiaSpecies and Subsequent Sjögren’s Syndrome. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:636180. [25] SLISZ T, VASAKOVA M. The burden of corticosteroid overload in severe and difficult to treat asthma: how to reduce this? Curr Opin Pulm Med. 2020;26(1):90-96. [26] CHEN H, SUN J, HUANG Q, et al. Inhaled Corticosteroids and the Pneumonia Risk in Patients With Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: A Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Front Pharmacol. 2021;12:691621. [27] 罗秋锐,宋小琴,王荣丽.sirtinol与地塞米松对哮喘模型小鼠体内沉默信息调节蛋白1和白细胞介素5水平的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(17):2720-2725. [28] CARAMORI G, NUCERA F, MUMBY S, et al. Corticosteroid resistance in asthma: Cellular and molecular mechanisms. Mol Aspects Med. 2022;85:100969. [29] CANNA RL, LICCARDO D, ZHANG P, et al. Yap/Taz regulate alveolar regeneration and resolution of lung inflammation. J Clin Invest. 2019; 129(5):2107-2122. [30] 支佳琦,王青青.肺泡上皮细胞在肺部免疫中的作用[J].中国免疫学杂志,2018,34(10):1596-1601. [31] ASPAL M, ZEMANS RL. Mechanisms of ATII-to-ATI Cell Differentiation during Lung Regeneration. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(9):3188. [32] PARIMON T, YAO CF, STRIPP BR, et al.Alveolar Epithelial Type II Cells as Drivers of Lung Fibrosis in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(7):2269. [33] OBENG E. Apoptosis (programmed cell death) and its signals - A review. Braz J Biol. 2021;81(4):1133-1143. [34] LI ZY, WU YF, XU XC, et al. Autophagy as a double-edged sword in pulmonary epithelial injury: a review and perspective. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2017;313(2):L207-L217. [35] ANDREA M, SUSANNA B, FRANCESCA N, et al. The emerging role of type 2 inflammation in asthma. Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2021;17(1): 63-71. [36] HAMMAD H, LAMBRECHT BN. The basic immunology of asthma. Cell. 2021;184(6):1469-1485. [37] RAO SP, RASTLE-SIMPSON S, DILEEPAN M, et al. Procedures to Evaluate Inflammatory and Pathological Changes During Allergic Airway Inflammation. Methods Mol Biol. 2021;2223:217-236. [38] RAVANETTI L, DIJKHUIS A, DEKKER T, et al. IL-33 drives influenza-induced asthma exacerbations by halting innate and adaptive antiviral immunity. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2019;143(4):1355-1370.e16. [39] CHAO CL, WANG CJ, HUANG HW, et al. Poria cocosModulates Th1/Th2 Response and Attenuates Airway Inflammation in an Ovalbumin-Sensitized Mouse Allergic Asthma Model. Life (Basel). 2021;11(5):372. [40] LI Q, ZHAI CM, WANG GD, et al. Ginsenoside Rh1 attenuates ovalbumin-induced asthma by regulating Th1/Th2 cytokines balance. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2021;85(8):1809-1817. [41] SONG YL, WANG ZG, JIANG JZ, et al. DEK-targeting aptamer DTA-64 attenuates bronchial EMT-mediated airway remodelling by suppressing TGF-β1/Smad, MAPK and PI3K signalling pathway in asthma. J Cell Mol Med. 2020;24(23):13739-13750. [42] UMANNOVA L, MACHALA M, TOPINKA J, et al. Benzo[a]pyrene and tumor necrosis factor-α coordinately increase genotoxic damage and the production of proinflammatory mediators in alveolar epithelial type II cells. Toxicol Lett. 2011;206(2):121-129. [43] 赵蕊,陈芳艳,韩黎.肺泡上皮细胞应对烟曲霉感染过程中胞内双特异性磷酸酶表达规律的研究[J].中国真菌学杂志,2020,15(3): 129-133. [44] 张静.p38MAPK信号通路与LPS致大鼠Ⅱ型肺泡上皮细胞线粒体分裂的关系:离体实验[D].天津:天津医科大学,2020. |
| [1] | Yan Le, Zhang Huiping, Dai Lintong. Mesenchymal stem cells for allergic rhinitis: a meta-analysis based on animal experiments [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 977-984. |
| [2] | Li Li, Li Xiao, Li Duchenhui, Zhang Jie, Xiao Tianjiao, Kang Jiabing, Tian Ai. Regulation of interleukin-4 on osteoclast differentiation during bone regeneration guided by bone replacement materials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(34): 5455-5461. |
| [3] | Tang Li, Pan Yao, Zhu Guochen. Epidermal neural crest stem cells of hair follicles regulate the local expression of inflammatory factors after facial nerve injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(33): 5249-5255. |
| [4] | Peng Mengzhu, Yang Xiangang, Xing Lili, Li Guojun. Exhaled breath condensate specimens for testing airway health during exercise [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(23): 3755-3762. |
| [5] | Luo Qiurui, Song Xiaoqin, Wang Rongli. Effects of sirtinol versus dexamethasone on the levels of recombinant sirtuin 1 and interleukin-5 in asthmatic mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(17): 2720-2725. |
| [6] | Li Li, Zhuo Jin, Zheng Ling, Zhou Ling, Wang Qisong, Luo Lan, Luo Kai. Effects of different induced polarization methods on the proliferation, apoptosis and phagocytosis of rat bone marrow-derived macrophages [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 4032-4037. |
| [7] | Yu Dan, Xu Guanglan, Zhao Mei, Li Jiao, Li Guosheng, Wang Guangyao, Lin Hao, Zheng Manli, Li Yuanling. Significance and possibility of stem cells and multiple cell derived exosomes in the treatment of chronic respiratory diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 4053-4057. |
| [8] | Wu Qi, Liao Ying, Sun Guanghua, Zhou Guijuan, Liao Yuan, Liu Jing, Zhong Peirui, Cheng Guo, Deng Chengyuan, Wang Tiantian. Changes of subchondral bone in rat models of knee osteoarthritis treated by elcatonin [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(5): 709-715. |
| [9] | Wei Jianghong, Jia Aijun, Ma Libing, Wang Yueling, Qiu Lulu, Xiao Bing. Th-17 regulatory cytokines promote interleukins-17A and 17F production by neutrophils during asthma [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(31): 5044-5051. |
| [10] | Yang Hongxia, Shi Qinghong, Weng Minhua, Zhang Jianyong, Zhao Jianjun, Chen Ling. Effect of human amniotic mesenchymal stem cell transplantation on airway goblet cell proliferation and mucin 5ac expression in asthmatic mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(25): 4050-4055. |
| [11] | Ge Xiahui, Zhang Guorui, Guan Wenbin, Bai Chong. Galectin-1 secreted by bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells may suppress airway inflammation in an asthmatic mouse [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(25): 3937-3943. |
| [12] | Wu Guangwen1, Liu Shuru2, Chen Jun3, Lin Jie1, Zhao Zhongsheng1, Ye Jinxia1. Mechanism of Duhuo Jisheng Decoction for treating knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(19): 2965-2971. |
| [13] | Chen Na, Xie Tie-min, Zhang Yi-fan, Wang Jiang, Wang Qing-feng. Preparation and inflammation suppression of pH sensitive chitosan/dexamethasone sodium phosphate nano-drug delivery system [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(22): 3550-3556. |
| [14] | Lin Ying, Hu Jin-zhang, Zhuansun Yong-xun, Ran Pi-xin, Chen Rui, Du Yu-mo, Lin Lin, Li Jian-guo. Exosomes from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells regulate the balance of Foxp3+ Treg/Th17 in asthmatic mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(17): 2637-2643. |
| [15] | Zhuansun Yong-xun, Zhang Wei, Du Yu-mo, Ran Pi-xin, Chen Rui, Lin Lin, Li Jian-guo. Effect of mesenchymal stem cells on airway inflammation in asthmatic mice depleted of CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(5): 742-747. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||